Durable, reliable, resistant to all types of external influences, suitable for any type of soil, inexpensive - pile foundations made of screw piles meet all these requirements. This fact is confirmed by positive reviews from professional builders and owners of houses built on foundations of this type.
The construction of pile-screw foundations is quite simple. This design consists of individual elements - screw-in piles, interconnected into a single system that has the highest load-bearing capacity and resistance to seasonal soil movements, the effects of groundwater and other adverse factors.
A leading manufacturer of pile products, ZVS LLC offers to buy foundations on screw piles in Moscow and the Moscow region. Our prices for pile-screw foundations are among the lowest in the region. You can order a cost estimate by phone or on the website.
Pile foundations: indications for arrangement
Unstable soils are far from the only reason for constructing a pile foundation
Unstable soils are far from the only reason for constructing a pile foundation. In cases where the construction site is located on very dense soils, such a foundation is also the only correct solution. Benefit - no need to deal with a large volume of excavation work and a significant reduction in the cost of using heavy equipment. And this:
- digging pits;
- removal of soil to dumps;
- delivery of a large amount of mixture for concrete mortar.
Ultimately, it will be possible to do without arranging formwork. Example: when installing a pile, you need to remove 0.2 m2 of earth, which means that an ordinary drill or even a shovel is quite suitable. The construction of a strip foundation will require much greater physical and monetary costs.
How to make a pile-strip foundation with your own hands: step-by-step instructions
The installation of a pile-strip foundation begins with the preparation of the territory. We clear the site of unnecessary debris and remove the top fertile layer of soil.
Marking and excavation work

The drawing and calculations should be ready by this time. We transfer the drawing to scale to the construction site. To do this you will need:
- stakes;
- rope.
We determine the first angle using a device (theodolite) or take a nearby structure as a reference point. We drive in the necklace. We mark the second corner opposite the first at the required distance and drive in the second necklace. We stretch a fishing line or rope between them.
Next, we do the same with the remaining corners. We mark for the outer and inner sides of the wall. The width between the walls will depend on the house you are building.
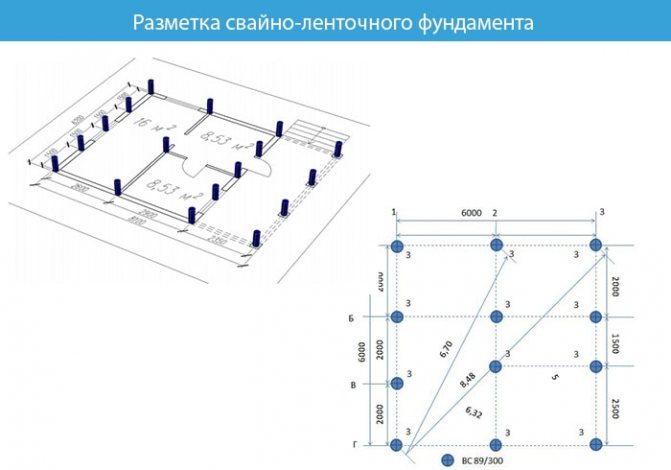
Important! For convenience, when digging a trench, move the stakes at a distance of 0.5 m from each corner.
We dig trenches according to the markings, for this you will need:
- bayonet and rock shovels;
- wheelbarrow (for removing soil).
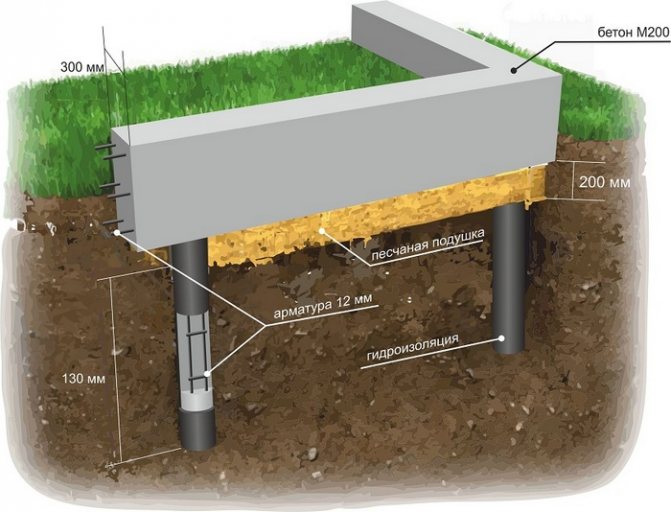
As an example, we will consider a shallow foundation. Therefore, we make the width of the trench 0.5 m by 0.1 m wider than the future tape. So that there is a gap for installing the formwork structure. Using the example, we deepen it to a distance of 0.5-0.7 m.
