Compliance with regulatory requirements guarantees a long service life of any structure.
In the case of constructing a pile-supported structure with an overhanging base, the owner is faced with the task of closing the gap between the house and the ground with a fence.
What materials are used to install the gap, is insulation and waterproofing necessary? Answers to questions in the article.
What is a pick-up
Before talking about how to properly carry out picking and what materials are best used for it, it doesn’t hurt to first understand what it is and what its main task is.
Any building has a base, even those whose base is pillars. Unlike a monolithic strip foundation, a columnar foundation leaves a lot of free space under the structure, which must be insulated so that the heat does not escape from the house in winter and the floor is warm. It is also necessary to protect this free space from precipitation.
That's what pick-ups are for. They are installed between the supports of the building. The following materials can be used for them: bricks, wooden boards, rubble boards.
The height of the fence from the surface of the ground should be at least 50 cm. Experts recommend installing a high base of the house, as this promotes greater heat retention in severe frosts. In addition to thermal insulation qualities, the fence also plays an aesthetic role.
Of course, every builder who builds a foundation on his own has a question: how to make a fence for a columnar foundation? Work on its construction can be divided into several stages. Let's consider a device for collecting from boards.
- A trench is dug between the supports of the structure, the depth of which should not be less than 20 cm.
- A layer of coarse sand or crushed stone is poured onto the bottom. It is advisable to use a mixture of these materials. After backfilling, they are moistened with water and compacted well.
- A beam is attached to the supports, in which special grooves for the boards are pre-made. The thickness of the board varies between 2-5 cm.
- The boards are laid on a compacted layer of sand and crushed stone and inserted into grooves on a beam or log.
- All boards must be treated with special means that protect the wood from rotting.
- The lower part of the fence is covered with expanded clay or other porous material with high thermal insulation properties.
A few words about the characteristics of a columnar foundation
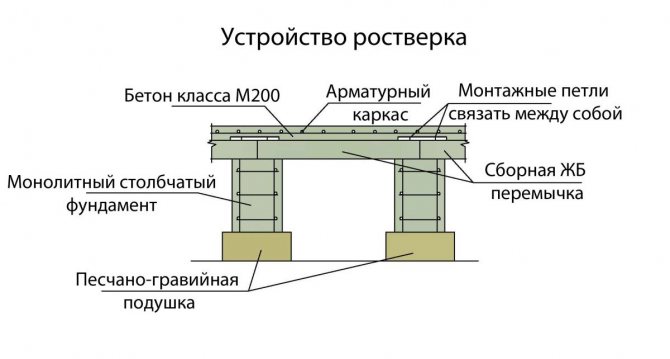
Diagram of a columnar foundation with a reinforced concrete foundation.
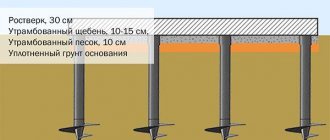
As the name itself makes clear, a columnar foundation is made of pillars placed in the ground.
The upper above-ground parts of the pillar supports rise at the same height. The installation of a columnar foundation is possible in one of 2 options: pouring pillar supports directly on the site (monolithic type) or assembling ready-made reinforced concrete blocks on site.
The first option involves a simpler foundation construction plan, which is why it is in demand among individual developers.
The supports are placed at the corners of the house and along the entire perimeter at a distance of at least 2 m from each other. Suitable materials for pillars are wood, brick, concrete, rubble stone.
The advantages of this type of base are considered:
- low cost - this type of foundation is 2 times cheaper than a strip foundation;
- the labor spent on its implementation is the same number of times less;
- the soil under a pillar structure remains more stable than under a strip structure.
There are also disadvantages:
- the complexity of the arrangement of the plinth space and the work on its insulation;
- The only way to insulate such a structure is to make a fence.
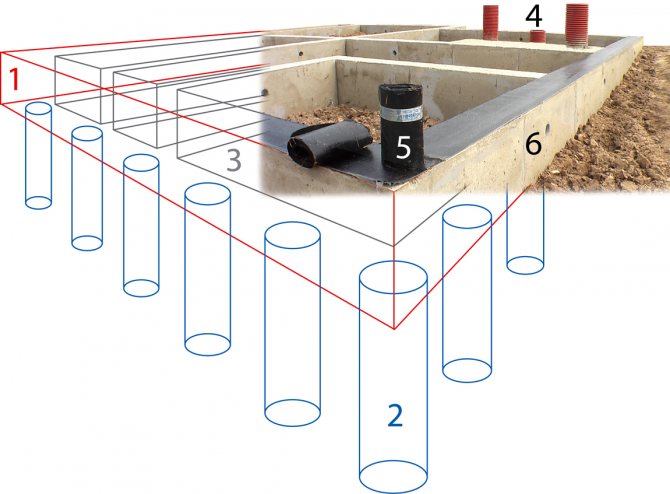
Scheme of a reinforced concrete survey plan that combines the function of taking in: 1- survey; 2-column foundation; 3- internal space; 4- communication pipes; 5- roofing felt (waterproofing); 6- ventilation holes.
How much to deepen the pillars depends entirely on the characteristics of the soil itself, on the level of groundwater rise, and on the depth of freezing.
Supports are distinguished by the level of depth at which they are laid: shallow (at a distance of 400-600 mm) and deep (below the freezing mark).
In order to reduce the consequences of soil mobility (which is possible in the cold season), a sand cushion is placed under each support.
Increasing the area of the sole is possible by installing a prefabricated or monolithic reinforced concrete slab whose dimensions exceed the area of the supporting part of the pillar.
As an option, you can use modified forms of pillars, the top of which is much narrower than the sole.
A fence is a method of delimiting the basement space from the external environment, which is typical for pile and columnar foundations. The fence blocks the empty space between adjacent foundation pillars, as well as between the lower part of the house and the surface of the ground, thus forming a plinth (room under the floor).
The fence is designed to protect the space of the base from the penetration of precipitation, wind, cold, debris, animals, and birds. An insulated fence is a warm floor in a house.
You can build a fence in several ways, each of which will depend on the material chosen.
Materials used for the collection device
Wooden boards can be replaced with cement-bonded particleboard. But this material has a significant disadvantage - low thermal insulation properties. Therefore, the slabs will have to be additionally insulated from the inside, covered with slag or expanded clay.
If brick or stone is used as the pick-up material. The technology of the device is similar to the technology of removing from boards, but in addition to the sand layer it is necessary to install a welded metal frame (steel wire with a diameter of 5 mm is suitable for it), which is filled with concrete. Next, stones or bricks are laid on the cement mortar.
Of course, a fence made of natural stone looks beautiful and very organic, but in this case it will be quite difficult to carry out the laying, especially for those who are faced with such a task for the first time.
In addition to boards and bricks, asbestos cement sheets can be used for lightweight structures (for example, garden houses). This construction option is quite economical. In order to protect the material from moisture, it is impregnated with drying oil and coated with weather-resistant paint.
Insulation
Ensuring thermal insulation of the false base is an important stage of construction. In practice, the following options are used (or a combination of several of them):

