November 1, 2020 Stroyexpert Home page » Foundation » Installation
Cutting down piles
One of the most common types of foundations has become a pile foundation on steel or reinforced concrete piles. The technology for installing supports is divided into screw and driven. With any method, to continue construction it is necessary to cut them at the same height. How piles are cut down will be discussed later.
Jackhammer
The method can be applied
- for small volumes of work, if ordering special equipment is impractical (for example, when building a cottage).
- using an excavator with a jackhammer attachment

Flaws:
- Large labor costs.
- Low speed.
- Shock vibration and rumble.
- Damage to the fittings is possible.
- There is a risk of damage to the pile body (crack formation).
Methods for cutting piles
In practice, several methods are used to level pile supports. The use of a particular technology is influenced by:
- Composition of the material from which the pile is made.
- Pile dimensions.
- Availability of necessary technical equipment.
The cutting of pile heads can be done manually or mechanized. In the first case, all work is done using hand tools: a jackhammer, a grinder, scissors for cutting reinforcement, etc. The mechanized method involves the use of special heavy equipment, and the cutting of supports in this case is carried out without the direct application of human physical force. When mechanized cutting of piles, two types of technical equipment can be used - cutting cutters and hydraulic mechanisms.
The entire process of leveling pile heads is regulated by the provisions of SNiP “Construction of pile foundations” of 1982, paragraph 3.4. According to this standard, it is possible to begin leveling felling of supports only after all piles have been buried and an acceptance certificate has been drawn up with a diagram attached to it. After this, a technological map of the upcoming work is drawn up, and cutting lines are marked.
To mark the cutting line, you must use precision tools - a laser level or level. The reference point marked on the lowest pile is taken as a reference point: each subsequent marker is measured from it. It is not allowed to count the height of each pile from the zero ground level. In this case, there may be a large discrepancy in the height of the supports due to unevenness of the soil surface.
Hydraulic cutting of pile heads
The most modern and popular method of felling.
- The equipment is connected to the working boom of a crane or excavator.
- Connected to the hydraulic system.
- The piston compresses the head, exerts pressure on the cutting teeth, crushes the concrete, and removes it from the reinforcing frame
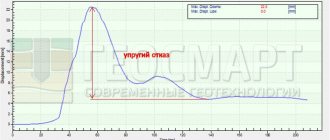
The force exerted on the pile during the crushing process is about 1000 tons.
Before
After cutting
Advantages of the method:
- High efficiency (from 250 piles per work shift by two workers using one excavator).
- Simplicity of the workflow.
- No noise.
- A neat cut, no cracks form along the body of the pile.
- The fittings are not affected.
- The equipment is reliable, damaged parts are easily replaced.
Flaw:
for small volumes (for example, suburban construction), the use of special equipment is unprofitable.
The need to align the heads
Today, there are several types of pile technologies, each of which has its own pros and cons, its own area of application and technical nuances. All pile foundations are divided into:
- Driven - when piles are driven into the soil using physical force. Most often, mechanical or manual impact hammers are used for these purposes, less often - vibrating mechanisms and machines that press the pile into the ground with its own weight.
- Bored. In this case, holes of the required diameter and depth are drilled in the ground, into which reinforcement is laid and concrete is poured.
- Screw. The piles of such a foundation are made in the form of a pointed pipe, around the lower end of which a spiral-shaped metal petal is installed. The deepening of such a pile occurs due to its rotation around its own axis using a special device - a pile driver. At the same time, the pile itself, going deeper into the ground, works like a corkscrew screwed into a cork.

The depth of pile supports, as well as their height above the soil surface, is regulated by design documentation. This depends on the depth of strong soil rocks, the mass of the future building, its technical features, etc. Depending on these aspects, the type of piles is selected and a specification of the structural elements of the foundation is drawn up. The piles serve as supports for the top frame or grillages, on which, in turn, the entire building rests. In this regard, for a properly equipped pile foundation, the top of the supports should be located at the same level.
In reality, achieving such an ideal result is almost impossible. When driving piles, the variation in height can reach tens of centimeters. This indicator is influenced by the geological parameters of the soil, the size of the piles and the method of deepening them. But, nevertheless, construction standards require the most even arrangement of pile supports relative to the horizon level.
To level the supports, the piles are cut to the same height.
We cut off the piles with our own hands
Depending on the material of the supports, cutting down the pile heads can be done using various tools and can be carried out both by specialized construction teams and by the owners of the land plot themselves. We will describe below professional methods of performing this type of work. First, let's look at how you can cut down piles using available tools without the necessary qualifications of workers.
We cut steel supports
Quite simple and easy to do on your own is cutting piles made from round steel pipes. We are talking about screw supports equipped in the lower part with a single or double-thrust screw, which facilitates the process of penetration into the ground to a depth of more than 2 meters.

Trimming metal supports using a grinder
To position the heads of such piles in one horizontal plane, which will ensure high quality installation of any structure on them, the racks must be cut. This is done as follows:
- For any corner support, as a rule, the required level is marked using a white marker. A simple method will help you get an even horizontal line on a round pipe. It is enough to take a flat strip of paper, wrap it around the pile and align the edges. You can mark the required horizontal line on top of the sheet.
- Using a grinder with a metal disc installed on it, carefully cut a line along the entire perimeter to a depth of about 1 mm;
- Next, according to the intended risk, the pile is cut down;
- To mark and determine the general horizontal plane from the cut first support, use a laser level to mark the required cutting height on the remaining pipes.
Cutting concrete piles is a difficult task
For high-rise buildings, reinforced concrete piles are often used instead of screw piles. Poured supports, which are a cylindrical frame with steel reinforcement installed in it, filled with concrete mixture, can be made to the required general level. The hammers need to be further trimmed.
It is much more difficult to cut piles made of reinforced concrete than steel ones. In this case, there is often a need to preserve the reinforcement bars protruding above the cut support for the installation of a common head trim - a grillage. The main tool for solving this problem is a pneumatic jackhammer.

Do-it-yourself felling of concrete piles
Cutting down piles, the technology of which is described above, is not suitable for concrete supports. At the same time, there are common points in both processes:
- Similar to metal ones, reinforced concrete piles are marked, indicating the required cutting level. A marker and a sheet of thick paper are also suitable for this.
- A groove is cut along the marking line to a depth of 1.5-2 cm.
- Then, gradually, at the required level, pieces of the pile heads are broken off using a jackhammer until the concrete is completely destroyed;
- If there is no need to make a grillage, the exposed reinforcement bars are subsequently cut off using a grinder with a metal disc.
The disadvantages of this method of cutting piles are increased noise during operation and large formation of cement dust, which may be inadequately perceived by residents of neighboring areas. When installing a large number of supports and to speed up the process, it is better to use the forces of professionals. They not only have the necessary equipment for cutting piles, but also the experience in using it.
Control during the construction of pile foundations
| Stages of work | Controlled Operations | Control (method, volume) | Documentation |
| Preparatory work | Check: | Passports (certificates), inspection report of hidden work, general work log |
| — availability of a quality document; | Visual | |
| — the quality of the surface and appearance of the piles, the accuracy of their geometric parameters; | Visual, measuring | |
| — the presence of a breakdown of the pile field; | Visual | |
| — availability of PPR for the installation of a pile foundation; | Same | |
| — availability of an inspection certificate for previously completed earthworks; | Same | |
| — presence of pile markings; | Same | |
| — compliance of piling equipment with the project. | Same |
| Driving piles and cutting pile heads | Control: | General work log, pile driving log |
| — accuracy of installation at the place of immersion of piles; | Measuring | |
| - failure rate of driven piles; | Same | |
| — amplitude of vibrations of piles at the end of vibration loading; | Same | |
| — position in terms of driven piles; | Same | |
| — marks of pile heads; | Same | |
| — verticality of the axis of driven piles; | The same, 20% of piles selected at random | |
| — dimensions of defects in pile heads. | Technical inspection, each pile |
| Acceptance of completed work | Check: | Certificate of inspection of hidden work, as-built geodetic diagram |
| - actual deviations of driven piles from the alignment axes in plan and from the design elevation; | Measuring, each pile | |
| — compliance of the location of the piles in the plan of the pile field with the project. | Visual, measuring |
| Control and measuring instruments : metal tape measure, plumb line, level, theodolite, tacheometer. |
| Incoming and operational control is carried out by : a foreman (foreman), a surveyor - during the work process. Acceptance control is carried out by : quality service workers, foreman (foreman), representatives of the customer’s technical supervision. |
SNiP 3.02.01-87 “Earth structures, foundations and foundations.”, clause 11.6, table. 18 (excerpts from table)
or
SP 45.13330.2012 “Earth structures, foundations and foundations.”, clause 12.7.5, table. 12.1 (excerpts from table)
| Technical requirements | Limit deviations | Control (method and volume) |
| 1. Installation of piles at the immersion site with diagonal or diameter dimensions, m: | Without conductor, mm | With conductor, mm | Measuring, each pile |
| up to 0.5 | ± 10 | ± 5 | |
| 0,6 — 1,0 | ± 20 | ± 10 | |
| over 1.0 | ± 30 | ± 12 |
| 2. Magnitude of failure of driven piles | Should not exceed the calculated value | Same |
| 3. Amplitude of oscillations at the end of vibration immersion of piles and pile-shells | Same | Same |
| 4. Position in plan of driven piles with a diameter or cross-sectional side up to 0.5 m inclusive: | Same |
| a) single-row arrangement of piles: | |
| across the axis of the pile row | ±0.2d |
| along the axis of the pile row | ±0.3 d |
| b) bushes and strips with piles arranged in two and three rows: | |
| extreme piles across the axis of the pile row | ±0.2d |
| the remaining piles and the outermost piles along the pile row | ±0.3 d |
| c) a continuous pile field under the entire building or structure: | |
| extreme piles | ±0.2d |
| medium piles | ±0.4d |
| d) single piles | ± 5 cm |
| d) column piles | ± 3 cm |
| 5. Position in terms of driven, cast-in-place and bored piles with a diameter of more than 0.5 m: | Same |
| a) across the row | ± 10 cm |
| b) along the row with cluster arrangement of piles | ± 15 cm |
| c) for single hollow round piles for columns | ± 8 cm |
| 6. Position of piles located along the bridge facade: | In respect of | Axis tilt | Same |
| a) in two rows or more | ±0.05d | ±0.1 d | 100:1 |
| b) in one row | ±0.02d | ±0.04 d | 200:1 |
| 7. Markings of pile heads: | Same |
| a) with a monolithic grillage | ± 3 cm |
| b) with a prefabricated grillage | ± 1 cm |
| c) foundation without grillage with prefabricated cap | ± 5 cm |
| d) column piles | – 3 cm (± 3 cm in SP) |
| 8. Verticality of the axis of driven piles except rack piles | ± 2 % | Measuring, 20% of piles selected at random |
| 13. Continuity of the shaft of piles made by underwater concreting method | The pile shaft should not have discontinuities | Measuring, testing samples taken from cores drilled into piles or in another way |
| 14. Continuity of the trunk of hollow cast-in-place piles | The trunk should not have concrete spills with an area exceeding 100 cm2 or exposures of working reinforcement | Visual, each pile |
| 16. Requirements for pile heads, except for piles to which loads are transferred directly without a head (platform joint) | The ends should be horizontal with deviations of no more than 5°, the width of concrete chips along the perimeter of the pile should not exceed 50 mm, wedge-shaped chips at the corners should be no deeper than 35 mm and a length of at least 30 mm shorter than the embedment depth | Technical inspection, each pile |
| 17. Requirements for pile heads to which loads are transferred directly without a head (platform joint) | The ends must be horizontal with deviations of no more than 0.02, have no concrete chips around the perimeter more than 25 mm wide, or wedge-shaped corner chips to a depth of more than 15 mm | Same |
| Note: d is the diameter of a round pile or the smaller side of a rectangular one. |
Not allowed!
— immerse piles with cracks larger than 0.3 mm.
Requirements for the quality of used structures
GOST 19804-91 “Reinforced concrete piles. Technical conditions." , clause 1.3.11, table. 3
or
GOST 19804-2012 “Prefabricated reinforced concrete piles.” , clause 6.13, table. 3
| Name of deviation of the geometric parameter of the pile | Name of the geometric parameter of the pile, mm | Maximum deviations, mm |
| Deviation from linear size | The length of the prismatic (cylindrical) part of the pile with non-prestressing reinforcement at the length of the pile: |
| up to 8000 incl. | ±25 |
| St. 8000 to 16000 incl. | ±30 |
| St. 16000 | ±40 |
| The same, piles with prestressed reinforcement | ±50 |
| Size (outer diameter) of the cross section of the pile: | |
| up to 250 incl. | +15;-6 |
| St. 250 to 500 incl. | +20;-8 |
| St. 500 to 1000 incl. | +25; -10 |
| St. 1000 to 1600 incl. | +30; -12 |
| St. 1600 to 2500 incl. | +40; -15 |
| St. 2500 | +50; -16 |
| Pile wall thickness of types SP, SK and SO: | |
| up to 120 incl. | +10;-5 |
| St. 120 to 250 incl. | +25;-6 |
| Point or tip length | ±30 |
| Distance from the center of the tip or tip to the side surface of the pile | 15 |
| Distance from the center of the lifting (mounting) loop, pin, sleeve and slinging mark to the ends of the pile | ±50 (50 in the new GOST) |
| Deviation from straightness of the profile of the side faces of the prismatic part of the shaft (guides of the cylindrical surface) of the pile along the entire length, mm: | ||
| up to 8000 incl. | — | ±25 |
| St. 8000 to 16000 incl. | — | ±30 |
| St. 16000 | — | ±40 |
| Deviation from perpendicularity of the end plane: | ||
| in the head of the pile and the pile-shell | — | 0.015 side size (diameter) of the cross section of the pile |
| in the junction area of a composite pile of solid square section | — | 0.01 side size (diameter) of the cross section of the pile |
| in the junction area of the composite pile-shell | — | 0.005 side size (diameter) of the cross section of the pile |
The following are not allowed on the surface of piles:
- sinks with a diameter of 15 (20 new GOST) mm and a depth of 5 (10 new GOST) mm;
- concrete sagging more than 5 mm high;
- local concrete chips at the corners of piles with a depth of more than 10 (20 new GOST) mm and a total length of more than 50 (100 new GOST) mm per 1 m of piles;
- concrete and shell fragments at the end of the pile;
- cracks, with the exception of shrinkage cracks, more than 0.1 mm wide.
Review of models from leading manufacturers
The construction market today offers various models of equipment for cutting piles from such well-known manufacturers as Taets, Delta, Pilemaster, Kinhan
.
Pilemaster
Pictured is Pilemaster equipment for cutting piles
Equipos especiales Pilemaster SA is known not only in its homeland in Spain, but throughout all European countries. This brand is represented in Russia. Keeping up with the times, the company, together with a Spanish partner, has launched the production of equipment of European standards to solve highly specialized construction problems. This made it possible to offer Russian builders modern equipment at competitive prices. The time for extending and retracting the tooth (one cycle) is 8-10 seconds, this makes it possible to cut off 1 m of pile per minute, without taking into account the time required for moving and transporting the cut head.
The video shows the operating principle of equipment from Pilemaster for cutting piles
The potential of pile-cutting equipment is 4-5 thousand pile heads, then an inspection is needed to replace the teeth (30 thousand rubles for 4 pieces). The synchronization of the teeth is ensured by an active extension synchronization system or (in a simplified version) a ring circuit for connecting the power cylinders. It takes 15-20 minutes to install the tooth, which can be changed directly at the construction site. The equipment has a one-year warranty. The network of warehouses with consumable components covers all regions of Russia: Moscow, St. Petersburg, Yekaterinburg, Novosibirsk, Krasnoyarsk.
Taets
In the photo - Taets equipment for cutting piles
The Taets company from Holland, founded in 1978, is one of the leaders in the production of pile-cutting equipment. Its reputation is impeccable, but the high cost of installations does not allow small construction firms to take advantage of their advantages. The payback period for Taets equipment is several years, and this circumstance does not increase the demand and its implementation among foundation-building organizations. Taets has 9 different models of nozzles for cutting piles, but only two of them are acceptable for the Russian market, the rest do not comply with GOST.
Video showing your image using Taets equipment
Cutting speed ─ 1 m.p. piles ─ at Pilemaster level. Installation potential ─ 4-5 thousand pile heads, subsequent change of teeth - 200 thousand rubles for 4 pieces. Replacement in this case is only possible in a factory setting, since the technology involves heating and cooling the tooth to fix it. The synchronization of the cylinders is ensured by the active extension synchronization system. The equipment has a one-year warranty.
Kinhan
In the photo - Kinhan equipment for cutting piles
The Italian company Delta is based on equipment from the Chinese brand Kinhan; today it is produced under the domestic brand Impulse SV400. And although the manufacturer denies the similarity with Chinese analogues, it is positioned precisely as Chinese. Installation potential ─ 3-4 thousand pile heads; when replacing teeth, new ones cost 120 thousand rubles for 4 pieces. The replacement procedure is only possible under factory conditions, since heating and cooling are necessary to fix the tooth. Warranty period ─ 1 year. Consumers familiar with this equipment compare it to Pilemaster or Taets.
The video shows the process of cutting piles using Kinhan equipment
But experts note differences in the power cylinders (Ø is much smaller than other models), which means that its power and performance are much lower. The technical specifications on the dealer website indicate a productivity of 160 piles per shift, which is 20% lower than Pilemaster or Taets. The synchronization of the operation of the power cylinders is not ensured by anything. When choosing a supplier, these parameters must be taken into account.