Features of slab-strip foundation
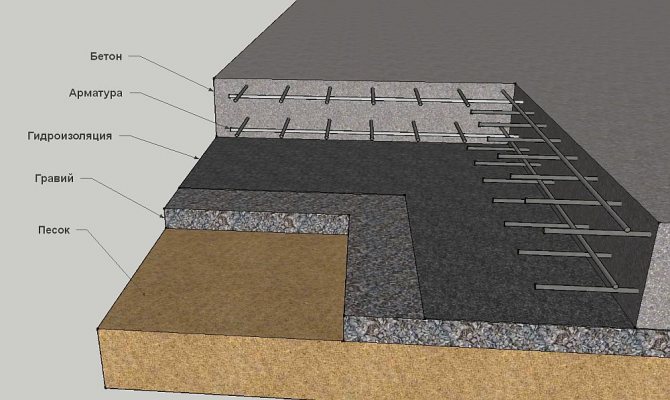
Layout of a monolithic slab-strip foundation:
- priming;
- sand and gravel cushion;
- geotextiles;
- footing;
- waterproofing;
- monolithic slab;
- concrete slab reinforcement
Table No. 1. Advantages and disadvantages
Application area
The inverted bowl is used for the construction of light wooden, frame cottages, and timber houses. Uncommon for low-rise aerated concrete structures. Because the plate distributes the load onto a shallowly buried strip (stiffening ribs). The entire weight of the house falls on them; heavy houses cannot stand it in this case.
The inverted bowl type of base is expensive due to the costs of concrete mortar, formwork, reinforcement, drainage and other work.
A slab-strip foundation (inverted bowl) is used in case of unstable soils. Such as: heaving soils, weak soils, high groundwater levels and high seismicity.
Construction of a slab foundation
Before construction begins, it is necessary to conduct a site survey. The type of foundation, thickness of the pad and concrete slab are selected based on the composition of the soil, groundwater level and loads. Work begins with uprooting plants and clearing the soil at the building site to about the size of a spade. Each type of slab foundation has its own characteristics, but the main stages remain the same.
Work order
Construction stages:
- Excavation of soil for a foundation pit.
- Making a foundation cushion from compacted sand, crushed stone or a combination of layers of different materials. Before backfilling, geotextiles are laid on the dry bottom of the pit so that the backfill does not mix with the soil.
- Concrete preparation, footing, is a layer of lean concrete of at least 100 mm for additional waterproofing and leveling the bottom of the pit. There are different opinions among builders regarding the need for this stage. Sometimes they refuse it, but the decision depends primarily on the type of soil.
- Groundwater drainage. Pipes for draining groundwater are laid in a pit under the foundation cushion with the required slope (5 mm per linear meter).
- Waterproofing is necessary if groundwater comes close to the base of the foundation . In this case, concrete with its porous structure will absorb water, which will lead to corrosion of the reinforcement. If the groundwater level is low, waterproofing is not necessary.
- Insulation of the foundation under the slab. The first method is to lay insulation (expanded polystyrene) under the entire area of the slab. When laying a heated floor, use PPS with a thickness of at least 30 cm. The second method is to insulate the foundation walls, lowering the PPS below the base, and the blind area, slightly extending beyond the edges.
- Reinforcement. Depending on the specific gravity of the structure, the thickness of the concrete slab is calculated and the diameter of the reinforcement .
- Installation of formwork. The cheapest option is made from boards with natural humidity from 40 mm, usually 50x150. Thinner formwork may not be able to hold concrete, which will lead to violation of linear dimensions. If the formwork is removable, then after its removal the boards are reused for scaffolding or subfloors. Chipboard or polystyrene foam are also used as permanent formwork to immediately create a warm contour around the foundation.
- Pouring concrete.
- Removal of formwork, treatment with bitumen primer (primer).
- Filling the blind area - performed after completion of the exterior finishing.
Useful: We are building a foundation for a frame bathhouse or frame garage
All steps are clearly shown in the video:
Selection of base material
The decision on the choice of material for backfilling is made on the basis of SNiP and site analysis. The main criterion is the water saturation of the soil.
If the area is dry, use sand with a small layer of crushed stone . If the soil is saturated and there is water in the pit, then sand is abandoned in favor of crushed stone. The minimum thickness of sand backfill is 20 cm.

The ideal option is to order a soil study at the construction site, based on it, make a project, calculate the thickness of the pad and the height of the slab.
A special case is an artificial embankment with a difference in height
The main disadvantage of a slab foundation is its inability to be used in areas with large elevation differences. In some projects, in order to level out the difference in height, they build an embankment of crushed stone . If you make an elevation out of sand, there is a danger that the house will settle.
To prevent the embankment from spreading, you need to carry out additional actions: Expand the soil section by 3-4 meters compared to the foundation, dig a pit, fill it up and make an embankment of crushed stone. Crushed stone “does not spread”, unlike sand, and a stable base is obtained on which the foundation is built.

When building a frame house on a slab foundation, the budget is taken into account. To estimate the cost of the foundation, the cost of work and materials at each stage is calculated and summed up. The main cost items: digging a pit, compacting sand, waterproofing, insulation, reinforcement, construction of formwork and concreting. The estimate takes into account the costs of fasteners for formwork, costs of drainage and storm sewerage.

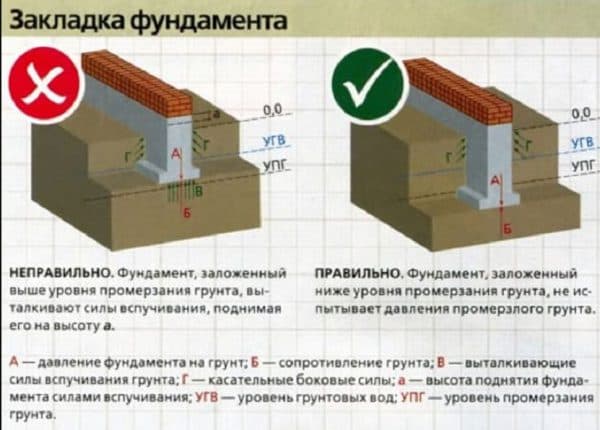
In frame house construction, different types of foundations are used: strip, columnar, pile. With heaving soil, there is a danger of the foundation being “pushed out” if it is buried above the freezing level. The slab foundation is called “floating” because of its ability to redistribute loads caused by heaving.
A slab lying on a sand cushion does not crack and the walls of the house do not deform. Such a foundation is reliable and does not limit the number of storeys, so cottages of 2-3 floors are built on it, reducing the building area and saving space on the site.
How to make an inverted bowl foundation with your own hands
Marking and excavation work
We transfer the project drawing to the construction site. We do this using cast-offs (stakes) and a theodolite. Between them we stretch a rope along the internal and external axes of the walls. The corners of the foundation must be without deviations from the norm (90 degrees). To check the angles we draw a diagonal.
After marking, we move on to earthworks. For a slab foundation, dig a small pit up to 1.5. Depending on the soil, it could be less.
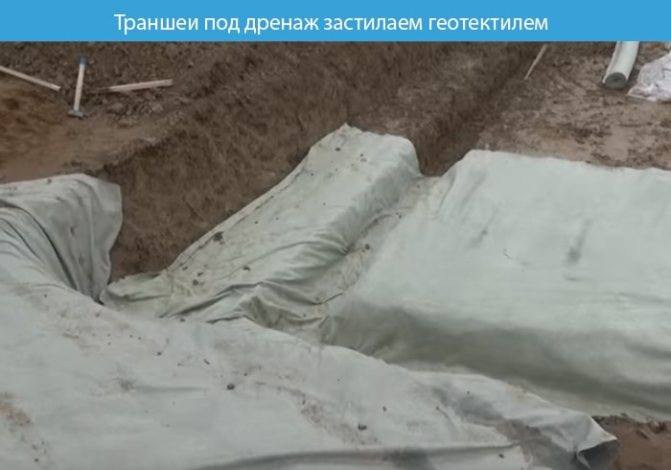

