Very often in construction the technology of laying pile foundations is used. Different types of piles provide the ability to perform different tasks in the construction industry.
When driving pile pillars, it is necessary to control the quality of the work performed, compliance with all project requirements, including permissible deviations of installed piles (SNiP 2.02.03-85 and SNiP 3.02.01-87).
Regulations
The design and installation of these products, which bear the entire load of the facility being built, is subject to a set of serious requirements regulated by regulatory documents. There is no single GOST, the scope of which extends to bored piles.
The requirements for them are united by the following building codes and rules:
- 02.03, approved in 1985, which are called “Pile foundations”;
- 02.01, developed in 1987, called “Earth structures, foundations and foundations”;
- 03.01 issue of 1984 entitled “Reinforced concrete and concrete structures”.
Despite the fact that these regulatory documents were developed and approved quite a long time ago, their requirements are relevant at the present time. What parameters must pile foundations meet? Why are these norms fundamental? Let us consider in detail what requirements bored structures must meet.
Construction specialists and design engineers will find a lot of useful information in the presented material. After all, they are united by the main task - ensuring the reliability of the building and compliance with all the requirements established by the standards!
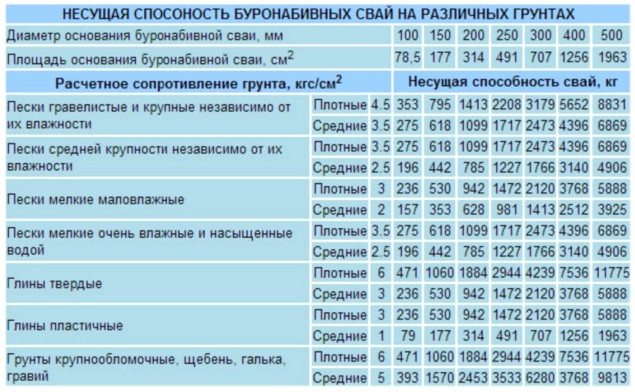
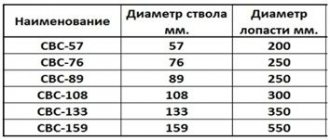
Table for determining the bearing capacity of 1 m/p bored pile-rack
Quality control of pile installation
The quality of installation of the pile supporting structure should be monitored throughout the entire work process. It is affected by:
- The quality of the material used in the installation of the structure;
- Strict compliance with all approved rules for driving piles;
- Correct placement of pile rods according to the project;
- High-quality work when deepening piles;
- Control of ensuring high strength of the pile foundation.
Of all these areas, the last one is non-standard. To perform this control, two methods are used: statistical and dynamic. For stuffed ones - only statistical.
Statistical method
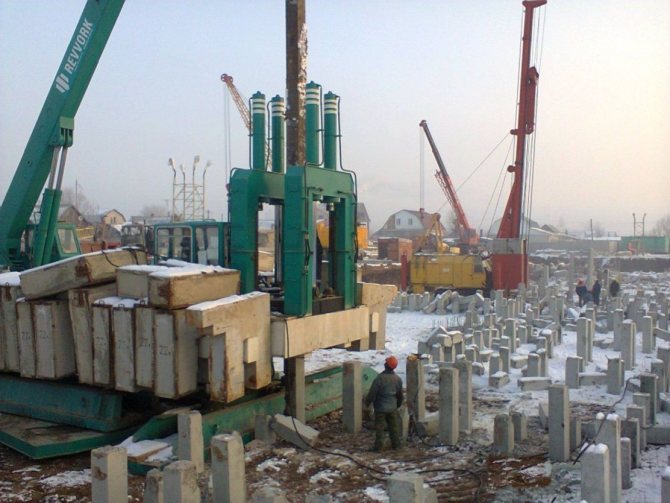

A statistical method for monitoring load-bearing capacity is used after completing the installation of a pile structure, before starting further work on the construction of the future building. To do this, it is necessary to load the structure with a certain load or provide pressure on it using a hydraulic press until slight movement occurs.
