During operation, the underground part of the house is subject to significant loads, so its construction should be approached responsibly. Timely identification of weak soil layers, carrying out calculations and following installation technology will help get rid of a lot of problems, including uneven settlement of the building, which is fraught with deformations and destruction of the entire structure. First of all, the foundation must be protected from moisture, since water is its main enemy. Its negative impact causes destruction of the underground part of the house and the basement, characteristic cracks appear on the walls, and doors and windows stop closing.
The need to waterproof the foundation
There is an opinion that the foundation does not undergo any changes during the operational period. Supposedly, it is resistant to rotting, decomposition and corrosion. In fact, the foundation built under the house requires additional protection without fail. Many people are interested in whether it is necessary to waterproof a strip foundation?
Water located deep in the soil can penetrate into basements and even into walls located above the soil level.
It is no secret that seasonal freezing of water in walls contributes to their destruction. A similar process occurs with the upper sections of the object’s base. A structure whose foundation does not have a waterproofing layer will not last long.
Protecting the base from heaving
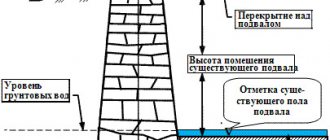
Heaving is the rise of groundwater in winter under the influence of frost. It occurs in soils that have a large amount of moisture in their structure. At the time of building a house, a layer of cushion is laid on soils with this problem using gravel and washed sand. These materials make it possible to resist soil heaving. It is important to know that such a pillow will save the foundation of the house only for a few years. To ensure a much longer period of safe operation, fiberglass should be additionally laid around the perimeter of the bedding.
A post shared by Vasily Ignatov (@vas_vas_supervas) on Aug 13, 2019 at 3:36am PDT
Soil heaving occurs during autumn and spring; moisture accumulates around the base of the house, after which it penetrates into the soil layers. Then, moisture penetrating into the soil forms a clay mixture, which subsequently washes away the cushion. If you use additional protection for the foundation, that is, fiberglass, this destructive mass will be filtered. After cleaning, only water flows to the pillow, and it does not have a negative effect.
To reduce the impact of soil heaving, a drainage system is used. It makes it possible to reduce the moisture content of the soil layers, thereby reducing the amount of water. The drainage consists of several pipes that are installed in the soil at a slight slope. It is necessary for better moisture outflow. To filter the clay mass, both edges of the pipe are covered with crushed stone. The drainage system is discharged into the sewer.
Types of waterproofing
When, at the time of design work, the option of constructing a strip foundation is selected, certain studies are required to help in the correct execution of the work:
- the base should be below the freezing point of the soil;

- the groundwater level is taken into account;
- the requirements for the waterproofing coating may change taking into account the purpose of the facility under construction;
- it is necessary to carry out a study of the area on the issue of a sharp increase in water levels during flood periods or during heavy rainfall;
- An important factor is the force of soil heaving, which changes its level.
Any of these conditions may affect the depth of the foundation trench that must be dug and the use of moisture protection materials.
Based on the principle of location, the waterproofing coating applied to the foundation can be divided into horizontal and vertical. Each type has different implementation options.
Horizontal
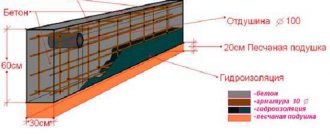
This protection option is carried out before the construction of the foundation begins in order to prevent the penetration of drops of moisture from the thickness of the earth. It represents a special foundation, sometimes even somewhat larger than the perimeter of the future structure.
For a small-sized building, pouring a sand-cement screed in a ratio of 1 to 2 is sufficient. In the process of constructing a residential building, it is necessary to carry out intensive preparation:
- Sand is poured and compacted along the bottom of the trench, the layer height of which should be from 20 to 30 cm;
- the first layer of this pillow can be made of clay;
- a screed is laid over the sand layer, the thickness of which varies from six to eight centimeters;
- you need to wait two weeks for the solution to dry completely;
- the screed is covered with bitumen, roofing felt is laid, and mastic is applied again;
- The final stage is pouring another screed.
Once the solution has dried, you can begin to build the foundation. If the planned object is being built from wood material, it is recommended to carry out the upper horizontal insulation of the base from water. Otherwise, moisture will penetrate the wood and cause rot.
Vertical
The main difference of this type is that its implementation is possible not only during construction work, but also on the finished object.