Trenches for drainage work are dug along the perimeter of the pit, 50 cm wide. Geotextiles are laid to a depth of 50 cm, then corrugated pipes are installed. And inspection wells are installed with a slope of 4–7 degrees.
Drainage pipes are located at a distance of 60–70 cm from the foundation and lie slightly lower.
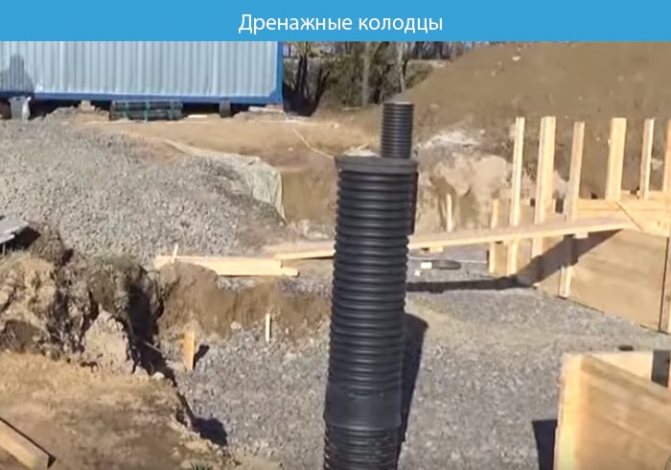

The trenches and the area are filled with 15-25 cm of crushed stone, leveling the area and making a stable base.
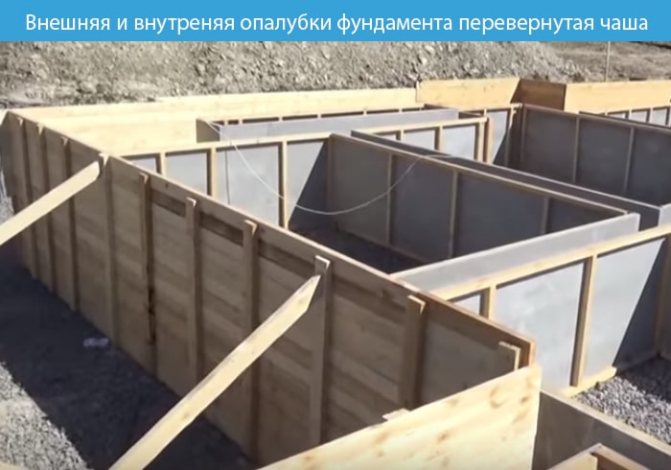

For the outer sides of the base, a structure is built from removable formwork. Panels made of wood, plywood or chipboard 3–5 cm thick. The height of the structure depends on the height of the ribs of the inverted bowl.
In order for the formwork to withstand the load from concrete, spacers are installed. Along the entire perimeter every 50–60 cm.
The inner side of the foundation is made of permanent formwork. As a rule, it is 15–20 cm lower than the outer one. The sides are strengthened between each other with pins.
Bowls are formed between the tape, which are filled with sand and compacted with a vibrating plate.
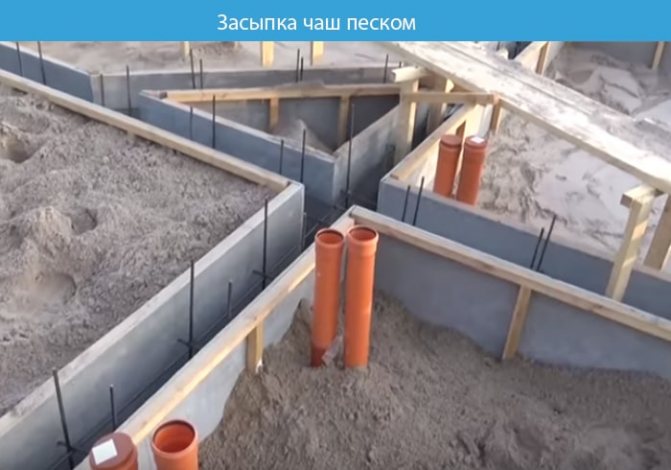

