Areas with such soil compositions are not the best options for construction work, because it is necessary to solve the problem of neutralizing seasonal heaving of the soil, because its movements can create a danger not only for the foundation, but also for the entire structure. For this reason, experienced craftsmen advise building a shallow foundation on heaving soil, which can cope well with the resulting loads and is not subject to uneven settlement and deformation. This type of base is easy to build and fits almost any object.
What is the danger
Soil heaving is a natural phenomenon that can occur when a couple of factors coincide:
- availability of water;
- lowering the temperature below 0 degrees.
Water is an unusual substance. Only it is capable of expanding at the moment of freezing, causing the soil to increase its volume. At the same time, tension arises, tending to push the foundation out of the ground.
Deformations of a uniform nature do not pose a particular danger to the building, but during heaving they occur unevenly. In the middle of the object, the temperature of the soil cover is higher, the effect of heaving is not so strong. Closer to the edges, this phenomenon intensifies, as the heating from the rooms decreases. External walls rise more than internal ones, which causes cracks to form in the walls and foundation.
Advantages, disadvantages
Advantages of shallow foundations:
- small volumes of earthworks;
- less consumption of building materials: concrete, reinforcement, hydro-, thermal insulation, sand, gravel;
- ease of installation - no knowledge or skills required;
- price-quality-time ratio.
Flaws:
- low load-bearing load – low-rise construction from light building materials;
- lower fracture strength compared to buried foundations.
Types of foundations for heaving soils

When building on such soil composition, it is recommended to use certain foundation types. The best option is to install non-buried or shallow foundations that can perfectly withstand natural phenomena in winter.
Shallow belt
It is popular, can provide reliability and long-term operation, and is easy to build without requiring large financial expenses.
Shallow columnar
They are used if the support piles can be mounted below the soil freezing level. This feature helps save money on the construction of the base, while maintaining its high degree of reliability. This type of foundation is installed when the site has loam, groundwater is close to it, and the soil is damp and swampy. During construction, steel pipes protected by a cement-sand layer, reinforced concrete supports, and asbestos-cement pipes filled inside with concrete mortar are used.
In problem areas, pile foundations are also used, which are not in great demand.
Their construction requires the use of special equipment, which entails unexpected costs. This option is used on lands with a soil freezing depth of one and a half meters.

Piles are made of concrete or reinforced concrete, or wood can be used. Experts recommend installing the following piles: screw, cast-in-place, simple and cast-in-place reinforced concrete piles. If you choose this option for construction, you will have to install a drainage system.
Developer reviews
Numerous reviews confirm that a shallow strip foundation is the best option for individual construction.
Many people like this solution because of the small volume of work, the possibility of carrying out construction on their own, and the economical use of money.
Developers who built exactly this option recommend tape dimensions of 40 by 40 cm and reinforcement of three greasy rods for a small object in order to increase the rigidity of the base. In this case, the peppered rods should be installed in increments of 0.5 m.

