To determine what foundation depth for a two-story house will be considered optimal, you need to take into account many factors and make the correct calculation. When building any house or structure, the only indisputable thing is that a foundation is required. This is a foundation whose strength and durability guarantees the safe operation of a two-story building for many years.
What affects the depth of the foundation?
Determining the depth of the foundation approximately or “by eye” is unacceptable even for the simplest structure. Competent and accurate calculations are required, based on the characteristics of the building itself and the environment. To do this, the following must be taken into account:
1- level of soil freezing;
2- soil quality and depth of its layers;
3- location of groundwater;
4- the presence under the foundation of a cushion of sand and gravel 10-30 cm thick (this value must be taken into account when digging a trench);
5- design features of the house (presence of a basement, ground floor);
6 - total load on the foundation;
7- weather and other external conditions;
8 - selected foundation type;
9- budget allocated for the construction of underground structures.
The level of freezing varies in different regions. So, in warm climates, a depth of 0.6 m will be sufficient, but in areas with harsher winters, the foundation will have to be deepened by at least 1.5 m.
Determination of basic soil parameters
The main soil parameters on which the depth of the foundation depends include the type of soil, the level of freezing and groundwater flow, and the terrain.
Determining the soil type
To calculate the depth, you need to find out what type of soil is located under the future house. Soils are:
- heaving (clayey, loamy)
- slightly heaving (mixed)
- non-heaving (rocks, sand).
To find out the type of soil, you need to provide a sample of it to specialists. Based on the result obtained, initial calculations can be made. The most reliable are non-heaving soils, since they can withstand any load. The optimal foundation depth for a one-story house on such soils is 0.5-1 m. On mixed soils, it is recommended to deepen the foundation by 0.8-1.3 m, on heaving soils - by 1.3-1.8 m.
Determination of groundwater and freezing level
To find out the groundwater level, you can also contact the relevant specialists or determine it yourself by digging special wells - pits - at the site of the future house.

They need to be deepened by 2-2.5 meters, which makes it possible to establish both the presence of groundwater and the depth of soil freezing.
Taking into account the terrain
In addition to the specified soil parameters, it is also necessary to take into account the terrain. The easiest way to lay the foundation is on a flat surface. And the area with a slope must be leveled as much as possible or left as it is, but the calculation of the depth should be carried out from the lowest point.
Based on the results of the soil study, the appropriate type of future foundation is selected.
Rules for choosing a foundation for the construction of a building made of timber
The material from which the building will be constructed is not the only criterion that influences the type of its foundation. When deciding the issue of choosing a foundation, a number of other criteria are taken into account.
Criterion No. 1: soil type
The calculation of a reliable and durable foundation is based on the soil characteristics at the construction site:
- its type;
- location of groundwater (GW);
- freezing depth.
The best way to determine the type of soil is geotechnical exploration. If you neglect this and make an assessment by eye, a mistake in choosing a foundation is possible. An unstable foundation will lead to deformation of the foundation, and then the building erected on it.
Clay soil consists of particles that resemble scales. Between them are capillaries. Through them, moisture easily seeps into the clay and quickly evaporates. In the first case, the soil becomes viscous; when it freezes, it increases in volume, and heaving may occur.
Dry clay can withstand heavy loads better, but when wet it loses its load-bearing capacity. In order for a foundation based on such soil to become a reliable support for the building, it must be laid below the freezing depth. In general, clay is far from the best option for laying a foundation.
Loam has a slightly better load-bearing capacity. It contains from 10 to 30% clay. Soils that are approximately half sand are classified as sandy. Loose non-plastic sand is not an obstacle to water. It almost does not freeze, which means that heaving processes do not occur in it. If moistened layers of sand are well compacted, they can better withstand quite high loads. The larger and cleaner the sand, the greater the loads it can be subjected to. If you have to build on such soil, any foundation will do.
Each type of soil has its own specific load resistance parameters. They are key when calculating the foundation.
Criterion No. 2: groundwater
Water, both groundwater and surface water, also have a great influence on the strength of the foundation of timber buildings. Water horizons that lie deep and do not come close to the surface pose no danger to the foundation of a house. If the water is close to the surface of the earth, the best option is a pile-screw foundation.
You can determine the depth of groundwater yourself if there are wells in neighboring areas. Geological surveys of the site provide a more accurate result.
Criterion No. 3: terrain of the site

If the site is flat, without any differences, there are no restrictions on the choice of foundation. If a building is built from timber on a slope or on a construction site with differences, the best foundation is a pile foundation. The piles will be of different heights in order to better level the base.
Criterion No. 4: freezing depth
The best foundation is considered to be one whose base is below the freezing depth mark. Taking into account the fact that a timber house is relatively light, we can accept such an option as a shallow foundation. If the level of hot water is high, the loads created by heaving forces are reduced by installing drainage under the base.
