When constructing large buildings with large dimensions and weight, it must be taken into account that they will exert significant pressure on the ground. They need a support that can withstand such pressure. Therefore, builders use deep foundations in such cases. This type of base part of the building differs from others similar to it in the depth at which it is laid.
Such foundations are erected not only for large building dimensions. They are also created in cases where the building will be located at a sufficient depth, if serious horizontal loads are expected, or if there is excessive pressure on the soil in its upper layers. Such a foundation is placed at a depth that is beyond the freezing level of the soil.
When laying the foundation to great depth is necessary
The need to arrange deep foundations arises in the following cases:
- When carrying out construction work in difficult ground conditions;
If the construction site is dominated by loose, low-density soils, building a house on such soil, especially if it is a heavy brick structure, is strictly contraindicated. The weight of the building, exerting a vertical indentation load on the foundation, will cause it to shrink.
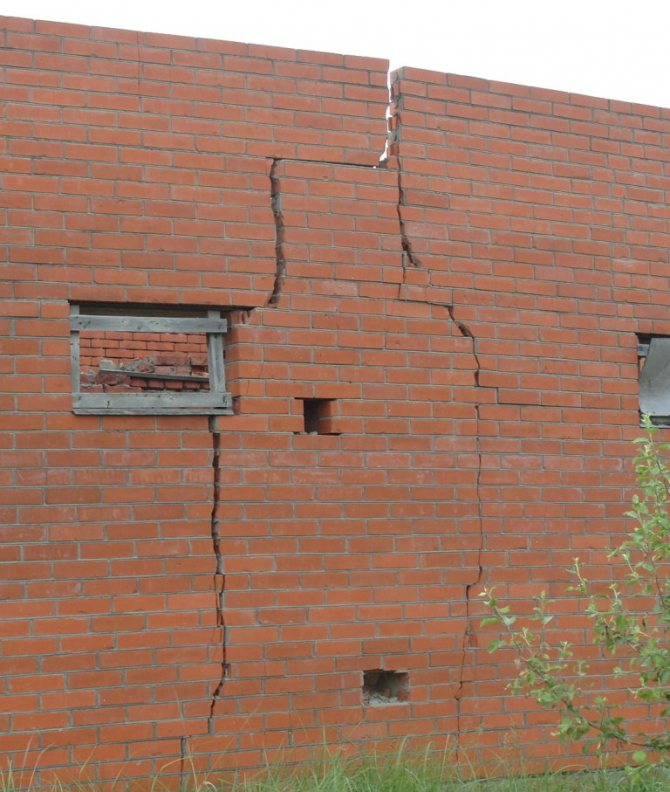

Rice. : The result of uneven shrinkage of the foundation
Shrinkage can be uniform or uneven. With uniform shrinkage of the building, the house can sink 10-20 centimeters deep into the soil; with uneven shrinkage, only one of its sides will sink, but as a result of such deformation, cracking of the walls, plinth and foundation strip will occur, curvature of door and window openings, which will lead to an emergency condition Houses.
Expert advice! When constructing deep foundations on problematic soils, the upper low-density layer of soil is opened, and the foundation rests on a deep layer of soil, which has a much higher density and load-bearing capacity, which reduces the risk of foundation shrinkage to a minimum.
- When building houses on heaving soil;
Soil heaving is the tendency of soil to change its volume as a result of freezing groundwater. Heaving forces begin to affect the foundation of the house in the cold season, when the soil freezes and the moisture with which it is saturated turns into ice.
When moisture transitions from a liquid to a solid state, its volume increases by 5-10% of the original, which is due to the different nominal mass of one cubic meter of water and ice.
The increased volume of the soil begins to expand in all directions. Since the lower layers of soil have a high density and mechanical load has no effect on them, heaving soil has only one direction of movement - upward. It puts pressure on the foundation located in the ground, causing it to be pushed out and deformed.