Experts recommend strictly maintaining the composition of the components and proportions for preparing the concrete mixture so that the base turns out to be reliable. At the same time, they advise not to take breaks in work, to pour concrete in layers, but at once, carefully compacting each of them.
As useful tips - study the soil characteristics on your site, correctly draw up a work plan, follow the technology of reinforcement, pouring and installing a waterproofing layer. If you have even the slightest doubt about your own capabilities, seek help from experienced professionals.
Execution of work
The technological process of construction is as follows: marking is carried out, a trench is dug, a cushion is laid, a drainage pipe is laid (if there is a need for this), a blind area with insulation and waterproofing is made, a reinforcing frame is installed, concrete mortar is poured or blocks are installed, insulation is performed. There is nothing complicated here, and you can easily build a shallow foundation on heaving soil with your own hands. To ensure that the construction process does not cause difficulties, we provide some recommendations for the design and calculation of shallow foundations on heaving soils.
Preparatory work and calculations
Before starting the construction of a shallow strip foundation on heaving soils, the need for concrete is calculated.
Its mass is determined based on the geometric parameters of the foundation and the density of the solution. To find the volume of the base, I take the length of the foundation equal to the perimeter of the building and the length of the internal walls of the load-bearing type, multiply by the width and height of the tape, having first converted the values to meters.
The density of the concrete solution depends on its brand. From its volume we subtract the need for reinforcement (volume of metal), and we get the required amount of concrete mixture. Multiplying this value by the density of concrete, we get its mass.
We proceed to preparatory work, for which the dimensions of the foundation are transferred to the area planned for construction. The contours are marked with a cord stretched over pegs.
To build an even rectangle, you need to compare the values of its diagonals, which should be equal.
The next stage of constructing a shallow strip foundation on heaving soils with your own hands is preparing the site for construction. It must be cleared of debris and the top layer of fertile soil removed.
A trench is dug to the required depth. As a rule, this value is about fifty to seventy centimeters, twenty of which are allocated for the construction of a sand cushion. After this, the side walls of the foundation trench are lined with waterproofing material. To do this, use roofing felt or a special film.
Sand is poured into layers at the bottom of the trench and carefully compacted until the height of the cushion reaches two tens of centimeters.
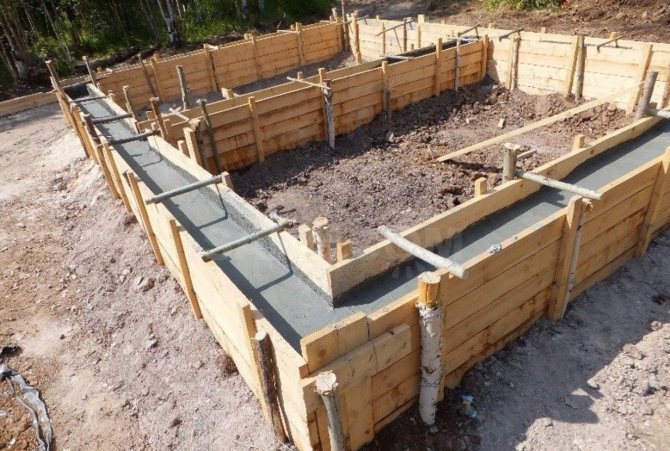
Construction of formwork

It is best to use edged boards for this. They are firmly fastened so that the formwork panels do not fall apart under the pressure of the concrete mixture.
The shields are placed along the foundation trench on both sides, supported by beams. To give additional strength, they are connected by jumpers. The height of the shields must correspond to the value of the base part remaining above the ground.
Reinforcement
In order to give the concrete mixture the required strength, a reinforcement cage is laid at its base. To weave the mesh, steel rods with a cross section of 1.2–2 cm are used, which are tied with simple wire.
For each row, use from four to six rods. The work is quite doable with your own hands, since the mesh is easy to knit. A foundation with such a frame will last much longer, since this option is less exposed to temperature changes.
In corner areas, you will need to additionally install reinforcing angles.
When installing a reinforcement grid in a trench, it is recommended to use a plastic pipe from which supports are cut. This precaution is necessary to ensure that the sharp edges of the metal do not prematurely damage the waterproofing layer.

The finished mesh is laid carefully, the structure must be a single whole to form a monolithic rigidity. Particular attention is paid to reinforcement, since the frame essentially represents the foundation skeleton.
Waterproofing
Before installing the reinforcement frame, a waterproofing layer is installed. To do this, simple polyethylene, old roofing felt or other bitumen-polymer materials are laid out over the sand cushion.
The waterproofing material is laid in such a way that its edges protrude beyond the formwork panels.
Concreting
The final stage of foundation construction is pouring concrete mortar into the prepared trench. It is prepared immediately before concreting begins. For this you will need:
- clean sand;
- cement material;
- water;
- crushed stone.
It is not recommended to skimp on the brand of cement, since the strength of the entire foundation depends on this condition.
When pouring the mixture, it is necessary to vibrate using special equipment or a simple stick. The main goal is to remove air bubbles that form void areas. This work will give your foundation additional strength.