Foundation options for a one-story house
One-story houses are erected on a strip, slab or column-pile foundation. Columnar and shallow strip foundations are suitable for the lightest buildings. On heaving soils, slab and pile foundations are preferable.
1. Strip foundations
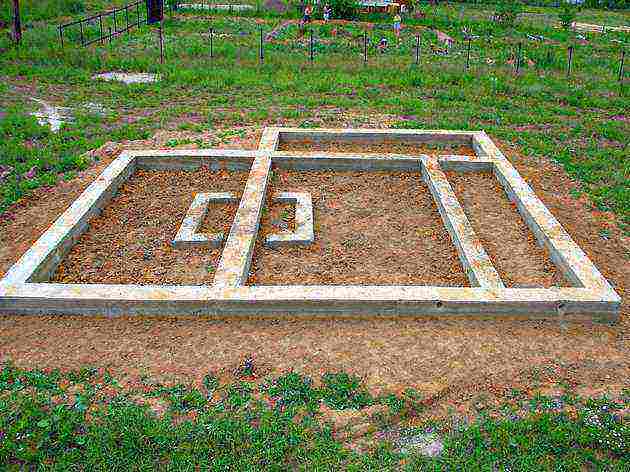

There are two types of such foundation:
- shallow - the maximum depth of the foundation for a one-story house is 60 cm. This means a floating foundation, subject to heaving phenomena in the soil, which is located under the base of the foundation. This solution is not suitable for massive buildings with heavy weight;
- recessed - made in the form of a monolithic reinforced concrete strip laid below the freezing level of the soil. This option is used for houses with heavy structures.
2. Column-pile foundations

The simplest columnar foundations are usually used only for very light buildings. More massive buildings require the installation of bored or screw pile foundations.
3. Monolithic slabs

This option is suitable for most cases and involves laying a monolithic slab with pouring into a pit or even without penetration into the ground. The main disadvantage of such a foundation is its very high cost.
Slab or monolithic
This is a monolithic product, constructed in the form of a reinforced concrete solid structure over the entire area occupied by the building. Its main application is the construction of houses on heaving soils, including those with a heterogeneous structure, marshy soils, and quicksand. In these cases, the option of a shallow or non-buried foundation is used. The latter is laid directly on the soil layer. This option is called a “floating slab”.
It is an almost ideal option for houses of medium mass, such as two-story brick houses and houses made of expanded clay concrete. It is especially suitable for lighter houses made of wood, foam concrete and related materials, as well as for frame-type houses. The recessed version of the slab foundation is used in the construction of houses with a ground floor (with a basement). In this case, the slab serves as the floor of the lower level of the house.
A slab foundation is the most expensive of all types of foundations. But its cost is justified by its high reliability and preservation of the integrity of the house’s structural elements. As the condition of the soil changes under the influence of seasonal temperature changes, the slab, which has great rigidity, rises and falls evenly without deflection or bulging.
The height of the foundation, when using the slab option, for a two-story house is taken to be no more than 40 cm. This is enough to build a house from any material.
Recommendations for calculating foundation depth
After the final determination of the soil parameters and type of foundation, a final calculation is performed, based on the results of which the optimal foundation depth for a one-story house is established.
This calculation is strictly individual, but its implementation requires compliance with the following recommendations:
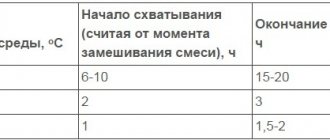
- Any foundation should be laid 10% below the soil freezing level. So, when the soil freezes to 100 cm, the trench should have a depth of 110 cm.
- On loose soils in a temperate climate zone, it would be most advisable to lay a shallow strip foundation (monolithic with poured mortar or prefabricated with ready-made blocks). On average, such a base has a depth of 45 - 100 cm.
- For mixed, slightly heaving soil in harsher winter latitudes, a foundation deepened by 1-2 meters is more suitable.
- For a one-story brick house, the best option would be a recessed strip foundation with reinforcing pillars.
- In clayey or swampy areas, even under a house with a lightweight structure, it is necessary to lay a monolithic slab foundation with piles. The depth of such a foundation can reach 2.5 meters.
Many developers prefer to solve various construction problems, guided by the “in reserve” principle. In other words, if, in accordance with all calculations, the sufficient depth of the foundation for a one-story house is 1 m, in reality, to prevent possible problems, a trench of 1.5 m is dug. Such a precaution only entails unnecessary costs.
In most regions, weather and all other natural conditions have not changed for thousands of years. Therefore, no unforeseen changes will happen in this regard. Therefore, even small deviations from established standards will be completely unjustified. If the calculation is done correctly, no “reserves” are required.
The main rule for determining the parameters of the foundation is the following: the more competently the foundation is built, the less the house will be exposed to negative factors.