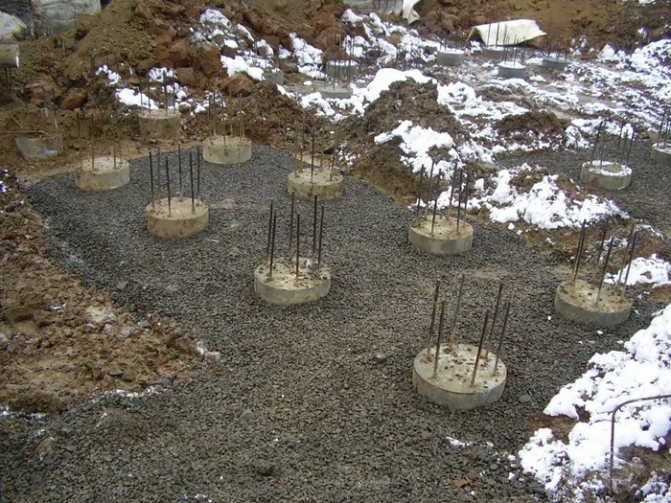
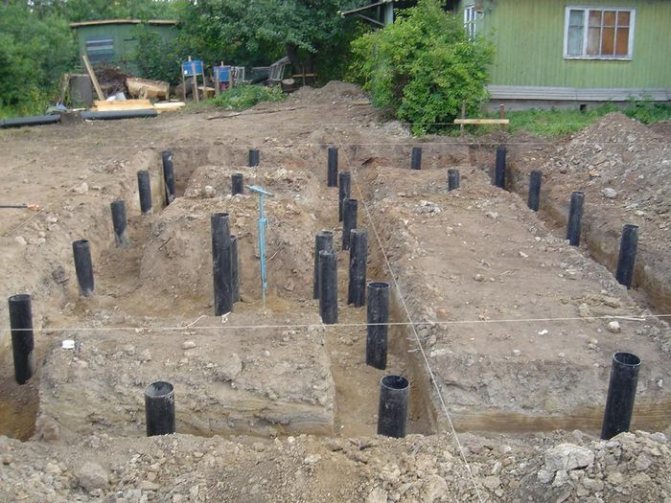
When the trench is ready, we proceed to drilling a hole for the piles. To do this you will need: a drill or a tractor with a drill.
We make a well below the soil freezing level, approximately 0.4 - 0.5 m (so that the pile rests on stable soils). With a diameter of approximately 0.1 - 0.15 m.
Installation of foundation piles
We use bored piles.
To install bored piles you will need to perform the following steps:
- We make a sand bedding 0.1 m thick and compact it.
- On top we install a difficult formwork made of asbestos cement (we select the pipes from the calculations as 1/3 of the width of the concrete strip).
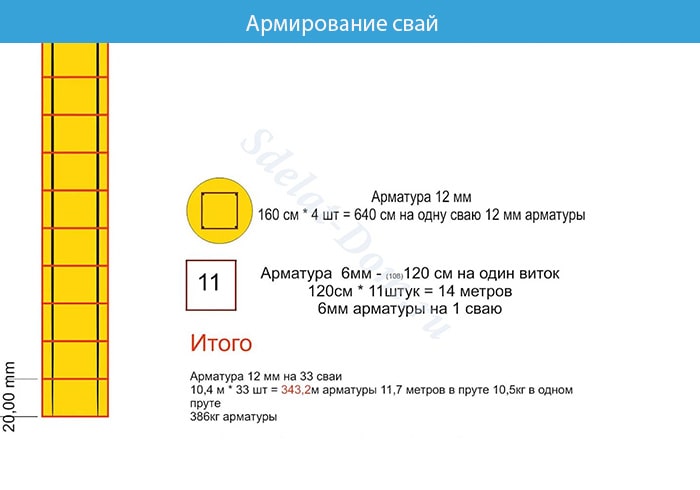
- We strengthen the piles with a reinforced frame. We tie 4 rods together with wire. We take the thickness of the reinforcement to be at least 10–12 mm, and the length should be enough for tying with a concrete tape. The frame should not touch the walls of the formwork.