Rice. : Impact of vertical and tangential heaving forces on the foundation
Expert advice! When designing deep foundations, the main factor in their calculation is the depth of soil freezing - if the foundation is laid below this depth, it is not exposed to vertical heaving forces (pressing on the supporting base of the foundation), and the remaining tangential impact is effectively leveled by sprinkling the foundation walls with non-heaving materials ( sand and gravel).
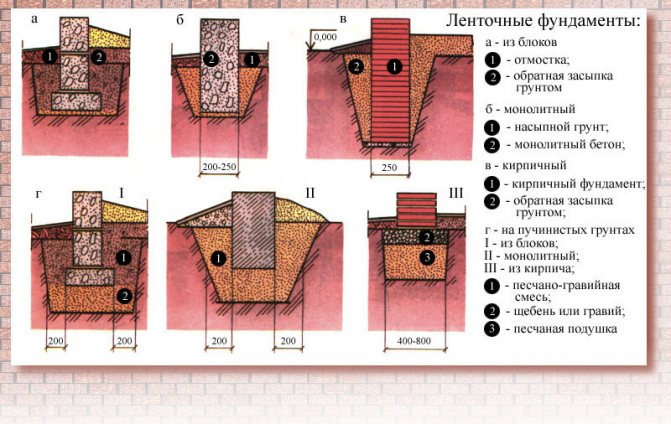
Rice. : Types of backfilling of different types of strip foundations
- When constructing buildings with a basement.
Deeply laid foundation strips not only support the house, but can also be used as walls for the basement or basement. The construction of a pitch, when arranging a deep foundation, does not greatly increase the cost estimate of the project, since additional costs are associated only with digging a pit for the basement and concreting its floor.
Reinforced concrete slab
The slab base is used for the installation of buildings on sites where there is a high level of groundwater. It is also widely used in areas where the soil has non-standard properties. A slab foundation allows you to avoid soil deformation under the influence of groundwater and seismic influences of nature. When constructing a foundation from a monolithic slab, spatial reinforcement is installed around the entire perimeter of the building. The monolithic slab can be brought to the construction site in a finished state or built on site. Before starting work, or rather its first stage, the removal of the fertile layer of soil is considered. On the site where the construction of the building will take place, depending on the type of soil and the presence of sand, they begin with laying a cushion and its direct compaction. To strengthen a monolithic foundation, it is worth using reinforcement made of metal with a diameter of one centimeter.
To connect the reinforcement frame of any foundation, you can use welding or special wire. A structure made using reinforcement is necessary to strengthen the overhead metal mesh. The frame must be installed so that it is hidden by ten centimeters of concrete mixture. This type of deep laying construction imparts long service life and reliability to the slab as a whole. For a long time, not a single crack, deformation or various ruptures form in it. When the soil moves, the structure moves with it. Before installing the reinforcement skeleton on top of the sand cushion for the foundation, it is necessary to lay roofing material or a similar material in one layer that will hold the concrete consistency.
The insulation layer must be laid in one piece; this will make it possible to increase the strength of the deep foundation. If all construction conditions are not met, or rather the stage of laying waterproofing, the pores of the slab base may become wet, which will lead to its death.

Where is a deep foundation used?
The excellent load-bearing characteristics of the foundation have made it the de facto main type for high-rise buildings made of brick and precast concrete. At the same time, when carrying out survey work, it is not advisable to focus on deep foundations in places with high groundwater levels. In such cases, all efforts may come to naught; there will be no solid support on the ground.
Deep reinforced concrete foundations are expensive structures, the construction of which requires quite a lot of financial and time costs.
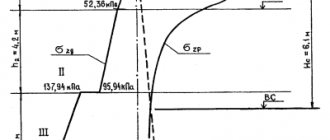
It is rational to build deep foundations in soil conditions in which the depth of soil freezing does not exceed 2.5 meters and the groundwater level is less than the GPG.
Expert advice! When laying foundations to a depth of more than 2-2.5 meters, the labor intensity and cost of excavation work associated with digging trenches and pits, and the amount of required consumables, sharply increases.
In such cases, it would be more rational to use pile foundations based on bored or driven reinforced concrete piles, the bearing capacity of which will be no less, and the final cost will be an order of magnitude lower.
