The construction of any object begins with the foundation. Modern contractors use different techniques in the construction of houses, shopping centers, domestic buildings, and industrial facilities. Depending on the purpose of the building, the location of the building’s construction, the reliability and durability of the entire structure, a pile or strip foundation is chosen. Each installation technology can be better in different respects. It all depends on the characteristics of the soil, the purpose of the structure, the timing of construction and other important characteristics taken into account during the construction of the facility.
Foundation on stilts
This design resembles a lattice installed on poles. The pillars are placed under all the main points of the building and connected by a grillage. The main attention is paid to places with high loads and corners. The foundation of small buildings reproduces the design of the building; for large structures a solid base is chosen.
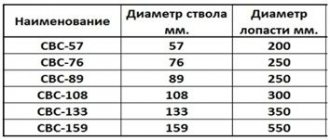
The supports can be wooden, metal, concrete or reinforced concrete. The steel element is made in the form of a cast pipe. Blades are attached to the screw type, with the help of which the element is screwed into the soil.
When purchasing poles, it is necessary to inspect the welding points. The joint must be covered with bitumen mastic or other anti-corrosion agents.
A reinforced concrete slab or strip or metal beam is used as a grillage. When installing a log house, the grillage is the lower crown. It is laid on mounting platforms welded to the piles.
Foundation construction method
Depending on the type of material, piles are screwed, inserted or driven into the ground. In the latter case, elements with a blunt end and a sharp tip are used. A special technique is used to drive in the posts.
For a bored foundation, wells are constructed into which hollow pillars are installed. After reinforcement, the base is poured with concrete. Small holes are prepared for screw supports, into which they are screwed perpendicularly with a drill or a special tool. After installation, they are leveled horizontally and strapped.
Features, advantages and disadvantages of foundations on piles

In fact, each pile is an unusual structure with blades, with the help of which it is screwed into the soil layer to a pre-calculated depth. Screw piles are cast or consist of steel elements firmly welded together. The undoubted advantage of the pile structure is that it has a high load-bearing capacity and can cope with heavy loads.
The best option for using screw piles is in places where the soil is problematic. In other words, a pile foundation is suitable for clayey, loamy, peat and swampy soils, as well as for areas where there is a significant difference in height. The cost of pile foundations is affordable, and installation of structures is carried out in the shortest possible time.
The disadvantages include such indicators as the lack of a basement, the impossibility of laying various technical communications.
Pros and cons of a pile foundation
The main value of this type of foundation is its high strength. The wall thickness is 4-6.5 mm.
The advantages include:
Pile foundation.
- Economical. Construction of a pile field will cost 30% less than a foundation strip.
- Resilience to climate change. This means that the installation of supports can be done in any season. In winter, to drill holes, the top layer of soil is heated.
- Long service life - up to 200 years.
- Possibility of erecting structures on slopes and uneven areas. On difficult terrain with a slope of more than 15°, jibs, spacers, and ties are additionally used.
- Suitability of the foundation for the construction of buildings in a swamp or on loamy, clay and peat types of soil.
- Small amount of excavation work.
- High installation speed.
The disadvantage of a pile foundation is its susceptibility to corrosion. When installing low-quality products, it will be difficult to count on the strength of the structure. Also, due to the nature of the piles, it cannot be used on rocky soils.
The technology for constructing such a foundation limits the possibility of arranging a basement or ground floor. More funds will be required to insulate the free space under the floor. At the same time, there are projects of pile fields for the construction of underground garages.
Advantages of screw piles
A foundation on a screw base is erected on complex mixed soils that are susceptible to swelling. In this case, the piles are screwed in to a sufficiently large depth, which cannot be done with columnar elements. Piles perfectly withstand the presence of reservoirs, underground sources, excessive soil moisture and mixed rocks. Elements are placed at a distance not exceeding 1000 - 3000 mm. The frequency of screwing depends on the future load on the foundation.
Piles are easy to use, but are not used for all large-sized buildings with heavy loads. Unlike a columnar foundation, screw piles are installed at any time of the year, and the premises are put into operation regardless of the season. The structure, built on a columnar foundation, is put into operation in the same season in which it was built. After construction, the pillars must settle, unlike a pile foundation, which is ready for further construction immediately after installation.