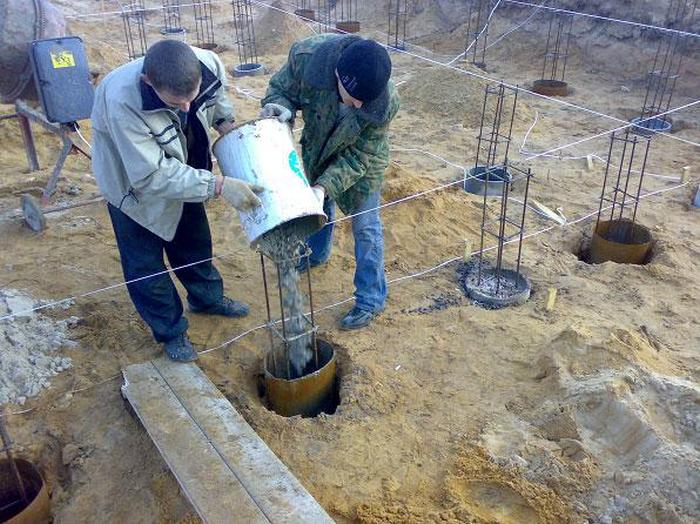
- The last stage is pouring. We prepare a concrete solution of grade M200-M300.
Important! For screw and submersible piles, you do not have to dig a well. Screw ones are screwed into the ground, and submersible ones are mounted using a special machine (pillar).
Sand and gravel bed
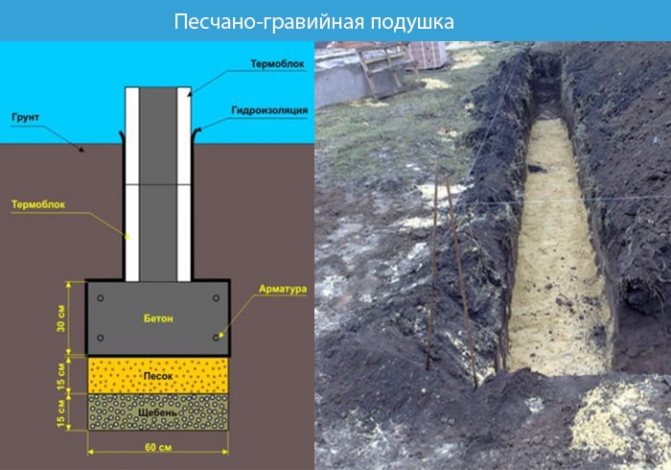
We lay geotextiles, preventing the pillow from flooding with groundwater.
There are two types of bedding:
- Gravel-sand mixture. Proportion for preparation (gravel/sand – 2/3) The thickness of the pillow will be 20–30 cm.
- We fall asleep in layers. The first is a 15–20 cm layer of coarse sand, and the second is a 20 cm layer of fine crushed stone or gravel.
Important! Any non-metallic materials are suitable for backfilling. For example, expanded clay, blast furnace slag and others.
Grillage formwork
The formwork of the foundation strip is created from wooden panels. Boards, plywood or chipboard are knocked together. The thickness of the shield structure should be 3–5 cm to withstand the load.
We bury the shields into the bedding by 5–7 cm from the outer and inner sides. We strengthen the corners of the formwork, because the load acts on them the most.
Along the perimeter we strengthen the structure with racks every 0.5-0.8 m, and the outer and outer sides are fastened together with studs.
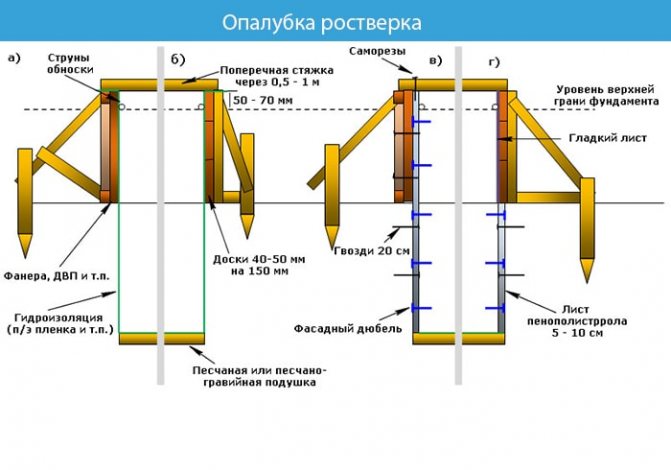
Formulas for calculating lumber for formwork can be found in the article.