The foundation is the foundation on which, like earth on three pillars (according to authoritative ancient scientists), your future home will stand. Although the cost of pouring it sometimes makes up the majority of construction costs, no specialist will advise you to save on it. This can not only cause subsidence of a one-story or two-story house made of timber, changing its correct geometry, but also poses a potential danger to the well-being of all residents. Therefore, the depth of the foundation for a two-story house made of timber, its type, and the time for hardening are issues that require consultation with a professional and accurate calculations.
Despite the fact that the structure of a log house is considered light, it still has a significant weight, under the influence of which a foundation built without preliminary calculations can crumble and become unusable. The depth and type of foundation is influenced by the number of storeys of the building, its area, and the thickness of the timber used, because all these factors affect the total weight of the house. Not the least role in choosing the type of foundation is played by the type of soil, the height of the groundwater table, and the nature of soil freezing. It’s better to have a load-bearing capacity built into the foundation, to put it simply, with a reserve. After all, if you are planning a reconstruction or adding a second floor, you cannot do without this reserve.
Only after the projects of houses and cottages made of timber have been approved can it be determined what type of foundation to choose for the house, as well as to what depth it should be poured. There are several common options in such situations:
- Tape. The most popular currently for the construction of log houses. To fill it, a trench is first dug around the perimeter of the building, and formwork is built on top of it. The depth, depending on the weight and size of the house, can range from 50 centimeters to 1.5-2 meters, the thickness is one and a half times the thickness of the walls. For pouring, concrete is used, additionally strengthened by reinforcement. Such a foundation will take from a week to two months to acquire hardness.
- Columnar. This is a more budget option, suitable only for lightweight structures: bathhouses, small prefabricated one-story houses made of timber, gazebos and terraces. Wells are drilled around the perimeter and inside, and formwork is built around them on the ground surface. Concrete of a grade suitable for weather conditions is poured, and the pole is additionally strengthened with reinforcement. Such a foundation is buried 50-100 centimeters. By reducing the cost of purchasing materials and paying for work, the price of such a base is significantly lower.
Laying the foundation can begin in early spring, after preparing the site and purchasing all building materials involved in construction. After it hardens, after about a month, without delay, it is necessary to begin assembling the log house and complete the installation before the end of the season. Since a foundation left without load over the winter can become deformed and begin to crumble. Take care of a reliable foundation for your country house made of profiled timber or logs for its durability and safety!
“What type of foundation should I choose when building a one-story house?” - a question that concerns many people who decide to build a house on a country plot with their own hands. The foundation of a house is perhaps its most important part, on which the future of the building, its reliability and ease of living depend. As with a number of other construction issues, the foundation for a one-story house is selected based on the design of the house, the materials from which it will be built, the economic feasibility and financial capabilities of the developer. In this article we will give examples of grounds that are currently very popular. All you have to do is decide which type of foundation is right for your situation.
Foundations used for the construction of two-story buildings and their laying depth

There are three base options suitable for a two-story building:
- Tape base;
- Pile construction;
- Slab base.
The tape is a closed reinforced concrete structure that runs along the perimeter of the building and under all the walls. A strip foundation is used for a two-story house made of foam blocks, gas blocks, wood, brick or thin-walled slabs. The strip base is intended for construction on stable and slightly heaving soils.
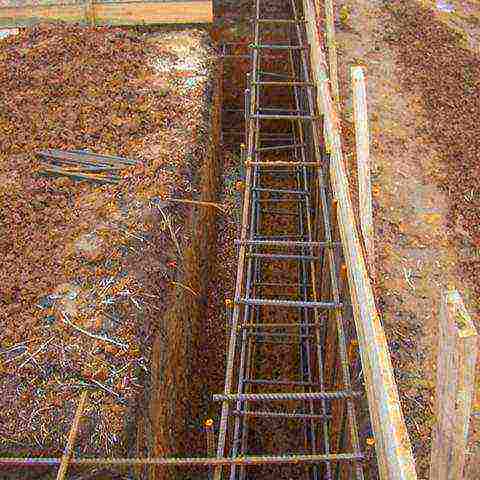

The optimal depth to which such a foundation should be laid is determined based on the type of structure being built. Two-story houses are considered low-rise buildings, so for a house made of non-massive material (wood, light blocks, SIP panels) a shallow foundation can be used. For buildings made of heavy materials, it is better to choose a recessed option: the depth of the foundation for a two-story house made of brick or stone should be equal to the freezing depth, plus 30-40 cm.
A foundation on piles consists of supports buried in the ground around the perimeter of the house and under its load-bearing walls. Most often, the piles are connected by a grillage - a closed loop running along the boundaries of the building. Piles are ideal for areas where unstable soils predominate; in addition, thanks to such supports, it is possible to build a building on a slope.
