Reconstruction of the foundation is always a necessary measure. Even a properly designed foundation with a large margin of safety can be destroyed. The formation of cracks, shedding of the surface layer and other external signs indicate that the supporting structures are in disrepair. This may be due to natural conditions, exposure to an aggressive external environment, improper maintenance or depreciation wear of the material.
The way out of the situation is a major overhaul or local reconstruction. However, the foundation needs to be reconstructed not only if the structure loses its functionality.
Why is reconstruction carried out?
The foundation is the part of the building that is subject to particularly strong impacts. Most often, it is the supporting structures that are under constant loads that require repair. You should not delay starting repair work if the foundation has begun to deteriorate or if an increase in load is planned.
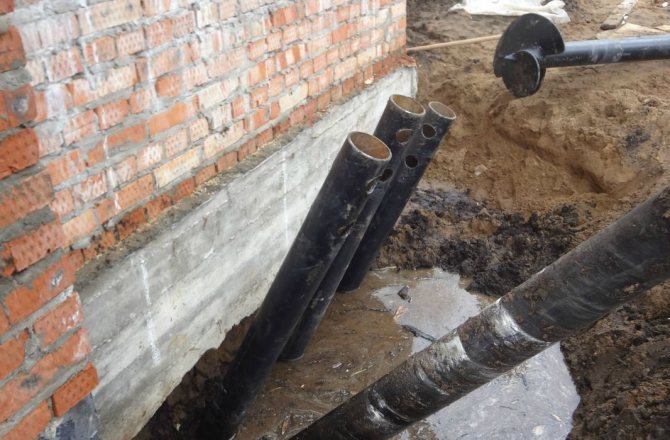

Strengthening the foundation with bored piles
The types of work performed can be classified as follows:
- Widening of grillages and strip foundations associated with an increase in the thickness of the wall frame;
- Transplantation of the foundation onto external pile columns;
- Increasing the depth of the foundation associated with the installation of equipment or the organization of the basement;
- Strengthening foundation soils by silicization or heat treatment;
- Increasing the bearing capacity by the method of through installation of bored piles and rods.
Before starting foundation repair work, you should determine the current condition of the support, as well as the type and amount of work required. Sometimes it is irrational to carry out large-scale events; it is enough to just carry out external cosmetic repairs, but often it is necessary to overhaul the load-bearing part of the foundation.
Determination of labor intensity of work
Foundation reconstruction includes two subtypes of work - repair of above-ground and underground parts of the foundation. The fundamental differences lie in the purpose of each type of repair and the complexity of the associated activities. Reconstruction work is rarely limited to restoring the above-ground part of the foundation; most often it is necessary to open up the soil around the perimeter of the building in order to construct a foundation pit.
The reasons for reconstructing foundations are based on changing operating conditions and the following needs:
- Increased load on the foundation;
- Violation of the integrity of the foundation or waterproofing layer;
- Violation of foundation stability due to deterioration of foundation soils;
- Increase in the general indicator of soil deformability;
- Displacement of structural units associated with the melting of soils and displacement of the centers of gravity of structures.
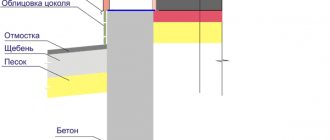
Destruction of the integrity of the foundation slab is often caused by shrinkage of the foundation soil, the consequences of partial washing out of the bearing layer by ground and sedimentary waters; construction work carried out nearby and simply wear and tear of structures caused by the aging of the material (for example, exposure to frost heaving).
The degree of wear of structures is determined visually. For concrete structures, the crack opening value is measured using special strain gauges. This will make it possible to find out at what speed the destruction of the structure occurs. The degree of destruction of concrete is determined by impact - shedding of the surface layer will be a sign of delamination of the concrete stone.
It is quite difficult to independently conduct an external inspection and determine the level of work required. Poorly designed components placed at inappropriate locations on the plan can have the opposite effect by placing additional stress on the foundation. The inspection of the building should be entrusted to specialists.
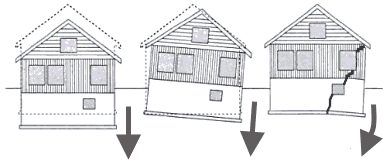
Foundations exposed to excessive frost heaving of soils are deformed in various directions. By determining the linearity of the supporting part of the structure, the points of concentration of depreciation fatigue of the foundations are identified. Geological and hydrogeological surveys will show changes in the condition of the soil. Taking into account the data obtained as a result of analyzing the condition of the building, a reconstruction plan is drawn up.
How to repair the foundation of a wooden cottage
Unlike stone or brick houses, country houses are usually made in the form of a log house or frame building from timber or vulture panels. The weight of such a building can be two to three times less than a brick building, which greatly simplifies the procedure for repairing the foundation of a wooden house with your own hands.