To install the formwork you will need:
- plywood or board thickness – 3–5 cm;
- self-tapping screws;
- studs and posts (for strengthening).
Important! We install ventilation and communications.
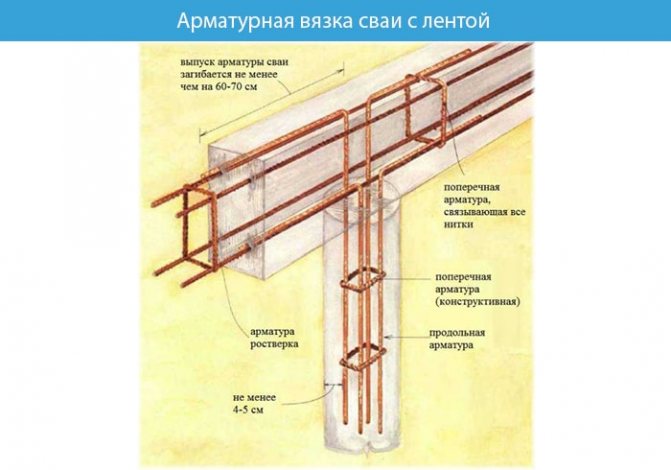
Grillage reinforcement
The reinforced frame is connected using spatial knitting. Strengthening the foundation with A3 class corrugated reinforcement with a diameter of 12–14 mm. The rods are placed longitudinally to each other, and connected to each other with 3–6 mm wire at a distance of 40–60 cm. At the same distance, reinforcement bars are installed vertically, forming a square.
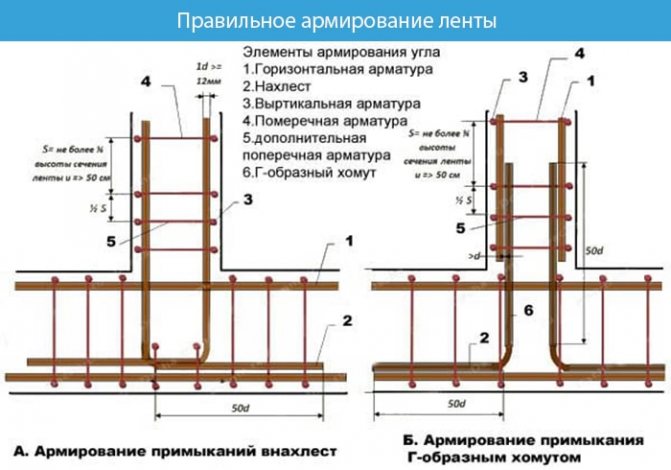
The corners of the reinforcing frame are connected by curved rods on the outer and inner sides at the bottom and top, the rods are connected with annealed wire.
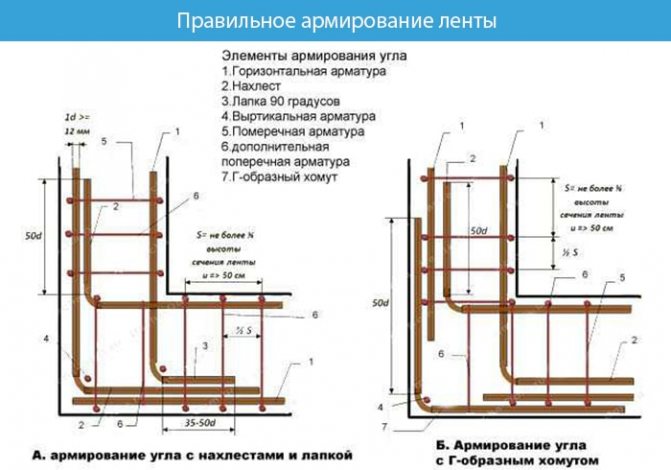
The finished design of the reinforcing belt is connected to the reinforcement of the piles.
Fill
We fill the pile-strip foundation with concrete of class no lower than B15.
To prepare cement you will need:
- cement;
- sand;
- crushed stone;
- water;
- concrete mixer.
Recipe! Preparation of concrete class B15 grade M200 per 1m3. Proportion for mixing in a concrete mixer: cement, sand, crushed stone - 1 / 3.5 / 5.6 (kg). Add water by eye to form a heterogeneous mass.