In this case, specialists can use various materials - polyurethane mastic, rolled bitumen, polymer-based membranes. Each product differs in strength, service life, elasticity, application method and price.
Before making the final choice, it is recommended to determine the differences between materials for waterproofing and clarify their advantages and disadvantages.
Polyurethane mastic or bitumen?
There are many types of waterproofing compounds on the market. Thanks to the development of the chemical industry, these products are becoming more and more advanced. If previously you could only rely on bitumen, now there are more durable alternatives.
What is the difference between bitumen and polyurethane mastic? Bitumen is one of the oldest building materials, accessible and cheap. Polyurethane mastics appeared on the market not so long ago, but they are distinguished by their strength and elasticity, which lasts for many years. Bitumen loses these properties very quickly. Its strength lasts for several years, then the physical and chemical properties of the material weaken. Polyurethane mastics can last more than 40 years.
Publication from Himtrust (@himtrust_ru) Sep 28, 2020 at 4:47 PDT
Polyurethane is not only resistant to moisture, atmospheric pressure and chemicals, but also resists abrasion.
What to choose? If we are talking about large-scale work, then it is cheaper to use bitumen, for example, for the construction and repair of roads. Polyurethane is needed where we are faced with non-trivial tasks. For example, it is necessary to insulate an overpass, foundation, bypass, or roof.
Types of waterproofing
It is possible to install waterproofing on a strip foundation with your own hands, without the involvement of appropriate specialists. But before starting work, it is necessary to decide on a suitable option for constructing a protective layer and clarify the technological features of the work.
The materials that can be used to waterproof a strip foundation in the ground are four groups:
- coating;
- sprayed;
- roll;
- pasting.

The entire technology for performing waterproofing work will depend on the final choice.
Bitumen
Mastic is used for coating. The main advantages of this method are:
- acceptable price;
- high level of elasticity;
- excellent indicator of coating hydrophobicity;
- ease of work;
- good level of adhesion.
There are also certain disadvantages:
- relatively short service life. After about six years, the mastic loses its elasticity, becomes brittle, cracks appear on the surface of the layer, and the degree of protection decreases.

But today the construction market offers a lot of options for coating compositions based on polymers, rubber, and latex. With their help, enhanced protective characteristics are created:
- elasticity and adhesion improve;
- The spread of temperature conditions increases during work.
The workflow is straightforward. First, the surface is cleared of construction debris and dirt. After this, the base is treated with primers that have a deep level of penetration. As soon as the soil has dried, it is allowed to apply a waterproofing layer. The coating should be solid.
Roll
In such cases, roofing felt, isoelast, aquaizol and other rolled materials are used, which are divided into two types:
- adhesive – attached to bitumen mastic or other compounds with adhesive properties. There are self-adhesive materials;
- floating - to perform it you have to use additional equipment - a gas burner, a blowtorch.
The method is distinguished by its simplicity of execution, long operational period, excellent moisture resistance, reliability and good strength indicators against mechanical influences.

The deformability capabilities and resistance to chemical compounds of a material are determined by its basis. Rolled material made of fiberglass or fiberglass does not have high deformation abilities and resistance to chemicals, but polyester has such qualities.
Rolled materials for waterproofing the foundation can be used in combination with coating materials.
The sequence of work is as follows:
- prepare the surface, which must be dry and clean;
- bitumen is applied;
- roofing material is glued using the floating method;
- The sheets of material at the joints are overlapped by fifteen centimeters and processed with a torch.
Sprayable
This waterproofing option is considered innovative. It can be used to construct any foundation during repair work of old coatings. There is only one drawback - the price, which is not acceptable for everyone.
The advantages are as follows:
- long service life;
- high degree of adhesion;
- ease of work;
- no seams;
- fast hardening;
- environmental cleanliness and absence of toxins;
- UV resistance;
- good degree of elasticity.

The work is performed in the following sequence:
- the surface is cleaned and coated with an antiseptic composition;
- Seamless waterproofing coatings are applied using a special spray device;
- as an additional measure, the surface must be reinforced with geotextile material.
Penetrating
An effective and expensive method of applying a waterproofing coating. Materials for this are usually prepared from cement, quartz sand and certain additives. The application method is similar to plastering. But today on the construction market you can purchase compounds that are applied by spraying or coating.
With this method, special elements in the form of crystals are created in concrete voids that repel liquid.
Clay
A simple and effective method that perfectly protects against water. A trench is dug around the foundation to a depth of 50–60 cm, and a cushion of gravel or crushed stone up to five centimeters high is placed at the bottom. Then clay is poured in layers and compacted thoroughly. It will act as a buffer for moisture.

