Comparison of the two types
To make the right choice, you should compare the characteristics of both types of foundation:
- On what types of soil can it be used? If we are talking about a monolithic slab, then this is a universal method. It is used on almost any soil, even with low bearing capacity. Strip foundations are used on slightly heaving or non-heaving soils.
- Construction speed. No particular advantages have been identified for any type. When pouring concrete, in any case, you will have to wait at least 21 days to gain the required strength.
- Cost price. Here the strip foundation wins a little. When constructing it, less material is wasted.
- Life time. This is probably the most important characteristic. Contractor companies installing bases from monolithic slabs indicate a guaranteed service life of 15-30 years. But if all the work is done correctly and the base is properly maintained, then such a structure can serve for up to a hundred years. In the case of a strip foundation made by pouring high-quality concrete, the guaranteed service life reaches 150 years.
You can compare based on other characteristics, but using those already given above you can easily decide on the type of foundation for your new home.
What's better?
You won’t answer right away. It all comes down to the fact that there are different circumstances and opportunities. For example, it is worth considering the type of soil and the expected load. If you have an area where the groundwater is deep and the soil freezes shallowly, then you can use a shallow strip foundation (if the house is small and has 1 floor). There is no point in constructing a monolithic slab.
If we take equal conditions, then many differ in their judgments. Some argue that a monolithic foundation is considered universal and needs to be built. Others say the opposite. But judge: servicing a slab foundation is inconvenient, since there is no basement in which communications can be hidden. And the absence of a base will affect the service life.
What to choose
Which type of base should you prefer? First of all, you should pay attention to the quality of the soil in the place where construction will take place. If its load-bearing capacity is low and its heaving is high, then it is better to take a closer look at monolithic slabs.
The strip foundation has its advantages. Firstly, there are several design options depending on the depth of installation.
If the building is one-story and made of lightweight building material, then choose a non-recessed or shallow-recessed option. In this case, the consumption of materials is reduced, which means there is an opportunity to save money.
Secondly, many homeowners like a long service life. If all the work was carried out in compliance with the technology and there were no savings on the quality of the concrete mixture, then the structure will last up to a century and a half. In addition, home owners always have the opportunity to carry out repair work. Although they are complex, they are quite real. The same cannot be said about a foundation made from a monolithic slab.
Another advantage of the strip structure is that it becomes possible to create basements. To do this, it is enough to deepen the foundation to the required dimensions. The technology will not change in the future. Formwork is also made, a reinforcing frame is made, and concrete is poured. In the case of a monolithic slab structure, the creation of basements is impossible.
When making your choice, you need to take into account all factors. First of all, the geological and climatic features of the region are taken into account. The design of the house itself and the presence or absence of basements are also taken into account. Only by assessing the influence of all factors can you accurately determine the choice of foundation.
Block foundation for a residential building
Block foundation: features and stages of construction
Blocks for foundation construction are a modern building material that is popular due to its successful combination of affordability and impressive technical characteristics.

Manufacturers offer a wide range of blocks with different operating parameters, which allows you to select a material based on individual requirements.
Before constructing such a foundation, it is recommended that you familiarize yourself with the main positive and negative aspects of this option, as well as the specifics of installation. All these features are discussed in detail in this article.
Features of constructing a foundation from blocks
Device and types

The optimal structure of a block foundation usually looks like this:
- A sand cushion that is placed directly on the ground.
- Concrete base with reinforcement.
- Waterproofing layer.
- Asbestos cement sheet with a smooth surface.
- Concrete blocks, depending on the technology, are laid in 2-3 rows.
The use of blocks allows the construction of two main types of foundations:
- Columnar structures are considered a budget option. It is advisable to use this technology in regions with a harsh climate, where there is a significant depth of soil freezing, as well as with sandy soil or when it is highly acidic. They are usually erected during the construction of baths, outbuildings or panel houses.
- Strip structures are suitable for the construction of small residential buildings with low weight, for example, country cottages.
Advantages and disadvantages
In addition to the already mentioned affordability, the construction of block foundations has the following positive aspects:
- The ability to withstand the effects of not only severe frosts, but also sudden changes in temperature. Such frost resistance is achieved by adding special additives to the base material of the blocks, which makes it possible to use them even in regions with extreme climatic conditions.
- Increased degree of resistance to various chemicals and aggressive environments. This allows the blocks to be used during construction in areas with soil characterized by high acidity.
- The impressive strength of the material increases its reliability and service life of the foundation.
- A wide range allowing you to select blocks of various shapes, sizes and compositions.