There are many types of supports, each of which is suitable for a specific application. At the same time, it is better to make pile foundations for buildings made of light materials. When piles are installed, the depth of the foundation for a two-story house (made of timber, foam blocks or gas blocks) should reach 8 m.
The slab base is a solid reinforced concrete platform, which is located under the entire area of the building. This type of base was created specifically for installation on difficult soils: heaving, heterogeneous, quicksand and peat bogs. A slab is one of the best solutions for the construction of medium-weight houses, which are considered buildings with two floors.
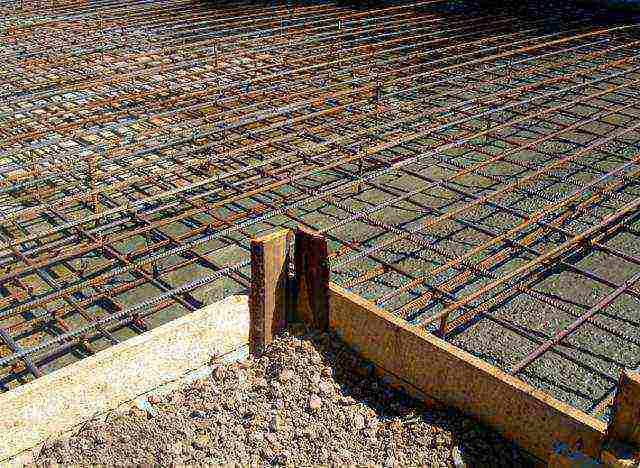

It is possible to use a slab foundation for a two-story house made of foam blocks, wood or SIP panels, but such a solution can hardly be called advisable. The monolithic base was created for laying under more massive buildings. Other foundation options may be suitable for buildings made of lightweight materials. In addition, the installation of a reinforced concrete platform is quite expensive. But if a house is being built from heavy material, there is no need to save.
Considering that the mass of a two-story building for a slab foundation is insignificant, then, for example, when laying a foundation for a two-story brick house, its depth can be only 40-50 cm.
Video depth of foundation for a house:
Criterias of choice
In each individual case, there may be several ways to resolve the issue of building a foundation. Decisive roles belong to:
- groundwater level, i.e. the depth at which the first signs of aquifers appear. The lower this value, the more restrictions are placed on the use of simple and accessible solutions;
- the state of the soil, the depth of occurrence of individual soil layers: heaving - clay, loam, sandy loam, as well as weak and non-heaving - rocks, sand, etc.;
- design features of the house, including the need to build a basement and ground floor;
- the total load from the house, which depends on the materials used;
- the budget allocated for the “zero cycle”, which implies the construction of underground structures. It goes without saying that most of us will give preference to the most affordable option that combines all the required parameters of the future home
Pile
This is an analogue of a columnar foundation, in which piles are used instead of pillars, transferring the load from the house to the load-bearing soil. Depending on the type of piles, there are various options for such a foundation. In individual housing construction, when constructing houses from lightweight materials, bored piles are most often used. For a two-story house made of foam blocks, the optimal foundation will be bored piles with a monolithic grillage. It is not difficult to make it yourself, without resorting to the involvement of highly paid specialists and heavy construction equipment.
Foundation options for one-story buildings
The construction of one-story residential buildings is carried out on strip, slab and column-pile foundations. The lightest buildings, for example, houses made of timber, are erected on columnar and shallow strip foundations. For the most part, they are convenient to use when constructing a foundation for an extension to a house. In difficult conditions, when the soil leaves much to be desired (heaving, high groundwater level, etc.), preference is given to slab and pile foundation types.
Tape bases
There are two types of strip monolithic foundations:
- MZF is shallow, the depth of which for a one-story house does not exceed 600 mm. In essence, we are talking about a floating foundation, which is subject to heaving phenomena from the soil lying under the base of the foundation. That is why this solution is usually used for non-massive wooden houses;
- a monolithic reinforced concrete strip buried deeper than the soil freezing depth (SFG). This option is suitable for heavy buildings, for example, as a foundation for a house made of gas silicate or brick
We recommend reading additional materials on strip foundations, which you can find here and here.
Columnar and pile foundations
If columnar foundations were known long before our time, then pile foundations, including pile screw foundations, appeared relatively recently. And with the development of TISE technology and similar methods for constructing pile foundations, the popularity of bored foundations has increased.
As a rule, the simplest columnar foundations are relevant only for very light buildings, for example, for frame garden houses. More serious buildings require other solutions: the use of bored or screw piles, which you can install with your own hands.
In the article “Bored foundations” you will find the information you are interested in on the construction of these types of foundations. If you plan to build a relatively light garden house, then it is quite possible that you will find the article on columnar foundations useful, which can be found here.
Monolithic slabs
A win-win option in most cases involves the construction of a monolithic slab, which can be poured either in a pit, or without even going deep into the ground. The weak point of such a foundation is its high cost. In the article “Slab Foundation” you can familiarize yourself with the main features of the construction of this type of foundation.