The mixture is carefully compacted and leveled so that building materials can be easily laid on the surface of the foundation.
How to calculate
Let's find out what features of calculating the necessary parameters exist.
To find out the weight of the future shallow foundation, it is necessary to take into account the density of the building material from which the house will be built. In addition, it is necessary to take into account the dimensions of the future building: its length, width, area, number of floors, height.
If the foundation is of a strip type, then the weight of the internal load-bearing walls must also be taken into account. If it is columnar, then it is enough to take into account the weight of only the external walls of the future house.
The video shows how to calculate a shallow foundation:
It is necessary to calculate the volume of all building materials that will be required to form the foundation: the amount of concrete and the total length of the reinforcement. It will also be interesting to learn about how the old foundation under a wooden house is replaced.
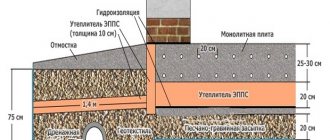
Insulation of the foundation
This is done without fail. The insulating layer simultaneously performs the functions of waterproofing, protects the foundation from soil heaving, preventing it from freezing under the object. For this purpose, the foundation is insulated from the outside, and an insulated blind area is installed.
To form the insulating layer the following is used:
- Styrofoam;
- extruded polystyrene foam;
- polyurethane in liquid state.
The latter option involves the involvement of experienced specialists who have special equipment to perform such work. To save money, many developers use one of the first two insulation methods, the technology of which is practically the same.
You need to know that not every brand of foam is suitable for insulating a shallow foundation. For such work, it is recommended to use special materials of the PSB-35 (50) brand.
Expanded polystyrene is considered a more modern option for insulation, it is resistant to compression, does not allow moisture to pass through, and is an environmentally friendly material. But its cost is slightly higher than that of polystyrene foam.
The effectiveness of insulation will be higher if the horizontal layer of material is located at the level of the foundation base. The most effective method is a combination of insulation measures with polystyrene foam along the blind area at the level of the sole and the base itself to the point where the walls begin. Insulating only the part located in the ground is ineffective. If the project provides for a basement part, it must also be insulated.
Having laid the insulating material horizontally, a sand cushion is poured. A blind area made of concrete or other moisture-proof material is made around the foundation.
If there is no heating at the site under construction, it is recommended to lay penoplex under the base of the foundation sole along the entire length of the line. Under unheated parts (verandas, extensions, garages), so that they are not torn away from the main object during soil heaving, insulation material is laid under the foundation.
Features of clay soils
The main problem when designing a building on clay soil is frost uneven heaving. However, paragraph 5.9 of the set of rules SP 22.13330 of 2020 specifies measures to reduce the influence of deformations in soils on reinforced concrete structures intended for operation inside the soil.

The principle of frost heaving is as follows:
- soils contain particles of clay, which are saturated with moisture (rain, groundwater, melt water, wastewater);
- freezes to a certain depth in winter (not the same in different regions);
- water in the lenses of clay flakes increases in volume by 9%;
- soils tend to push out reinforced concrete structures located in them;
- or overturn them when forces are applied to the side faces of pillars, strips or piles.
Attention! The most dangerous component of the swelling process is moisture, because... when saturated with moisture, even sand becomes heaving, then frost sets in, or rather freezing; in the absence of freezing, no soil will heave. Soils themselves are not heaving; it manifests itself in the presence of two components - frost and water.
The classic methods of protection against frost heaving are the following technologies:
- drainage - the installation of a circuit of perforated corrugated pipes along the perimeter of the foundation allows you to collect moisture and drain it by gravity into an underground reservoir;
- replacement of clayey soils with non-metallic material - natural soil is removed under the bottom of the tape, slab or pillar, an underlying layer of crushed stone and sand 40 - 80 cm thick is created (it will not work without drainage if water is saturated);
- insulation of the blind area and basement - used only for slab and strip foundations, it allows you to prevent freezing by preserving the geothermal heat of the subsoil;
- backfilling with the same inert materials that were used for the underlying layer (sand, crushed stone) eliminates pull-out forces from tangential loads on the side surfaces of pillars and strips.
Clays and loams by default have a high design resistance to prefabricated loads from the building. Therefore, the problem of shrinkage is completely absent. The issue of choosing a foundation is decided from the standpoint of the available budget and the need for a basement floor.
How to determine clay soil
After choosing the type of foundation (deep strip for the basement floor, MZLF for a brick cottage, pillars for a log house, piles for a dwelling on a slope), you need to order a geological survey of the site or do it yourself.
The clay content in a building spot can be determined without laboratory analysis:
- the clay rolls into a thin rope, the ball of it practically does not crack when squeezed with your fingers;
- Loam can be rolled into a thick rope (from 1 cm); when the ball is compressed, small cracks form on it.
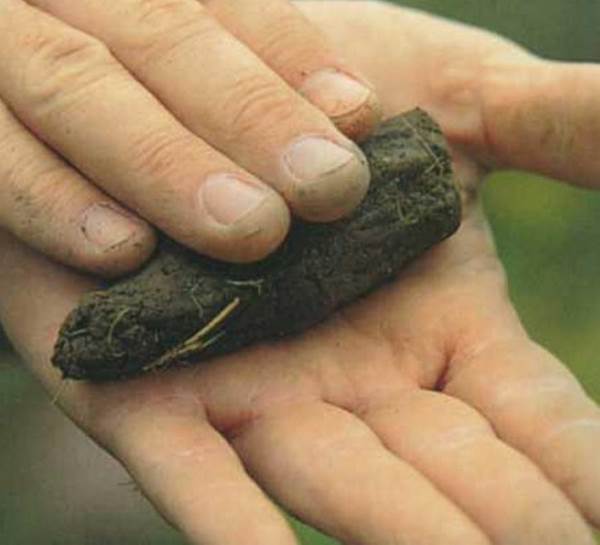