Despite so many advantages, the material is not without certain negative aspects, which are as follows:
- The use of large dimensions requires the involvement of construction crews and special equipment, which adds additional financial costs and complicates the construction technology.
- The need to seal all seams and gaps, otherwise the foundation of the building will collapse, and cold and dampness will begin to penetrate into the building.
- The strength is quite high, but it is still lower than that of a monolithic structure.
Preparatory work
The construction of the foundation will be preceded by preparatory work, the algorithm of which is described below:
- Carrying out a preliminary calculation of a block foundation; for this purpose, special software is most often used, with the help of which the main technical characteristics of the structure being built are entered and the blocks are laid out. This will allow us to determine the fastening features of individual structural elements at the initial stage.
- During the calculations, it is necessary to determine the location of communications, since they will require holes to be made in the blocks. Information about this should be indicated when purchasing the material.
- Creation of a paper or electronic project of a construction site, on which the places where equipment, material and other objects will be placed should be marked.
- Primary preparation of the construction site involves removing the top layers of soil. The fastest way to carry out this process is with an excavator; The removed soil should be placed nearby as it may still be needed for backfilling.
- It is necessary to inspect the resulting pit and mark the axes of the future walls of the building. For these purposes, you can use wooden pegs and a fairly strong fishing line.
- At the final stage of preparatory work, internal drainage can be organized using the base, although this is not a prerequisite if high-quality waterproofing of the floor and walls of the building being constructed is ensured during construction.
pros

The slab base is widely known and quite actively used in construction. This situation is caused by the following advantages:
- The simplicity of the technology - the ability to carry out work by people without qualifications or install the slab base with your own hands.
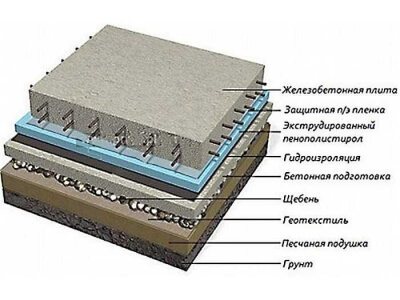
- No need for complex excavation work. The slab foundation is a shallow foundation, which means it is immersed in the ground above the level of winter freezing of the soil. Hence the need only to level the plane, remove the top layer of soil and carry out drainage backfill.
- The high strength of the slab provides reliable support for the building. Slab foundation with grillage: the advantages are that the thickness of the base is from 25 cm, and the concrete is significantly reinforced with reinforcing sheathing.
- The surface of the slab is the floor of the basement. This results in simultaneous construction of the base and construction of the ceiling, which significantly saves construction time.
- Possibility of construction on problematic soils. High groundwater levels create serious problems for builders. The slab foundation has a large area, which reduces the specific weight of the building. The pressure per square centimeter is much lower than with foundations with a small area of contact with the ground, which is why the loads from below are distributed evenly - they simply move the slab along with the building during movement.
For reference! The load-bearing capacity of the slab material has a significant margin of safety.
Advantages and disadvantages of a monolithic slab base

The slab has a high level of supporting non-essence, which allows it to withstand quite powerful loads
The following advantages of this building can be highlighted:
- Large support area. Which will cope with weak-bearing soils;
- High level of supporting non-entity, which allows it to withstand quite powerful loads;
- Simplicity of the pouring process;
- Primitive design that does not require complicated calculations;
- Minimum need for additional materials;
- It is not necessary to have formwork;
- Ease of earthworks.
To all these advantages, it is necessary to highlight the disadvantages:
- Large volume of materials;
- High bending load, which requires the installation of a powerful reinforced frame;
- With a monolith, the possibility of using underground utilities disappears. Even if they are laid, it will be impossible to carry out repairs;
- If this is a low-slung structure, then it is in no way compatible with basements.
Minuses
Slab foundation: the pros and cons should be considered as a whole, because along with a lot of advantages, the slab type of foundation has some disadvantages that should be taken into account when choosing the type of foundation:
- High material costs. The need to create a powerful thick slab requires a large amount of concrete and metal for reinforcement.
- Construction is carried out in stages, which requires a lot of time. Each stage is completed only after the previous one has been completed, which slows down the work and increases construction time.
- The need to carefully level the area and completely remove the top layer of soil. Construction equipment required.
- There is no possibility of equipping a basement (a basement can only be made by combining the slab with the floor of the basement).
Some disadvantages can be considered features of this type of foundation. For example, the time spent on building a foundation results in savings on arranging the floor of the 1st floor, and site planning is done almost everywhere, since the presence of a layer of turf is unacceptable when constructing buildings (with the exception of pile foundations).