Departments
Accounting
The accounting department has all the necessary information about the receipt of payments from Clients for services provided by GlavFundament (sale of screw piles, construction of foundations on screw piles, express geology, design of foundations on screw piles, civil and industrial facilities). Each Client has the opportunity to promptly receive information about the receipt of his payment to the organization’s account. The department's tasks also include issuing invoices and documents closing the reporting period.
Vasiliev Denis Alexandrovich
Corporate department
The Corporate Department is responsible for fulfilling contractual obligations to Partners for the supply of screw piles to the GlavFundament company (quantity, nomenclature, assortment, timing and other terms of delivery). The department provides assistance in working with other departments and separate divisions of the company, providing the Partner with marketing, technical and logistics support, and promptly compiles financial estimates and other documents.
Head of Corporate Department
Kopev Evgeniy Sergeevich
Human Resources Department
The HR department of the GlavFundament company occupies a responsible position in the development of the organization's plans in terms of providing it with labor resources, carrying out selection, admission, official employment, adaptation, accounting and dismissal of employees.
The tasks of the department include carrying out work on the formation and preparation of a reserve of personnel for appointment to appropriate positions, advising senior management and heads of departments on personnel policy issues in the development of projects, the production of screw piles, and construction. The department evaluates the performance of each employee of the organization.
Head of HR Department
Dubovik Elvira Gizetdinovna
R&D department
The Research and Development Department (R&D) is engaged in research into the nature of the joint work of screw piles with soil, development and implementation of innovations in the field of pile foundation construction.
The department’s specialists create technological solutions that make it possible to reduce work time and reduce costs without compromising quality.
The department’s tasks also include organizing scientific cooperation with departments of construction universities dealing with foundation engineering problems, providing consulting and information assistance to employees of the company’s structural divisions.
Head of R&D Department
Glazachev Anton Olegovich
Sales department
The sales department is the link between the company and the Client, carrying out the interaction process from the first contact to the end of the contractual relationship.
The department provides consultation, preliminary calculation of the cost of screw piles purchased by the Client, technical support, and conclusion of contracts.
Head of Regional Sales Department
Akatiev Sergey Nikolaevich
Advertising and PR Department
The advertising department is a structural unit tasked with determining the direction, planning and organizing advertising campaigns, as well as developing advertising and information materials.
The advertising department of the GlavFundament company carries out work on advertising its products (screw piles) and services provided (installation of foundations on screw piles, design and redesign of foundations and buildings/structures), and is working on concluding agreements for advertising products and/or services with third-party organizations.
In addition, advertising department specialists promptly notify Clients about various promotions and advertising campaigns, plan participation in exhibitions, and enter into agreements with organizing committees of fairs and construction forums.
Sergin Roman Petrovich
Purchase department
The purchasing department makes decisions regarding the purchase of raw materials required for the production of screw piles, being responsible for concluding product supply contracts and selecting suppliers.
Department employees provide information on the purchase of materials necessary for construction, advise on price categories, and also quickly calculate the cost and delivery time of screw piles to a particular region to organize the delivery of cargo to any point in Russia or the CIS countries.
How to lay the foundation at great depths
Laying a foundation to great depths is labor-intensive and involves a whole cycle of production processes. Digging trenches involves repeated passage of construction equipment, and concreting always means large labor costs and material costs for raw materials. Excavators and bulldozers with additional attachments are used to carry out excavation work. Not a single concreting of even block-based foundations can be done without lifting equipment, such as a tower or truck crane. In conditions of a continuous construction cycle, the requirements for mixing and laying concrete increase several times.