Based on the force exerted, a conclusion is drawn about the load-bearing capacity of the pile. This method is quite reliable, but requires a lot of effort and time (from 4 to 12 days). Therefore, it is mainly used for quality control of bored piles.
Dynamic method
The dynamic method is a conditional assessment of the load-bearing capacity of pile rods based on the failure rate. Various methods are used to determine it. For example, the use of a failure meter - a device with a scale with pointers moving along it. This device is placed directly on the ground or attached to a pile. During the period of deepening the pile, one of the rods moves. Its position indicates the residual failure value. During slight reverse movement of the pile, the second pointer moves upward and indicates the elastic failure value.
When performing quality control of pile installations, it is necessary to constantly ensure that the deviation of the piles does not exceed the design tolerances.
Pile classification
In accordance with SNiP, driving piles used in construction is carried out using various methods. According to the method of deepening, piles are divided into the following types:
- Concrete-reinforced piles of the driving principle, which are pressed into the ground using vibration or hammers.
- Reinforced concrete supports-shells, the formation of which is carried out by excavating the soil and filling it completely or partially with mortar.
- Concrete, with the possibility of reinforcement, cast-in-place piles, during the construction of which a concrete solution is poured into a well obtained by displacing soil.
- Reinforced concrete, obtained by the soil drilling method, in which steel reinforcement is placed in the wells and a concrete mixture is poured.
- Screw piles, which are a steel pipe with a screw part, the immersion of which is carried out by screwing.
Let's take a closer look at bored structures, which are the most widely used and in demand in construction. According to the method of construction, they are divided into drilled and driven piles.

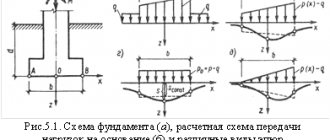
Pile foundations should be designed based on the results of engineering-geodetic, engineering-geological, engineering-hydrometeorological surveys of the construction site
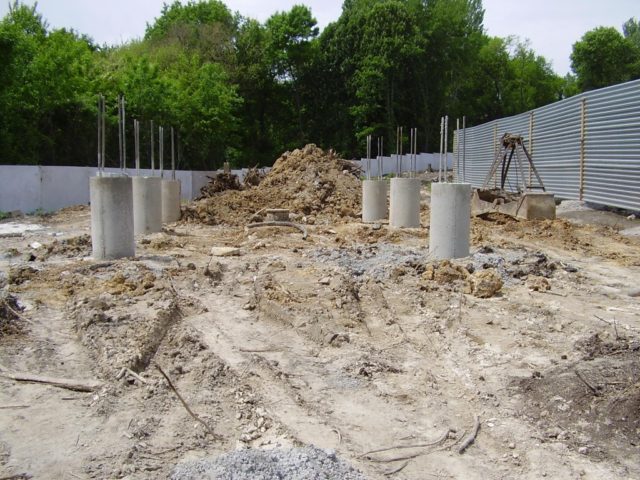
Construction and types of pile foundations
A grillage is mounted on the foundation supports. Its presence is not required. In prefabricated buildings, in order to save costs, a grillage is not built.
A certain distance is maintained between the bottom of the house and the ground. This is necessary to protect the structure from the effects of surface water. The height of the piles depends on the depth of the dense layers of soil on which the base of the foundation will rest.
Piles are long rods of rectangular, pyramidal or circular shape. For ease of immersion into the ground, their ends can be pointed or have metal “coils”, like a drill.
Foundation designs may be different. They depend on:
- type of piles;
- their location under the building;
- nature of work in soils;
- grillage designs.
There are two types of pile foundations.
- On hanging stilts. This design is more complex in calculations. Its technology involves the presence of a large number of piles. After driving, the upper part is cut off and the structure is strengthened by installing a prefabricated reinforced concrete head. Concrete is poured into the cavity formed between the head and the pile. The load on the supports is transmitted through the grillage. It is performed under load-bearing walls in the form of cross beams. For strength, the piles under the beams can be arranged in two rows. The load is transferred to the ground by friction of the piles against the side walls.