The underground foundation of a building is the most significant and important structural element. The service life of the building, its thermal insulation characteristics, the level of indoor humidity and a healthy atmosphere depend on how correctly the calculations were made and how carefully the technologies were followed when laying the foundation.
Despite the apparent simplicity of the issue, the foundation for a one-story house must be carried out in strict accordance with design calculations and the use of design materials.
Why is it important to consider the foundation depth?
The construction of one-story buildings by many non-specialists is carried out without calculating the foundation depth and height using generalized tabular values taken from SP 22.13330.2011.
Many people use them to construct a frame building, believing that since it has minimal weight, many influencing factors can be neglected.
For most cases, this is quite reasonable, and the selected parameters are quite sufficient to ensure the required level of strength and reliability. However, quite often many factors are not taken into account, which in a particular situation can play a negative role. An example would be the laying of a buried strip or slab foundation in soil with minimal bearing capacity (sandy loam or alumina), where the total mass of the structure is critical.
As a result, approximately 25-40% of financial resources from the total cost of the object will be spent on construction, which will not be justified.
Exceeding or reducing the safety factor relative to its optimal value can have significant disadvantages that will reduce the service life of a one-story house, especially a brick one. Therefore, it is important to correctly calculate the backfill depth based on SP 22.13330.2011.
Factors affecting burial depth
The depth of placement depends on the type of soil, the mass of the structure
To determine how deep the foundation should be, it is necessary to study the operating conditions of the future structure. Calculation of the technical characteristics of the base is made after:
- work was carried out to study the soil at the construction site;
- the landscape has been studied or a construction spot has been cleared;
- a building plan has been drawn up, defining the area, weight of walls and ceilings.
At the stage of studying and collecting data about the location of the future building and the quality of the soil, the following parameters must be determined:
- soil type;
- average annual precipitation;
- groundwater level;
- depth of soil freezing;
- altitude differences in the terrain of the site.
Taking into account the design features of the house, its weight, the presence or absence of an underground or basement floor, they choose the type of foundation and calculate the depth to which to dig the foundation for the house.
Depending on climatic conditions, the size of the trench will vary.
The colder it is, the more seriously you need to approach the issue of installing the foundation.
The depth of the foundation is always greater than the level of soil freezing: in southern latitudes a depth of 60 cm is sufficient, in northern regions it will be necessary to go at least 1.5 m deep.
Technical specifications
Before starting construction, you need to know what the height and depth of the foundation for a one-story house should be. These dimensions can be calculated with only initial data on the planned thickness of the walls and the material of the buildings in general. First, you need to calculate what bearing capacity the soil has in your region.
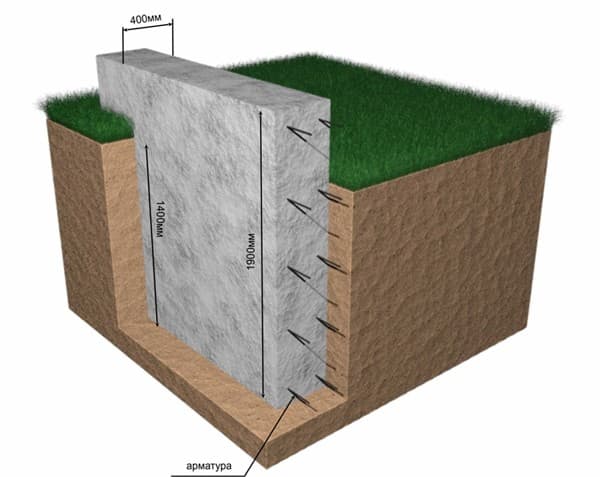
Photo - shallow foundation
You will find this indicator in the geological bureau of your region. Then you need to calculate how much pressure the building exerts on the foundation. To do this, all loads are summed up: floors, roofing materials, walls, doors, windows, insulation, etc. The resulting number is multiplied by a conditional coefficient of 1.3 - this is the approximate pressure that will be exerted by furniture and residents. A certain number of tons will come out - this is the mass of the building.
Next, you need to calculate the dimensions of the foundation. Here, each type has its own characteristics. For example, if with pile and columnar everything is very simple (the selected support and the weight of the house is divided by its load-bearing capacity), then with strip and monolithic it is more complicated. The minimum permissible depth for a foundation for a one-story house with an attic is 30 cm for rocky soil, 60 for sand and 85 for loam. For greater reliability, similar indicators can be taken for a monolithic slab, but in this case it will be very expensive. This is a normally buried foundation; for a wooden structure or frame house you can make a shallow foundation, but its parameters need to be calculated more accurately.