The finished concrete solution is poured into the tape in portions or layers, compacted. Compact with a deep vibrator for uniform shrinkage along the tape and expel bubbles (or use a bayonet shovel to go around the perimeter). After pouring, cover with film and leave to harden. From 25–30 days, the base takes a solid, solid form, ready for insulation and blind area.
Waterproofing and insulation
For the tape you need to make waterproofing and insulation. To increase its durability by strengthening the structure by reducing moisture resistance.
There are several types of waterproofing:
Coating. The tape is treated with bitumen or epoxy mastic - this is a moisture-proof material. Rolled. We cover the tape on all sides with roll materials: Bikrost, TechnoNIKOL: external, internal and on top. Penetrating. At the stage of creating a concrete solution, a special additive is added - a primer. The special properties of the primer additive can reduce the porosity of concrete, while reducing its moisture permeability.
Advice! A good result shows an integrated approach. A combination of penetrating injection into a solution with a coating or roll material.
The base tape is insulated from the outside with penoplex or extruded polystyrene foam. The material is attached with slabs to the foundation together with the plinth. The advantage of the materials is a high heat saving coefficient, as well as resistance to moisture and rodents.
Houses on stilts - what it looks like

The main load falls on underground supports buried in the ground, reaching dense and stable layers
As a rule, an uninformed person categorically refuses a pile foundation, suggesting the construction of the foundation only in hot countries on the coastal strip. However, speaking about the ground part of the structure, it can be noted that the general appearance differs little from conventional pedestal structures used to provide support for secondary structures. The main load falls on underground supports buried in the ground, reaching dense and stable layers. Benefits:
- redistribution of weight load;
- ensuring the stability of the building under the threat of heaving, waterlogging, and soil displacement;
- reduction of movements in case of soil instability.
Moreover, a house on a pile foundation will not be saturated with moisture from the ground (snow, rain), which means that the underside of the structure will remain dry and last much longer.
Another reason for arranging the foundation on supporting elements is the complex terrain of the construction site. A foundation on piles will cope well with factors such as:
- decrease and increase in ground level;
- the presence of relict trees on the site, whose root system would not be trimmed.
When arranging such a foundation, the use of heavy equipment will not be required, which means that the garden plot will not undergo significant changes. And if this is a pile-screw foundation, then you can build next to historical monuments, of course, if the city planning committee allows this.
Turnkey project cost
The cost depends on the following factors:

dimensions of the structure;- complexity of hydrogeological conditions at the site;
- the complexity of the project itself;
- costs of preparatory work;
- the amount of machinery and equipment involved;
- the number of engineers, surveyors, designers and operators involved in the work.
The average market cost of planning screw, cast and driven foundations starts from 100,000 rubles. The customer will have to pay extra for an additional calculation of settlement in each section (from 20,000 rubles), as well as statistical and dynamic tests on the site.
In addition to the results of engineering calculations, specialized companies provide recommendations regarding measures aimed at minimizing settlement and deformation.
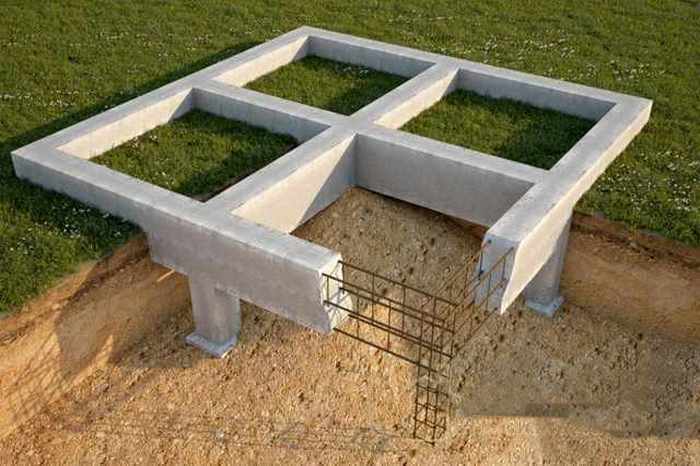
Construction of a pile foundation

Pile foundations are structures not intended for the construction of houses made of dense piece material (brick, concrete blocks)
It will be useful for a novice builder who has preferred a foundation on free-standing supports to know the structure of a pile foundation in order to think through the location of the house, create a project and take into account the necessary nuances.