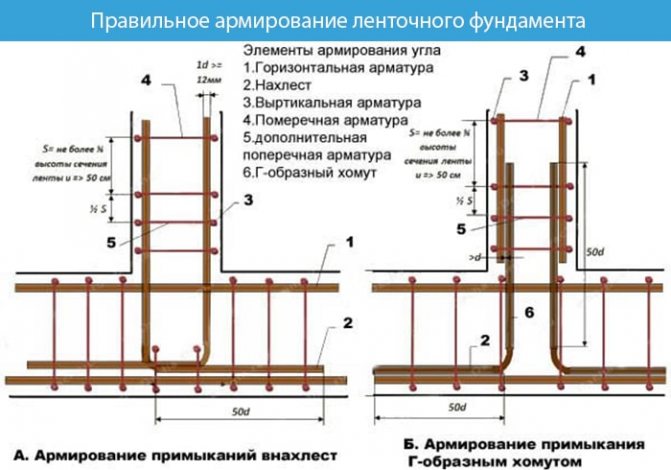
Reinforcement
Reinforcement begins with a tape (stiffening rib). Using reinforcement with a diameter of 12–14 mm. The longitudinal rods are connected with clamps made of reinforcement with a diameter of 6 mm and tied together with wire.
Important! The reinforcement should not be interrupted at corners and joints.
Scheme of correct reinforcement of corners and junctions of the tape:
The reinforcement frame of the slab is knitted from two horizontal meshes. The mesh is made from longitudinal and transverse rods with a diameter of 12–16 mm, the cell size is 15x15 cm (to save 20x20 cm).
The corners of the slab are also strengthened with clamps made of 6–8 mm reinforcement.
Foundation slab reinforcement diagram:
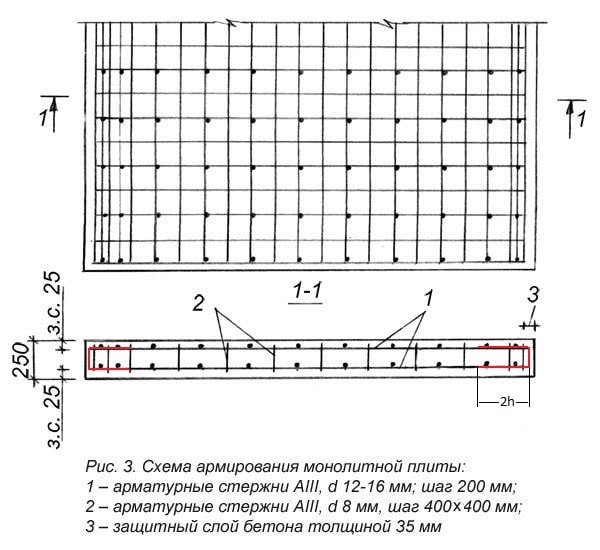
Advice! Knitting of reinforcement with wire is done both manually and using a semi-automatic knitting tool.
Pouring the slab and ribs
Concreting the foundation must be done continuously, pouring the slab and ribs at one time. Pour the solution in layers starting from the tape or stiffening ribs. After each layer we compact it with a vibrating plate. Then we move on to the stove.
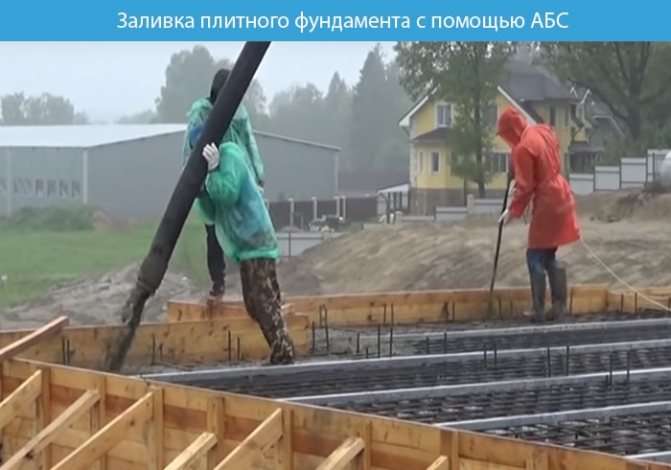

Preparation of concrete mortar:
- knead by hand (the method is energy-consuming, suitable if you have a small pouring area);
- using a concrete mixer (it will save your time and energy; you don’t have to buy it, but rent it);
- ready-made concrete mixer trucks (called ABS with ready-made mortar, it costs more than previous options, but pouring is much faster).
Recipe! We mix concrete class B15 with grade M200 per 1m3. Proportion for preparing the solution in a concrete mixer: cement, sand, crushed stone - 1 / 3.5 / 5.6 (kg). Add water by eye to form a heterogeneous mass.
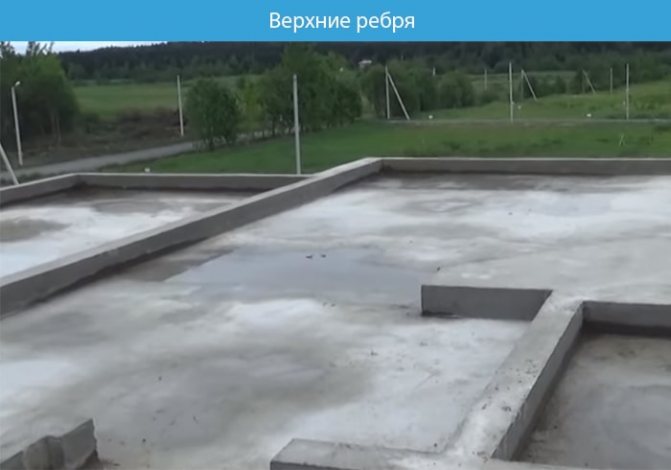

After completing the work, it is necessary to cover the finished foundation with film. And leave for 30 days so that it gains strength.
Important! During hot periods, the foundation is moistened. Due to moisture evaporation, hardening may occur unevenly. This affects the load-bearing capacity of the structure.
Waterproofing
The shelf life and strength of the tape ribs can be increased by using waterproofing. Protecting from moisture and making the structure waterproof.
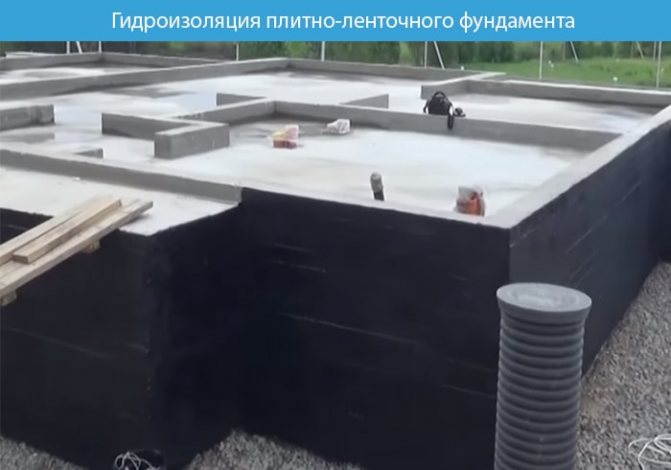

There are several types of waterproofing:
- Coating. The tape is treated with bitumen or epoxy mastic - this is a moisture-proof material.
- Rolled. We cover the tape on all sides with roll materials: Bikrost, TechnoNIKOL: external, internal and on top.
- Penetrating. At the stage of creating a concrete solution, a special additive is added - a primer. The special properties of the primer additive can reduce the porosity of concrete, while reducing its moisture permeability.
Thickness calculation
The planned thickness of the base depends on several factors. First of all, it is necessary to determine the type of floating slab with the required degree of rigidity. Depending on the location of the stiffeners, two types of supports are distinguished:
- bowl-shaped plate . The stiffeners are directed upward, so the end result is similar to grillage beams, firmly fixed to the main structure with vertically mounted reinforcement;
- inverted bowl . In this case, the stiffeners are directed downwards. This helps to slightly raise the foundation slab above the ground, as well as insulate the foundation using a USHP slab.
In addition, when calculating the thickness, it is necessary to take into account the minimum distance between the reinforcing mesh, which must be at least 10 cm according to accepted standards. The protective layer of concrete should be up to 5 cm, and the top support up to 7 cm.
The minimum value of the thickness of a slab support without stiffeners of any type is calculated depending on the selected house material:
- three-story brick buildings - from 40 cm;
- two-story house made of wood, aerated concrete or brick - 30-35 cm;
- frame buildings - 20-30 cm;
- utility rooms and two-room cabins - 10-15 cm.
If stiffeners are included in the foundation, the thickness of the central part must be reduced by 10-15 cm. This can significantly increase the load-bearing strength, however, such a structure is not recommended for building a house on sandy and peat areas. As a rule, when constructing a base slab on unstable soils, additional reinforcement of the base is used through additional bedding or vertical drains.
When building a house on difficult soil types, it is recommended to wait for the foundation to shrink for 8-12 months.
Inverted bowl foundation: description, pros and cons
The basis of any building, residential or non-residential, is the foundation. The choice of its type is influenced by the following factors: the type of soil at the construction site of the future building; the amount of melt water, as well as the depth of groundwater; climate features of the area, for example, the depth of soil freezing, the average amount of precipitation in winter; seismicity of the area; number of floors of the building.
There are other circumstances that are taken into account when calculating the foundation, but it is best to entrust such work to a specialist.
a brief description of
According to the type of construction, foundations can be columnar, strip, pile, pile-grillage and slab.
Strip foundation - a concrete strip with a reinforcement frame inside. Installed under all load-bearing walls of the house. This type of base is inexpensive and easy to implement. Suitable for buildings in areas with low groundwater levels, light frame houses.
More complex and expensive is a monolithic slab foundation . This foundation is a solid slab poured under the entire building. There are several types of slab foundations:
- In the form of a solid monolith.
- In the form of a monolith, supplemented with stiffening ribs or grillages.
Plates with stiffeners are divided into:
- With ribs pointing upward. A perimeter tape encircles the top of the slab. Popularly called a bowl.
- With ribs pointing down. The slab lies on the frame in the form of a continuous strip (the foundation is an inverted bowl).
- Combined type.
The inverted bowl foundation advantageously combines the properties of strip and monolithic foundations.