None of these activities can be done with sandy loam, especially sand.

After which it is necessary to plan a set of works to prevent swelling, depending on the selected foundation:
- pillars - only below the freezing mark, drainage around the perimeter at the level of the sole, a foundation pit for each pillar, backfill layer thickness from 40 cm on all sides, the blind area is insulated only for a low grillage;
- tape - a full range of similar works;
- slab - insulation of the blind area over the drainage.
Attention! For pile foundations with a hanging grillage, all of these measures can be eliminated completely. If bored piles are concreted into formwork made of polyethylene pipes, tangential swelling forces can be ignored; the soil cannot pull out the structure due to the smooth outer walls, however, when calculating, it must be taken into account that the load-bearing capacity of the piles will decrease due to the loss of the side faces, which means more frequent repairs will be required. installation. The situation is similar with screw piles, in which heaving forces are also not taken into account during design.
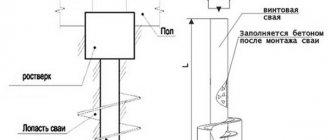
Shallow strip foundation on bored piles
This foundation option includes a monolithic reinforced concrete strip and bored piles. This shallow columnar foundation on heaving soils can be erected independently.

The piles will pass through a layer of heaving soil and rest against denser layers that have better load-bearing capabilities. This method of building a foundation is also justified in areas with close groundwater.
To determine the optimal depth for drilling wells, a test screw pile is driven in to determine how deep the dense layer lies. After this, wells are drilled, asbestos pipes, polyethylene or roofing felt are installed in them, reinforcement is inserted, the ends of the bark should protrude by about forty centimeters, and concrete mortar is poured.
As soon as the piles have hardened, you can begin reinforcing the monolithic tape, connecting the general frame with the pieces protruding from the supporting elements.