Piles will not distort the building regardless of temperature changes, soil freezing, increased humidity and other negative environmental influences. The same cannot be said about the columnar base. Elements will begin to wear out, some may crack, restoration will be needed, and this is an additional investment.
Strip foundation type
The strip foundation looks like a solid reinforced concrete structure laid along the entire perimeter of the future building. Due to its high strength, it is used in the construction of both wooden and monolithic structures. The base consists of a hardened mass of reinforced concrete or building blocks fastened together. When building a bathhouse or shed on dry soils, it is possible to construct a belt of ceramic bricks.
Method of constructing a strip foundation
Laying the foundation is preceded by a large amount of excavation work. First, a trench with a width of 0.4 m is dug along the contour of the building. The choice of pit size is influenced by the nature of the soil and the calculation of the expected load.
There are several options for this design, among which the most common are:
- Recessed strip foundation. It is installed below the soil freezing level and is used on heaving soils, as well as in the construction of concrete and brickwork.
- Non-buried base. The design is used for SIP panels and panel buildings.
- Shallow tape intended for log houses and frame houses. This foundation is placed at a depth of 0.4 -0.7 m. To protect against groundwater, drainage geotextiles are laid in the trench and a sand-crushed stone “cushion” is filled in. The density of each layer is at least 20 cm. If necessary, install a leveling screed.
Construction of a strip foundation.
Then waterproofing materials and insulation are laid. External waterproofing with an overlap on the walls is used depending on the construction conditions. To compensate for heaving forces, extruded polystyrene foam is placed under the tape.
At the final stage, the formwork is installed, the reinforcing belt is installed and the concrete solution is poured. The last procedure must be performed at once. Otherwise, joint seams will form on the surface, which reduce the strength of the base.
Which is better: concrete strip foundation or screw piles?
Its service life depends on the quality of the foundation. Thus, in accordance with GOST 27751-2014 “Reliability of building structures and foundations. Basic provisions" for buildings and structures of mass construction under normal operating conditions, this period is at least 50 years.
In order for a concrete structure to operate without any complaints throughout the entire specified period, as we said above, the concrete mixture must be of high quality, the quantity and diameter of the reinforcement must correspond to the design, and some other quality characteristics must also be met:
- operating conditions are taken into account (operation of the building/structure in conditions corresponding to the design ones);
- the properties of the materials used and possible means of protecting them from negative environmental influences are taken into account (the level of humidity inside the building does not change, the waterproofing is properly installed);
- the estimated environmental influence is taken into account.
At the same time, the service life of 1 mm of carbon steel (St20) without coating in sandy loams and loams, which are most often found in Russia, is at least 40 years (more information about different grades of steel in the article “Use of various grades of steel in the production of screw piles” ). That is, provided that the residual metal thickness of 2.5 mm is maintained, a pile with a shaft wall thickness of 4 mm will retain its load-bearing capacity for the entire period provided for by GOST. And with a shaft wall thickness of 6 mm or more, the service life of a foundation on screw piles will be comparable to the service life of a concrete foundation made in accordance with all technological requirements (more details: “Calculation of the wall thickness of a screw pile shaft”).
Selection of the optimal thickness of the shaft wall and pile blade for a specific object is possible only on the basis of data on the corrosive aggressiveness of the soil at the construction site. The diameter of the trunk is selected individually (including on the basis of data on corrosion aggressiveness), which, albeit to a lesser extent, still affects the service life (more details “Express geology: geotechnical and geological-lithological studies and measurements of the corrosive aggressiveness of soils” ).
To clarify the calculation of the service life of screw piles, it is recommended to check the residual thickness of the shaft wall for compliance with the design loads.
In aggressive soil conditions (ash, slag), which, although rare, still occur, the service life of 1 mm carbon steel (St20) without coating will be reduced to 20 years. However, even in this case, screw piles will comply with GOST standards in terms of durability, especially if you use thick-walled rolled metal.
It is worth mentioning that some companies recommend galvanized piles as a solution for such soil conditions, which is completely wrong. In accordance with the formula derived by the American Steel and Alloy Institute (AISI), the service life of an 85 micron thick zinc coating, even under the most favorable conditions, does not exceed 15 years. A highly aggressive environment dramatically increases the rate of corrosion of zinc, which prohibits its use (clause 9.2.8. SP “Protection of building structures from corrosion”).