- On retaining piles. Rack piles must have a wide base. They are immersed in the ground until the depth of solid soil layers is reached. This type of foundation is used in the construction of private houses.
The pile foundation can be located:
- under free-standing supports;
- in the form of ribbons, under the walls of a building in one or several rows;
- in the form of bushes, under each of the columns. This placement is used in the case of a frame load-bearing structure.
Drilling support elements
The designs of drilled piles differ in the method of their formation, which provides for:
- Concreting of wells made in various types of soil, located both above the groundwater level without strengthening the walls, and below, with the walls fixed with clay solution or casing pipes.
- Using a prefabricated vibration core to compact concrete circular supports.
- Compaction of crushed stone fed into the face.
- Formation of a cavity in the supporting part obtained by explosion followed by filling with concrete mixture.
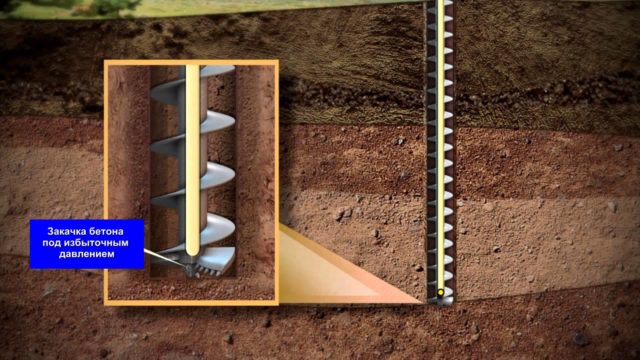
- Injection injection of cement-sand composition or concrete mortar into a pre-drilled cavity with a diameter of 15–25 cm.
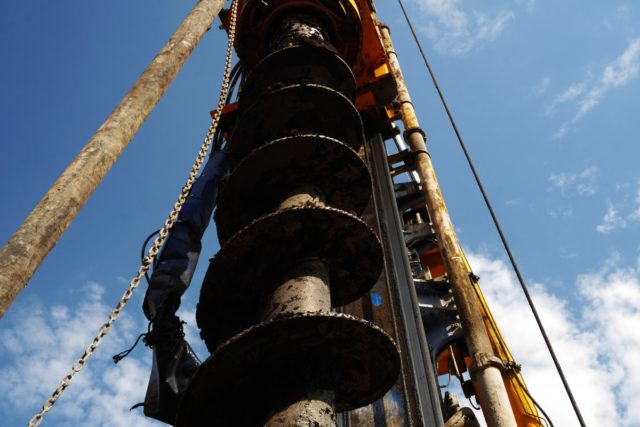

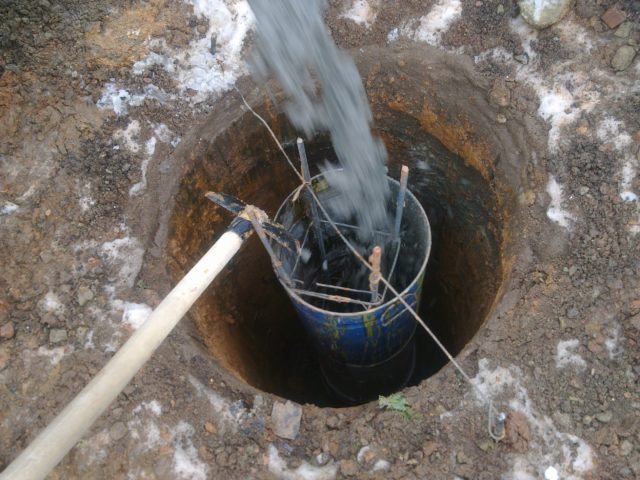
Drilling a well for bored piles
Preparatory activities
According to the provisions of SNiP, before installing bored piles, engineering surveys should be carried out to determine the design forces that the foundation will absorb. Pile foundations are developed based on the results of the following types of surveys carried out at the construction site:
- geological;
- hydrometeorological;
- geodetic.