Installation of formwork
The formwork is erected for a shallow type of foundation; there are no requirements. For work, you can use any wood material: boards, slabs, panels, however, for permanent formwork, it is better to use asbestos-fiber flat slate, a material that is resistant to aggressive external environments and rotting processes.
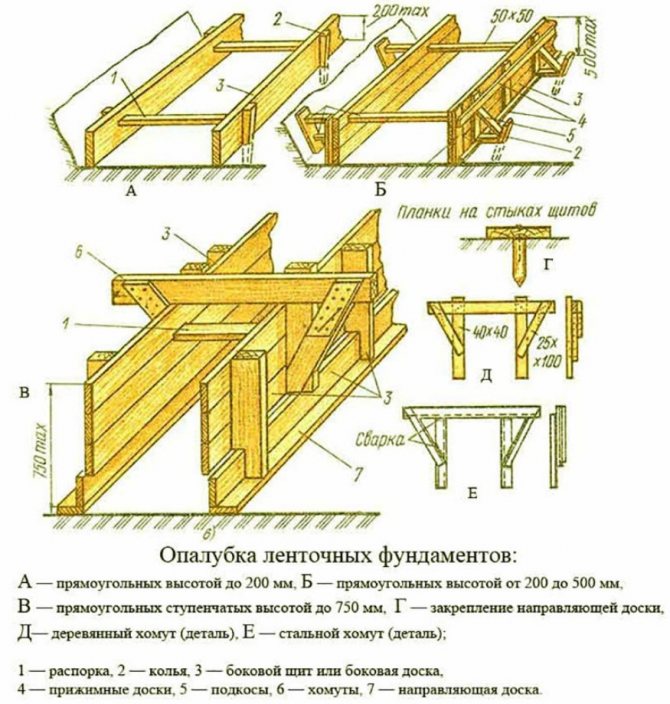
Formwork
The formwork is assembled out of place; panels are pre-made and installed on a frame prepared in the trench. For reliability, the latter is reinforced with spacers and cross members.
Backfilling and compaction
The sand base is an intermediate link connecting the base of the building to the ground.
When pouring, it is necessary to comply with the technical requirements:
- Make slopes with a steepness of 1:1.5;
- Strengthen by sowing grass, turf and other available methods;
- Make sure that the dimensions in the upper part coincide with the dimensions of the outer side of the building being constructed, increased by the size of the berm (1.5 m);
- Make a slope of at least 3° from the center to the outer perimeter.
The sand and gravel mixture is compacted using vibrating tools. Among them:
- Vibroleg. Powered by a diesel or carburetor engine. Used in areas with limited space, for example, when laying a foundation base. The working part of the apparatus is a heel 33 cm long and 15 to 30 cm wide.
- Vibrating plate. It is used in the arrangement of slab-type foundations.
- Vibratory roller. Used to compact the sand layer on large construction sites.
Which sand to choose
Three types of sand are used in construction:
- Career. Allowed for use at zero stages. Considered low grade. Contains a large amount of clay. A high percentage of clay inclusions reduces the strength of the solution.
- Nautical. It contains a lot of shell fragments and sharp pebbles. Requires pre-cleaning.
- River. Popular sand for pillows. Characterized by the absence of clay. There are no impurities that degrade the quality.
All types of sand presented on the construction market require gradation.
Small fractions (less than 2 mm) are compacted too tightly and cause significant shrinkage. Used in the construction of gazebos and verandas.
Medium fractions (2-3 mm) are suitable for forming a cushion under the foundation of one-story residential buildings.
The base substrate for high-rise buildings is formed from coarse sand. Mixing with gravel helps improve its properties.
Fill
Concreting should take place in one day - there should be one layer of concrete. For large volumes, it is necessary to carefully organize the work and agree on the delivery of concrete.
To concrete the base you need a lot of concrete, you will have to order it delivered in a mixer.
Concrete is poured in two ways: along a tray, using sleeves. Served from different sides, leveling in the formwork is much easier. It is necessary to monitor the consistency of the solution - it should be quite liquid and homogeneous. If the composition is too thick, you need to inform the mixer operator; dilution of the concrete with water is provided.
Liquid concrete is needed to facilitate concreting and obtain a high-quality foundation - if the concrete composition is not uniform, the formwork will not be filled evenly.

Concreting
After concreting is completed, the poured formwork is protected from rain and sun. If the weather is hot outside, you will have to take care of the concrete - periodically water it with water so that it does not crack during accelerated drying.
Concrete will gain strength over several months, but to continue construction work on the construction of walls, you can begin after 4 weeks.
Video – laying the foundation:
Materials for creating a pillow
Even judging by the name, a “sand pillow” is made from sand, but not just any sand, as it might seem, but coarse-grained sand.
The ideal option is coarse gravelly sand. It is “coarse” sand or medium-fraction river sand that will resist possible shrinkage of the structure.
But many experts recommend using a sand-gravel mixture to create a layer, citing better drainage and compensation properties.
In fact, for the compensation layer you can use any less heaving material that resists compression well.
It is much more important to protect this layer from the influence of moisture during seasonal increases in groundwater levels. To do this, you need to prevent the soil from mixing with the sand cushion by laying a layer of geotextile between them.
Why is it needed?
A sand base is the basis of the foundation. It must be poured when laying prefabricated strip and slab bases.
It contains several functions:
- Leveling the bottom of the pit and trench (saving concrete mortar);
- Reducing soil load;
- Compensation for soil movements during spring floods;
- Improvement of subsiding, unstable soils;
- Replacement of excavated heaving soil in order to increase the load-bearing capacity (the strength of the foundation increases, its integrity is maintained, and durability increases). It is used in the construction of buildings in wetlands with peat soil;
- Disposal of rain and melt water (drainage);
- Destruction of capillary connections, preventing the rise of moisture from the upper layers of the soil and its penetration into the foundation;
- Protection of the foundation from freezing;
- Ensuring the stabilization of the structure, reducing the degree of shrinkage. (Sand resists excessive expansion and compression).
- Depreciation of the foundation of multi-story buildings.