Depth
When constructing a slab foundation, it is necessary to remove the top turf layer by at least 40 cm. After this, the prepared area should be covered with non-metallic material with a minimum clay content. When constructing a slab support, it is recommended to consider the following points:
- If the house is planned to be constantly heated, you can use a minimal layer of insulation, since when heating the room the soil underneath will not have time to freeze;
- When heating the house periodically, it is necessary to additionally lay a layer of expanded polystyrene under the slab and blind area. This minimizes the risk of heaving due to temperature changes.
Typically, when the top layer of soil is removed by 30-40 cm, the depth of the slab foundation is up to 10-20 cm. In order to further raise the house to avoid contact of the walls with the soil, it is recommended to additionally construct a brick plinth or monolithic beams under the load-bearing walls. It is also a good idea to treat the base with liquid bitumen mastic. It will provide waterproofing of the surface.
Advantages
- Construction of buildings with high groundwater levels . Then the floor of the premises on the first floor is at a sufficient height and is reliably protected from moisture. Protection against water is usually provided by special waterproofing, which is supplied in rolls. Place a waterproofing film between the concrete layer and crushed stone.
- Possibility of erecting buildings on heaving soils . Such soils include clay, loam and sandy loam. These soils do not filter water well, retaining it and not allowing it to pass into deeper layers. The design features of the foundation, its thermal insulation and correctly calculated blind areas provide good drainage and prevent the destruction of the building from temperature fluctuations.
- A monolithic slab with ribs pointing down is often used instead of a regular slab. This replacement allows you to save on building materials. With a smaller slab thickness, the structure does not lose in overall strength, since the stiffening ribs compensate for this difference.
- The use of stiffening ribs allows you to evenly distribute the weight of the building along the entire perimeter of the base.
- After finishing, the monolith slab can be used as the floor of the first or basement floor , which significantly saves money.
- Thanks to the stiffening ribs, the base is resistant to bending deformations.
- Possibility of constructing buildings on soils with weak bearing capacity . In this case, an inverted bowl foundation is an alternative to a deep strip foundation, allowing you to save on excavation work.
- Possibility of building buildings on bulk soils .
- Since the upper part of the slab is quite flat, this easier to arrange the basement . The dimensions of such a room are small, that is, you can make a small cellar under the kitchen, but there is not enough space for an underground garage.
Flaws
- Due to the fact that most of the load from the building goes to the grillage, this type of foundation is not suitable for creating heavy structures . Therefore, it is undesirable to build massive brick or stone houses on an inverted bowl foundation.
- Like any monolithic structure, it is advisable to fill the inverted bowl foundation at a time . If the filling is done in stages, first the tape, and after some time the main slab, then over time a crack will appear at the joint and the building will begin to collapse.
- The complexity of the formwork and reinforcement scheme , as well as the mandatory presence of a good waterproofing layer.
- The cost of constructing a building with a deeply buried rib foundation is much higher in northern latitudes due to the great depth of soil freezing. Therefore, in most cases, piles are used there.
- The disadvantage of any monolithic foundation is that they are not applicable on complex , such as mountainous landscapes. If the height difference is more than two meters along any of the walls of the structure, piles must be used.
- From an economic point of view, the construction of buildings with monolithic foundations on areas with dense or rocky soil, as well as on soils with deep groundwater, is unprofitable .
- The difficulty and increased cost of work in winter is a disadvantage of any concrete or reinforced concrete element of a structure. In order to pour concrete at low temperatures, it is necessary to carry out a number of additional measures, for example, heating the mixture and maintaining the optimal temperature. Also, when working with concrete, special antifreeze additives are required to lower the freezing point of water. All this increases the cost by at least a quarter.
- If the building plan involves placing utilities under the monolith slab, then at the stage of building the foundation it is necessary to make special channels , lay capsules and casings. Otherwise, during repair work you will have to violate the integrity of the slab.
Important! If the building is planned to have a basement, then it is better to lay communications on the floor.
Having considered all the advantages and disadvantages, we can come to the conclusion that an inverted bowl foundation is one of the best options for the construction of small structures, for example, country houses and cottages, in areas with heaving soils in central Russia. This type of foundation is not suitable for northern latitudes, mountainous areas, as well as multi-story construction and massive structures.
Types of slab foundation
For frame houses, different types of slab foundations are used: “bowl”, “inverted bowl”, “slab with caisson”, USP. Foundations differ in load distribution, slab shape, presence of “ribs,” and method of installing reinforcement and formwork.
Solid slab
A solid monolithic slab is made without ribs, so constructing formwork and reinforcement is quite simple; this is the most suitable method for beginners. The reinforcement is knitted directly on site, the cell size can be easily “adjusted” to the location of engineering systems and walls. No special equipment is needed to excavate soil.
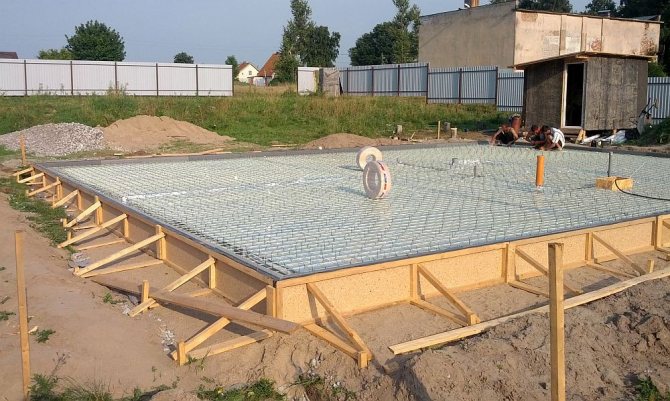