The features of the construction site, the forces acting on the foundation, and the features of the operation of the structure are also taken into account. Only after this, according to SNiP, is the type of cast-in-place foundation, the dimensions of the supports, and the method of their arrangement determined. The design organization is responsible for the reliability of the survey results.
Drilling and ramming operations are preceded by planning the construction area at a given level. Then marking is carried out and coordinates are fixed in the conditions of the construction site.
The locations of bored supports are documented by a special act containing information on tying piles to elevations.
The exact value of the bearing capacity of a bored pile is calculated using a formula that takes into account several parameters
Pile foundations (SNiP)
Pile foundations must meet the requirements listed in SNiP 2.02.03−85. This document has 13 sections.
- The first section of SNiP “pile foundations” describes what kind of research needs to be carried out to select a foundation design.
- The section contains a list of all kinds of piles, methods of their installation and requirements for the materials from which they will be made.
- The third section of SNiP “pile foundations” provides information on how to correctly make basic calculations ; lists of regulatory documents indicating the design characteristics of materials of piles and pile grillages, soils.
- The fourth section of SNiP “pile foundations” contains all the formulas for calculating the bearing capacity of various piles and provides tables with calculated soil resistances and coefficients necessary for calculations.
- The fifth section of SNiP specifies GOST with requirements for field tests, their required number and rules for calculating the load-bearing capacity of piles based on research results; tables with calculated data.
- The sixth section of SNiP contains instructions for calculating deformations.
- The seventh section of SNiP contains data on which it is necessary to design the foundation.
- The eighth section of SNiP lists the features of designing foundations in areas with subsidence soils.
- The ninth section of SNiP specifies the design features of foundations in swelling soils.
- The tenth section of SNiP contains design features in mined areas.
- The eleventh section of SNiP lists features for seismic areas.
- The twelfth section of SNiP contains information about the features of supports for overhead power lines.
- The thirteenth section of SNiP describes the features for low-rise rural buildings.
When constructing buildings, the first step is laying the foundation. The reliability and strength of the entire future building depends on it. When soil with weak bearing capacity is found on a site, it is advisable to opt for a pile structure.
Influence of climatic factors
According to the recommendations of SNiP, driving piles in wet soils is carried out if the ambient temperature is not colder than -10 degrees Celsius. If the temperature changes below the specified value, it is necessary to carry out a set of measures aimed at protecting the fresh composition from freezing, as well as ensuring the uninterrupted operation of drilling equipment. Special requirements for the implementation of construction activities must be indicated by the design organization of the work in a special project.
Permissible deviations

Unlike others, the installation of piles according to its technology involves some deviations from the design indicators in the horizontal and vertical plane. Gradual screwing in of piles requires constant checking of all levels.
Even if the structure is set up perfectly at the beginning of the process, deviations may occur at any time during immersion. The reason for this may be soil heterogeneity or any other obstacles.
When carrying out work on pile installation, levels should be constantly monitored. It is necessary to take into account the possibility of deviations from the axis and ensure that they do not exceed the tolerances.
Let us present some indicators of permissible deviations when deepening piles. During the installation of rectangular and square rods, hollow and round driven rods with a diameter of less than 50 cm, permissible deviations when positioned in one row are along the axis of the row - 0.3d, across - 0.2d (d is the diameter of a pile with a circular cross-section or the length smaller side of a rectangular rod). For single rods - 5 cm, for columns - 3 cm. If the rods are arranged in several rows, the so-called cluster or tape method, then the permissible deviations are:
- for the extreme ones: along the axis of the row – 0.3d, at the intersection of the row – 0.2d;
- for the rest: along the axis of the row - 0.3d, at the intersection of the row - 0.3d.