After calculating the depth, you need to decide on the width. The minimum permitted width of a strip foundation is 25 cm, and it is very important that the sole, i.e., the base of the support system, is slightly wider than the top. Of course, the thickness of the walls plays a big role here. Masters advise taking a size for the width of the foundation that is 5-10 cm greater than the thickness of the walls. You can choose the right proportions based on the finished building design.
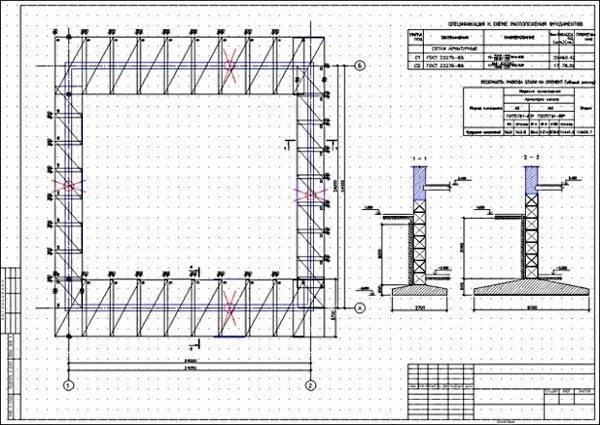
Photo - foundation project for a one-story house
Soil definition
There are several ways to determine the type of soil
The type of soil has a significant influence on the depth of the foundation.
To correctly calculate the size of a pit or trench, it is necessary to determine the type of soil at the building site.
The table describes 5 types of soil:
| 1 | Highly heaving | Sandy loam no more than 0.5 m, loam and clay no more than 1 m. |
| 2 | Medium heaving | Sands by 0.6 m, sandy loam by 1 m, loams by 1.5 m, clay - 2 m. |
| 3 | Low heaving | Sands - 1 m, sandy loam - 1.5 m, loams - no more than 2.5 m, clay 3 m. |
| 4 | Conditionally non-heaving | Sands from 1 m, sandy loam - more than 1.5 m, loams from 2 m, clay over 3 m. |
| 5 | Non-heaving | Doesn't matter. |
This classification is included in the standards for checking the stability of underground foundations.
The degree of frost heaving is determined based on the level of natural soil moisture and the position of groundwater during the period when freezing begins.
The depth of the foundation for a garage, gazebo or other light building on heaving soils should be calculated especially carefully. If the depth level is insufficient or there is an error in the thickness of the base, soil with a high degree of frost heaving will squeeze the base out of the ground during the freezing period.
Terrain and types of foundations
For large differences in height, it is recommended to choose a pile or mixed foundation
In addition to the type of soil, it is important to understand both the evenness and uniformity of the topography on the building site. Sites with a slope must be leveled.
If it is not possible to level, then the minimum foundation depth is calculated taking into account the lowest point, and if large elevation differences are observed in the area, then the type of foundation is selected either mixed or pile.
In practice, there are 4 main types of building structure:
- columnar,
- pile,
- tape,
- slab.
Types of structures
Before starting construction work, it is necessary to develop design documentation. These are diagrams and drawings that will help you choose the optimal type of supporting base. For a one-story house you can make the following foundation with your own hands:
- Monolithic;
- Columnar;
- Pile;
- Tape;
- Columnar-flying.
Monolithic is a type of construction when a large trench is dug under the future house, repeating or slightly exceeding the area of the building itself. It is compacted with sand or crushed stone cushions, and then filled with cement mortar. Sometimes foam concrete or gas silicate is used, but most often such materials are used in the construction of a country house. Sometimes such a support is built by installing a ready-made monolithic slab of concrete and reinforcement, which significantly reduces construction time.

Photo - monolithic foundation with a sole
Columnar is a very popular type of base, which is considered one of the most economical options. It can be made using poured pillars, installing supports from foam blocks or bricks, and also driving concrete foundations into the ground. Mainly used for wooden houses, block or residential premises made of timber.
Pile is an analogue of columnar, but it is used on problem soils. At first glance, the unreliable support system copes well with high loads - on average, one pile can carry up to 18 tons. Pile construction is used on sand, rocky and clayey soils, and houses are also built on swampy soils using this system.
A strip foundation for a one-story residential building is, in most cases, the ideal solution. Due to the combination of high load-bearing performance and economical consumption of building materials, most home craftsmen choose just such a system for their home. The strip type of base can also be made from block bricks, aerated concrete, foam concrete, cement mortar and reinforcement bundles.
Columnar-tape or strip pile is a combined type of load-bearing structure for a private house. In most cases, it is a simple structure with point supports, which are additionally reinforced with a grillage. But some craftsmen use a more complex system for their buildings. The technology of internal pillars is the principle of building a foundation, when first a trench is dug, suitable in depth for the foundation. Afterwards, additional cylindrical holes are dug in it, and they, together with the upper trench, are filled with solution.