In some cases, a choice is made in favor of other types, for example, a combined pile-slab or road slab foundation, as well as an insulated Swedish slab (USP) or an insulated Finnish foundation (UFF).
Strip-pile foundation
This type of foundation contains all the advantages of piles and tape. In the photo you can see exactly what the strip-pile foundation looks like.

The advantage is that there is not a continuous strip in the ground, which will require quite a lot of concrete and consumables, but piles or supports. This does not affect the quality of the foundation in any way, but the time for constructing the structure is significantly reduced. The same can be said about finances. More details about how to build a strip-pile foundation are discussed in this video.
Which foundation is better: strip or slab?
Before starting construction, the question of whether a strip or slab foundation must be resolved: which one is better to choose in a particular case?
The choice of foundation type is decisively influenced by the geological conditions of the site.

Groundwater level, soil composition, freezing depth in winter - all these factors are taken into account when determining the optimal foundation option. Unfavorable indicators for any of them are grounds for revising the project and changing the type of foundation to a more suitable one.
For reference: the need to choose between a slab or strip type of base may arise if there are conditions that allow one to accept both points of view.
When deciding whether a strip or slab foundation would be better, choose a strip based on the following considerations:
- average freezing depth;
- low groundwater level;
- sandy or mixed soils;
- absence of seasonal soil movements and heaving processes.
This is the most successful combination of conditions for using a strip foundation. In addition, the need for a basement, saving money on materials and reducing construction time are taken into account.
For choosing a slab foundation, the conditions are more stringent:
- high groundwater level;
- medium or high degree of soil heaving;
- The composition of the soil is clay and loam, which do not allow water to pass through.
Which is better: a strip foundation or a monolithic slab in the above cases? Such circumstances will not allow the construction of a buried foundation, and ground movements will create a serious problem for the integrity of the building, so the slab option in these conditions will be the most preferable.
In cases where both options can be accepted with some reservations, then when deciding whether a foundation is slab or strip: which is better, the selection criteria are financial considerations, the need for a basement and the possibility of doing construction work with your own hands.
To simplify the work, but at slightly higher costs, a slab type is suitable, but for more trained builders, in the context of the need to save money, it would be more correct to use a strip foundation.
Reinforced concrete foundations as a leading technology in suburban housing construction
If developers have an eternal debate regarding the choice of materials for walls and roofs: what is better and what is worse, then as soon as the question concerns the foundation of the building, there is no disagreement. In this area, the absolute leader today is concrete.

Although, until recently, in the last century, foundations were sometimes built from brick or dense shell rock, now no one would even think of putting their house on a foundation made of these materials.
Reinforced concrete (reinforced concrete) is currently used for these purposes. By all characteristics, this is the cheapest, most durable, and most durable material, and there is simply no other choice.
However, if there are no problems in choosing a material for the foundation of a building today, there are disputes in the choice of its design.
Thus, in the private housing construction market there are four main types of foundations:
Foundations on pillars or piles are only suitable for small wooden dachas and household buildings: sheds, bathhouses, etc. It is quite difficult to build a residential building for permanent residence on them, since they do not “support the weight” of heavy walls and ceilings well.
Obviously, for more serious cottages: 2 or 3 floors, with an area of 150 sq. m. m. It is better to consider strip and slab foundations. Let's look at their advantages and disadvantages in more detail.
Approximate price per 1 sq. m
Here the answer to the question is clear: a slab foundation is one of the most expensive types of foundation, which is caused by the high consumption of concrete, reinforcement and waterproofing materials.
Different sources indicate different amounts of costs caused by the need to work in different conditions, so there is no clear answer to the question, what is the price of 1 sq. m. m slab foundation does not exist.
Using calculations from different organizations and comparing the values declared by them, it is possible to indicate the boundaries of expenses with more or less acceptable accuracy. Monolithic slab foundation price for 1m2 will be from 2 to 4 thousand rubles/sq.m. m, but these figures should not be taken as a final conclusion.
Differences in delivery distances, site conditions and local geological conditions can significantly change amounts and make costs either lower or higher.
Which foundation is cheaper: slab or strip? The first will be many times more expensive due to the higher consumption of materials, and practice shows that the estimated cost amounts when choosing a monolithic slab base must be increased by 1.5–2 times to cover unexpected and unaccounted for costs.
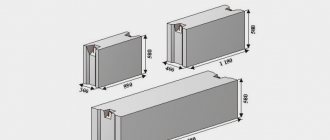
Slabs for strip foundations.
Welcome, my dear, to the pages of the site umnyestroiteli.ru, now we will discuss strip foundation slabs, find out how strip foundation slabs are laid correctly, as well as where you can buy slabs for strip foundations and at what price.
