Strip foundations are gradually becoming a thing of the past. This situation is associated with an attempt to reduce the cost of the construction process. A strip-type foundation requires a large consumption of building materials, which leads to an increase in construction costs. Cost reduction becomes possible if you use a columnar foundation for a column.
Area of use of glass foundations
The purpose of such an unusual foundation is considered to be the transfer of load effects from load-bearing elements and floors through columnar pillars mounted in glass blanks.
The tops of the supporting elements are also firmly connected to the grillage structures, which can be mounted at a significant elevation in relation to ground level.
Glass-type column foundations are used:
- during the construction of column structures for industrial purposes;
- when constructing multi-level underground parking lots;
- as load-bearing foundations for bridge structures, overpasses and power lines;
- for the installation of frame structures that are long and located on unstable soil compositions with various horizontal stratifications;
- in situations where there is a need to provide an indicator of the strength of objects located in regions characterized by seismic instability;
- when the design assignment provides for the placement of columns under floors, the span sizes of which vary from six to nine meters.
Glass-type foundations for mounting columns are the only optimal method, in accordance with GOST, for the construction of machine hangars, condenser and compressor rooms in the nuclear power industry.
Article navigation:
- Concrete bases for a column. Prefabricated column foundation.
- Monolithic column foundation.
- Strip foundation.
- Strip monolithic foundation.
Design Features
The design differences of the glass foundation for the support column, the maximum parameters and permitted loads, the dimensions of the support base and the type of frame reinforcement are determined by special GOST 23 972 80. The main elements of the foundation structure are:
- monolithic type support cushion, characterized by large round or rectangular shapes and having waterproofing protection. The cushion can be manufactured in a factory or poured directly at the installation site with a preliminary installation of a sand and gravel layer;
- a cup holder made of reinforced concrete, located in the central part of the foundation slab;
- columns of a certain length, made of metal or reinforced concrete, which are installed in a glass;
- a support column holding a load-bearing beam on which the floor elements of the future building are located.
The supporting pillars may differ in length, but the edge remaining on top must necessarily remain only horizontal.
According to calculations, a glass-type foundation slab for columns, taking into account the expected load effects, can occupy an area of twelve to fifty-two square meters. It can be monolithic or prefabricated, while its surface in the first case is horizontal, and in the second – inclined.
In the industrial sector, preference is given to the monolithic type, as it is easier to install and does not require special financial costs for renting special equipment.
The glass and the slab can be made in the form of a single monolithic structure, or both of these elements are connected by means of reinforcing frames. This question is determined by the characteristics of the soil composition and the expected loads from the structure.
The glass elements are reinforced with horizontal and vertical reinforcement, rigidly connected to each other. Installation of foundations of this type is carried out on stable soil.

On sites with heaving and subsidence soil compositions, the use of glass structures is prohibited due to the uneven impact on the foundation in different places.
Calculation of the base

Before you begin work, you should draw up a project for the future structure. To do this, you need to calculate the expected load on the base of the building. Based on this, you can determine the required number of supports, their size, the structure of the frame reinforcement, and choose which type of foundation will be most preferable.
When choosing a particular type of foundation, the characteristics of the soil on which the construction will be carried out must also be taken into account. Depending on the mass of the building and the type of soil, the depth of the foundation is determined.
When designing a foundation, you need to consider the following nuances:
- More dense soil can withstand greater loads.
- The larger the base area, the more mass it can take on.
- In the case of high groundwater levels, the lowest point of the foundation should be below the freezing level of the soil.
When drawing up a project for a future building, you need to strive to ensure that its entire mass is more or less evenly distributed across all supports. In addition, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of the soil at each individual point where the supports are laid. All of them must be located in a homogeneous layer of soil, with similar characteristics.
If this cannot be achieved, then in places with weak soil it will be necessary to provide a cushion of gravel or crushed stone, or make adjustments to the foundation design.
Nomenclature and technical requirements
Monolithic glass-type foundation slabs are used for the installation of prefabricated reinforced concrete columns. The cross-section of the glasses may vary, and the weight of the structure depends on this. For example, a glass-type foundation for columns 400 x 400 mm weighs about five hundred kilograms, and a glass-type foundation for columns 300 x 300 mm will be somewhat lighter, but a crane will still be required to install it.