As in the case of brick houses, in a dacha, the outer cladding of the basement surface of the walls is the first to fly off. If the building is installed on a concrete strip, the remaining plaster must be beaten down to the concrete, and the entire strip base must be carefully inspected. It is possible that the plaster was cut off by the top layer of soil that rose due to frost heaving. If no cracks are found, you will need to lay a repair mesh and plaster the base again.
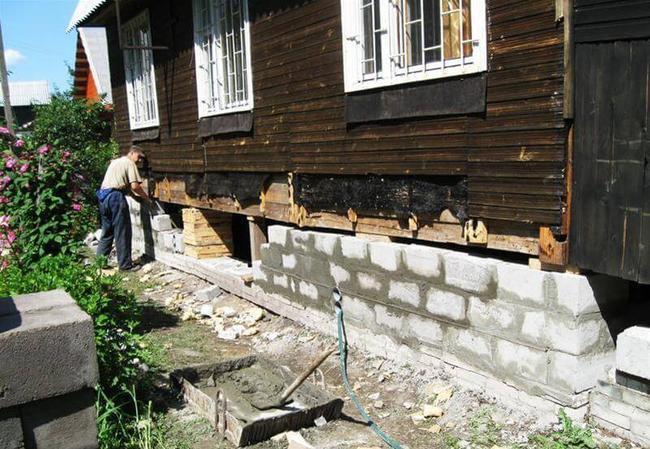

The situation looks much worse if the masonry or concrete casting has cracks.
Reconstruction technology
The reason for starting reconstruction of the foundation can be not only various types of destruction and deformation of the support, but also an increase in the total load. For example, an increase in the number of storeys of a building, shrinkage of the soil on the site and other reasons require strengthening of foundation structures even in the absence of external signs of aging of the support. Technological techniques used in construction to strengthen foundations differ according to the type of compatible foundation structures. Watch the video to see what the main reasons contribute to the destruction of the foundation.
The most common causes of foundation failure:
- Poorly compacted subsidence or slumping foundation soil has been washed out by groundwater;
- Soil washing out by rainwater due to poorly constructed external drainage systems and flooding of basements;
- Construction of new buildings within existing buildings in violation of safety standards;
- Exceeding the permissible number of freeze/thaw cycles and general wear and tear of the material;
- Excessive dynamic loads on supports.
All these reasons can lead to a decrease in the bearing capacity of the foundation. Which requires mandatory repairs.
Reconstruction of strip foundations
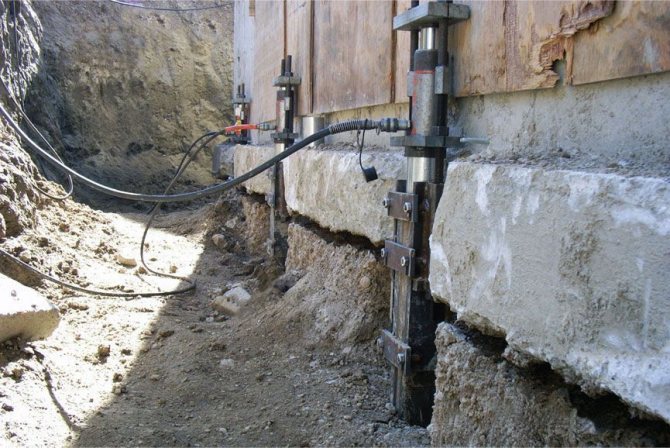