Deviations for hollow cores with a diameter of 0.5–0.8 m and bored piles with a diameter exceeding 0.5 meters:
- for strip placement: along the axis of the row – 15 cm, at the intersection of the row – 10 cm;
- for cluster placement: along the axis of the row - 15 cm, at the intersection of the row - 15 cm.
For hollow round rods for columns, the permissible deviations are 8 cm.
The total number of piles with deviations from their number according to the project should not exceed:
- for strip placement - no more than a quarter of all piles used;
- for piles and columns - 5% of all installed piles.
Such deviations are not considered critical and are almost completely eliminated during the installation of the strapping or fastening of the heads. The vertical placement of the rods must be done much more accurately.
Specifics of reinforcement
According to the requirements of building codes and regulations, when constructing pile foundations, it is necessary to ensure their strengthening through reinforcement. For this purpose, strong steel reinforcement is used, united by a single frame by welding.
The spatial structure consists of reinforcement bars located at equal intervals around the perimeter of the circle. If the diameter of the rods is more than 1.8 cm, the frame must include more than six longitudinal rods, the distance between which should not be less than 400 millimeters. It is preferable to use AIII reinforcing steel for longitudinal bars.

Reinforcement of piles is carried out with vertical rods of a periodic profile (diameter 12-14 mm)
Protection of the steel reinforcement frame from the destructive effects of corrosion is achieved by maintaining a protective concrete layer. Ensuring the immobility of the reinforcement frame is ensured by plastic tubes, the dimensions of which are:
- diameter – 9 cm;
- length – 7 cm.
Requirements for the work area
Before starting drilling activities, it is necessary to carry out a set of works aimed at preparing the construction site:
- Install fences in the work area in accordance with the construction master plan.
- Disconnect and move from the event area all communications located above and below the zero mark.
- Free the work site from temporary structures and unnecessary buildings.
- Remove and fold the plant surface of the soil in certain places.
- In accordance with the marks specified in the project, the flatness of the base should be ensured.
- Carry out drainage or dewatering.
- Cover the surface of the site with a crushed stone cushion, on top of which it is necessary to lay slabs.
- The area of the construction zone must allow the placement of a set of technological devices (drilling rig, concrete pump, equipment for delivery and unloading of concrete) and have convenient access roads.

Calculations of pile structures of all types should be made for the impact of loads transmitted to them from a building or structure
Boring activities are carried out after monitoring the coordinates of the prepared site and checking the location of the axes of the supports of the future foundation.
Building codes and regulations require the use of truck-mounted concrete mixers and self-propelled equipment for its transportation. It is allowed to deliver pre-mixed dry components to the work area and add water before starting concreting.
Advantages of pile foundations
Pile structures have the following advantages :
- reliability of design;
- ease of construction work;
- quick installation;
- minimum draft;
- refusal of extensive earthworks;
- Possibility of use on weak and swampy soils;
- possibility of construction on uneven surfaces;
- the ability to perform work at any time of the year.
Disadvantages include :
- complexity of calculations;
- impossibility of application for multi-storey buildings;
- the need for special equipment during installation;
- impossibility of installation in areas of rock deposits and horizontally moving soils;
- lack of basements in buildings;
- low quality when making and installing piles yourself.
Features of the technology
How, according to GOST, are bored supports arranged? What stages does the manufacturing process involve? In general, the implementation of the support involves two main stages:
- directly drilling a cavity in the soil;
- filling the resulting well with concrete mortar with preliminary installation of a reinforcement frame.
There is a feature required by building codes. The well and solution have a limited period of use. Over time, their quality decreases. The cavity and the solution become unsuitable for further work. Therefore, GOST regulates the period between the completion of drilling and concreting, limited to 8 hours.