sheets or slabs of facing material are attached to the profile system through a layer of heat-insulating material;- the insulation (for example, extruded polystyrene foam) itself is a hanging screen, which is then primed and plastered;
- The fence is insulated from the underground space by spraying polyurethane.
How to insulate a fence
Wooden columnar foundations with a fence must be insulated, because if you leave an unclosed free space under the floor, not even the most powerful boiler will be able to cope with the heat loss resulting from such an illiterate approach to insulating the house. In order to increase the thermal insulation of a house, do the following:
- a frame made of a metal profile is attached to the support posts;
- sheets of expanded polystyrene or polystyrene are attached to the assembled frame;
- on the outside, the heat-insulating material can be covered with sheets of corrugated sheets; they are secured with self-tapping screws;
- when the pick-up is installed and an additional layer of thermal insulation is attached to it, the free space of the trench is completely covered with slag;
- if drainage or sewerage pipes pass between the supports, do not forget to install holes for them;
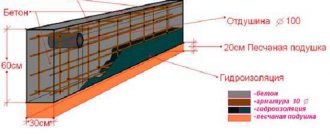
- It is also necessary to take care of ventilation. It is advisable to place the ventilation holes 20 cm from the ground level, equipped with grilles. For the winter period they are closed with plugs. The size of the windows is sufficient to maintain 10x15 cm.
Waterproofing
Even when the facing material is initially characterized by moisture resistance, moisture penetrates into the underground through the gap from the blind area. Dampness promotes the formation of mold, mildew, and significant heat loss. Ventilators help ventilate the space, but do not completely solve the problem.
In such cases , the place where the fence does not meet the blind area is sealed:
- use rolled hydrophobic material (TechnoNIKOL, Bikrost, etc.);
- they run the sheet under the cladding of the false base, fixing it to the frame mechanically;
- the lower edge is laid under paving slabs or any other material laid on the blind area and acting as a path.
Useful tips
The installation of a columnar foundation must comply with certain standards. For example, the thickness of the fence will vary depending on the material used for its construction.
- for concrete mortar this parameter is 10 cm;
- for natural stone – 20 cm;
- for brick – 12 cm;
- for boards – 25 cm.
In addition to thermal insulation, you need to remember that any material must be reliably protected from the harmful effects of precipitation, for which it is protected with a waterproofing layer.
Experts recommend waterproofing using bitumen mastic and roofing felt. To do this, the bitumen is heated and the outer surface of the intake is treated with hot water. Roofing felt is applied to the bitumen, treated again with hot bitumen and a layer of roofing felt is laid again.
From the outside, the fence can be waterproofed with a layer of cement mortar. It is prepared by maintaining a 2:1 proportion of sand and cement. The solution is applied to the wall, leveled, sprinkled with a layer of dry cement and wait until it sets. After this, a layer of rolled waterproofing is laid on top. Next, it is trimmed with decorative material: special panels imitating masonry, corrugated sheets, decorative stone.
Articles on the topic

