The key factors when choosing a foundation and its depth are as follows:
- Type of soil.
- Soil freezing depth.
- Seasonal groundwater level.
- Loads on the foundation (calculated based on the specific weight of the structure).
- The terrain (for example, the slope of the site).
Regardless of the project: it is standard or individual, it is necessary to examine the site of the proposed construction and take into account the properties of the soil.
Before carrying out work, we suggest that you read the article - what you need to know before starting to pour the foundation: typical mistakes.
Geological section of the site
You need to know that the main factor influencing the depth of laying the foundation for a house is the soil. Find out what type it is, what its quality and content are. You need to make a geological section of the site on your own, for this you will need a shovel and working hands. Start digging a hole measuring 1.5 x 1.5 m, no less, so that it is comfortable to be inside. The depth of the pit should be approximately 3 m.
If you don’t want to dig a hole and strain yourself, then you can turn to the relevant state archives, where you can find a geological section of the site where your future home will be located. You will receive a diagram of the site, or you can make your own diagram, which will be more reliable and relevant.
Using a tape measure, measure each level of soil that you encounter during excavation. Draw everything schematically on a sheet of paper, keep the scale, you can use some symbols, the main thing is that you then understand your drawings and diagrams yourself.
The most common order of occurrence of rocks looks something like this:
- Topsoil and vegetation on it. This is the most unreliable support for construction, since the soil absorbs moisture well, it is loose and uneven. This layer can reach up to 1 m in depth and is home to various insects, roots and rodents. Before starting construction, you will need to get rid of this unreliable layer, dig it out completely, it will not be able to become a strong support for your house.
- Peat bog or silt. This layer of soil cannot be called reliable either; you cannot build a house on it.
- Sand. Sands can be used as a foundation for a house. There are different types of sand, its strength will depend on the type of sand:
- gravelly;
- fine-grained;
- medium grain;
- coarse-grained.
- In addition to these sands, there may be silty sands; here the groundwater level must be taken into account. The higher their level, the less reliable.
- Clays, loams and sandy loams. Their strength depends on the water level in them. Water, like fine-grained sands, reduces the endurance of the soil. If the water level in clays, loams or sandy loams is high, then they can bend and deform even under their own weight.
Focus on the features of your site, on the soil layers, explore and measure each level with accuracy.
In document SNiP 2.02.01-83 “Foundations of buildings and structures” you will find all the necessary information for your home.
The basic rule for the depth of the foundation is that the higher the building, the deeper the structure should lie. If you do not follow this rule, then in the future your building will tilt or cracks will form on the walls. In addition to the height and design of buildings, you need to take into account nearby buildings, groundwater levels and underground channels.
Return to contents
Features of aerated concrete blocks
Here we will consider those characteristics that have a direct impact on the foundation for a house made of aerated concrete. Before choosing a type, you need to consider the following features.
Aerated blocks are piece material. Even with the right choice of masonry mortar and compliance with the technology for performing the work, they are poorly connected with each other. This factor results in the fact that the walls of the building are extremely sensitive to various deformations of the base.
If the foundation for a house made of aerated concrete subsides or, conversely, rises from the ground, cracks may appear on the walls of the building. In most cases the cracks will be inclined. The opening width and length depend on the scale of displacement of the supporting part of the building. To prevent damage, it is necessary to provide reliable supports that will resist various types of displacement. The design must connect the wall from individual blocks into a single system.
The task of the foundation is to prevent such phenomena
The foundation for aerated concrete needs a less powerful foundation than for a brick house. This is caused by the lower density of the material, and, accordingly, the mass. For comparison, the density of aerated blocks ranges from 350 to 700 kg/m3, while a brick wall will have a density of 1800 kg/m3. Blocks with a minimum density cannot be used as structural elements; the material of load-bearing walls weighs from 500 to 700 kg per cubic meter.
Despite the advantages of blocks compared to brick, it is worth remembering that the material is inferior to wood. The building will also be heavier than a frame house. When selecting foundations for houses made of lightweight aerated concrete, it is necessary to take this feature into account.
Strip foundation
There are several types of strip foundation:
- From blocks.
- Monolithic.
- Brick.
- On heaving soils (blocks, monolithic, brick).
Most often in the construction of private houses, the use of shallow monolithic strip foundations is observed. This type is the most economical and is easy to install, which cannot be said about the deep-seated method.
You can choose the foundation for the house that will meet your requirements. You should take into account the characteristics of the soil, your economic capabilities, the height of the future structure, the groundwater level and many other factors. Make your choice based on a combination of factors.
A shallow monolithic strip structure is a continuous line of concrete, which is located strictly under the load-bearing walls of the building. The principle of operation of a strip monolithic structure is that the entire weight of the building falls on this support, which distributes the load evenly to the ground.