Repair of strip foundations is carried out in two ways - by placing them on external piles and by drilling through cast-in-place piles. The first method requires partial opening of the side surface of the foundation slab. With a certain step along the perimeter, strips of soil are released to provide access to the foundation surface and further laying of outrigger beams. Each pair of piles is fastened with transverse beams to the foundation and longitudinal beams to each other.
Then all the beams are monolied and, after the concrete has fully gained strength, they are compressed. The strapping device is the final stage of transferring the load to the external piles, after which the trenches are backfilled.
Strip foundations are the most popular type of supporting structures, especially in individual housing construction. Therefore, there are a lot of technologies for strengthening and reconstruction of both prefabricated and monolithic tapes. There are techniques that allow you to increase even the depth of laying strip foundations.
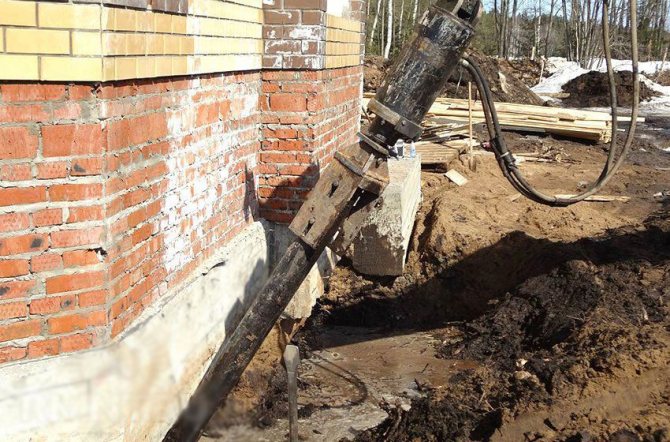

In addition, it may be necessary to increase the width of the upper edge of the foundation. To do this, the perimeter of the building is divided into sections ranging from two to three meters in length. The soil is removed to the bottom level of the support, through one gripper, to prevent the freed foundation soil from bulging out. Intermediate areas are removed only after backfilling has been completed and exposed areas have been compacted. The open side surface of the foundation is washed with water pressure, then anchors are drilled into the body of the monolith, formwork is installed and the concrete mixture is poured.
When strengthening the tape using the through drilling method, there is no need to make pits. The wells are drilled with a pneumatic drilling auger through the soil layer, then reinforcement cages are lowered into them and the concrete mixture is poured. The number of piles is determined not only by the required load-bearing capacity, but also by the size of the building - it is not recommended to drill through piles more often than through three well diameters.
Slab, column and other types of supporting structures, except piles, are strengthened in the same way.
Reconstruction of pile foundations
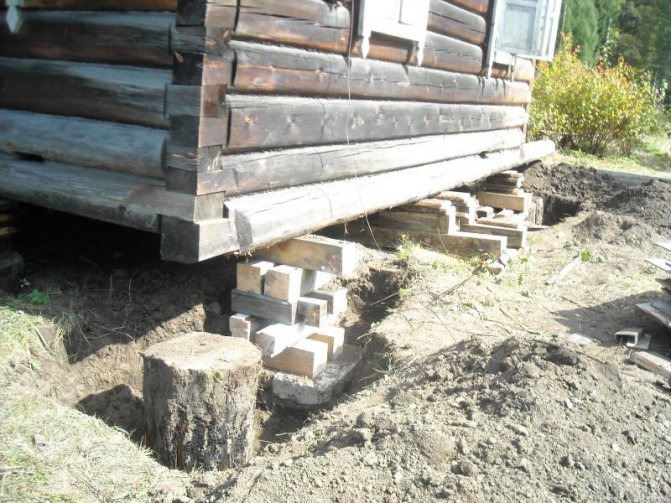