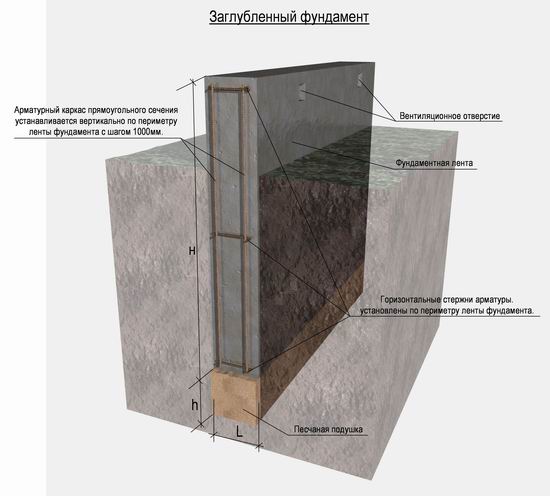
Figure : Recessed foundation
Popular types of deep foundations
Construction practice has shown that the most optimal type, in terms of the ratio of the complexity of the work and its cost, should be considered in-depth strip foundations.
The number of production processes is significantly reduced.
Deep foundations may include the following types of foundations:
- Columnar
- Tape
- Slab.
Let's look at each of them in more detail.
1. Strip foundations.
The most popular type of deep foundation is a strip foundation. Its popularity is due to the order of magnitude lower cost of time and finances for arranging such a foundation, in comparison with a slab foundation, and high load-bearing capacities.
Firstly, when constructing a strip foundation, excavation work is significantly reduced - digging trenches for a foundation strip is an order of magnitude faster than digging a full-size pit. Secondly, the amount of consumables - concrete and reinforcement - is greatly reduced.
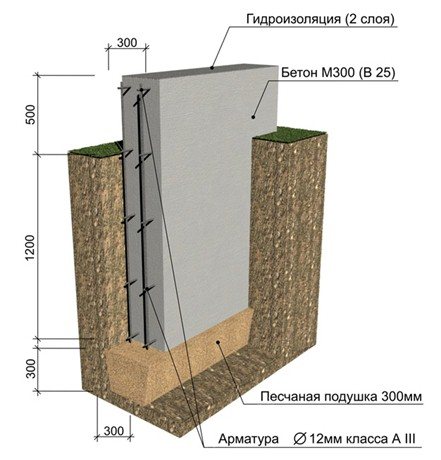
Rice. : Scheme of deep strip foundation
Expert advice! The load-bearing characteristics of strip foundations are sufficient for any low-rise buildings - made of brick, frame panels, logs, foam concrete or aerated concrete.
Deep strip foundations demonstrate good resistance to heaving forces and horizontal soil shifts.
2. Slab foundations.
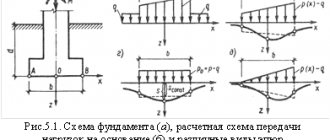
Such foundations are a monolithic reinforced concrete slab, at least 50 centimeters thick, buried in the soil below its freezing depth.
The construction of deep slab foundations is rational in the following situations:
- when constructing heavy buildings on weak, low-density and bulk soil;
- for mixed soils with different degrees of compressibility and load-bearing characteristics;
- at high groundwater levels.
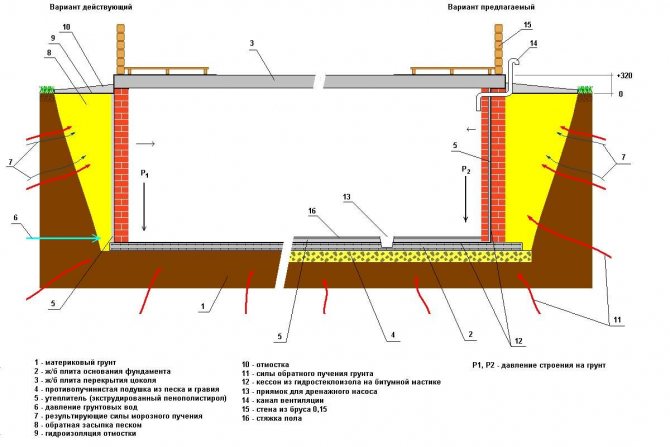
Rice. : Diagram of a deep slab foundation with a basement floor
In terms of load-bearing characteristics, slab foundations are superior to all other types of foundations; even multi-storey buildings can be built on them; however, in private construction, monolithic foundations have not gained much popularity due to the labor-intensive construction and high financial costs of implementing the project.