The main disadvantage is the increase in the budget due to the large volume of concrete work. When constructing yourself, it is necessary to take into account that it is impossible to mix so much concrete at one time.
The decision on the thickness of the slab foundation for a frame house is made after geological research. In most cases, for a standard 6x6 frame, a thickness of 200 mm is sufficient, for 8x8 - 250 mm, 10x10 - 300 mm. It is not recommended to locate the house below 200 mm so that the wooden parts of the structure do not suffer from capillary moisture.
Foundation - “inverted bowl”
For light houses, the “inverted bowl” slab, with the ribs down, is a popular and practical solution. Using ribs, they raise the floor level without creating a thick layer of concrete under the entire area of the house.
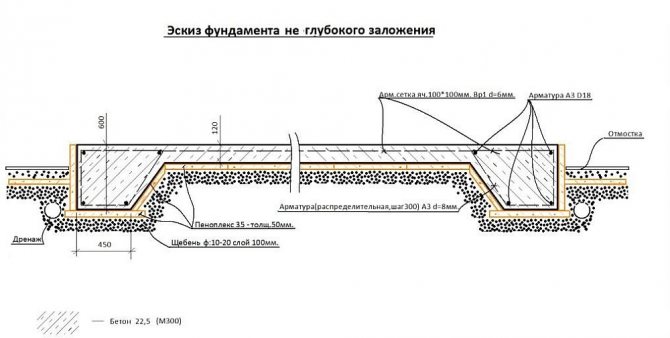
The main load, which in the case of a classic monolithic slab is distributed over the entire area, with an “inverted bowl” falls on the ribs. Permanent formwork is installed inside , the cavities are filled with sand, and the entire foundation is poured in one go. The advantage of the “inverted bowl” is the speed of construction and relative cheapness due to the saving of concrete.
Stove - “bowl”
In this type of foundation, the ribs are raised upward, playing the role of a base and giving the structure additional strength. It turns out to be a kind of “trough”, the load is distributed over the entire area.

The voids are filled with expanded clay and sand, and insulation and a floor are installed on top. The method is considered universal, suitable for different types of houses, but is expensive due to the need to raise the floor level with backfill and insulate it.
Slab with caisson
A slab with a caisson (recess) is convenient if you need a small cellar. When digging a pit under the main slab, a recess is made in the right place for the caisson. Rocky soil can be a problem as you need to dig to great depths.
Useful: Frame gazebo - build with your own hands

The advantage of slabs with a caisson is the organization of a place for storing crops, the disadvantage is the complex installation of fittings and the need for high-quality waterproofing. It is necessary to have an accurate design so that after the construction of the partitions it does not turn out that access to the storage is organized in an inconvenient place.
USHP is a new technology
USP, insulated Swedish plate, is a technology actively promoted by many developers. With this method, the contours of the heated floor are laid directly in the slab. The main advantage is energy efficiency and reduced heating costs. However, for a specific project of a frame house on USHP, you should compare the difference in budgets for different types of foundations and calculate when the resulting heat savings will pay off.
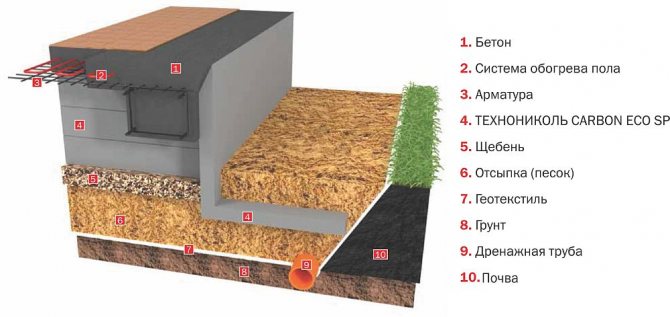
Flaws:
- high costs;
- complex construction technology;
- the possibility of damage to the insulation by rodents;
- all communications are carried out in the slab , so you need to be sure of the calculations and output coordinates;
- Typically, composite reinforcement is used for USP, for which sufficient statistics on service life and operation have not yet been accumulated.
The feasibility of constructing a foundation in the form of an inverted bowl
Among the types of foundations for objects under construction, the “inverted bowl foundation” is especially distinguished. The design owes its name to its cross-sectional view. Along the entire perimeter, the monolith has stiffening ribs that give the slab the appearance of an inverted bowl. With this configuration, the slab base receives additional rigidity and significantly improves load-bearing capabilities.

Feasibility of application
Compared to other foundations, an inverted bowl is a fairly large and expensive structure. Developers are forced to pour this type of foundation under the following conditions:
- with shallow groundwater flow;
- there are heaving soils on the site;
- weak soil compositions lie at great depths;
- the building under construction has a large mass;
- The area allocated for development is characterized by high seismicity.
Construction of a bowl-shaped foundation will cost a decent amount of money.
It is quite natural that every customer strives to save as much as possible, for which it is necessary to make accurate calculations of the future foundation. But it must be remembered that the main function of the foundation is to ensure the reliability and stability of the entire facility.

Monolith thickness
The design solution determines the thickness of the slab and the dimensions of the stiffeners. To calculate the thickness of concrete, certain data are used:
- maximum weight of the structure per square meter of base;
- calculated resistance of soil composition;
- load-bearing capacity of a monolith with ribs.
Calculation actions establish the dimensions of the slab, the class and volume of concrete material, the amount of metal reinforcement, and the parameters of the foundation ribs.
Practice has proven that the ribs present in the foundation reduce the thickness of the slab monolith by ten to fifteen centimeters.
It is prohibited to build a foundation on freshly poured soil. A fresh embankment is not capable of creating the necessary design resistance, and the object will be subject to shrinkage every year.
The outer edge of the load-bearing wall made of brick stone should be located at a distance of thirty centimeters from the edge of the monolithic slab. If you plan to install columns, the support axes should be located on the plan so that the vector at a forty-five degree angle from the center of the column does not go beyond the boundary of the reinforced concrete mass.
Base slab-bowl MPLC
The bowl-shaped foundation is the most powerful, ideal for walls made of concrete blocks and brickwork. The inside is filled with sand, allowing you to get floors on the ground. Clay soils are not able to squeeze the base to the surface by heaving forces. The structure is protected from high levels of groundwater and aggressive environments by waterproofing.
The downside is the highest possible construction budget that the bowl-shaped slab has. Therefore, it is usually chosen for difficult geological conditions, monolithic, concrete, brick walls of multi-story cottages. Such a house will never crack the walls and will not require periodic repairs.
Foundation depth
When determining this parameter, it is necessary to take into account that the side edge of the slab base must be raised above the soil surface by at least fifteen centimeters. This is necessary in order to isolate the brickwork of the basement part of the object as much as possible from the soil or from the blind area.
Based on numerous calculations of the FPP under different conditions, an average slab depth of ten to twenty centimeters was derived. It follows that the stiffeners sink by thirty-five to forty centimeters.
Selection of fittings
The main load effect in the concrete mass falls on longitudinal metal rods having a periodic profile. For light structures, steel rods with a diameter of 1.2 cm are used. If it is planned to build a more massive structure, then the size of the reinforcing rods reaches 1.6 cm. Sections of the same reinforcement are used as transverse links of the frame base; sometimes smooth rods of 0.8 cm in size are used.