Strip foundation slabs are a triangle without an upper part, a sharp end, more precisely in the photo on the left you can see slabs for strip foundations and are intended for use in the construction of prefabricated strip foundations for residential and non-residential buildings and structures, in dry and water-bearing soils, with the expectation that the water-bearing soil will not have an increased aggressiveness of the environment, waste, alkali, etc. Strip foundation slabs are used in places where seismicity does not exceed a threshold of 9 points, but a monolithic strip foundation is built in places with seismicity up to 4 points according to Medvedev, and slabs are made from heavy grades of concrete.
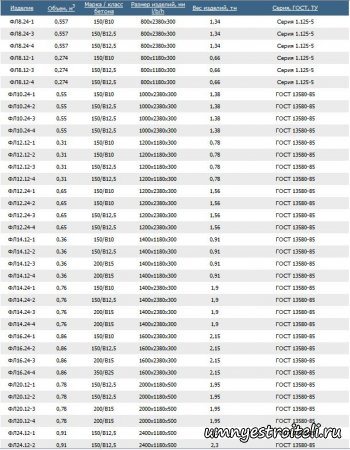
What types of strip foundation slabs are there?
Strip foundation slabs come in different sizes and characteristics, have their own weight, length, width and height, all data on slabs for strip foundations can be seen in the table below, where L is the width of the strip foundation slab, h is the height of the strip foundation slab and b is the length of the product in our case, slabs for strip foundations, and so look at the table with the parameters of slabs for strip foundations; when you click, the table enlarges.
Where to buy, buy strip foundation slabs.
New slabs for strip foundations can be purchased from the manufacturer’s factory, of course, at not low prices, but there is a much more convenient option, since our construction service is Construction from A to Z. Enakievo-Donetsk is engaged in the dismantling of unfinished residential and industrial buildings that have not been put into operation and which have not stood for even ten years, so the slabs for strip foundations are almost like new and you don’t have to worry, the slabs for strip foundations are without defects and you don’t have to worry about these slabs, which undergo additional testing for compression and expansion, broken and with visible defects slabs for strip foundations are used for backfilling or for the construction of one-story houses and light structures. Strip foundation slabs and other products that we offer can be seen in the article “Selling reinforced concrete structures”.
How strip foundation slabs are laid.
Strip foundation slabs are laid using foundation block technology, which is described in detail in the article prefabricated foundation, where you will learn in detail what you will need to independently assemble a prefabricated strip foundation. Well, in short, the situation is like this: before laying the slabs for the strip foundation and creating a monolithic belt, it is worth making a level base, which is achieved by tamping the base, adding 40 centimeters of bedding and tamping it. Pouring concrete onto the resulting base, thereby creating a preliminary even layer of concrete with reinforcement five centimeters thick.
Need for construction
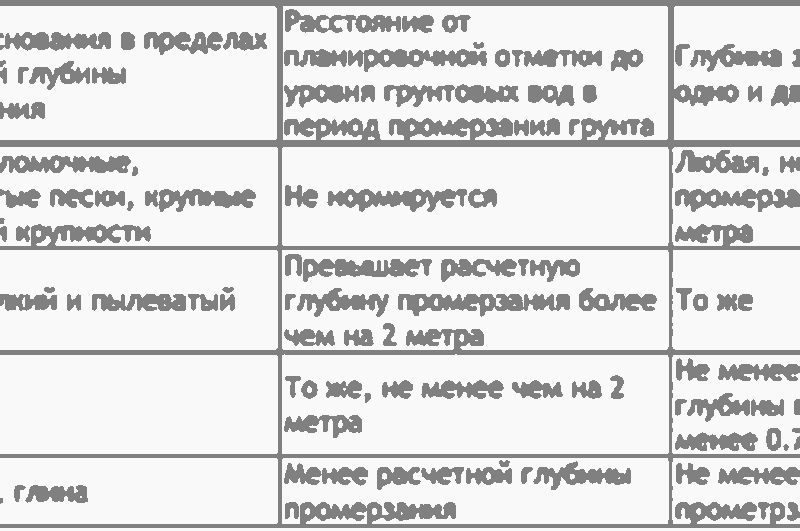
Calculation table for a strip foundation for a house.
As you know, in our climate the top layer of soil freezes in winter. The water contained in it expands when it freezes, and the soil, as a result, swells. When freezing to a depth of 1.5 meters, soil swelling can amount to 10-15 cm.