3. Columnar foundations.
The columnar base consists of a system of supporting pillars, evenly distributed along the contour of the external and internal walls of the building in increments of one and a half to two meters.
Columnar supports can be made as monolithic structures - by pouring concrete formwork, or created from prefabricated materials - foundation blocks, bricks or foam concrete.
Rice. : Diagram of a deep columnar foundation
Expert advice! The load-bearing characteristics of columnar foundations are not enough for the construction of heavy buildings made of brick; such foundations are used as support for light one-story residential and ancillary buildings made of frame panels and wood.
The columnar base does not imply the possibility of arranging a basement or ground floor. Such foundations require mandatory tying with a metal or wooden grillage, since unconnected pillars are highly subject to deformation due to horizontal soil shifts.
Pile foundation for a private house
The types of pile foundations are similar to columnar foundations, but they are installed differently. Piles, pre-fabricated at the factory, are driven into the ground. We need special equipment. The pillars are dug in, sometimes made on site. Also, a reamer is always placed on the piles. As mentioned, tape is poured onto the poles only in the case of TISE.
Like pillars, piles are good for heaving, water-saturated soils. In order to achieve stable layers of soil, the foundations have to be driven in many meters. This is a standing pile system. If the solid ground is too far away, they make hanging ones.
They transfer the load to the supporting soils with their side surfaces, without ever reaching the stable soil with their bases. You have to rely on compressible masses, for example, sandy loams and loams. In them, hanging piles hold negative, compressive frictional forces.
However, during the freezing of heaving lands, positive ones also arise. These push the piles out and cause the structure to stretch. Be sure to check the selected piles for resistance to them. Among the advantages of buoyancy forces, we point out the increase in the bearing potential of the foundation in cold weather.
A pile foundation, whatever it may be, is beneficial only in swampy soils. If a private house is being built on these, it is worth consulting with smart engineers, since the task ahead is difficult.

Laying a strip foundation
To lay a strip foundation, you do not need to dig an entire foundation pit; you just need to confine yourself to trenches for the foundation blocks. At the same time, the quality of the foundation does not depend in any way on the chosen approach. The main load from the building is borne by the soil, and the denser it is, the better for the structure as a whole.
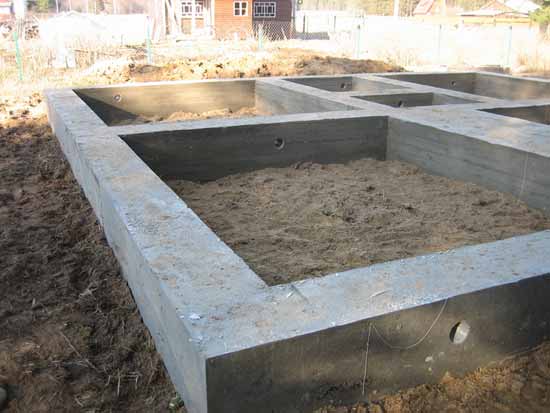

Fig .: Deep strip foundation
Practical work on laying a strip foundation should be preceded by the foundation design stage. Calculation of the foundation involves identifying the required depth of its laying, which is determined based on the depth of soil freezing, groundwater level, geodesy of the construction site and technical characteristics of the building being constructed.
Work on laying strip foundations to great depths is carried out in the following sequence:
- Construction site preparation;
The construction site is cleared of surface vegetation, the fertile layer of soil is removed to a depth of 10-20 cm (one shovel bayonet). If necessary, the area is leveled.
- Marking;
Marking the future strip foundation begins with marking the load-bearing wall of the building, then perpendicular walls are marked and the correctness of right angles is checked using the Egyptian triangle method. The foundation tape is marked along both the external and internal contours.
Rice. : Scheme for checking foundation marking angles
- Excavation;
A trench for the foundation is dug either manually or mechanized. Since the depth of the trench is quite large, digging may be accompanied by the collapse of its walls.

Rice. : Scheme for strengthening the walls of the trench
Expert advice! To avoid soil shedding, the trench walls are reinforced with plywood or fiberboard panels, which are installed using horizontal struts.