Construction technology
The construction of a foundation in the form of an inverted bowl is carried out in certain stages, and the whole technology looks like this:
Excavation
The algorithm for their implementation is as follows:
- the top layer of soil is removed using special equipment to achieve the required level of the soil base;
- a specialist uses instruments to mark axes and corner sections, marking the boundaries of the future foundation;
- Benchmarks made of wood material are displayed. The upper edge of the slab base and the height of the crushed stone cushion are marked along the vertical posts. Self-tapping screws are screwed into horizontal boards and cords are pulled, which at the intersection determine the corners of the object;
- along the entire perimeter of the construction site, a ditch is torn off, which is necessary for the installation of ribs;
- the entire site is carefully compacted.
Arrangement of the pillow
The compacted bottom is covered with crushed stone, the layer thickness of which should reach the reference mark. Compaction is carried out, after which the height level is checked with a tacheometer, the horizontal is checked, the flaws of which are eliminated with a layer of sand.

Problem areas are further compacted. Similar measures are carried out in places where stiffeners are installed.
Waterproofing
With the help of this protective layer, a barrier is formed for groundwater that can enter the concrete base of the object.
Waterproofing is of no small importance in preventing the leakage of cement laitance from the mortar mass into the soil. Otherwise, the concrete becomes loose and loses strength.
The prepared site and ditches are covered with polyethylene or a special membrane. The latter is more expensive, but guarantees the reliability of the waterproofing layer.
The formwork panels are made of coniferous wood and fasteners. You can use panels made of multi-layer moisture-repellent plywood. This material is durable and reliable and can be used many times. If the developer wants to save money, then such formwork can be rented.
The panels are assembled and stored on a specially prepared site. As soon as everything is ready, they are placed along the perimeter of the future foundation in such a way that the upper edge exceeds the level of the monolith by fifteen to twenty centimeters.
When installing formwork panels, it is recommended to control the vertical and level of the top edge. Polyethylene is spread inside the boards so that the concrete mass does not leak through the cracks.
An important feature is the creation of reliable braces, thrust elements and ties.
If you install extra stops as insurance, there will be no harm. Weak fasteners will cause destruction of the formwork fence, unnecessary financial costs and an increase in construction time.
Peculiarities
The construction of objects on foundations in the form of an inverted bowl has its pros and cons:
- work is allowed to be carried out on a site with shallow ground moisture. The floors of the facility are located high and are not exposed to the negative effects of water. To construct a protective layer, it is recommended to use polystyrene foam or rolled materials for waterproofing. The use of fine crushed stone ensures excellent drainage;
- a reliable drainage system protects the foundation from swelling of the soil composition. A blind area with a heat-insulating layer does not allow the walls of the premises to freeze;
- The construction of an object on a monolithic base in the form of a bowl is carried out using various materials.

An important advantage of such a foundation is the economic effect. The bottom line is that the average height of the slabs is twenty centimeters. This means that its production requires the optimal amount of mortar mixture, reinforcement and other building materials.
The need for additional finishing work on the floor surface is completely eliminated. At the bottom of the base there is a layer of waterproofing that protects the respiratory system from radioactive components contained in the soil composition.
Slab with caisson MPLCHK
This type of monolith is used in the construction of small wine and food cellars and allows them to be installed in any room of the house or garage. Its disadvantages:
- in the complex design of formwork and reinforcement belts;
- the need to fill in one step;
- This slab requires thorough waterproofing.
The difficulty is that you need to approach the installation of communications with special care, since if you miscalculate even 20-30 cm when putting utilities into operation, you can say goodbye to the aesthetic appearance of the interior and the comfortable use of the room.
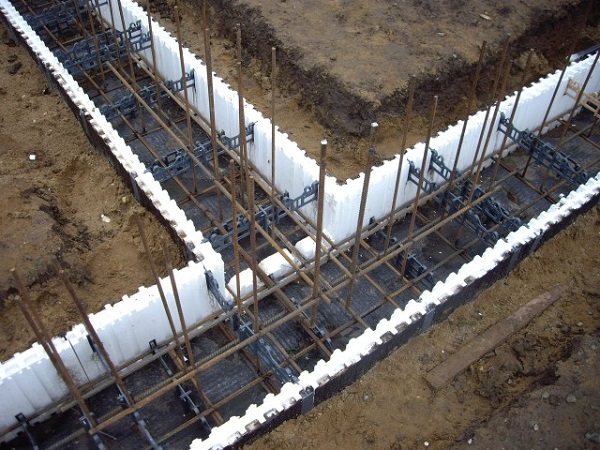