The volume and technology of work depends on which part of the foundation requires reinforcement - piping or pile columns. The nature of the damage is also an important factor. To eliminate surface cracks formed as a result of corrosion and weathering of the top layer of concrete, shotcrete is used - covering the foundation with cement-sand mortar under pressure. Before starting work, the surface of the foundation is thoroughly cleaned with metal brushes or sandblasting units, blown off dust and washed with water. A layer of solution is sprayed onto a fine-mesh metal mesh.
More serious cracks and other types of damage are also filled with cement-sand mortar. A cement mixture is driven into pre-drilled holes in the foundation body with a diameter of 40 mm under a pressure of 0.5 MPa. The recommended drilling step is at least one meter, and the length is no more than 0.5 of the width of the hole when drilling from two sides and no more than 0.8 when drilling from one side. For cementing, a water-cement solution is used in a ratio of 1:10 to 1:4, respectively.
If the pile is destroyed irrevocably, the structure should be replanted on external pile columns. The work is quite labor-intensive, but sometimes it represents the only way out of an emergency situation. Watch the video on how to replace the pile.
Repair of pile columns is carried out in two ways. The protruding parts of high piles are reinforced with metal clips. To do this, a metal shell with a steel thickness of at least 100 mm is fixed around the pile. The length of the cage is the length of the protruding part of the column plus a depth of at least one meter. Small-diameter piles are strengthened by drilling - a circular trench up to one and a half meters deep is dug around the post, into which cement-sand mortar is injected.
Foundation soil strengthening technology
Silication and thermal fixation methods are used to reduce soil subsidence. The first method is to drill blind wells around the perimeter of the building. Using injection units, a solution of liquid glass is supplied into the wells, fixed by electric current. After two days, the tension is relieved, since the solution has time to be completely distributed in the soil and effectively consolidate it. A sign of subsidence soil is the formation of cracks on the side surfaces of the foundation; local soil failures and shrinkage of individual land plots.
The soil stabilization technology allows not only to prevent further subsidence of the foundation, but also to increase the bearing capacity of the foundation. Various solutions are used as reinforcing injections, including urea resins and cement-sand mortar.
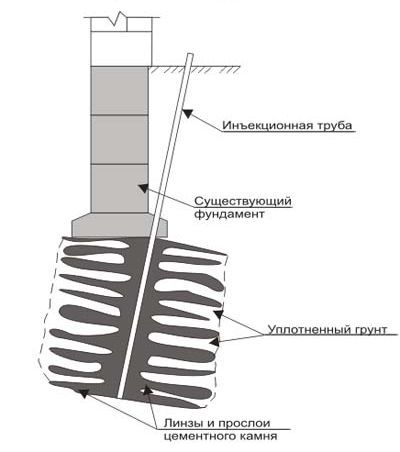
Foundation soil reinforcement scheme
Thermal strengthening of soil is also one of the methods of strengthening soil, which is actively used in conditions of weak soils, when it is impossible to use technologies that require the full or partial opening of underground structures. The thermal enhancement process takes place in the following sequence:
- Wells with a diameter of 100-200 mm are drilled along the perimeter of the building;
- A valve is installed with a combustion chamber and fittings to regulate the pressure of oxygen and fuel supply;
- Carefully seal all structural components;
- Install supply units and pipelines;
- They burn the soil;
- The installations are dismantled and the wells are filled with compacted local soil.
Wells are drilled using rotary, percussion or auger units. Fuel is supplied under natural pressure, and the temperature in the well should not exceed 1100 degrees. There are a lot of other technologies for strengthening foundations, but they are used in special cases and are practically not used in individual housing construction. It is also possible to use proprietary engineering solutions created specifically for a specific building.
Urgent repair measures
Before choosing a method to strengthen the foundation, you need to perform two priority procedures:
- Determine the cause of damage to the foundation, which in most cases allows you to carry out work to strengthen the foundation at the lowest possible cost;
- If possible, temporarily strengthen the building's load-bearing structures to prevent a more severe accident.
For example, you can temporarily repair a columnar foundation by installing additional supports, sewing or staples together a cracked wooden grillage, tape, or part of the destroyed masonry. Any methods of strengthening the foundations of buildings, such as banding or installing external supports, which do not require intervention in the supporting structures, will only improve the situation and make the building safer.