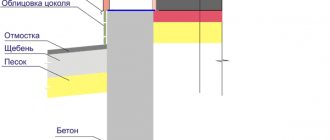
- Backfilling of the compacting cushion;
To create a compaction cushion, sand and fine gravel or crushed stone are used. The thickness of the layers is the same, as a rule, it is 10-15 centimeters. Sand is the first layer; after backfilling, it is watered and thoroughly compacted.
- Creation of formwork;
Formwork for pouring concrete is made from planed boards 2-3 centimeters thick. The boards are connected using vertical planks and fastened with nails or self-tapping screws.
Important! The height of the formwork should be greater than the depth of the trench, since the foundation strip will also form the base of the house.
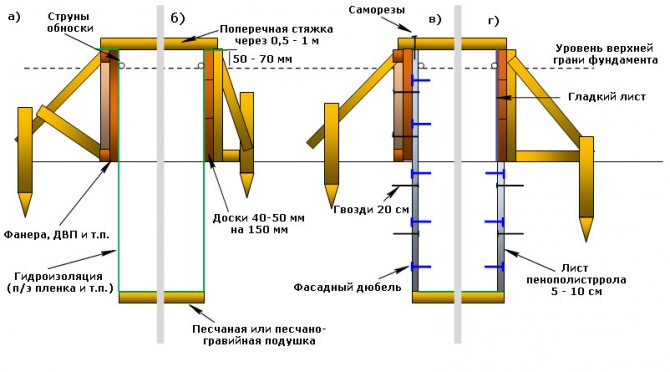
After installation, the formwork is covered from the inside with waterproofing material, which is needed to prevent concrete from leaking into the cracks between the boards.
- Reinforcement;
To reinforce the strip foundation, a double-circuit reinforced frame is used, consisting of vertical rods and horizontal jumpers.
Expert advice! The thickness of the reinforcement rods for the vertical contour should be 12-14 mm; for vertical connecting elements, smooth reinforcement with a diameter of 8-10 mm can be used.
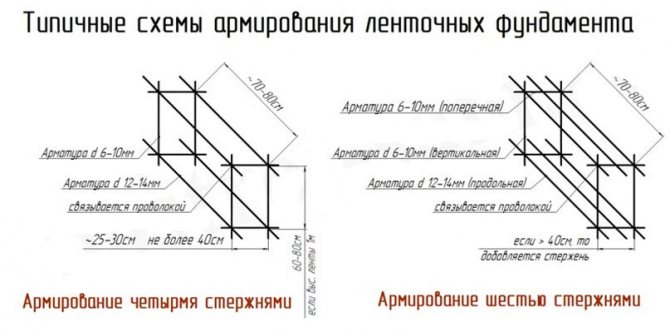
Rice. : Scheme of reinforced frame for strip foundation
The reinforced frame is connected using tying wire or welding. The first option is more preferable, since when a welded connection is made, the structure loses its elasticity and the concrete strip resists bending loads less well.
- Concreting;
The pouring of a strip foundation is carried out simultaneously or layer by layer (provided that a new portion of concrete will be poured before the previous layer sets). Heavy concrete made of M300-M400 cement is used for pouring.
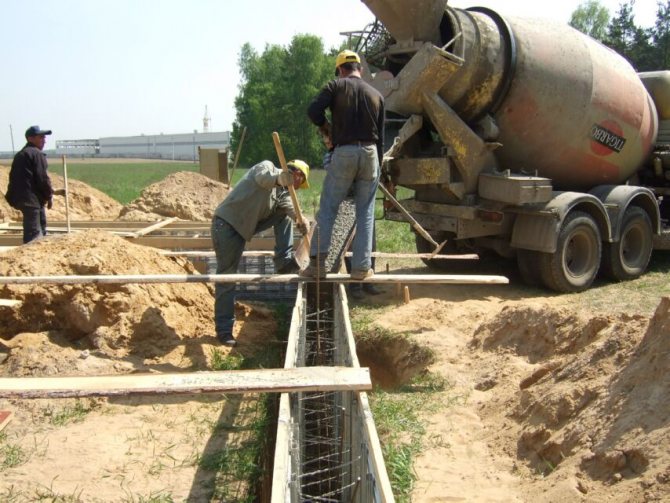

Rice. : Concreting a deep strip foundation
Compaction of concrete using vibration compactors or bayonet reinforcement bars is mandatory.