Pros and cons of strip foundations
Among its advantages:
- resistance to the negative effects of groundwater;
- versatility;
- reliability;
- availability of self-installation;
- long service life;
- Possibility of arrangement of the ground floor or basement.
The disadvantages include:
- Large financial expenses. Premises under a common roof have different shrinkage, which can lead to the destruction of floors and roofs. The construction of additional walls with expansion joints can prevent the appearance of cracks. This type of foundation is economically beneficial only on rocky soils and if it is necessary to arrange an underground floor.
- Labor intensity of work.
- The need for dismantling during repairs.
- Limited use on weak and uneven soils. The monolithic option is suitable for all types of soil except peat bogs. The prefabricated tape should not be used for installation on slopes or in wet or heaving-prone areas.
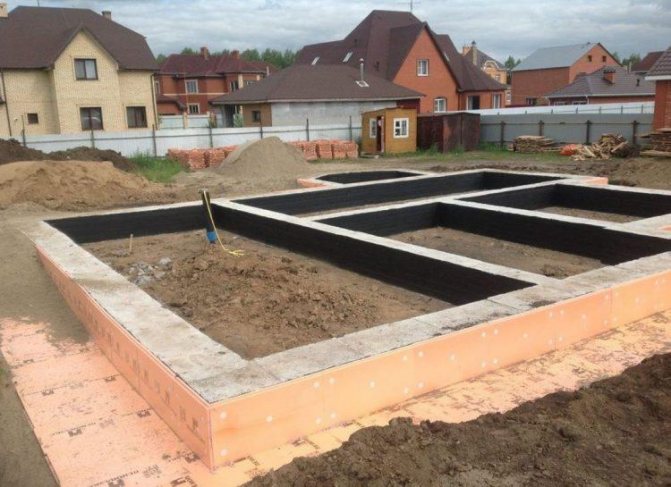

Strip foundation.
Columnar foundation
A columnar foundation can be built from a wide variety of building materials, for example, from natural stone or brick, and a wooden house made of profiled timber or frame-panel will stand perfectly on such a support, but only if the characteristics of the soil do not cause even minimal concerns.
The pillars are erected at the corners, where the walls intersect, under the frame posts (at points where loads are concentrated). It is advisable to make the distance between the pillars a multiple of the pitch of the bottom frame beams, usually 1.5-2.5 m; the minimum cross-section of brick pillars or concrete blocks is 500x500 mm (for lightweight houses, a smaller cross-section is possible). The walls, together with the thermal insulation material, should not exceed a thickness of 250 mm, and the ceilings, with the exception of the basement, should be wooden. The pillars are placed strictly vertically, and concrete beams are installed on top of them (support for masonry walls). On such a foundation it is possible to build houses from cellular concrete.
A fence is placed between the pillars - a light wall that insulates the subfloor, protecting it from snow and moisture. Its surface throughout the entire house must be uniform in shape and texture. It is made mainly of brick or concrete, with a minimum wall thickness of 10-12 cm and a depth of 200-300 mm into the ground. In the case of heaving soil, the pick-up is placed on a sand cushion 150-200 mm thick and at least 300 mm wide. There are also decorative fences made from antiseptic-treated boards or asbestos-cement sheets. Base panels that imitate natural stone masonry are also used.
Columnar foundation without grillage
It is rightfully considered the most economical and simple type of foundation. It is erected in the form of pillars and is used in the construction of buildings that do not require continuous strip support (frame houses, wooden log houses, etc.).
The option when the bottom mark of a columnar foundation can be located below the standard freezing depth is reliable; the forces of frost heaving will not affect the base of the foundation. The shallow-depth version, if constructed correctly, is no less durable, not as expensive and is used more often.
If the soil contains clay, then under each pillar, up to the full freezing depth, with a downward margin of 20 cm, replace it with a mixture of clean coarse sand with crushed stone or gravel. The sand bedding is watered generously and compacted.
The heavier the house, the more powerful the pillars should be and the spacing should be more frequent, but not less than 1.5 m from one another (usually irrational, material consumption is high), and the value should not exceed 3 m. On average, the spacing of pillars should be 2 m The cross-section of the pillars depends on the material and production technology.