Important! Pile foundations are structures not intended for the construction of houses made of dense piece material (brick, concrete blocks). It is necessary to carefully and in advance calculate the weight load on the supports, take into account the number of floors and the total area of the house. However, for buildings made of wood, timber, light panel houses, a foundation on piles is the most correct and optimal solution.
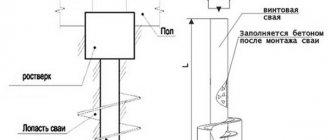
Piles are long rods buried in the ground to the required length to ensure the strength and durability of the entire building. Piles can be made in advance from wood, metal, or the structure can be made in the ground itself by digging holes and pouring concrete mixture. Elements prepared in advance are equipped with a pointed end (and blades in the case of screw piles), which greatly facilitates the deepening process.
What is a pile foundation and areas of application
Grillage
Grillage is a base element that serves as a support for the entire structure of the building being erected: wall panels, roof
In addition to piles, the foundation requires the installation of a grillage. A grillage is a base element that serves as a support for the entire structure of the building being built: wall panels, roof. Representing a slab, the grillage plays the role of a shock absorber, softening the load on the piles. The main weight of the building presses on the grillage, then is transferred to the piles and soil.
The peculiarity of a grillage is that it can be created above the ground, at ground level or under the top soil layer. The first and second options are clear, but if you look at the section of the latter, the underground grillage is more like a strip foundation, and many builders call it “reinforced strip foundation.” The grillage is constructed by creating a light formwork frame and then filling it with concrete mixture.
Thus, the section of the pile foundation represents the pile elements themselves, buried in the ground, with a grillage arranged on top of them. But it also happens that creating a grillage is not necessary. For example, when building a wooden house, this function is taken over by the first crown of timber elements.
Application area

The laying of pile-strip foundations can be carried out in all regions with different climatic conditions and on areas with any terrain.
Construction can be carried out on the following types of soil:
- layered;
- loose;
- heterogeneous;
- heaving;
- complex in composition;
- with high groundwater levels;
- frozen.
Scope of application of structures:
- private low-rise buildings;
- dachas;
- cottages;
- sheds;
- baths;
- garages, provided there is a gentle ramp;
- berths and piers;
- buildings on a slope and above depressions when leveling is not economically viable.
High-rise and heavy houses are installed on thick and powerful piles, where the role of the tape as a load-bearing element in such structures is practically absent. It is used to create an even support for the ceiling to prevent deformation under the weight of the structures on top.
Types of pile foundations, design features

The choice of deepening method determines the material and manufacturing technology of the structure.
To determine which “sole” is suitable for a building, you need to determine the type of soil, the weight load and know all the types of foundation on individual supporting elements:
- Friction Piles – This type of foundation requires many piles held in the ground by friction. The elements do not have dense and complete support on the layers of soil, as if hanging in it. The use of such a foundation in individual residential construction is ineffective and costly due to the complexity of the calculations.
- Retaining piles must penetrate well into the soil, reaching especially dense layers. Such a foundation will withstand very serious loads and will last for an extremely long time. Taking this technology as a basis, it would be useful to conduct soil reconnaissance. If the decision is positive, the foundation on retaining elements can be used as the basis for the construction of cottages, garages, and secondary private buildings.
The method of deepening pile elements differs:
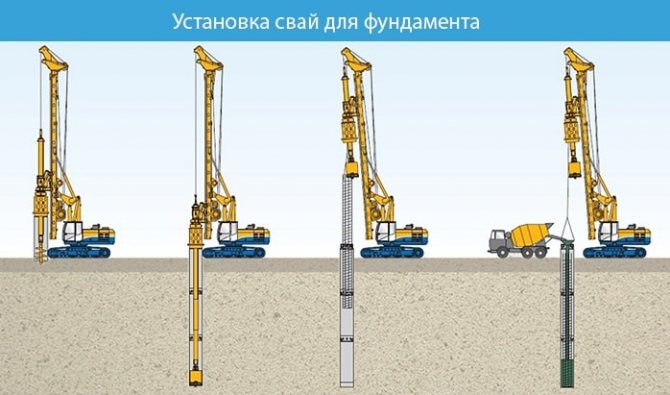
- Driven piles are equipped by pressing or driving into the ground with vibratory hammers.
- Drilling wells and pouring concrete is a technology for creating cast-in-place reinforced concrete and concrete elements.