Pipes and a caisson are laid in front of the formwork, which is why it is so easy to miscalculate the size of the internal partitions. But this technology has more advantages - the owner of the building receives a monolith structure with a technical underground or cellar, convenient for placing a water pump or storing food and canned goods for the winter.
Calculation of the foundation of an inverted bowl
Among the many varieties of foundation structures, the type of building foundation that stands out is the “inverted bowl foundation.” The original name of the support structure arose due to the cross-sectional appearance of the base. The monolithic slab is equipped along the perimeter with stiffening ribs “extended” into the depth of the soil. It is these ribs that give the foundation the appearance of an inverted bowl (IBC). Thanks to this configuration, the slab base of the structure acquires additional rigidity and significantly increases its load-bearing capacity.
Conditions for the construction of the PFC
The FPF, in comparison with other types of structures for similar purposes, is a rather massive structure. The costs of material resources (concrete, reinforcement, formwork, etc.) per unit area of the building’s base exceed those of other supporting structures.
An inverted bowl foundation is one of the most expensive options for constructing the foundations of buildings and structures.
A number of conditions “force” construction owners to make a choice of this type of foundation:
- high groundwater level;
- presence of heaving soils;
- large thickness of soft soils;
- heavy weight of the building;
- high seismicity rate.
General advantages of all types of monolithic slabs
Such a foundation is always strong, it is more reliable compared to tapes, grillages and pillars. The load on the ground is distributed, so there are no difficulties with the construction of internal partitions and their removal if necessary - if redevelopment is desired in the future.
The advantages are that it is possible, taking into account the individual characteristics of the structure and for economic reasons, to choose one of the types of monolithic slabs.
The monolith is durable - no regular repairs are required. The slabs are resistant to cold, therefore, having started construction in the winter, you can safely freeze the construction and continue in the spring.
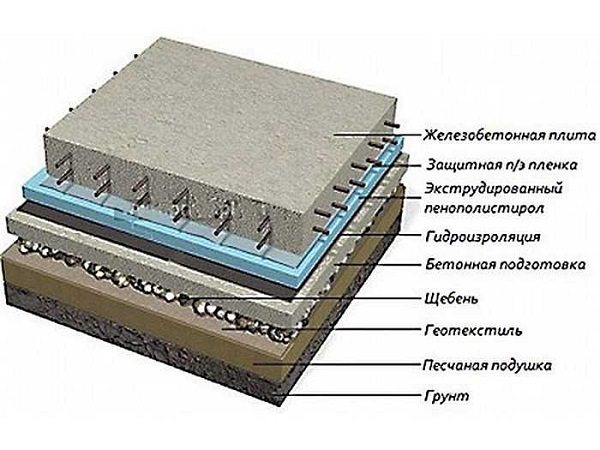
No special equipment is required to dig the foundation.
Monolithic foundation slabs are durable - the house can be three-story with an attic, the monolith can easily withstand the load. The construction of blind areas will not cause any particular difficulties - they can be easily insulated using polystyrene foam to prevent them from freezing on the sides.
PPF calculation
The construction of a PFC costs a considerable amount of money. The customer’s desire to build the foundation of the house at minimal cost is understandable. The more accurately the foundation calculation is made, the more money will be saved. On the other hand, the FPF must ensure a reliable and stable position of the entire building.
Monolithic slab thickness
The project determines the optimal thickness of the monolithic slab and the dimensions of the stiffeners. To accurately calculate the thickness of a concrete slab, use the following data:
- maximum load from the weight of the house per unit area of the base;
- calculated soil resistance;
- load-bearing capacity of a reinforced concrete slab with stiffeners.
PPF device diagram
The calculation determines how thick the monolithic slab should be, the brand and quantity of reinforcement, the volume of concrete mortar, and the dimensions of the foundation ribs. As practice has shown, the inclusion of stiffening ribs in the slab design makes it possible to reduce the slab thickness by 100 - 150 mm.
The construction of a foundation on freshly poured soil is strictly prohibited. A recent embankment may not have sufficient design resistance. A building constructed on such a foundation will produce annual settlement.
The outer boundary of the masonry of load-bearing brick walls should be at least 300 mm from the edge of the slab. In the case of installing columns (to support a terrace or second floor ceiling), the axes of the supports must be located on the foundation plan in such a way that the vector at an angle of 45 o from the center of the column does not extend beyond the reinforced concrete base.
Constructing the vector of the zone of influence of the column on the foundation
For a two-story brick house, it is enough to build a foundation slab 250 mm thick with ribs 600 mm high.
Depth of the PPF
When calculating the depth of the foundation, it should be taken into account that the side of the slab must protrude above the ground by at least 150 mm. This is necessary so that the brickwork of the basement of the house is maximally isolated from the ground base or from the surface of the blind area. The height of the slab under the plinth may be different, but not less than the minimum size.
Based on numerous calculations of the PPF under various conditions, it is possible to derive an average indicator of the depth of the slab, which is equal to 100 - 200 mm. Consequently, the immersion depth of the ribs will be 350 - 400 mm.
Selection of fittings
The main load in the FPF array is borne by longitudinal rods of a periodic profile. For a small, lightweight structure, reinforcement with a diameter of 12 mm is used. If the building will be built from heavy structural elements (brick, reinforced concrete), then longitudinal rods with a diameter of 16 mm are taken to make the reinforcement frame of the slab.
The cross braces of the frame are made from pieces of reinforcement of the same diameter. In some cases, smooth 8 mm reinforcement is used.
Inverted bowl foundation construction technology
The technological process of the PPF device consists of several stages:
- Excavation.
- Laying a crushed stone-sand cushion.
- Waterproofing device.
- Installation of reinforcement frame.
- Formwork works.
- Pouring the formwork with concrete.
- Caring for concrete mortar.
Excavation
Excavation work is carried out as follows:
- use a bulldozer to remove the fertile layer of soil until the desired level of the soil base is reached;
- a geodesist engineer, using modern geodetic instruments (level, tacheometer), marks the axes and angles marking the boundary of the foundation;
- Install reference structures from wooden boards and bars. On the vertical posts, mark the upper level of the slab and the height of the crushed stone backfill. Self-tapping screws are attached to horizontal boards. Threads stretched from self-tapping screws mark the corners of the house at the intersection;
- ditches are dug along the perimeter of the site for the installation of stiffeners;
- The entire site is compacted using special equipment.
Laying crushed stone-sand cushion
The compacted area is covered with crushed stone. The thickness of the crushed stone layer is made corresponding to the marks on the benchmarks. After compaction, the layer level is checked with a tacheometer, and the horizontal is checked with a level.
Sand filling eliminates all defects in the horizontal surface of the pillow. Additional compaction of problem areas of the site is carried out.
In ditches under the ribs, the same actions are performed.
Waterproofing device
Waterproofing is necessary to install a barrier to the penetration of moisture from the soil into the concrete mass of the base of the building.
It is necessary to note the important role of waterproofing in preventing the leakage of cement laitance from the concrete mortar into the ground. If this happens, the concrete monolith will become loose and significantly lose its strength.
How to make an inverted bowl foundation
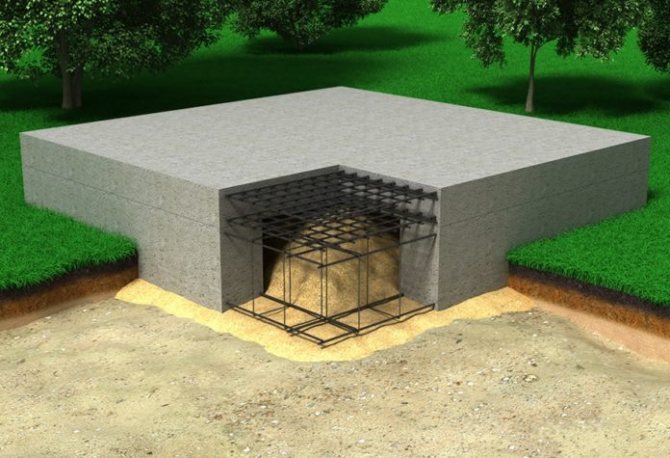