Return to contents
Search for rational construction of foundations on black soil
In order to see the full picture, you need to order geological surveys that show:
1. terrain features;
2. groundwater level;
3. soil structure;
4. freezing depth;
5. load-bearing capacity of each layer.
The lack of analysis leads to the following results: walls sag, glass flies out, door frames become deformed.
– pile-grillage foundation with a hanging grillage (more expensive and stronger);
– complete pouring of concrete;
– for a strip foundation under subsidence soil (which is cheaper and unreliable).
It is likely that the options will not suit you. Then the most rational solution is to excavate the black soil (partial or complete) and install a slab foundation. Partial excavation also implies partial replacement with a gravel-sand mixture. Some types of tamping machines will be needed. Alternatively, you can completely compact or compress the black soil to create a strong foundation for the foundation. This solution requires the import of a lot of heavy construction equipment, which is not always physically and financially feasible.
Conditions for using a strip shallow monolithic foundation
- The soil is non-heaving and homogeneous.
- Low groundwater level.
- There are no plantings (tall trees).
- The soil is not organic (peat).
- There are no joints in the ground.
- The area is not floodable.
When calculating the minimum, soil freezing must be taken into account. Soil freezing is the depth to which the soil freezes in cold weather.
The impact on the foundation is directly dependent on the groundwater level and the depth of freezing; the greater these values, the higher the level of heaving. A high level of heaving creates extrusion of the shallowly buried strip base. In order for it to overcome the forces of heaving, the structure must be buried.
The maximum depth for a strip foundation is 2.5 m.
It may be less if favorable conditions accompany it.
Sometimes the degree of freezing does not affect. For example, if the soil consists of sand and there is no heaving.
Return to contents
Types of foundations for a house made of aerated concrete
Before starting construction, you need to know that to create a basement or basement floor, you will need to make a deep strip foundation. If the area where the house should be located has large differences in height - more than 1.5 m, then it is necessary to erect a pile-screw grillage.
Let's take a closer look at the possible foundation options.
Slab foundation
If the house is to be built on “difficult” land, where groundwater is close to the surface, you should opt for a monolithic slab. They are divided into 2 varieties: with and without stiffeners.
A slab without stiffeners is suitable only for small buildings. You cannot build a house or cottage on it. For an aerated concrete house, you will need to make a shallow foundation with a slab with stiffeners. The fittings will provide the following properties:
- good load-bearing capacity;
- resistance to soil freezing;
- resistance to ground movements and stability.
A monolithic foundation with stiffening ribs makes it possible to build 2-3 storey houses from aerated concrete. The slabs can also be used for sandy soil where there is no heaving.

The disadvantages of such a foundation include:
- the inability to make a basement in the house, since the slab will lie under the entire foundation of the building;
- the cost of such a foundation will be high due to the large volume of mortar and reinforcement.
Strip foundation
This is the most popular type of foundation not only for aerated concrete houses. It can be used for 2-3 storey buildings. To create such a base, high-quality concrete and 120 mm reinforcement are used.
It is not recommended to make a foundation from aerated blocks, since they have a low density and are not able to provide sufficient rigidity. The material will absorb moisture from groundwater and quickly become unusable.
If you want to make a block foundation, FBS blocks (solid foundation block) are perfect for this. These are large rectangular blocks weighing 300 kg. Their advantage is that they are installed very quickly (using special equipment). The disadvantage of FBS is the presence of technical seams between the blocks. They are best suited for the construction of a basement or basement.
The main parameters when creating a strip foundation are: the width of the trench, its depth and diameter.
For a shallow foundation, the depth is 50 - 70 cm. If you plan to make a basement in the house, then you will need to make a buried foundation of 1.5 m.
It is also necessary to take into account the depth of soil freezing. The width of the trench can be determined using calculations. It depends on the weight of the entire structure.
Most often, the width of the strip foundation trench for an aerated concrete house is 40 - 50 cm.

Pile and column foundation
These types of foundations are characterized by high construction speed and material savings. In addition, piles and pillars make it possible to conduct construction on difficult soils. Piles and pillars are installed pointwise along the entire perimeter of the future house. To install the pillars, you will need pre-prepared recesses.
A grillage is installed on top of them, connecting all the pillars or piles into a single platform. The weight of the future building is evenly distributed over all supports.
What advantages does this type of base have?
- you can work at any time of the year;
- reduction and uniform distribution of weight and settlement of the house;
- The closed contour of the grillage increases the stability of the entire structure.

Dependence of foundation laying on freezing depth
The depth of the supporting structure is affected by the depth of freezing of the ground. This value varies, it depends on the region where your future home will be located.
- If freezing is up to 2 m, then the depth of the structure is 0.5 m.
- If freezing is up to 3 m, then the depth of the structure is 0.75 m.
- If freezing is more than 3 m, then the depth of the structure is 1 m.
If the soil is heaving, this has an adverse effect on the structure; it needs to be made deeper. Depending on the depth of freezing of heaving soil, the following levels of strip foundation are recommended:
- If freezing is up to 1 m, then the depth of the structure is 0.5 m.
- If freezing is up to 1.5 m, then the depth of the structure is 0.75 m.
- If freezing is up to 2.5 m, then the depth of the structure is 1 m.
- If freezing is up to 3.5 m, then the depth of the structure is 1.5 m.
The groundwater level can affect the depth of the foundation. If the water level is very high, then it will have to be placed deeper than normal.
The maximum above ground level should be 4 times its width. The internal space should be filled with sand. The height above the ground must be equal to or less than the height of the part that is underground. Most often, the height of the base above the ground is 50 cm.
When drawing up a project for the foundation of a future bathhouse, builders first of all determine its type - and it directly depends on the exact soil on which the construction will take place. Which, however, can be determined at home. It is about ways to determine soil types and where it is better to place your foundation that we will talk today.
What types of foundations are used?
All foundations, depending on operating conditions, can be divided into four large groups:
- columnar;
- pile;
- tape;
- slab.
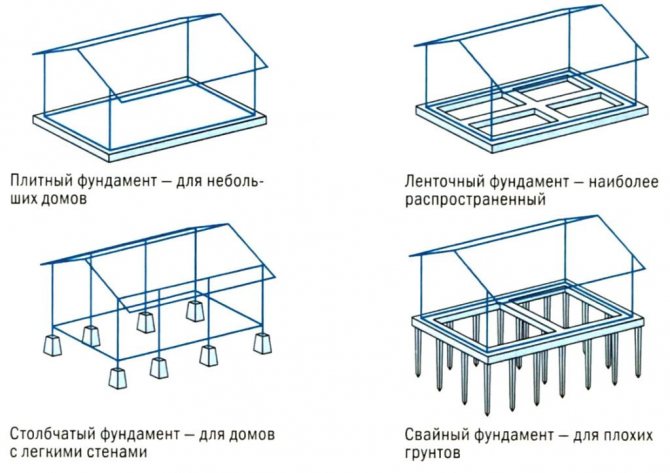
Variants of bases used
The first and second in private construction (taking into account the most popular sections) have a relatively low load-bearing capacity. Such elements only work under compressive loads. It is especially advantageous to make them from concrete, since this material has good compressive strength. Also recently, metal screw piles have become widespread.
The strip foundation absorbs mainly compressive loads. When installed on soft soils, slight bending effects may also occur. If a monolithic foundation is made in accordance with the technology, they do not cause problems.
The use of a slab foundation is different in that this structure works on bending and pushing. Concrete does not resist such influences well. To prevent damage, a mixture of sufficiently high grades is chosen for filling, and reinforcement is prescribed with special care. Before installing the slab, it is recommended to calculate its strength and rigidity. Only a professional designer or constructor can perform such work.
How to determine the type of soil yourself?
There is a simple home test for this:
- Step 1. Take a small portion of soil from the area where the bathhouse will be built in your palm and moisten it generously with water. You need to roll up a rope from this cake and bend it into a ring. If it's sand, you can't do this. A ring made of sandy loam will immediately crumble into small fragments, loam - into 2-3 parts, but a ring made of clay will remain intact.
- Step 2. Carefully examine the particles of earth in your hands - are there many grains of sand in it that exceed 1.2-1.5 mm in diameter? If yes, then the foundation will be built on sandy soil.
But to find out whether the foundation will end up on clay soil, do another test - shake a little sand in a glass of water. If it becomes very cloudy, it means that, unfortunately, there is a lot of clay in the selected soil.
- Step 3. Determine the presence of water in the ground. After all, a foundation on swampy soil is quite a challenge. And the most undesirable in this regard are sandy loams and dusty sands - and all because the small clay particles in them, which act as a lubricant between large ones, allow the soil to actively absorb water and poorly release it. Just a small movement - and they easily turn into a floating state. In such soil, the foundation may begin to sink and shift to the side... What to do? First of all, you need to make a cushion of crushed stone or coarse sand, as well as good drainage to remove excess moisture.
Sometimes it is necessary to completely replace a weak layer of soil with soil with more reliable characteristics. And the most proven method is an embankment of non-heaving soil and a foundation that is built on it. This way, two birds are caught at once - the general level of the local area is raised and the soil parameters are improved.
- Step 4. Determine the groundwater proximity level. This can be done by simple observation: are there any wells nearby and what is the depth of the water in them? Is the well higher or lower than the height of your site and by how much? The second point is communication with neighbors, who need to find out how dry it is in their basements and whether there is water there.
The most extreme method is to make a hole with a fishing drill, wait 2 hours and check the water level with a wooden batten. If it turns out that the level of underwater water (builders call it by the abbreviation UPV) is 1.5 meters lower than the depth of soil freezing, then even foundations on heaving soils can be built with the same rigidity as on medium heaving soils. But it is worth remembering about capillary rise and seasonal saturation of soil moisture, which completely depends on the landscape and the abundance of precipitation specifically in this area. That is why it is advisable to check the soil moisture in the area where the bathhouse will be built in the fall - before the natural freezing of the soil begins (see step 5).
- Step 5. Determine soil moisture - preferably in the fall. To do this, roll a ball out of the ground and watch it. If it crumbles right away, it’s low-moisture soil; if it holds, it’s wet.
Types of clay soil
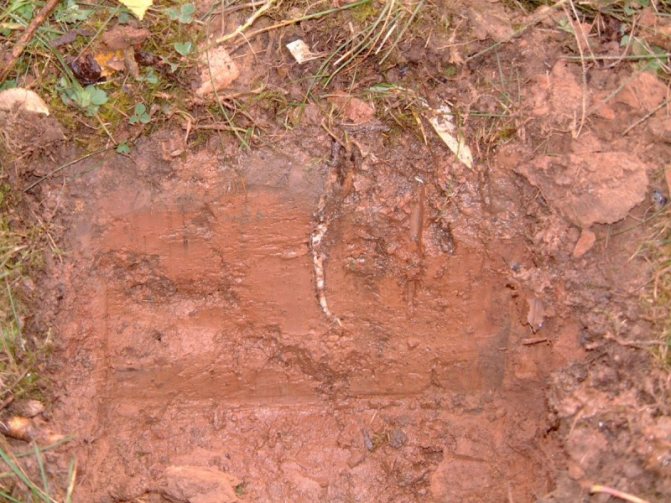

Soil with clay content more than 30%
Soils are classified by the percentage of clay they contain. If its proportion is 0.05-0.1, such soil is called sandy loam. Soils with 10-20% of this component qualify as loamy. Such a composition already imposes restrictions associated with taking into account the tendency to heave. For example, a columnar foundation on loam, especially one not equipped with a grillage, will be unreliable. Like other types of soil, its swelling in winter is affected by the water level. Soils in which there is more than 30% of it are considered rich in clay. They absorb a lot of moisture.
You should definitely not build a house on plastic clay located in a lowland near a reservoir. If there is no other option and it is necessary to erect a building on such soil, piles are used to arrange the foundation.
Due to its qualities, glacial clay is more suitable for residential buildings, subject to careful compliance with building codes.
What foundation - for what soil?
The integrity and longevity of the entire bathhouse depends on how well the foundation is built. Therefore, carefully choose which zero level is best to build on a specific soil - taking into account, of course, the weight of the construction of the bathhouse itself.
Solid strip foundation - for a solid bath
Strip foundation is the most expensive and durable of all existing ones. It is placed on almost any soil, and where the soil is more or less stable, its shallow-buried version is used.
Its subtype - strip-pile reinforced concrete foundation is built where the soil is sufficiently water-filled, the area is on slopes or on quicksand soils. And, if the bathhouse is not planned to be too heavy, this option in itself is no worse than a monolithic slab.
Monolithic slab foundation - for the most fragile soils
This foundation is a lifeline for those who are going to build their steam room on water-saturated, almost viscous soil. This foundation is being built on a swamp in the truest sense of the word. For such swampy and peaty soils, only a large area of the foundation base is literally suitable - for those who loved physics at school, the term “pressure area” says a lot.
And for those who were not given this subject, we will give a more accessible example: in boots a person will always drown in the thickness of the snow, but in skis - never, because they have a larger contact area with the surface of the snow.
Columnar foundation - better with dressing!
The columnar foundation itself is not bad - it is suitable for most types of soil and lasts for many decades if built correctly. But builders always recommend making a columnar foundation with a bandage - the so-called ryndbeam. Thanks to it, you can even build brick baths on such a foundation - if their walls are not too thick. And such a bellow can be placed both on the surface of the ground and with a slight depth - that’s all the secrets.
Pile and pile-screw foundation - bathhouse on the rock!
Once upon a time, piles were used only in the construction of bridges, lighthouses and piers, but no one thought of building a hut “on chicken legs” for many years. But now pile, pile-grillage and pile-screw foundations are becoming more popular day by day.
And all because it can be erected on almost any soil - the main thing is to reach the freezing level, where the soil is compacted to the limit, and fix a pile on it - driven, screw or cast-in-place.
A house can be built in any area. It is good if there is stable soil and the installation of the foundation can be carried out according to the usual standard norms and requirements. Another thing is unstable, swampy soils. This requires additional costs not only for equipment, but also for proper design, taking into account the specifics of the construction site. Swampy areas are not the most suitable basis for construction. But even here, subject to all norms and requirements, it is possible to build a high-quality, strong foundation that will serve as a reliable foundation for the house for many years. The main requirement is the correct technology for building foundations on unstable, wet soil. The article describes in detail what kind of foundation to choose for a foundation on swampy soil when planning construction in such a problematic place.
Swampy soil is a difficult base for a foundation. In this case, two types of foundations can be used: pile and slab. A pile foundation is reinforced with metal or concrete piles; a slab foundation is made in the form of a monolithic reinforced concrete slab, which is poured onto a sand-granite bed.
Slab
A slab foundation is designed to ensure that the load of the building is uniform across the entire base of the slab. Such a base can withstand increased loads and is used not only in individual, but also in industrial construction.
Slab technology is applicable on heavily swampy soils, unevenly compressed soils, and with a high groundwater supply. However, the disadvantage of such a foundation is that it is inappropriate to install it on slopes. If there is even a slight slope, the slab can “slide”. The special advantages of a slab foundation include its high load-bearing capacity. The only drawback here is the increased consumption of materials, which is a very painful fact for individual construction.
To pour such a foundation, you will need many times more reinforcement and concrete than when installing a foundation on solid soils, which, naturally, will entail an increase in the entire final cost of the building.
Pile
Installing a pile foundation in swampy areas is more reasonable and has its advantage in the direction of uneven terrain. Piles can be placed in any hard-to-reach place, on slopes, on any technically difficult soil. Among the advantages of a foundation on piles is not only its installation in hard-to-reach areas with complex terrain and unstable soil, but the advantage is the speed of installation of piles and an affordable price.
The opinion that a pile foundation is more suitable for small, lightweight structures is incorrect. By increasing the number of supports, the highest possible bearing capacity of the foundation is achieved, which is in no way inferior to the parameters of the slab base. However, at the same time, the costs of such a foundation will increase and its cost will be equal to that of a slab foundation. When constructing reinforced, heavy structures, this fact should always be taken into account when it comes to the cost-effectiveness of a pile foundation.
What types of foundations are used?
All foundations, depending on operating conditions, can be divided into four large groups:
- columnar;
- pile;
- tape;
- slab.
Variants of bases used
The first and second in private construction (taking into account the most popular sections) have a relatively low load-bearing capacity. Such elements only work under compressive loads. It is especially advantageous to make them from concrete, since this material has good compressive strength. Also recently, metal screw piles have become widespread.
The strip foundation absorbs mainly compressive loads. When installed on soft soils, slight bending effects may also occur. If a monolithic foundation is made in accordance with the technology, they do not cause problems.
The use of a slab foundation is different in that this structure works on bending and pushing. Concrete does not resist such influences well. To prevent damage, a mixture of sufficiently high grades is chosen for filling, and reinforcement is prescribed with special care. Before installing the slab, it is recommended to calculate its strength and rigidity. Only a professional designer or constructor can perform such work.
Preparatory stage
At the first stage of construction, a full soil study is carried out. For this, a hand-held probe can be used to take soil samples. This method is used in the construction of light wooden buildings and structures.
The probe is lowered into a well 5 m deep. During the capital construction of stone or brick houses, serious geological exploration is required. In this case, the depth of measurements is 8-10 m. Wells for measurements are located in the corners of the future structure. There must be at least four such measurements (wells). Determine indicators of soil composition and depth of its layers; level, quantity and composition of groundwater. One more indicator is needed - this is the freezing point of the soil.
The upper layers of marshy soil are mainly peat. Clay and sandstone may follow. Peat is a porous, completely loose material with low compression resistance and increased instability. If the layer thickness is small, the peat is removed and the foundation is placed on the lower hard rocks. This is a shallow foundation. Its peculiarity is that the slab under the foundation is located above the freezing point of the soil. This base is suitable for light buildings.
A shallow foundation is arranged so that it can rise and fall slightly during heaving processes occurring in the soil. Thanks to this, it does not crack and retains its shape. This base is not used for brick and stone houses. If the peat layer on the construction site is deep enough (more than 5 meters), it is necessary to strengthen the foundation with piles.
Not only the peat layer is a problem when building a foundation on swampy soil. The second problem is the nearby groundwater. There are two ways to combat this problem:
- lower the water level;
- raise the area.
The installation of a drainage system helps to significantly reduce the groundwater level. To drain water from the construction site, trenches are dug to a depth of about two meters, and the entire drainage system is led to drainage wells. A layer of crushed stone is poured into the trench and drainage pipes are laid on it. Drained water from wells is pumped out using submersible pumps.
To raise the site, you need to make an embankment of stone and sand. To do this, remove the top, weak layer of soil and fill the area with a layer of stone and sand. Such an embankment is carefully compacted and compacted with rollers.
Self-soil analysis

The optimal time for geological exploration is spring. After all, it is during this period that groundwater is as close to the surface as possible. They can complicate construction work and even force you to reconsider your original foundation choice.
Several wells will need to be drilled in the area where the house is planned to be built. This can be done conveniently with a garden drill. The drilling depth is at least 30 cm from the soil freezing line. In the process, you can immediately evaluate and determine:
- soil composition;
- bedding levels and their uniformity;
- soil characteristics.
Slab foundation installation technology
The slab foundation must be made in accordance with all standards according to the following basic scheme:
- Removing the soil layer. Depth 1 m.
- Making a mound (pillow) from a mixture of gravel, stone and sand. The embankment is compacted and concrete preparation is done.
- Covering with waterproofing and thermal insulation.
- Making a frame from reinforcement. Tying the frame with wooden blind areas.
- Pouring concrete over the frame and its subsequent compaction with an industrial vibrator.
- Leveling the surface as a rule.
Features of foundation calculations
When calculating the foundation, a large number of parameters are taken into account. So, for example, not only the material from which you will build a house matters, but also insulation and insulation materials. The greatest importance is played by the total weight of the house with cladding and communications.
Calculation of the foundation for a one-story house
When building a one-story house, all figures given in the project are taken according to the minimum limit. So, for example, if a shallow foundation should have a depth of 50 - 60 cm, you should choose a depth of 50 cm. The sand cushion is also taken into account here. Trenches dug to a depth of 50 cm will be filled as follows:
- sand pillow - 20 cm;
- formwork is installed on the sides;
- a frame of rods connected to each other with clamps, 30 cm apart, is placed in the formwork;
- the gap between the formwork and the reinforcement should be 5 cm;
- concrete solution is poured.
When pouring concrete, it is advisable to have a concrete vibrator on site. With its help, you can remove excess air from the solution and make it more uniform and dense.
Calculation of the foundation for a two-story house
When working with the foundation of a two-story house, you should take the maximum parameters specified in the project. Here's how to fill a trench, 60 cm deep:
- sand cushion 30 cm;
- formwork;
- frame made of reinforcement 12 - 14 mm, secured with clamps, in increments of 20 cm;
- concrete solution.
When creating a columnar or pile foundation for a 2-story house, the dimensions of the supports will differ. They should have a larger cross-section than for a 1-story house. Their size is determined during calculations and indicated in the project.
When installing a monolithic slab, a thickness of 40 cm is suitable for a 1-story house, and 50 cm for a 2-story house.
Installation of a pile foundation
The main thing here is the piles. They can only be reinforced concrete or combined. There are three types of piles:
- screw metal;
- driven reinforced concrete;
- bored
Bored piles with asbestos-cement formwork are installed only when draining the supporting soil layer. They have fairly good load-bearing capacity. Screw metal piles are somewhat inferior in their load-bearing characteristics to bored piles, but they have high installation qualities: speed and ease of installation, ease of transportation.
A distinctive feature of screw supports is the ability to extend them to the required length. Driven piles are installed using pile driving equipment. At the same time, it is not always possible to use heavy equipment in individual construction.
The main criteria when calculating the number of support piles are the type and magnitude of the load. Regardless of the type, piles can be installed in the following order:
- Rows under the walls.
- Alone under a support.
- Bushes under the columns.
- Fields under strong vertical loads.
All calculations of the length and volume of piles are performed based on geological survey data in accordance with construction standards and regulations. The lower ends of the piles should rest on dense soil. It should be noted that on each of the foundations considered, any residential building in a swampy area can be installed. Any of the construction technologies is suitable for building a house; restrictions can only be related to the operating conditions of the building being constructed.
In conclusion, it should be noted that not all building materials are suitable for buildings in wet areas. For example, at high humidity it is not recommended to use foam concrete, expanded clay concrete, or aerated concrete due to the strong hygroscopicity of the material. Timber is also not the best material. On swampy areas, it is best to build brick, stone or frame houses. But the most important thing is to lay the foundation correctly and absolutely accurately. To a greater extent, it is precisely because of this that a house built according to all the rules will last a long time and reliably.
Let's start with the most serious mistakes that are made when building foundations. The first is the base of the trench; it must be strong and reliable. If, when excavating soil, you find a layered occurrence of rocks, then you need to stop at the height that will become the natural starting base for the construction of the foundation, but not higher than the freezing mark of the soil (meaning the construction of a buried foundation). It is impossible to build a foundation on black soil
, its structure does not allow it to be classified as a reliable basis.
In shallow ones, it is necessary to provide a sand cushion, since it is best compacted, does not retain moisture and is an inert, anti-heaving material. It is advisable to choose clean sands, without any clay or silty inclusions, of medium and coarse fractions.
Choosing the optimal foundation for an aerated concrete house
Korovin Sergey Dmitrievich
Master of Architecture, graduated from Samara State University of Architecture and Civil Engineering. 11 years of experience in design and construction.
When deciding which foundation is best for a house made of aerated concrete, several factors must be taken into account. First of all, the design features are influenced by the properties of the wall material. Foundations for houses built from aerated concrete must take into account some of the distinctive characteristics of this material.
Concrete works
It is very important to maintain the water-cement ratio, which should be such that there is enough water to hydrate the cement; practical experience shows that W/C = 0.6 is quite sufficient for a favorable course of the setting and hardening process of concrete. Very often, for better workability, builders increase the plasticity of the mass by adding water, which has an extremely negative effect on its density, strength and water resistance. Water not bound by the chemical process of hydration remains in the concrete body. After its evaporation, numerous pores and capillaries remain, which, like a sponge, absorb water from the atmosphere and soil. At subzero temperatures, the liquid inside the formed voids freezes, which inevitably leads to the destruction of the concrete stone and loss of its load-bearing capacity. Therefore, surface protection, such as waterproofing and hydrophobization, is not enough to maintain the integrity of the structure. It can protect against the harmful effects of excess moisture, but not against pressure water.
Requirements for the foundation for an aerated concrete house
The dimensions of the future foundation, its depth and height, are calculated according to the individual characteristics of the house. The design of the foundation should be entrusted to a specialist, since the durability of the entire house will depend on it.
The reinforcement and height of the foundation from the base must be carried out in such a way as to cope with possible soil movements. When creating a foundation for a house, you need to be guided by such factors as:
- maximum static load (walls, roof, partitions);
- temporary load (furniture, communications);
- relief of the site.
In addition, you need to know the geological features of the site. How deep does the groundwater go, what bearing capacity does it have, etc. The foundation must be equipped with vertical and horizontal waterproofing and insulation.
Under no circumstances should you skimp on materials for the foundation. Use concrete m200. Reinforcement should be made from special rods connected to each other with clamps.
Foundation waterproofing
Along with work to reduce the water resistance of concrete, we must not forget about waterproofing and protection from the effects of surface and groundwater. The most economical method is to apply a bitumen coating, but it is acceptable when access to the base of the building is not limited. If there is no gap between the foundation wall, then the waterproofing material is laid directly in the trench, pit, or attached to the formwork in such a way that the protective layer is not damaged when dismantling it. Roofing felt, roofing felt, and rolled glassine are often used. This applies to vertical insulation.
Specifics of the foundation for heaving soil
One of the key ones is the strip foundation, however, it is necessary to dig a special pit about 0.7 m deep under it. Having prepared the pit, the side walls are reinforced with waterproofing material, in particular polyethylene.
After this, the dry mixture is added in 2-3 layers approximately 15 cm wide, then it is all well compacted. The next stage requires formwork for the base.
Waterproofing is again installed on top of the pillow and a reinforcement frame is created.
It turns out that a non-buried foundation on heaving soil can easily withstand high pressure.
After this, concrete mixture is added to the formwork. Since it did not have time to harden, large reinforcement bars are installed.
Another small feature - it is advisable to knit the reinforcement. Welded reinforcement may be too brittle and brittle.
Less common is a pile foundation on heaving soils, since its construction requires the use of special equipment and high labor costs.
It is chosen only in cases where the freezing point of the ground exceeds 1.5 m.
Piles should be deepened by at least 3-4 m; as a result, products are often made from concrete or reinforced concrete of all types, in particular driven, driven or screwed.
A drainage system is created throughout the entire site of the house and the base is waterproofed.
An excellent solution may be a columnar foundation, which is constructed for frame buildings or low-rise buildings.
It, like a pile foundation, is created below the freezing level.
The main material for the construction of pillars is considered to be high-grade reinforced concrete, which can withstand a variety of loads and external pressure.
In this case, the anchor platform is attached to the supporting frame and will act as a support for the building.
You can build a columnar foundation with your own hands using asbestos pipes with a large reinforcement cage.
A layer of epoxy resin is created on the outside; as a rule, the reinforcement frame is made from wire approximately 10 mm thick.
A floating slab base on heaving soils is created together with unstable layers.
With this help, the walls of the house do not experience various deformations from the outside and, thus, do not collapse; the appearance of even small cracks is excluded.
The construction of a foundation on heaving soil as a monolithic slab can be created in two ways: slightly buried (when there is no need for a basement or plinth) or as a deep slab.