It is convenient to use ready-made pipes as permanent formwork when constructing foundation pillars. The best, but also more expensive option is metal and asbestos-cement pipes. If the budget allocated for the construction of a house does not allow you to use plastic sewer pipes with a diameter of 150, 200 and partly 250 mm as formwork, you can build a small cottage or a commercial building on them. It is not recommended to use pipes of a larger cross-section; it is better to pour square pillars in formwork made of wooden boards.
When constructing outbuildings, roofing felt is often used as formwork by rolling up a roll of several layers, installing it in a hole and pouring concrete into a roofing felt “straw”. In this case, we only advise filling it with concrete in layers, while simultaneously filling the cavity in the ground at the same level so that the roofing material does not tear.
It is possible to cast pillars in removable formwork. Their cross-section should be at least 20x20 cm, taking into account high-quality compaction of concrete and high quality of the mixture. Under a residential building, it is advisable to make pillars with a cross-section of at least 25x25 cm. The solution can be mixed in the proportion of cement/sand/crushed stone (9 or gravel) 1/3/5. The cement must be unexpired, grade 500 or at least 400, and not contain lime. Concrete must be compacted when pouring. The formwork is removed no earlier than 3 weeks after completion of the work.
There is an option for a columnar foundation made of rubble concrete in formwork. But it is very difficult to reinforce it with high quality, and because of this its strength is not high. Therefore, the cross-section of the pillars must be at least 50x50 cm.
Reliable brick foundation pillars (with a cross-section of 1.5 bricks) can only be made from suitable high-quality, well-fired brick, but this option is expensive.
Columnar foundation with grillage
A grillage is a load-bearing reinforced concrete beam that connects pillars from above; it is used in the construction of buildings made of stone and brick, when there is a need to support heavy walls along their entire length. The pillars are erected using the same technologies as in the construction of light houses, but their cross-section is larger and their pitch is more frequent.
The grillage can be concrete or made from factory elements installed on poles. It must be reinforced, the diameter of the horizontal load-bearing rods must be at least 12 mm, cross braces are placed every 40 cm. If the distance between the pillars and the load from the walls increases, then the frame must be more powerful.
The grillage should not rest on or be buried in the ground - in winter, the soil rising under the influence of frost heaving forces should be able to move freely vertically. If this is not the case, then the grillage may tear away from the pillars, which will lead to deformation of the foundation.
Which foundation is better, pile or strip?
- If you do not have sufficient knowledge, you can buy low quality piles. And this will lead to the fact that it is not worth talking about the durability of the constructed foundation. After all, metal can rust and reinforced concrete can crumble. This can lead to tragic consequences.
- Pile foundations cannot be used on rocky soil. The blades may break, and it will be quite difficult to achieve the desired depth. As a result, a shallow, unstable foundation is unsuitable for construction.
- It is impossible to build a basement under the building. The same goes for the garage.
- High labor costs to insulate the free space under the floor and decorate it.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Sauna in a private house with your own hands
If you believe the reviews, most people are satisfied with the quality of this type of foundation.
Distinctive soil features that must be taken into account
- Rocky and stony soils serve as an excellent site for construction, because water cannot wash them away, and they are also not afraid of frost.
- Clayey. There are three types of these soils: clay, loam and sandy loam. All three are a rather poor choice of location for construction, because they are highly susceptible to deformation and exposure to water, and have low density.
- Sandy. They allow liquids to pass through well, that is, water does not stagnate and does not threaten the building; they can be compacted and thus increase density. They are divided into the following types: gravelly, medium sand and fine silty sand.
- Organic. Perhaps the greatest number of problems arise with them; they are greatly deformed, sag, and have a loose consistency.
Types of soil deformations:
- Draft. It can occur immediately or over a long period of time due to the weight of the structure affecting the ground.
- Drawdown. Similar to the previous type, but can occur not only due to the weight of the house, but also due to groundwater.
- Uneven deformation. The most problematic type of soil movement, most often the cause is poor compaction of the soil.
- Ground movements. This is the swelling or compression of the soil, resulting in horizontal and vertical displacements of the soil.