The foundation is needed primarily to prevent these processes from distorting or destroying the house. In addition, it helps to evenly distribute the load on the foundation of the house, in other words, on the ground. Its design is determined by the weight of the structure, the type of soil, the depth of freezing, and the level of groundwater. Three fundamentally different types have been developed:
- Recessed - resting its base on stationary, non-freezing soil.
- Shallow (floating) - a solid and durable slab under the house, moving along with the thawing and freezing soil. Because of its strength, it prevents the house from collapsing or warping.
- An insulated monolithic slab that prevents freezing of the soil under the house, for which it is carefully insulated around the perimeter.
Structurally, foundations are divided into the following types:
- columnar - the cheapest;
- pile;
- tape type (prefabricated and monolithic);
- slab.
As already noted, the last two types of foundations are most often used for low-rise construction. The choice of a specific type depends on the design of the building, the magnitude of the loads transmitted to the base, and the bearing capacity of the soil.
Tape base
Scheme of strip foundation reinforcement.
For most of the European part of Russia it is traditional. The tape can be block (prefabricated) or monolithic. If a cellar is planned to be built under the house, then the foundation must be monolithic, otherwise the seams between the blocks will reduce the tightness of the structure and you will have to spend a lot on reliable waterproofing.
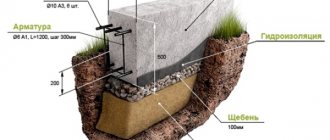
There is nothing particularly complicated in the technologies for constructing strip foundations. But to obtain a strong and durable structure you need to work hard and spend money. The depth of its laying should be at least 20 cm below the soil freezing level (in the North-West of Russia - 1.5 m). Only under this condition does the base rest on non-freezing soil that is not subject to swelling.
The material from which the foundation is constructed and the thickness of its tape are clearly related to each other:
- reinforced concrete - minimum thickness 10 cm;
- concrete – 25 cm;
- rubble concrete – 35 cm;
- stonework – 50 cm.
Scheme of a strip monolithic foundation.
Unlike other types, the tape manufacturing technology is distinguished by its functional simplicity, but requires large expenditures of building materials, primarily concrete. Requires formwork and sometimes a crane. The construction of such foundations is quite expensive and labor-intensive.
They are usually used in the construction of heavy houses: stone, brick, with weighted reinforced concrete or metal floors. They also have to be used where there is a threat of uneven settlement. In this case, the strip foundation works as a single monolith, redistributing loads over the entire area, protecting the building from deformation.
Prefabricated belt
Scheme for calculating foundation loads.
The blocks come in thicknesses from 30 to 60 cm. The first row of blocks is mounted on a concrete base 10 cm thick. The next rows of blocks are laid over the roof on cement mortar so that the seams in rows adjacent in height do not coincide with each other.
To build a rubble concrete foundation around the perimeter of the future house, first a trench is dug a little wider than the width of the wall. Then the trench is filled with large stones with small stones added to the voids between them. Finally, all this is filled with liquid concrete.
If a basement is planned, the foundation must reach the level of the ground floor. If there is no basement or cellar, it should rise 15-20 cm above the ground.
On an inclined section, blocks are laid in ledges from a lower level to a higher one. In this case, the length of the ledge should be twice its height.
Monolithic tape
Foundation construction diagram.
To fill, first dig a trench approximately the same as for a rubble concrete foundation. The bottom of the trench is covered with a cushion of coarse gravel or crushed stone 30 cm thick and carefully compacted. If the soil is dense and does not crumble, then the walls of the trench can act as formwork, and removable formwork will need to be installed only above the ground level.
To prevent the formwork from deforming under the pressure of poured concrete, additional stakes are driven into the soil to support the walls of the formwork. At the top, its edges are connected by strips so that they do not diverge. Large gaps in the formwork through which concrete can leak should be covered with pieces of some kind of film.
In loose sandy soil, the formwork will have to be installed to the bottom of the trench. Reinforcement is installed into the finished formwork and secured with soft wire, and then concrete is poured into the formwork. The hardening concrete is covered with straw mats or burlap and watered for 2-3 weeks so that the concrete sets and does not dry out. The end result is a reinforced concrete structure, strong and monolithic.
The recipe for preparing concrete for a monolithic foundation depends on the properties of the soil in which it is being constructed. In ordinary soils, the ratio of crushed stone, sand and cement in solution is 5:3:1. For wet soils, a ratio of 4:2:1 is recommended.
Shallow belt
This type of foundation is usually used for small stone and wooden houses. It is constructed in exactly the same way as an ordinary monolithic one, but with a laying depth of 50-70 cm. It can only be laid on slightly heaving soils. The construction of a basement or garage with such a foundation is unacceptable.