Expert advice! If construction is carried out in the warm season, the maturing concrete must be covered with oilcloth and regularly moistened, since when the concrete dries out, the surface of the foundation tape may become covered with microcracks.
Soil heaving. What to do?
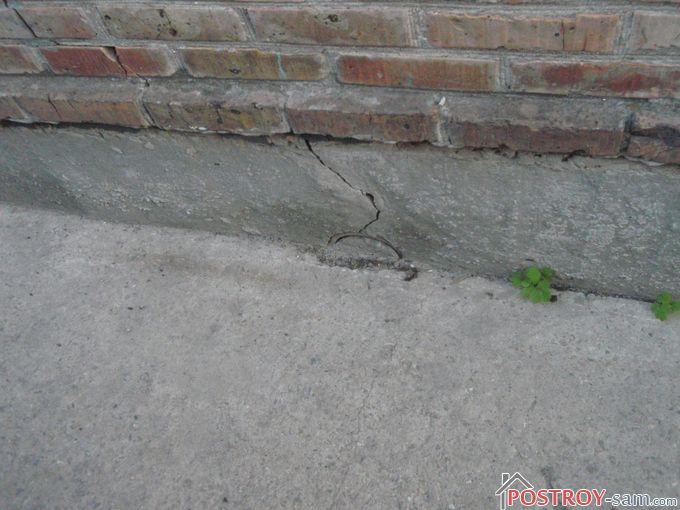

Frost heaving of the soil is one of those problems that are easier to prevent than to deal with their consequences. Each type of foundation has its own preventive measures.
If you have a strip foundation, be sure to make a high-quality blind area. This can be a traditional open concrete blind area about a meter wide, or a hidden one - a PVC membrane embedded in the ground. In any case, it will not allow water to pass under the base of the foundation, which will help avoid unwanted deformations in winter. For shallow foundations, insulation of both the structure itself and the blind area is especially important. This will help solve not only the issue of frost heaving of the soil, but will also have a positive effect on the energy-saving performance of the house.
If you have a TISE foundation, then the support zone for the columns is at a depth of 1 m 20 cm, that is, below the freezing zone. Just in case, it is advisable to form an air gap between the grillage and the ground, covering it on the side with an ordinary asbestos sheet. This foundation is not afraid of freezing. Even if the soil freezes and increases in volume, this is compensated by the air gap.
If you are building a shallow slab foundation, you cannot do without forming a drainage trough to keep the soil dry. When insulating the base and blind area, think about insulation under the slab. Extruded polystyrene foam or foam glass is best suited as insulation.
Foundation resistance to frost
It is known that a good indicator for deep foundations is resistance to frost heaving. This is the name given to the process of groundwater pressure on the foundation material. Frozen soil, already at zero temperature, begins to expand and affect the foundation walls, creating cracks in them.

Rice. : Foundation resistance to frost
During a repeated cycle of thawing and freezing, water enters through them into the foundation blocks, causing so-called frost heaving of the foundation. Such processes are excluded in foundations with a deep laying level, since they are calculated at a level below the soil freezing mark.
Using deep foundations for small buildings
It so happens that deep foundations are practically not used in the construction of low-rise buildings and buildings made of lightweight materials. There is a risk of construction defects due to insufficient shrinkage hardness of the soil. The structures of buildings of this type are lightweight. Therefore, for the construction of wooden cottages that are so popular today, it is unwise to use deep foundation technology.

Fig .: Low-rise buildings with deep foundations
In order to rationally use building materials, they resort to the method of laying a foundation on a sandy base. To arrange the latter, they resort to a multilayer coating, where each of them is wetted with water. With this approach, the foundation can have increased strength.