- Preliminary punching of the soil and installation of piles in pits with subsequent pouring are called drilled piles.
- Screwing piles into the ground to a certain depth is a screw pile foundation.
The choice of deepening method determines the material and manufacturing technology of the structure. Also, a lot depends on the placement of the piles and the materials from which they were made.
How to install piles correctly? There are several options:
- Arrange free-standing supports, having previously calculated their number.
- Make support strips, placing them around the perimeter of the building.
- Create pile bushes, placing them in front of columns near the supporting frames of the building.
A prerequisite is the vertical location of the piles, the permissible deviation is no more than 5°. The inclined option for installing piles is used only in soils subject to seasonal or constant horizontal movements.
Bored piles: device technology and calculation
The material from which the piles are made is determined from the technology for creating the foundation. In order for the elements to last for a very long time, they are created on site by pouring concrete mortar into the pits, then reinforcing the piles with rods. Hollow or solid steel piles are at risk of corrosion, so it is important to treat them with special compounds and carefully waterproof them.
Advice! If the choice is made in favor of wooden piles, then you should give preference to coniferous wood with mandatory impregnation with compounds against rotting, damage by water and other aggressive substances.
Regulation Guide and Aids
The general set of rules for the design and construction of pile foundations is reflected in the regulatory documents SP 50-101-2004 and SP 50-102-2003 - updated versions of SNiP 2.02.01-83, SNiP 2.02.03-85 and SNiP 3.02.01-87. The manuals regulate calculation formulas and technological stages of installation of various types of piles in different hydrogeological conditions.
In parallel, SP 11-105-97, SP 11-104-97, SP 11-102-97 and GOST 5686-94 describe the requirements for geotechnical, geodetic and environmental studies for construction. Pile foundations intended for operation in an aggressive environment should be designed in accordance with the rules of GOST 27751. In order to correctly assess climatic conditions, the designer must be guided by SNiP 23-01-99 and SNiP 23-01.
Requirements for reinforced concrete piles with various design features are set out in GOST 19804-91, No. 19804.2-79, No. 19804.3-80*, No. 9804.4-78, No. 19804.5-83 and No. 19804.6-83.
The purpose of designing a pile foundation is a calculation-based choice of the type of structure, parameters, and materials. In the process of engineering calculations, decisions are made on the need to take measures to reduce the effects of deformations of the load-bearing structure on the suitability of the structure being designed.
Work technology

Regardless of which base is chosen, the installation of pile foundations is carried out using the same technology
Regardless of which base is chosen, the construction of pile foundations is carried out using the same technology, differing in nuances:
- Construction site marking;
- Pile placement mark;
- Deepening elements into the ground by driving, screwing or digging wells and pouring concrete;
- Reinforcement;
- Pouring concrete mixture;
- Arrangement of the grillage.
The simplest version of retaining piles looks like this:
- Drill a well using a hand drill;
- Pour the concrete mixture into the bottom;
- Insert an asbestos cement pipe (vertically);
- Reinforce the element with steel rods, pour sand on the sides;
- Fill with concrete, avoiding the appearance of air pockets;
- Wait until dry.
Remember that the pipe must be inserted into the hole without waiting for the solution to harden so that the pipe is firmly fixed. Readiness occurs within 3-4 days, but the distance between the piles cannot be more than 2 meters.
Important! It is not allowed to cut the grillage with communication pipes or engineering structures.
Disadvantages of pile foundations

The slightest mistake in calculating the mass of the structure or the number of piles will lead to misalignment, which means the destruction of the entire structure
Speaking about the advantages and emphasizing the benefits of a foundation on piles, one cannot help but mention the disadvantages of foundations:
- The need for careful calculations. The slightest mistake in calculating the mass of the structure or the number of piles will lead to distortion, and therefore destruction of the entire structure;
- Quite a narrow niche of application. It will not be possible to equip such a simple foundation for a heavy brick mansion; you will have to further strengthen the foundation, and therefore it is better to immediately choose a more labor-intensive, expensive, but more effective foundation.
However, a separate bonus is the ability to independently arrange the foundation on piles. As for the weight of the structure, today manufacturers offer a lot of materials that are much more practical and convenient than ordinary bricks and concrete blocks, but weigh significantly less. Therefore, a pile foundation is a really good alternative to all types of foundations when it comes to private independent construction.