For your information! Temporary repairs of the building and even strengthening the foundation of a private house will not solve the existing problem, but the actions taken will make it possible to make diagnostics safe for life and health.
In any case, if there are signs of subsidence or destruction of the strip or pile foundation of a building, you should not dig out a blind area or backfill of load-bearing structures just to see how deep the crack or zone of delamination of the foundation has spread. This can be determined by calculation. It is necessary to dig holes or open a blind area with an already developed action plan for repairs and strengthening of foundations with cementation.

First of all, it is necessary to determine the groundwater level and the presence of voids under the foundation. Most often, there is a classic picture of subsidence and destruction of one of the corners of the foundation of the house. The reason for subsidence of a strip or pile is almost always groundwater and improperly executed drainage, which in many cases may be completely absent as an element of the foundation. Therefore, before thinking about how to raise a house with your own hands, you need to drain the water and dry the soil under the walls of the building.
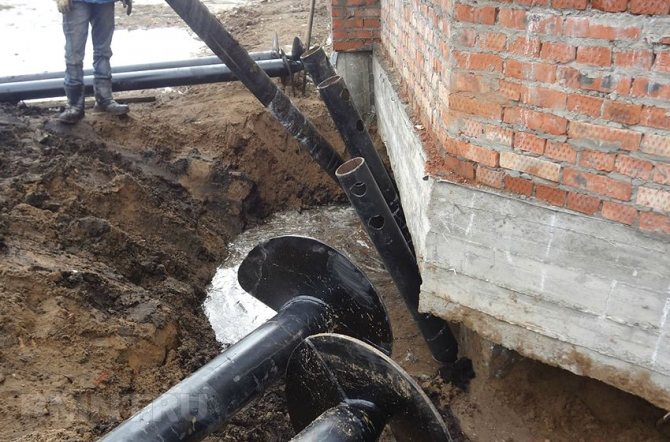

Initial wells are drilled along the perimeter of the building’s foundation, at a distance of at least one and a half meters from the blind area. It is enough to break through three corner trunks to understand whether the cause of all the problems is the pressure of groundwater on the walls of the strip foundation. Only after installing the pump-out pump in a few days can you begin to construct pits to examine the brick, rubble or concrete wall of the foundation of the building.
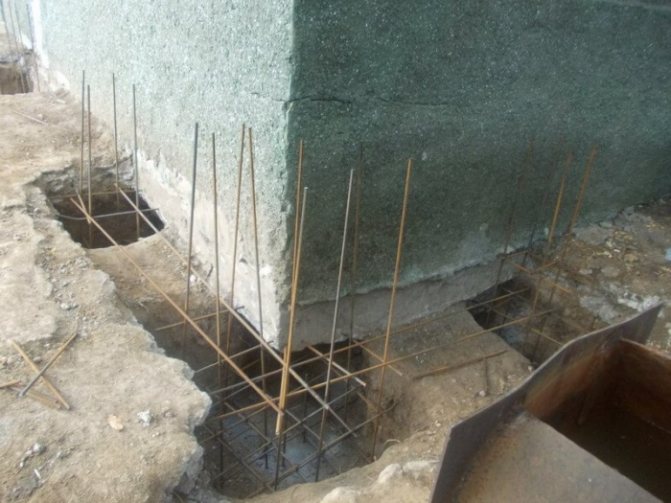

If, as a result of the inspection, several problem areas are identified, then the number of holes must be increased, but the wall cannot be opened by more than 25% without installing bandages or unloading supports.
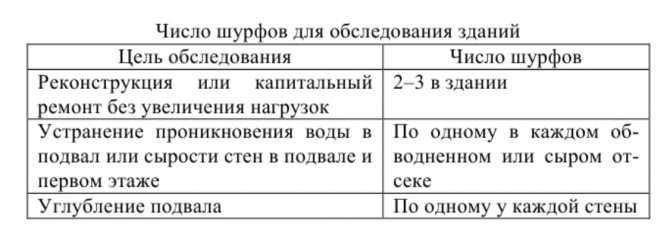
Based on the results of the inspection, the main decision should be made - to treat the masonry or plan to dismantle the foundation. In brick buildings, the last resort is resorted to only in exceptional cases, for example, to save a building of historical value. But even in this case, there is a considerable risk that the repair may result in the collapse of the building wall. Therefore, experts recommend treating the foundation with all available means.