Like a theater from a hanger, construction begins from the foundation. Even at the design stage, the owner almost always specifically presents the platform, guided by the needs and his own wallet - everyone knows that the base takes the lion's share of the budget. However, it is worth not only resorting to savings, but also taking into account the characteristics of the terrain and the nuances of construction, subject to which the foundation will be a durable skeleton of the entire house and the key to comfortable living.
Types of foundation. Relation to ground level
The total size of the concrete base, that is, the height, is conventionally divided into the underground part and the base. What determines the height of the foundation above and below the ground? The factors are:
- Type of soil and its behavior in the off-season. Sandy, marshy and capricious soils are a problem when constructing a foundation, which is taken into account at the design stage.
- Level of freezing and occurrence of aquifers. The foundation should not be built above these points. And it will require compliance with the rules of insulation and waterproofing.
- Object type – housing, bathhouse, outbuildings. The weight of the structure is important due to its number of storeys and the loads experienced.
- Purpose of the basement and basement.
It follows from the points that compliance with all conditions is extremely important for determining the height of the platform as a whole. What it looks like in practice:
Monolithic slab:
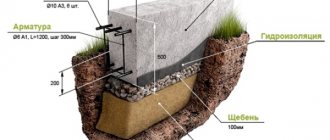
- According to SNiP, the minimum height of the plinth should be 20 cm. But for Russia, where the amount of snow cover is unregulated and interaction with moisture is detrimental to a wooden structure, this parameter is increased to 40 cm.
- The lower part, subject to freezing up to 1 m, is made with a depth of no less than this mark.
- The slab does not depend on ground movements - it is the most reliable, and, unfortunately, expensive foundation. But if designers are aware of active seismic features, then the height of the foundation for a slab-type house increases.
Thus, the general parameter for a monolithic platform in the middle zone of the country will be 1.2 m.
Floating foundation in conditions of high groundwater levels
If the structure being built is too heavy, for example, a brick house, then it is better to opt for a floating foundation.
This type of foundation can be built in a dry trench or pit, or in depressions filled with groundwater.
Floating foundation in a dry trench
To arrange the foundation in these conditions, you must perform the following steps:

Dry trench for slab foundation
- They dig a trench about 1 meter deep and 0.5 meters wide and cover the bottom with geological textiles. This material will prevent the bedding from moving if water washes away the soil.
- To give the foundation a rectangular shape, formwork is made.
- A sand cushion is constructed, the thickness of which should be 0.2 m. Gravel or fine crushed stone is poured on top of the sand. The thickness of this layer should be equal to or slightly greater than the sand cushion. Such a foundation will be a good protection for the foundation from groundwater. Each layer to be filled must be compacted thoroughly.
- The walls of the formwork and the cushion of sand and gravel are covered with waterproofing material, which will not allow the concrete solution to seep into the soil.
- Do not forget about the frame made of reinforcing bars. This design increases the reliability and stability of both the foundation and the entire house.
Floating foundation in trenches flooded with water
When the groundwater level is high, the dug pit or trench is filled with water. Under these conditions, building a reliable foundation is simply impossible. The concrete solution will absorb water, and dirt can cause unnecessary substances to enter the concrete, which inevitably leads to a decrease in its strength.
When planning the construction of a foundation in such conditions, it is important to properly organize water drainage and develop a drainage system. Otherwise, the work is carried out similarly to the construction of a floating foundation in dry trenches.
Tape base:

- The monolithic structure is deservedly popular among developers - the possibility of creating useful space in the basement, reducing costs.
- In severe winter conditions and freezing of the soil to a great depth, the size of the underground part will be up to 1.5 m.
- The base is arranged in accordance with its requirements - the installation of a furnace room, a basement. Boiler chambers require a precise approach, so the overall height is characterized by safe operation and regulated placement of equipment. That is, you won’t have to act in cramped conditions in case of emergency measures – fire, flood.
- For buildings made of wood, the heights of the basement floors always increase by an order of magnitude, regardless of terrain and soil conditions. Raw materials are capricious, and the higher they are raised above the ground, the more durable the object.
Thus, the optimal height of the strip foundation with the proposed boiler room will be about 2 m.
The foundation itself
The experience of builders, accumulated over many generations, is clear - the entire volume of the foundation must be laid either “in one piece at a time” or horizontally in layers (but this is no longer a completely standard situation). Since it was decided to abandon formwork, from the very beginning it is necessary to take care of protecting the foundation against dampness (that is, so that soil water does not erode it). One of the good options, which has been tested in practice by dozens of developers and invariably shows good results, is the technology of protecting the base of the structure from moisture using extruded polystyrene. This solution is more expensive than foam plastic and roofing felt, but has higher performance qualities. Let us now take a closer look at one of the schemes for constructing a formless foundation in detail.
Procedure step by step (using the example of a tape-type base)
- We clear the selected space two to three meters larger than the perimeter of the base. There should be no dips or bulges on the surface of the earth!
- When marking the construction site, drive stakes in the right places, stretching ropes between them. It is necessary to drive sticks or stakes into the ground and take them outside the desired area so that they do not become an obstacle to excavation work.
- The trench is torn off entirely by hand. This is the only way to achieve the greatest evenness of the walls, that is, the least shedding of soil downwards.
- We level the bottom.
To do this correctly, starting from the lowest point, use a hydraulic level to determine zero, drive the fasteners into the ground and stretch the threads between them. This method will give the highest evenness, incomparable with the visual determination of slopes and protruding places. Trenches without formwork - with deepening - We pour twenty centimeters of sand onto the bottom of the trench. Before compacting, it should certainly be wetted (even before laying, so that it does not turn into a mini-swamp). Tamping can be done either with vibrating plates or (in their absence) with oak or other hard wood ingots.
- A two-hundred-micron polyethylene film is placed, sealed with tape along the edges. This is necessary so that the concrete “milk” does not disappear before it works to increase the hardness of the structure. As much as possible, try to take a wider roll: this will allow for less sizing. If you really need to glue the joints, then do it on both sides. Single-sided sizing creates cavities that will become a source of getting wet in hot weather. The softened tape will come off and a hole will form. And if the protection that has lost its tightness does not save the trench wall from drying out, then this can even lead to the collapse of the entire wall.
- You can't get by with tape and polyethylene alone. You need to lay roofing material on top of them, overlapping it at the joints.
- If you need to build a foundation without formwork, when it rains, instead of polyethylene and tape, you should resort to a more capital solution - build a ten-centimeter layer of concrete on top of the ground. Use a five-centimeter layer along the walls. There must be at least five centimeters from the reinforcement to the ground in any plane.
- Reinforcement, as the instructions say, must be done both lengthwise and across.
Connect the reinforcement only with special wire, as welded structures will be less strong at the joints and will quickly collapse. Reinforcement of a formless trench - For the foundation itself, the higher the grade of concrete, the colder it is outside. Lightweight concrete (based on expanded clay or slag) will reliably protect against heat loss.
- Take the most purified components of the solution (gravel, water, cement and sand) if you make it yourself.
- When ordering concrete delivery, work with draining only wearing protective equipment (goggles, gloves and durable clothing that you don’t mind ruining), as the flow will be strong. Try not to pour concrete from a height of more than one and a half meters so that the layers do not fragment.
Pile grillage:

- The good thing about making bored rods or screw metal is that they allow you to save on expensive pouring and absolutely be below the freezing level of the soil.
- However, the grillage, that is, the above-ground part, is entirely dependent on the mobility of the soil and changes its height even before construction begins. Therefore, an independent device for safe operation must be carried out by specialists with appropriate calculations. The minimum height of the plinth when installing a pile grillage is 60 cm; for wooden buildings this parameter increases.
Based on the above, the height of one bored pile cannot be less than 2-2.2 m.
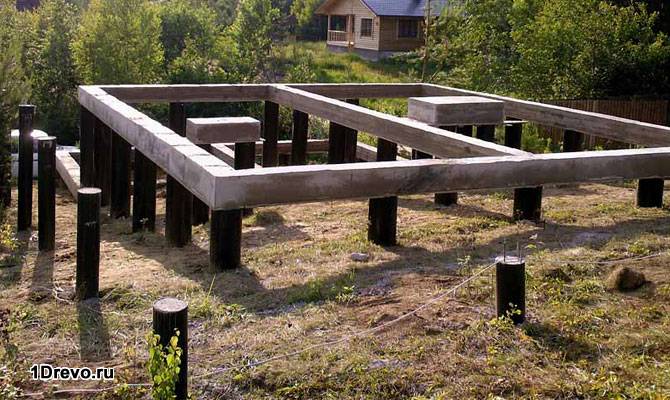

Advantages of a pile foundation and its application
Screw piles have been used in the construction of low-rise buildings since 1833 in Europe. Structures on stilts began to be used as supports for lighting in tidal zones. Afterwards, the piles found their application in the implementation of a wide variety of low-rise projects from garages to country houses. In Russia, pile foundations were first used in the territories of the Far North, where another platform for the foundation was not suitable. Afterwards, pile foundations began to be used in other regions of the Russian Federation. Now it is difficult to imagine the modern world without screw piles. Piles fit perfectly into any soil. You can build in any weather all year round.
Call us or Request a call
Changes in foundation heights
Much depends on the area where this or that foundation is laid; differences in elevation of the natural landscape will play an important role throughout construction and in future operation. For example, the owners want to get a two-story log cottage on the slope of a mountain or with other geological delights. In this case, the construction of any type of foundation must be regulated by the following:
- The set of all points on the foundation surface must be in a single plane. This must be steadily confirmed by construction levels.
- Removal of soil to the required amount of the underground part cannot be below the soil freezing level. That is, on the one hand, part of the foundation can be 3 m high, and on the other, 70 cm, depending on the steepness of the slope.
- If the height differences are observed, the consumption of concrete pouring increases, but at the same time the freezing conditions and the ideal level throughout the platform are met. Connivance will lead to destruction of that part of the foundation that is less than the level of freezing and groundwater.
When ordering a project for an object with difficulties in terms of varying ground heights, the owner will see in advance what the height of the foundation should be in this case. Perhaps, when converted to cash, he will choose a more level site.

Impact of high groundwater levels on the foundation
The basis of any foundation is a concrete solution, so the close location of groundwater has a harmful effect primarily on it. More precisely, concrete is not afraid of water itself; the destructive effect is exerted by salts and chemicals that make up soil water. As a result of their influence, the frozen solution becomes loose and begins to exfoliate. The first signs of concrete deterioration are stains and mustiness.
Another harmful effect of high groundwater is the erosion of the bottom of a trench or pit by incoming water, which results in a decrease in the bearing capacity of the soil, deformation and subsidence of the foundation. This problem can be solved by constructing a drainage system and draining water.