The main advantage of the method is its ease of execution. But for a residential property it can only be used as an additional degree of protection.
Features of the work
Waterproofing work to protect the foundation must be carried out during its construction, but if this condition is not met, it is allowed to carry it out later, although this will be much more difficult. You will have to dig out the entire foundation, working in sections, so as not to reduce the level of strength of the building. Start from the corners and complete waterproofing on sections of the walls.
It is better to combine vertical and horizontal types, alternating the sequence when applying the next layer.
Having excavated the foundation, we clean the base; it is not recommended to use water. Remaining soil is cleaned from seam areas and cracks.
The recesses on the foundation are filled with cement mortar or tile adhesive, then these areas are treated with bitumen mastic. Roofing felt material is fused, which will require a burner. The first layer is applied horizontally, overlapping the strips. The second layer of roofing material is fused vertically. The heat-treated strips adhere perfectly; the roofing felt at the corners of the house is not cut, but rolled up.

Simultaneously with the application of waterproofing, drainage is arranged and the blind area is poured.
Excess water in mortar
Almost all materials that make up plinth structures require the preparation of a mixture with water. Whether it's concrete, cement-sand mortar or tile adhesive, you can't do without water. The process of gaining strength of dry binders (cement, gypsum) when mixing with water cannot be characterized by the verb “drying”. The combination of water and clinker (binder) forms a chemical reaction, as a result of which microcrystals begin to grow. By merging with each other, they form a stone-like body from powder and liquid. Obviously, such a reaction requires a certain amount of water.
If there is a deficiency, full strength will not be achieved, and its excess will evaporate. In the latter case, voids (essentially micropores) form in place of the evaporated water. In the autumn-spring period, water enters them, which, upon subsequent freezing, initially turns the micropores into microcracks, and then with each subsequent freeze-thaw cycle, cracks grow in the body of the structure.
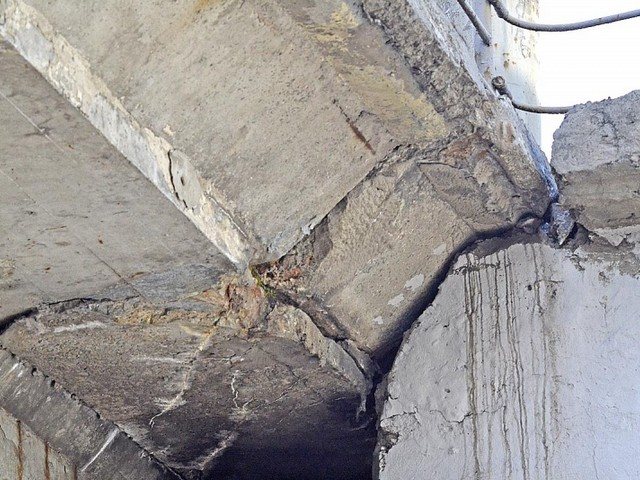

An example of the appearance of a reinforced concrete structure subjected to freeze-thaw cycles.
The issue of accurate dosing of water during the preparation of the mixture is not as simple as it seems. The exact quantity can only be measured for ready-made building mixtures. Not only do they come with instructions indicating the required amount of water, but they are also kept dry. However, the most widespread are concrete and cement-sand mortar. They contain sand, the moisture content of which is unknown at the time of preparation of the mixture, but the required amount of water added to the composition greatly depends on it.
But even by accurately measuring the moisture content of the sand, it is unlikely that it will be possible to prepare an ideal mixture - the resulting mobility and consistency of the solution (convenient for working with it) with an optimal water-cement ratio may turn out to be unacceptable for this type of work. Almost always it will be so for performing screeds. It is also inconvenient to plaster with a composition that is too thick. However, you should refrain from adding water! Improving the plasticity of the solution should be achieved by introducing special plasticizer additives. They reduce the friction forces between fractions of the composition and, without excess water, will allow you to perform the required type of work efficiently.