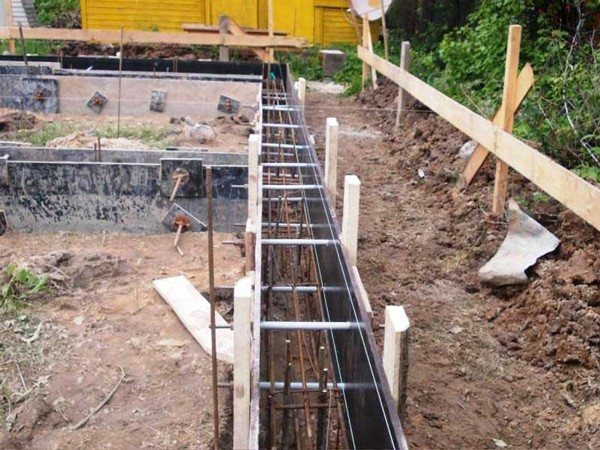

Photo - high strip foundation
All types have their advantages and disadvantages; to choose the right option, be sure to consult with specialists.
Video: foundation on screw piles
Columnar base
This type of base is good for use on a small budget.
Pillars as a foundation for a house are the most budget-friendly solution, so they are often used for garage construction or for a one-story country house.
They are made from blocks, bricks or by pouring into formwork. Thanks to the use of technological materials, this type of base is time-consuming.
Waterproofing and a sand cushion are laid at the base of each pillar. Supporting elements are placed in places of the greatest vertical load: the corners of the house and the intersection of load-bearing walls of the structure. It is very important that the pillars are strictly vertical. With this type of foundation, the depth of the foundation for a one-story brick house is no more than 0.8 m, of which 30 cm is the cushion and waterproofing, and 0.5 m is the height of the pillar.
Reinforcement
Strengthening the support is necessary to give the structure additional rigidity. You need to install reinforcement units at the intersections of the walls, as well as under load-bearing walls. Reinforcing wires are connected using ties or a welded joint.
Photo - reinforcement for strip foundation
The foundation for a brick two-story house must be additionally reinforced. This will help protect the base from stretching and deformation during use. It is best to use ribbed reinforcement for a tall building. It is suitable for a frame building and a house made of aerated blocks or gas silicate. Due to its uneven structure, it is this wire that provides maximum adhesion to the concrete foundation mortar.
Photo - strip foundation options
Piles
It is especially recommended to use piles on northern heaving soils
What is a pile foundation? When constructing this base, metal pipes with a blade at the end are screwed into the ground like self-tapping screws. Piles simultaneously support the building and distribute the load on the ground from the weight of the structure. The blade at the end of the pile prevents the structure from being squeezed out of the soil during freezing and heaving.
Such a foundation arrangement is especially relevant in the northern regions, where, due to climatic conditions and during winter freezing, the issue of squeezing out the foundations of light buildings and structures by heaving forces arises. In such conditions, piles are suitable both as a foundation for a garage and as a foundation for a one-story brick house.
For light buildings, metal bladed piles are used
How to determine the depth of foundation on piles? The depth of freezing is determined by the trenching method. The drill is screwed in to such a depth that the blades are below the freezing level in dense layers of soil.
The piles can withstand a tensile load of up to 330 Pa. In this case, the maximum pressure force during heaving is 0.2 Pa.
Metal blade piles are suitable for the construction of lightweight buildings. The technology of bored piles has been developed for heavy buildings.
The great advantage of such a foundation is that work on its construction can be carried out at any time of the year in any climatic conditions.
Preparatory work
When marking the site, it should be taken into account that the presence of a flat surface of the construction site with a small slope angle will protect it from flooding by rain and will further ensure the drainage of excess water that is formed as a result of rain and melting snow. Using pegs with a fishing line stretched over them, mark the outer part of the foundation.
Watch the video:
A level must be used. This tool will allow you to maintain horizontal alignment when marking. Next, retreating a distance equal to the width of the beam with a margin of 10-15 cm, mark the inner part. It should be borne in mind that the markings include not only the external contours of the house, but also all the partitions that are provided for by the project.
After marking work is completed, a pit is dug to the required depth, which should take into account the presence of a sand cushion 10-15 cm high. In this case, differences in soil heights must be taken into account.
If the structure of the house does not provide for the presence of underground rooms and basements, then to build the foundation you can dig a trench of the intended width. To ensure that its depth is the same along the entire length, use a water level.

After the trench is dug, a fishing line is pulled inside it, which will show the level of sand being filled. This simple technique will greatly facilitate the work of constructing a sand cushion. Next, sand is poured in, leveled and thoroughly compacted with a roller.
Strip foundation
The strip foundation design is a monolithic, solid, inextricable concrete pour, usually with internal reinforcement.
The foundation is placed under all walls of the building, including partitions that carry vertical loads. Along the perimeter, the base has the same cross-sectional dimensions.