In any case, for the production of foundation slabs of this type, a concrete solution with a strength index of B 15 and resistance to low temperatures F 50 is used.
In addition, the external surfaces of the slabs are treated with organic plastic materials that protect against moisture, so that the level of water resistance of glass slabs varies from W2 to W8.
In accordance with the technical conditions defined by GOST, the manufacture of foundations is carried out in compliance with certain requirements:
- a concrete solution of a grade of at least B2 is used;
- structures are installed after full strength has been achieved;
- water absorption does not exceed five percent, and this figure is achieved after installing a reliable waterproofing coating;
- all belts of the foundation structure are rigidly reinforced;
- the thickness of the concrete around the reinforcing bars must be at least three centimeters;
- cracks in the concrete product should not be more than 0.1 mm;
- strop loops are removed with a grinder; the impact method is strictly prohibited;
- Exposed steel bars in the foundation are not permitted.
Marking
The foundation is marked with paint on the side surface of the structure. The marking consists of one or two alphanumeric groups separated by a hyphen.
In the first group, according to GOST, the dimensions of the sole and the height of the product are indicated in decimeters, which are rounded to whole numbers.
The second group reveals the bearing capacity, as well as the type of permeability, if the foundation is intended for placement in aggressive environments.
Examples of notation:
- 1F13.8-1. Foundation for a column 300x300 mm with a base size of 1300x1300 mm, height 800 mm. Load-bearing capacity of group 1 for walls up to 250 mm thick.
- 2F20.9-2P. The transverse dimension of the column is 400x400 mm, the base is 2000x2000, height is 900 mm. It is possible to build walls thicker than 250 mm; low-permeability concrete is used.
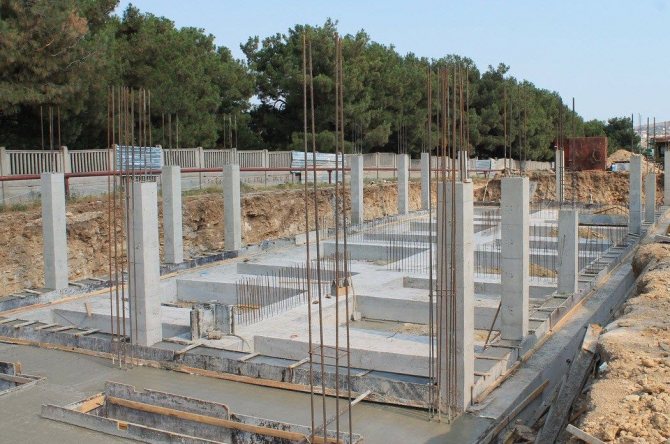
Construction technology
Foundations with glass-type elements are erected in full compliance with GOST rules under the supervision of experienced builders. The base is assembled simply, for which there is a whole technology:
- Before building the foundation, calculations are performed for individual monolithic or prefabricated structures. Paying close attention to the section, you can see the complicated reinforcement of the frame, which is the basis for the slab part and the glass. The elements of the frame base are calculated separately, as is the width of the glass itself. The plate parameters remain standard;
- the surface is prepared. The site allocated for construction is cleared of debris, the ground surface is leveled, and markings are made. It is necessary to level the surface perfectly, because the foundation slabs cannot be shifted (the permitted deviation is 1 - 1.5 degrees). If the surface is not level enough, it is allowed to add sand, the layer of which must be at least thirty centimeters in relation to the base of the foundation;
- the axes of the proposed base are marked. For this purpose, a wire or steel cable is installed on the cast-off, and broaching is done along the axes. The joint locations are clearly defined by the design solution, as are the lengths of the intermediate beams. With the help of which connections are made;
- The boundaries of the future foundation are drawn, and a trench of the required depth is dug. The bottom of the pit is leveled, a sand cushion is arranged, the bulk layer is compacted;
- Once the preparatory work is completed, they proceed to installation. The work is carried out in accordance with technology, vertical and horizontal accuracy is constantly monitored. After installation, the entire structure is reinforced, while the open glass plane is strengthened with metal rods;
- The installation of block elements ends with the concrete solution gaining the required strength. Then it is allowed to install the columns in the foundation glasses.

Arrangement of waterproofing
It is necessary to take into account that the foundation base, made in the form of a glass, is poured from concrete mortar, which is gradually destroyed by exposure to a humid environment.
For this reason, it is imperative to install a waterproofing layer over the entire outer surface. Let's figure out how to do this job:
- the entire surface of the foundation base is thoroughly cleaned of dirt and debris, uneven areas are leveled with thin concrete mortar;
- after the surface has hardened, it is treated with bitumen or other lubricant with a water-repellent effect and waited for several hours for it to dry completely;
- roofing felt material is rolled out over the bitumen layer, the joints of the strips are coated with heated resin or mastic;
- Sometimes roofing felt is laid in several layers. This precaution is taken when groundwater is close to the surface of the earth.