In country houses and cottages, after severe frosts, doors warp and flooring begins to creak. The walls of the building may also become warped. This situation is explained by the fact that during construction the composition of the soil was not taken into account and an inappropriate foundation was made. Before starting to build a house, it is important to understand what kind of soil is on the site and select a foundation for it. The best option for difficult soil is the “inverted bowl” design.
The main characteristic of this type of foundation is the presence of a base in the form of a slab and stiffening ribs (special walls along the perimeter of a detached structure to make it resistant to external loads) and a large distance from the ground surface. The need for its use is determined by the geological zone where the soil is located.
When a monolithic slab is needed:
- groundwater is at a shallow depth, in this case high floors will not be exposed to moisture coming from below. A layer of expanded polystyrene and rolled standard waterproofing is used as an additional protective barrier;
- the presence of heaving soil, clayey, with fine sand with high humidity, where when freezing, the resulting ice increases the volume of the soil. In these conditions, you need to make a drainage system, which is filled with concrete mortar to obtain a monolithic slab. The drying pad consists of medium-sized crushed stone that absorbs moisture well. A thermal insulation layer is added to protect the inside of the house from freezing;
- the monolithic base can support not only gas and foam concrete blocks, but also a heavier brick structure.
The use of such a foundation makes it possible to save on the amount of dry mixtures; the thickness of the monolith is only 20 cm. No additional finishing is required for the floor, since there is already a concrete base. The “bowl” pie uses the material hydrostekloizol. This is a high-quality waterproofing, its composition is fiberglass, covered on both sides with a binder bitumen composition with a special film that protects the building material from external influences and promotes its uniform heating during the process of processing the concrete base. Fiberglass with special additives increases service life up to 15 years. The layer completely blocks access to the interior of gases emitted by heaving soils.
Solid MPL slab
This foundation has virtually no disadvantages and is used for any construction technology without restrictions on wall materials or geology. The stove has advantages:
- minimal excavation without special equipment
- the simplest formwork that allows you to save your budget
On some soils with low groundwater level, it is possible to do without insulation, footings, or waterproofing, which will sharply reduce both the production time and the construction budget. For this, a one-time qualified consultation in a specialized class=”aligncenter” width=”628″ height=”472″[/img]
The disadvantage is traditionally the large volume of concreting. At home, it is unrealistic to mix so much mortar to fill the formwork in one go. In the absence of stiffeners, the reinforcement of the structure is greatly simplified. Reinforcing mesh can be knitted directly into the building area, taking into account the risers of utility systems and the configuration of the walls. This allows you to change the grid cell if necessary without additional cost.
Preparation of formwork
First, the area cleared of grass and debris is marked. The border of the fenced area runs at a distance of 1 meter from the proposed edge of the future pit. The depth of the hole being dug is one and a half to two meters. The clay is removed, and gravel is filled in an even layer along the entire bottom of the depression. A trench is dug along the perimeter of the rectangular base, 0.5 meters deep. It’s better to do this yourself with a shovel in order to trim the walls at the same time. Several pieces of corrugated pipes with an inclination angle of 70 degrees are installed throughout the trench at the same distance. Such inspection wells are needed to collect water and drain it into containers located at the bottom of the base. Geotextiles are placed at the bottom of the pit, covered with a layer of sand and gravel, 20 cm thick, on top. The resulting cushion is thoroughly compacted.
Stages of foundation construction
Due to its structural characteristics, the inverted bowl foundation is mainly used in the construction of low-rise structures. These include country houses, cottages, buildings on personal plots, etc. However, cases cannot be ruled out when an inverted bowl foundation is used to build a heavy house. As in any other construction of the base of a house, building a foundation like an “inverted bowl” with your own hands begins with preparatory activities. First, the area is cleared. Any kind of vegetation is removed from its surface, garbage is taken out, and only after thorough cleaning of the surface is marking done on it. It should be remembered that the cords must be pulled at a distance of at least 1 meter from the intended location of the pit.
When digging a pit, it is necessary to take into account some nuances. Its depth must be at least 150 mm. The organization of deepening involves removing a layer of clay, after which it is replaced with compacted gravel. After this, using a construction leveler, a perfectly flat surface is achieved without the slightest hint of any slope. After marking, you can begin to remove the top layer of soil from the building site. Then, using shovels, they dig a trench under the strip foundation (ribs of the slab). You can use the services of an excavator, but the walls of the recesses will not be perfectly smooth. In this case, you will need to trim them yourself using the same shovel. The depth of the trench should reach an average of 0.5 meters, and its thickness depends entirely on the characteristics of the soil on the site.
To organize inspection wells, corrugated pipes are laid in trenches. They are installed along the entire perimeter of the future building. A slope of 70 degrees will guarantee gravity flow of water, and there should be a container for liquid at the bottom of the structure.
Geosynthetics (in most cases, geotextiles) are laid at the bottom of the trench. After this, a cushion of a mixture of sand and gravel is laid. Its thickness must be at least 0.4 meters. Such a pillow can be made from river sand and coarse crushed stone. To do this, sand 20 cm high is laid on geotextiles in layers and compacted. Next, crushed stone is laid in a similar way, also 20 cm thick.
The next step is to organize waterproofing of the lower part of the future base. For high-quality execution, waterproofing is perfect. Ordinary polyethylene film is also suitable, when laying it you must maintain a minimum overlap of 10 cm.
So, the preparatory work for some of the trenches can be considered completed. Next, the formwork is erected. A high-quality design involves using plywood, OSB or planed boards as the main material. In order to follow the foundation construction technology, the bowl is completely turned upside down, we recommend watching a video about the correct selection of material for constructing the formwork:
After its construction, the bottom of the formwork is covered with non-external material, which is then compacted well. Its thickness should not exceed 10 mm, and for high-quality compaction you can use a vibrating plate. The sole of the tape is covered with waterproofing material, and polystyrene foam plays well as insulation.
Production of monolithic slab
To waterproof the surface, you can put an ordinary polyethylene film under the base with an overlap of individual pieces of 10 cm. Plywood or planed boards about one centimeter thick are suitable for formwork; they can simply be fastened with nails. A reinforcement cage is placed inside the structure. It consists of two belts, upper and lower, connected by rods. Each cell has the shape of a square with a side of 10 or 20 cm. The structure is placed in the formwork and leveled. Then the concrete mixture is poured. A solution designed for a large area of the house should not thicken during operation. It is better to order a car with a liquid composition. A stationary mechanical device can be used to produce a substance from a mixture of cement, sand and concrete. The process of filling cells is long and labor-intensive. A vibrating tool is used to form a flat surface. Filling must occur continuously until complete. According to the technology, concrete dries within three to four days. The result is a monolithic slab.
A wooden, brick or block house can be mounted on an “inverted bowl” foundation.
Base plate
It is necessary to understand that an inverted bowl foundation has its pros and cons, and in order to have more positive qualities, you need to take care of the high-quality execution of the monolithic slab itself - the basis of this type of base. The reliability of the structure primarily depends on the concrete mixture and the correct placement of the reinforcement. Thus:
- The reinforcement frame should consist of two belts fastened with vertical rods;
- The upper belt is located at a depth of 50 mm from the top of the future slab, and the lower belt is located at a height of 50 mm from the bottom point of the slab;
- One cell of the reinforcement cage should have dimensions ranging from 10x10 to 20x20 cm.
After laying the reinforcement inside the formwork of the monolithic slab, the concrete mixture is poured. Maki concrete M300 is well suited for this. The formwork is filled with concrete in one go. When pouring the slab, a special vibrating tool must be used to prevent air pockets from appearing in the structure of the future foundation, which in cold weather can cause cracks to form in the foundation.
Video of building the foundation of an inverted bowl for a house:











