Long before the start of construction of a capital structure, a whole range of measures is carried out to ensure the correct selection and further calculations of structural elements, in particular foundations. Testing of piles is carried out at the stage of engineering surveys and control checks during the construction period. During the work, the load-bearing capacity and possible deformations are determined, after which the data is compared with the calculated indicators specified in the design documentation. If necessary, adjustments are made to the type and dimensions of piles, as well as the technology for their deepening.
Stages of work at which static research is necessarily carried out
The implementation of these verification studies in accordance with the requirements of regulatory documents is carried out at several stages:
- The stage of research and design activities, which allows you to determine the cross-section, dimensions, estimates, which are provided for by the load-bearing capacity assessment
- Immersion and extraction phase, which provides the ability to relate design data to actual efforts
Carrying out this work helps to evaluate the optimal technical characteristics, allowing you to determine the optimal type of supports used. When carrying out calculations, the smallest of the achieved values is used, indicating the level of readiness for resistance.
As a rule, static and dynamic testing of piles allows obtaining the most reliable data. At the same time, the dynamic option provides the opportunity to obtain data of fairly high reliability.
For this reason, the dynamic option for conducting verification activities is chosen only in a situation where complex and large-scale construction is planned, requiring the use of a large number of support pillars in the foundation being created.
Static load tests of piles are sufficient when planning the construction of a private house from any materials.
FAQ:
How much does it cost to relocate equipment (mobilization)? Cost of relocation of equipment: 20,000 rubles. More details at the link: relocation of equipment. How much do static tests cost? Read more about static tests at the link: static tests of piles How to find out the exact price of the work and what is needed for this? The exact cost of the work can be determined after calculating the distance of the object, calculating the number of piles to be driven and their cross-section, and after analyzing the soil. When taking into account the seasonal discount, the price changes significantly for the better for you. You can focus on the cost, which is shown by our online calculator: Cost calculation. When can you start work, is there a free car? Depending on the scope of work and the remoteness of the facility, the average period is about 2-3 weeks after signing the contract. Availability of cars is almost always one hundred percent, but to be sure, it is better to clarify the information with us, directly by phone Contact list. What guarantees are there on your part? All work is carried out on time, the warranty on work performed is 3 years. Certificate of permission to work How can I pay for the work? Terms of payment. All payments with our company are made only by bank transfer. List of prices for work
Procedure for conducting static testing of piles
To obtain reliable and adequate results that meet the requirements of SNP guests, you will need to follow the procedure for carrying out the work. Pile testing methods include:
- Determining the number of supports required
- Selection of possible driving locations
After calculations of these parameters, control tests of piles are carried out during construction and test piles are driven. This activity is carried out only in those places that have the most negative soil conditions. The study areas in the preliminary phase showed the highest failure during driving.
Basic conditions
Any static tests are carried out no earlier than 24 hours after the test driving. You will also need to fulfill a number of conditions:
- When testing piles with a static load in the case of using bored piles, the test begins no earlier than after 80% of the concrete used for pouring has dried
- On thawed soils, piles are introduced evenly, in load steps, without impacts.
- When assessing large clastic soils, clayey soils and dense sands, work is carried out by deepening the piles to the first 3 load levels
Serious requirements are placed on the procedure for deepening piles. The loading structure is mounted to ensure precise central application of a strictly vertical load.
Determining the necessary parameters will only be possible by using those trial options that fully comply with the technical requirements based on the load-bearing characteristics of the soil and the required characteristics.
Static load testing of piles can be carried out with the additional use of a load-bearing cage, which strengthens the head of the pile. Such strengthening will allow for full testing of piles and identification of structural connections in soils. Such a thorough analysis makes it possible, even in the case of large-scale construction, to sometimes not carry out complex dynamic tests of piles; the technique is characterized by a significant cost.
Important information
The period of “rest” of a pile in accordance with the requirements of GOST and SNIP varies depending on the type of soil and type of soil:
- When diving into dense layers of sand or coarse debris, 1 day will be required to rest
- Supports immersed in sandy foundations must rest for 3 days after work.
- When working on heterogeneous masses and clay surfaces, 6 days can be allocated to rest the buried pile
- 10 days of rest are required to determine readiness to cope with the stress of digging into fine and water-saturated sands
- For soft, plastic, flowable clay fractions, the rest period should be 20 days
During testing, a successive increase in load is required. During this period, the settlement value is monitored using dial gauges. Electronic testing devices are also required, with a measurement step of 0.1 millimeter. This step should not be overcome within 60-120 minutes of observation.
What is included in the field testing program
Based on a certain list of documentation, various characteristics and requirements, a program for testing soils with piles is drawn up. GOST indicates that at the engineering survey stage the following should be taken into account:
- results of similar studies conducted previously for nearby buildings;
- forecast of possible changes in hydrogeological conditions;
- design features of the designed facility;
- design loads on the foundation structure;
- design marks for the bottom of the grillage and the level of territory planning;
- expected movements of foundation structures taking into account operating conditions.
A program for control testing of soils with piles is drawn up based on the following adopted in the design documentation:
- types and dimensions of piles;
- options for immersing structures;
- design forces and loads;
- soil conditions of the site.
The program items regulated by GOST include:
- number of structures being tested;
- test points in the plan;
- maximum loads, minimum movements and deformations;
- methods and depth of immersion, including design failure;
- the duration of “rest” or strength gain for bored piles;
- test setup diagrams, direction and nature of loads.
One of the GOST applications indicates the required number of points to be studied. With dynamic testing methods - up to 1% of all piles, but more than six pieces. With pressing static forces - up to 0.5%, but more than two units, and with pulling forces - more than 2% or three piles. SNiP puts forward similar requirements.
The program for testing soil with piles should include a feasibility study (feasibility study) that confirms or refutes the meaning of the research.
Features of dynamic testing
As mentioned earlier, GOST and SNIP requirements oblige dynamic testing to be carried out when designing the construction of massive buildings. It is appropriate in situations where the construction of a massive structure is expected on soils with a difficult level of stability. Including a multi-storey building.
This check is carried out using a hammer. In this situation, the support is gradually driven into the ground using a hammer. As the dive progresses, real and theoretical failure values are calculated.
Such studies make it possible to diagnose weak zones of the pile field and determine the load-bearing layers of the soil. Also, pile loading data will help to estimate the forces required for driving and which the driven supports are capable of absorbing.
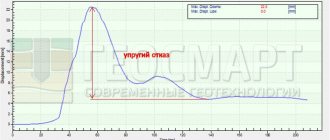
The results obtained are displayed graphically. The data helps to characterize the results taking into account the position coordinates, which are necessarily correlated with the applied efforts for the assessment.
What are the benefits of performing a live load assessment?
Experts name several factors that show the advantages of testing performed using a dynamic load over tests performed using a static load. The advantages include the possibility of using all currently existing types of supports.
This method is convenient when working with heterogeneous soils and some other factors.
Dynamic test loads
At each stage of testing, readings are taken from deflexometers. First, before loading the pile, a zero reading is taken, then immediately after the load the first reading follows, followed by sequential 4 readings every half hour. And then at intervals of an hour, and so on until stabilization (attenuation of movements). Conditional stabilization is usually called the rate of settlement of a pile in the ground of no more than 0.1 mm over the past hour.
The load when testing a pile with an indentation load is usually brought to such values that the total immersion of the pile will be at least 40 mm. During settlement of the pile into soils of solid consistency (dense sand, coarse clastic and clayey), the load is brought to the value determined by the test program, but this value should not be less than one and a half times the load-bearing capacity of the piles.
In engineering tests, the load when testing soils with a pull-out force is brought to values that cause the piles to emerge from the ground by at least 25 mm.
Loads during control testing of a pile with an indentation load do not exceed the design load on the pile, which is indicated in the foundation design.

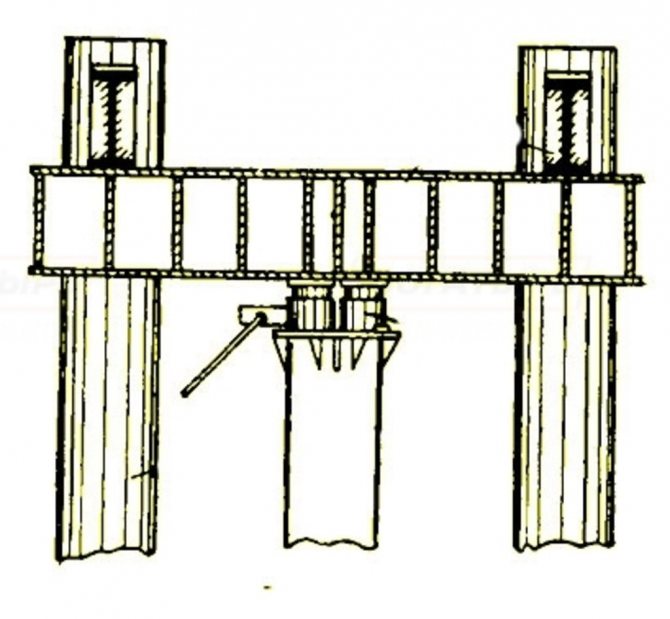
Hydraulic jack for testing piles
Unloading of the tested bored piles is carried out after reaching the highest load in the steps. Within 30 minutes, observations of elastic movements are made at each stage of loading. In case of complete unloading, observations are carried out for an hour. The pile is loaded without impacts, evenly, in load steps, the value of which is set by the test program. However, no more than 1/10 of the maximum load on the pile determined in the program is accepted.
| The movements of bored piles are measured with an accuracy of about 0.01 mm using two deflectors. The amount of settlement is calculated as the average value of instrument readings. |
| Deflection meter 6PAO |
At the end of the tests, a pile testing report is issued. All data is entered into the construction log.
Obvious advantages of static testing of piles
Static testing of piles ends up being somewhat more expensive than dynamic testing. But it is precisely this version of the study that helps to obtain the most adequate and reliable results. Such a test completely copies the real load that the foundation will have to withstand.
The load gradually increases during testing, which corresponds to the actual pressure that the building’s foundation will withstand during operation.
To adequately assess the capabilities of a pile foundation, the use of static tests helps determine the actual loads that the structure will experience. To obtain the most adequate and reliable result, additional load can be used.
In particular, when carrying out work independently, the adequacy of using the selected pile option can be checked by creating a load using reinforced concrete slabs. In this case, in most cases, the inspection work does not even require the involvement of an additional contractor. Carrying out the work yourself makes it profitable.
Dynamic and static tests, with the help of which the supports for the created foundation for a residential building are checked, become a guarantee of the durability of the created residential structure. Such work allows you to create a strong and reliable foundation, which for many decades will become the basis of a reliable residential building in which many generations of families will live.
What does preparation include, the main provisions of indentation load tests
Piles that are planned for future use must comply with the stated construction standards. Any deviation from the calculated loads and changes in parameters must be agreed upon with the designer. This may prompt additional research and recalculation of data.
Before carrying out work, it is imperative to develop and agree on a pile testing program with the designer of the construction site. It is not allowed to use rejected piles during testing, as well as materials that do not meet the characteristics stated in the documentation.
The documented test program specifies the selected testing method and the equipment involved.
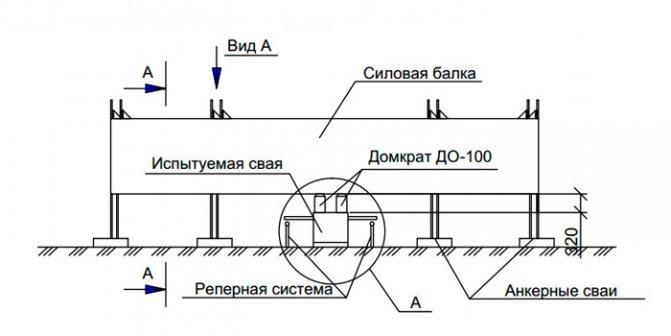
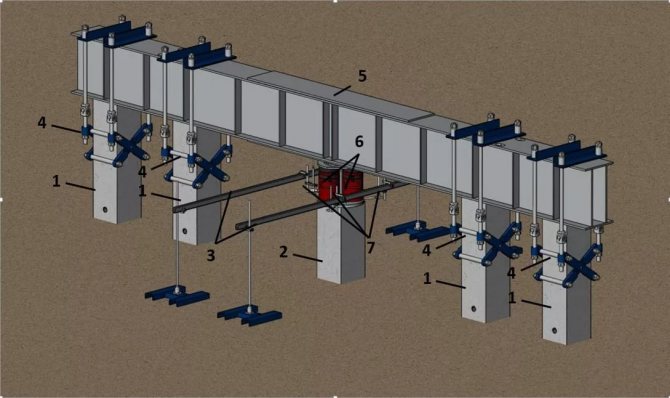
There are the following types of thrust structures for static testing:
- A loading platform that serves as a support for the hydraulic jack used.
- Beam system with anchor piles to absorb reaction forces
- When choosing a principle scheme for transmitting forces when testing piles, the planned load indicators should be taken into account. The first option, with a loading platform that transmits forces to the pile, is suitable for testing loads of no more than 200 tons. The use of the second method is justified for relatively large construction projects; the transferred load on the pile is calculated to be up to 1500 tf; it is justified if it is impossible to provide loads of a given mass, and the economic feasibility of the cost of installing anchor piles. When testing with loads over 2000 tf, in cramped conditions, usually pile foundations for bridges and hydraulic structures, the Osterberg method should be used; this method will allow work with loads over 10,000 tf, and does not require the installation of additional anchor piles.