Composite driven piles - reinforced concrete structures consisting of several elements, are used to create supports of considerable length - up to 36 m. The use of solid piles in these cases is difficult or impossible due to the limited capabilities of driving installations.
Pile reinforcement
The operating and installation conditions for driven and bored (or drilled injection) piles are different and determine the reinforcement.
SNiP 2-02-03 85
Reinforcement of driven structures
Incomplete (along the length) reinforcement is not allowed.
Additional reinforcement strengthens parts of the pile that experience increased loads: The upper part is reinforced with meshes (4-5 layers at a distance of 5 cm). Such reinforcement will allow the pile to better resist the blows of a pile driver; The lower part is reinforced with a conical cage connected to the reinforcement. This strengthens the tip of the pile, which during driving experiences significant loads when encountering stones and rocky soil.
Reinforcement of bored and drilled injection structures
In case of homogeneous soils, incomplete reinforcement (lower part) is allowed for hanging piles.
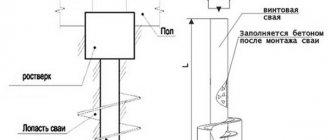
a – pile – stand, b – hanging pile
A hanging pile is a pile supported on compressible soils due to friction. Unlike a stand pile, which rests its lower part on incompressible layers of soil.
The reinforcement scheme for bored and drilled injection piles repeats the reinforcement scheme for driven piles, but the following elements are missing:
- Reinforcement of the pile head with mesh;
- Mounting loops and centering pin;
- Conical cages at the bottom of the pile.
Longitudinal type reinforcement
In stable, medium-dense soil (loam, clay, sandy loam), longitudinal reinforcement can be used. This reduces the cost of the pile, but reduces the bending and tensile strength. Piles reinforced longitudinally are not allowed for use in the construction of hydraulic structures and in earthquake-prone areas.
With longitudinal reinforcement, the reinforcement frame consists of parallel rods forming a volumetric frame (piles up to 30x30 cm - 4 pieces and 6-8 pieces per pile 40x40 cm). The diameter of the reinforcing bars is 12-15 mm and class A300 (A-II) or A400 (A-III).
Reinforcement of longitudinal-transverse type
With longitudinal-transverse reinforcement of reinforced concrete, a spatial frame is made, from longitudinal (diameter 10-15 mm and class A300 (A-II) or A400 (A-III)) and transverse (diameter 6-8 mm and class A240 (AI) or from the same material as the longitudinal) reinforcement. It is permissible to use reinforcing mesh rolled into a cylinder (for round piles) if it fits the cross-sections of the longitudinal and transverse reinforcement.
Reinforcement using the prestress method
The use of prestressed longitudinal reinforcement will significantly increase the pile's resistance to tensile and bending loads. For prestressed reinforcement, steel 30-ХГ2С or 35-ГС is used. Size 13 – 20 mm.
In private construction, reinforced concrete with prestressed reinforcement is not often used.
Reinforcement of the pile-grillage assembly
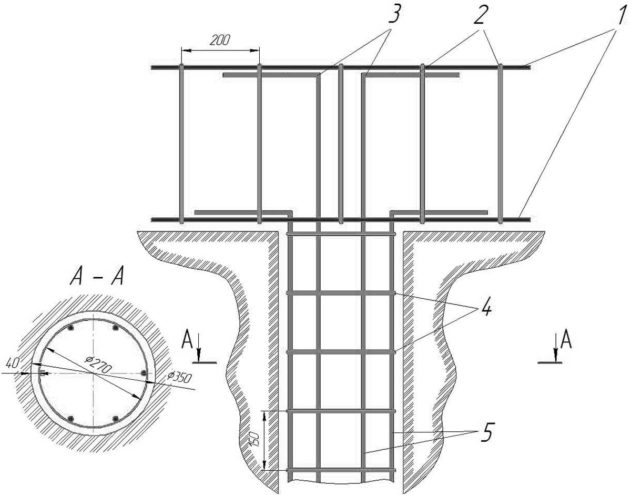
It is required to connect the longitudinal reinforcement of the pile and the longitudinal reinforcement of the grillage (1,3,5) using twisting or welding. The metal reinforcement of the pile is bent and connected to the longitudinal reinforcement of the grillage by welding or twisting with wire. For the reliability of the assembly, the length of the reinforcement must exceed 35 cm. Non-metallic reinforcement cannot be bent. In this case, they also connect the longitudinal reinforcement of the pile and the grillage at the intersection points and ensure that the pile reinforcement is embedded to a depth of at least 50 cm.
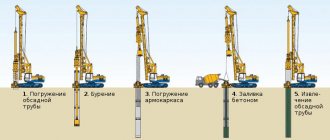
How piles are driven
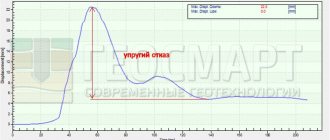
Reinforced concrete piles must be driven below the freezing level.
The main advantage of the pile foundation of a building is that, regardless of the soil temperature during its construction, the supports do not allow the structure to deform during operation under the influence of seasonal freezing and thawing of the soil. This strength is due to the fact that the structural elements of the foundation are driven strictly vertically below the freezing level of the soil.
Driving piles occurs to the limit of reaching a dense layer of soil if the soil is weak. Or by washing, if the soil is very dense. In this case, a hydrocopper and the necessary pile driver are used: water is supplied under pressure along the support, which softens the soil and reduces the friction force during deepening upon impact.
When constructing a pile foundation yourself, you should make sure that the support has the ability to go deeper as the load increases.
During the construction process, the load on the foundation will increase and the supports will lower.
If one of them hits an obstacle (stone, rock), this will lead to a redistribution of the load and, as a result, a skew of the building.
If the soil is frozen below the level of driving the support, then the work is carried out using a steam needle. A well is drilled, a needle is lowered into it, through which steam is supplied. After the soil thaws, the pile driver comes into operation and the support easily enters the ground.
Calculation
Let's look at the example of calculating reinforcement. You can take the parameters necessary for the calculation in your project. For our example we will assume the following:
- 16 piles in our foundation;
- Pile pitch – 2 meters;
- Pile height – 2 meters;
- The diameter of the pile is 20 centimeters.
Reinforcement will be carried out evenly along the entire length. The grillage-pile connection will require at least 35 cm for longitudinal reinforcement. Based on SNiP, reinforcement of a bored pile of this diameter must be carried out with at least 4 rods. 2.35*4=9.4 meters for one column, and 16*9.4=150.4 meters for all 16 piles.
In order not to waste time with scraps, take reinforcement 5-15% more than calculated.
We will consider the longitudinal reinforcement scheme. The reinforcement frame must have jumpers (clamps) with a step of 1 meter to maintain its shape. The jumper (clamp) is a circle or polyhedron (for 4 bars of longitudinal reinforcement, in our case a square). 3.14*0.2=0.63 meters – for one lintel or 0.63*3=1.9 meters – for one bored pile. 16*1.9=30.4 meters – for all 16 piles. To connect, use either welding or binding wire with a diameter of 1.2-1.7 mm. One twist will require about 30 cm of wire. 12*0.3*16=57.6 meters – for 16 bored piles. If you want to widen the pile at the bottom, you will need 10-15% more reinforcement.
Attaching the decking to the piles
To ensure that the pier or pier lasts for a long time, valuable wood with a high level of water resistance is used for flooring:
- acacia;
- larch;
- oak;
- merbau;
- ipe;
- garapa, etc.
Each of these wood species has a unique texture, aroma, and color. Reducing the cost of berth installation is possible by using water-repellent wood-polymer materials from which deck boards are made. These materials are cheaper than natural ones and have the following qualities:
- do not rot or decompose;
- do not deform (are not subject to drying out, swelling, cracking);
- do not require painting or opening with varnish;
- can withstand solar radiation and large temperature changes without loss (do not fade, do not fade);
- resistant to mechanical damage;
- Thanks to the non-slip ribbed surface, they allow you to move safely on a wet pier or walkway.
Installation of wooden or polymer flooring on a pile-screw base is carried out using the hidden fastening method. When finishing structures, they install swimming ramps, railings, mooring fenders for boats and other devices.
And the main advice. When building a small bridge or pier, you can try to do it yourself (if you have 1-2 assistants for screwing the piles). If you are planning to build a large pier that extends a considerable distance from the shore deep into the reservoir, contact specialists with the necessary skills and equipment.
Making frames
Let's consider creating a spatial frame for reinforcing the pile. Be sure to take into account the protective layer of concrete (3 - 5 cm). The layer between the reinforcement and the outer surface of a reinforced concrete product. Your frame should be smaller than the internal dimension of the formwork to provide a protective concrete layer. The length of the longitudinal reinforcement must be at least 35 cm greater than the length of the pile. Coating the reinforcement with an anti-corrosion compound will extend the service life of the foundation. We recommend doing this:
- cut longitudinal rods to size;
- bend the clamps onto the mandrel (prepare all the clamps for at least 1 pile);
- if a driven pile is reinforced, then set aside a distance from the ends for reinforcement with mesh and for a conical cage at the tip;
- secure the clamp (by welding or wire), step back one step of the transverse reinforcement and secure the next clamp, make sure that the frame does not lose its shape;
- if a driven pile is being reinforced, secure the mesh to the cap and the collar to the tip, mounting loops and a centering pin if used.
Berths on stilts
In any Russian village, located on the banks of a river or lake, you can see bridges for fishing and mooring simple wooden and duralumin boats. All these structures are built on stilts. In the old days, deciduous trees (alder, oak) were used as piles. Today, more durable modern metal structures are used more often.
There are two types of metal piles:
- driving;
- screw.
Driven piles are steel pipes with pointed tips that are driven into the ground with special machines - pile drivers. When constructing supports on water, driven piles are almost never used, since when driven in, their anti-corrosion coating is damaged and deformation occurs. Because of this, the piles often do not reach solid layers of the soil and cannot serve as reliable support for the pier. Access to the water is also often difficult or impossible.
Another thing is screw structures, which are ideal for water structures. Thanks to the screw-blade, they are effortlessly and smoothly screwed into the bottom soil with minimal risk of deformation of the pile body. The length of steel pipes with screws at the end can reach 11 meters (if necessary, they can be extended or shortened).
An important role is played by the thickness of the walls of the trunk and the diameter - the larger it is, the more significant the mass the pile can support.
Basic methods of extracting piles
According to the principle of operation, all equipment used to extract piles is divided into two groups:
- Using static forces on the extracted foundation elements (large jacks, winches with pulley systems and truck cranes).
- Using dynamic influences (double-action pile driving hammers and pile pullers (also known as vibratory drivers) extracting piles using vibration).
It is believed that the removal of piles using devices of the second group, especially vibratory hammers, is most effective.
Classification and marking of piles
GOST No. 19804 “Prefabricated reinforced concrete piles” provides for the division of reinforced concrete products into the following types:
- C - construction of a solid square section, composite or solid type;
- SP - a pile of square cross-section with an internal cavity, solid;
- SC - hollow structure of round cross-section, solid/composite;
- CO - pile-shell, composite/solid.
The piles have a unified marking of type C60.40-A800, in which:
- C - foundation pile of square section;
- 60 — length (in decimeters);
- 40 — cross section, cm;
- A800 - reinforced with reinforcement made of A800 steel.
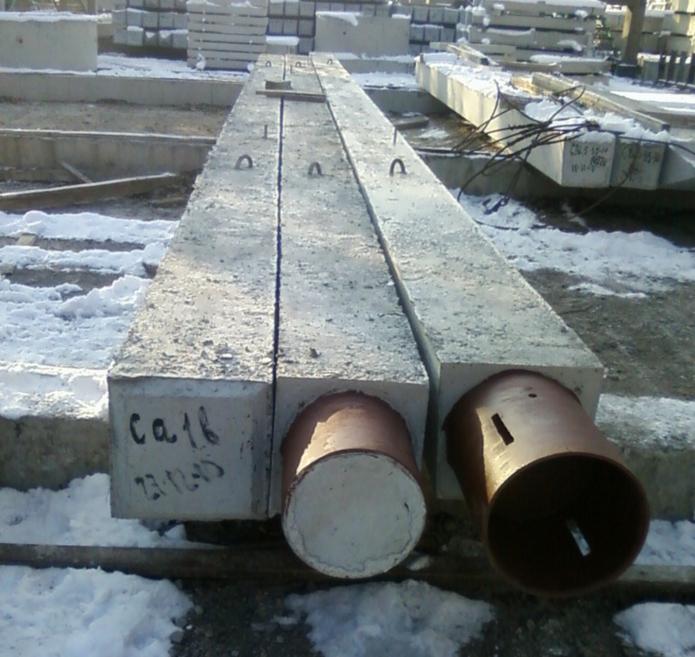

Rice. 1.1 : Composite square piles
Composite piles are structures consisting of several (2 or 3) interconnected parts. Such piles are used in cases where the length of solid supports is not enough to pass through the surface layers of unstable soil. Composite products differ in terms of marking - each of the component sections of the pile has its own nomenclature of type C60.20-В-СВ4, where:
- C – square pile;
- 60 — section length, dm;
- 20 — cross section, cm;
- B - upper part (H - lower);
- SV - connection by means of a welded joint;
- 4 — method of reinforcement.
Product diameter and load
They play a big role in the choice of material for the construction of the planned structure. The strength of the material, and, accordingly, the reliability and durability of the foundation as a whole depends on the size of the screw pile for the foundation and the size of the head. The dimensions of the head are proportional to the diameter of the pipe. Examples of ratio:
- 150*150*3 mm – 76 mm;
- 150*150*4 mm – 89 mm;
- 200*200*5 mm – 108 mm.
Screw piles with a diameter of 57 mm
Such elements can withstand a maximum weight of up to 800 kg. Screw piles of this size can be used on moist and moving soil. They are suitable for constructing fences made of metal and plastic mesh. Sometimes they are used as a foundation in the construction of gazebos and garages with light cladding.
Call us or Request a call
Screw piles with a diameter of 89 mm
The bearing capacity of the products is 1.4 tons. They are used in the construction of small country houses, garages, gazebos, bathhouses, and monumental fences. They tolerate areas of water bodies and underground sources well. They have excellent grip on the ground. Withstand heavy loads. The foundation on screw piles of this size is not subject to swelling. Screw piles of this diameter are suitable for the restoration of a wide variety of buildings. They will become a reliable support during the construction of piers and moorings.
Screw piles with a diameter of 108 mm
The bearing capacity of products of this size is 3.5 tons. Suitable for the construction of panel structures, log houses, bathhouses and timber buildings. They are used for the construction of warehouses, technical facilities and platforms. Installation of screw piles and the entire foundation is carried out using special equipment. It is not possible to carry out correct installation manually.
Screw piles with a diameter of 133 mm
The bearing capacity of the products reaches 6 tons. They are suitable for a wide variety of projects on any soil. The screw foundation will withstand structures made of concrete blocks, bricks, as well as monolithic structures. Piles of this size have maximum strength and stability. They have a long service life. Installation of the foundation can be carried out in any weather if special equipment is available.
Advantages of the driving method
The high productivity of the method, compared to static and vibration indentation, installation of piles in this way is common.
Impact method is used:
- When creating foundations for industrial and residential buildings.
- On the construction of waterworks, piers, and buildings on the water.
- For the installation of bridges.
- When installing power lines, laying main pipes.
The technology has limitations for use in urban areas, since the structure of the soil changes and dynamic loads are transferred to neighboring buildings. When using preliminary wells, these restrictions are removed, since driving is carried out with small blows.
The driving equipment is lightweight and small in size, so it can be used even on loose soil. Moreover, the piledrivers are equipped with a highly passable wheelbase.