Insulating a house made of sand-lime brick - stages of work, instructions, advice from masons

Electrical wiring diagram in a brick house - how to do the wiring, instructions, advice from masons

Brick ceiling - how to make, options, strengthening, instructions, advice from masons

How to put a zero on a foundation with a brick - methods, instructions, advice from masons

How to make a roof on a brick house - varieties, strengthening, instructions, advice from masons

Heating in a brick house - air, radiator, instructions, advice from masons

Waterproofing a brick plinth - horizontal, vertical, instructions, advice from masons
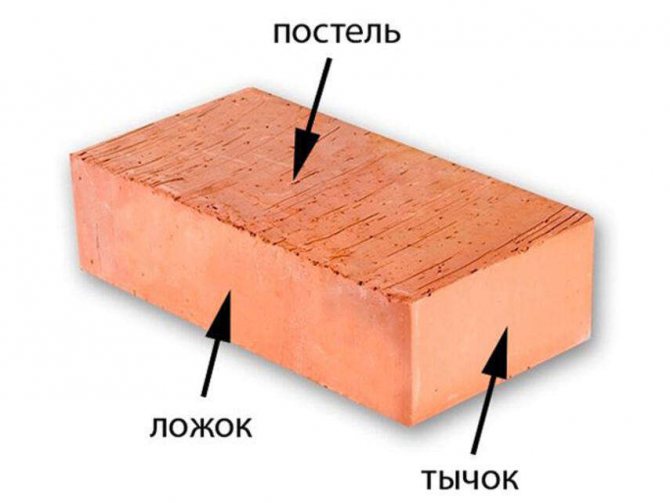
Brick sides - what they are called, characteristics, instructions, advice from masons
Reviews ()
Types of sheet piling walls
Sheet piling fences differ in the material used to make the sheet piling:
- wooden;
- reinforced concrete;
- PVC and composite;
- metal.
Metal ones, in turn, are divided into profile (Larsen tongues) and tubular. Tubular – high strength with increased stability, used in particularly difficult conditions. In most cases, Larsen tongues are used, most often trough-shaped.
Wooden tongues are almost never used today: they are cheap, but disposable. They deteriorate in the ground and cannot be removed without damage. Reinforced concrete has high strength. Theoretically, they can be dismantled, but this is never done because the process of removing them from the ground is too difficult and expensive. Reinforced concrete walls are left at the immersion site and included in the foundation design.

Plastic and composite sheet piles can be reused many times, but they are most often also left in the ground: due to their aesthetic appearance and resistance to corrosion, they are used as an integral part of the design when strengthening embankments. In terms of strength characteristics, they are inferior to metal piles.