Read also: Slab foundation technology, video
A pit of the required depth is dug under the foundation, the bottom of which is covered with ordinary crushed stone.
Blind area
At the base of the building there is another zone in which precipitation can accumulate, this is the junction of the top layer of soil and the foundation. In order to drain melt and rainwater from the base of the building, a blind area is installed. It is a platform around the perimeter of the house, which is installed at an angle of 15 - 30 0 and does not allow moisture to linger near the vertical part of the base. As a rule, its cut is a multi-layer cake, consisting of an underlying layer and a coating. The basis for the underlying layer is a sand and gravel mixture, which is well compacted by compaction. Then we lay the reinforced frame, the fact is that any coating works well in compression, and the reinforcing mesh will compensate for tensile loads. Afterwards the finishing layer is applied, it can be natural stone, concrete, asphalt or other suitable building material. To maintain the integrity of the surface, do not forget to lay expansion joints; linear expansion has not yet been canceled. The width of the platform ensures the collection of water from the roof, so approximately this size varies from 70 to 110 mm.
Features of aerated concrete blocks
Here we will consider those characteristics that have a direct impact on the foundation for a house made of aerated concrete. Before choosing a type, you need to consider the following features.
Aerated blocks are piece material. Even with the right choice of masonry mortar and compliance with the technology for performing the work, they are poorly connected with each other. This factor results in the fact that the walls of the building are extremely sensitive to various deformations of the base.
If the foundation for a house made of aerated concrete subsides or, conversely, rises from the ground, cracks may appear on the walls of the building. In most cases the cracks will be inclined. The opening width and length depend on the scale of displacement of the supporting part of the building. To prevent damage, it is necessary to provide reliable supports that will resist various types of displacement. The design must connect the wall from individual blocks into a single system.
The task of the foundation is to prevent such phenomena
The foundation for aerated concrete needs a less powerful foundation than for a brick house. This is caused by the lower density of the material, and, accordingly, the mass. For comparison, the density of aerated blocks ranges from 350 to 700 kg/m3, while a brick wall will have a density of 1800 kg/m3. Blocks with a minimum density cannot be used as structural elements; the material of load-bearing walls weighs from 500 to 700 kg per cubic meter.
Despite the advantages of blocks compared to brick, it is worth remembering that the material is inferior to wood. The building will also be heavier than a frame house. When selecting foundations for houses made of lightweight aerated concrete, it is necessary to take this feature into account.
Thermal insulation
No matter how much effort is made, it will not be possible to completely eliminate the ingress of moisture, but its destructive effect can be minimized. For this purpose,
measures to preserve heat. The concrete structure itself does not have heat-protective properties, so it is additionally insulated.
This will reduce the negative impact of negative temperatures on the moisture contained in the body of the foundation and the basement of the building. Extruded polystyrene foam is recognized as the most effective material today. Its structure is such that it does not absorb moisture at all and retains its thermal insulation properties for a long time, maintaining the bearing capacity and performance characteristics of the foundation. Basalt insulation, polyurethane foam and polystyrene are also used.
Cladding the base part is necessary not only for aesthetic purposes, but also for practical ones. The decorative coating protects the heat-insulating layer from mechanical damage and atmospheric influences.
Choosing the optimal foundation for an aerated concrete house
Korovin Sergey Dmitrievich
Master of Architecture, graduated from Samara State University of Architecture and Civil Engineering. 11 years of experience in design and construction.
When deciding which foundation is best for a house made of aerated concrete, several factors must be taken into account. First of all, the design features are influenced by the properties of the wall material. Foundations for houses built from aerated concrete must take into account some of the distinctive characteristics of this material.
Ventilation holes and vents
Dampness, mold and musty air in the premises are the result of improper operation of the ventilation system at best, and at worst, its complete absence. And there is no escape from this. Condensation of cold air, vapors and gases resulting from human activity, moisture from the ground - all this accumulates in basements and basements and, in the form of evaporation and water droplets, settles on the walls and inside structures, destroying and reducing their load-bearing capacity. In order to avoid this phenomenon, it is necessary to ensure air circulation using ventilation holes and vents. However, for a full-fledged process, air exchange must be commensurate with the volume of the premises and the total area of the vents. There are certain rules for the installation of vents that stipulate these parameters. So, to ventilate a space of 14 m2, the total area of the ventilated openings must be at least 0.09 m2. In terms of using ordinary pipes or boxes as vents, this will be equivalent to 10 round holes with a diameter of 11 cm and 2 rectangular holes, with sides of 225 and 200 mm. There must be at least two vents for air intake and exhaust; when using a larger number of holes, the following arrangement is recommended: the outer ones are removed from the corners of the building by approximately 900 mm, the rest are installed at an equidistant distance opposite each other.