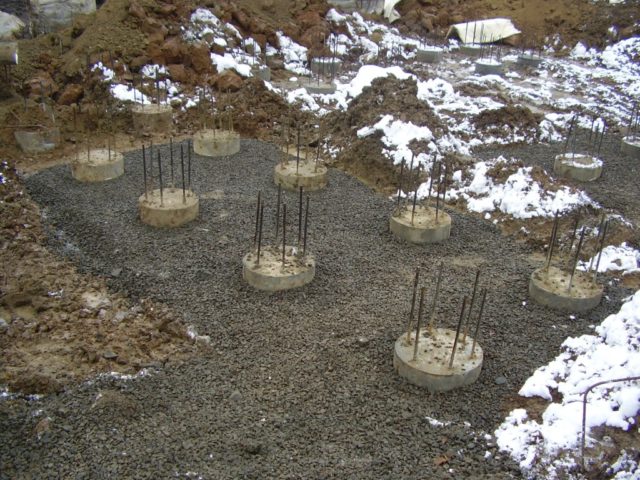

All calculations of piles, pile foundations and their foundations should be performed using the calculated values of the characteristics of materials and soils
The supporting structures are pre-drilled, according to the design, wells with installed reinforcement cage. Before pouring the concrete solution, the cavity is compacted, sealed with a clay solution, which prevents soil collapses, and then the volume is filled with a concrete composition. It is possible to use casing pipes or pour concrete directly into the well.
The manufacture and installation of supports are carried out according to the algorithm provided by the standards:
- First, the impact rig or drilling machine is installed at the drilling point.
- Drilling activities are carried out to form a well with certain dimensions (diameter, depth). Expansion at the bottom of the base of the structure allows you to increase the load-bearing capacity of the future support.
- A clay solution is introduced, which hydrostatically acts on the walls and prevents spalling of the well surface.
- Drilling products are carried away by the fluid flow and are removed to the zero level.
- Using lifting equipment, a reinforcement frame is placed into the prepared well, which can be placed along the entire height of the pile or at the surface. It all depends on the effort provided by the project.
- The reinforcement frame is fixed with non-metallic stops, providing a protective layer.
- The cavity is filled with concrete solution delivered by a concrete mixer truck. The concreting process, according to SNiP, should not exceed three hours.
- A special installation removes casing elements.
- The drilling and crane equipment is moved to the next point of work in accordance with the diagram given in the standard.
What errors can occur when installing piles?
When installing piles yourself, serious errors can occur. To prevent this, you should figure out where problems may arise.
- The first thing you need to pay attention to is the incorrect location. It is necessary that the installation occurs specifically along the intended line of the foundation layout. That is, the piles may not be located in a straight line, but deviated to the left or right of the axis. Incorrect placement can lead to uneven load distribution and further subsidence or distortion of the building.
- The next error is the deviation of the vertical position of the mounted structure. If the rod tilts even at a small angle relative to the vertical axis, then this is a serious violation. It is impossible to correct such an error with further immersion. The vertical position of the structure must be constantly monitored, starting from the first stage and up to the stop point.

The permissible vertical deviation of the pile is up to 2 degrees. Otherwise, a placement error will lead to instability of the structure, which will cause a loss of its rigidity.
- Mistakes are often made when leveling the rods horizontally. Some, making their work easier, level the horizontal by twisting the pillars. The correct way to do this is to cut off the excess length using a grinder. When the pile is unscrewed, the degree of rigidity is lost. This is fraught with subsidence of the structure, instability and instability.
- If the pillars are not immersed to the required depth, then this also entails a grave mistake. A correctly installed pile is when its base rests on high-density soil. This is what provides the structure with high rigidity and increases its load-bearing capacity.
The pile should be screwed in to a depth equal to the freezing depth of the soil plus 10–20 cm. On clay and peaty soils, until it completely rests on solid layers of soil.
- The next mistake is failure to concrete the pillars. In this case, moisture will accumulate in its cavity, which will lead to rust and destruction of the structure.
- Placing piles in relation to each other at a distance of more than three meters is also a gross mistake.