The foundation strip forms a continuous contour
Depending on the type of soil and the mass of the building, various shapes are poured:
- rectangular;
- trapezoidal;
- T-shaped.
The integrity and continuity of the base contour ensures uniform distribution of vertical and horizontal loads. This explains the strength, reliability and demand for this type of foundation. In addition to the shape of the base, it is important to determine at what depth to make a monolithic strip foundation. For a detailed presentation on strip foundation construction technologies, watch this video:
Shallow design is not suitable for heavy buildings
Depending on the weight of the building, the level of soil freezing, the location of groundwater and the type of soil, the depth and types of strip foundations can be different:
- shallow with a depth of no more than 0.6 m. The device is supposed to have a movable base, subject to soil heaving. Not suitable as a basis for the construction of heavy buildings;
- buried - a reinforced concrete monolithic frame laid below the freezing level of the soil. Used for buildings with basements that have a large mass.
It can be generalized that the recommended strip foundation and laying depth depend on the weight of the building and the type of soil heaving.
Let's look at the stages
Filling can be divided into 2 stages:
- Preparatory;
- The main one, that is, pouring concrete.

Preparatory work for arranging the foundation includes:
- Site marking;
- Installation of pegs around the perimeter;
- By pulling fishing line or construction thread over pegs;
- Installation of fittings;
- Construction of formwork.
Plate
Slab foundations can be installed on any type of soil
Like tape, a monolithic slab can be recessed or not. In the first case, the slab is poured into a pit and has high ribs. The main disadvantage of such a device is its high cost. But this is the only type of foundation that has no restrictions on the type of soil.
How to calculate the laying depth, and what should the slab be? The heaving of the soil does not affect the condition of the building on this basis, therefore this distance is determined based on the operational requirements for the building. For more information about building the foundation, watch this video:
The monolithic slab is a floating solid foundation and its installation is possible even on swampy or peaty soils, where the groundwater level is quite high.
The summary table shows the types of foundations, soil types and weight of the structure
| Columnar | sand of coarse and medium fraction, coarse, cartilaginous | suitable for heaving soils | small-sized, lightweight | |
| Pile | except rocks | suitable for non-heaving soils | the device is permitted at large freezing depths | any, without underground floor arrangement |
| Tape | sand of coarse and medium fraction, coarse, cartilaginous | suitable for heaving soils | lungs | |
| Monolithic slab | no limits | suitable for heaving soils | any heavy |
Recommendations for calculations
In case of mass construction, the calculation of the depth of construction is carried out by specialists at design institutes. More often, during individual self-development, the question arises: how to calculate the foundation for a garage, bathhouse or one-story cottage?
After receiving all the necessary data on the soil and the weight of the building, a final calculation is performed and the depth of the foundation is determined.
The depth, although within the same limits, will nevertheless always be different. On the same site, the foundation for a one-story or two-story brick house will differ significantly.
Each calculation is purely individual. If it is not possible to contact specialists, you can enter the data into an online calculator and find out the recommended dimensions adjusted for freezing depth. For more information on calculations, watch this useful video:
But there are a few general guidelines to follow:
- Any foundation is laid below the soil freezing level by 10%. If the freezing value is set to 70 cm, then the depth of the hole under the base should be 77 cm.
- For loose soils in temperate climates, it is better to use a strip base with a laying depth of 0.5 to 1 m.
- In the northern regions with slightly heaving soils, a foundation buried up to 2 m is made.
- In swampy areas or on clay, a slab would be an ideal option, and the depth of burial can reach 2.5 m, which allows you to make a basement.
The basic rule when calculating the foundation: a competent and reliable foundation is the key to a long service life of the building. It is worth noting that overdoing construction is also fraught with consequences, as is saving. A pit dug below the required level will not make the house more reliable, but will increase the consumption of materials and the area that will be negatively affected by soil and groundwater.
What should be the height of the foundation above the ground?
The construction of most types of foundations for a frame or brick house requires the presence of an above-ground part. Its main purpose is to provide protection from precipitation and temperature fluctuations of the load-bearing part of the structure, which is located underground. How tall should it be? On the one hand, it is logical to increase the above-ground part in order to also protect the house itself, but on the other hand, doing this will be expensive from a financial point of view.
It is recommended to install a strip foundation made of blocks or bricks or slabs for a frame or stone house with an elevation from the ground surface of more than 30 cm. Such a device will visually clearly separate the building from the foundation and improve the integrity of the object when operating under the negative influence of the external environment.
For regions with flooded areas or with increased precipitation, the upper part of the foundation should be 10 cm higher than the maximum flood level.
This fact must be taken into account and the appropriate dimensions must be applied to the drawing of the house using reliable data for a specific region of development. To simplify the task, you can look at ready-made house designs that were built nearby. But it is still recommended to double-check the accuracy of the calculations.