Foundation - the basis of any structure, which takes on the main loads from the roof, walls, ceilings, all contents in the house, its inhabitants, and even partially from weather conditions. Without realizing the seriousness of the approach to choosing the right type of foundation for the strength and durability of the entire structure, it is better not to even start construction.
Otherwise, if, for example, you choose exactly the same foundation as that of a neighbor or friend, your construction may end very badly or will be very expensive in terms of correcting errors. Even if the total area, number of storeys, type of walls, roof are identical, if everything is “like your neighbor’s,” this does not mean that you have the same type of soil, groundwater level, and soil moisture.
The figure below shows what happens to buildings or structures due to the inattention, negligence of builders/designers and incorrect choice of the type of foundation that is categorically inappropriate to the initial criteria.
Soil types
Since any unexpected behavior of the soil is dangerous for the foundation of the house, it is worth finding out in advance what can be expected from it in the future. The most common types of soil include:
- Rocky is the most reliable, tolerates sub-zero temperatures well and almost does not shrink under the weight of the foundation.
- Clayey is a weak type of soil, with constant swelling and subsidence. In winter, clay tends to absorb water and freeze strongly, and with warming it erodes and deforms even under its own weight.
- Clayey-sandy - unlike clayey soils, it is more convenient for construction, but much depends on the ratio of clay and sand in its composition. If there is more clay, there is a high probability of serious swelling.
- Sandy - does not swell, but is prone to subsidence. To avoid possible problems, you should correctly select the type of foundation and calculate the level of subsidence before starting construction work.
Conducting your own analysis
You can determine the foundation soil yourself without involving specialists. The simplest method for determining the composition of the soil is its contact and visual analysis.
A soil sample from the surface, and then from the depths, must be rolled into a kind of ball. If the soil is dry, it should be moistened.
You can visually determine which components are included in the sample by color and texture. For example, soil that has a reddish tint is clayey, and so on.
Then the sample must be crushed and ground. Depending on the composition, the result will be different.
If the ball crumbles easily, then sand predominates in this soil. If the sample is similar to plasticine, clay predominates. The presence of a large number of stones of various sizes indicates a rocky type of soil.
On heaving soils, it is especially necessary to carry out analysis at depth. On heaving soils, an improperly constructed structure can settle in winter and rise in summer, which leads to preliminary partial or complete destruction of the building. To learn how to conduct a soil analysis before building a house, watch this video:
On soil without a foundation, a well is drilled 50 cm below the expected freezing level or until water masses begin to accumulate in the well.
On heaving soils, loams, sandy loams and clay of heterogeneous structure predominate.
A large volume of moisture content, looseness and large voids, the presence of ice crystals when working in winter, indicates a high heaving index.
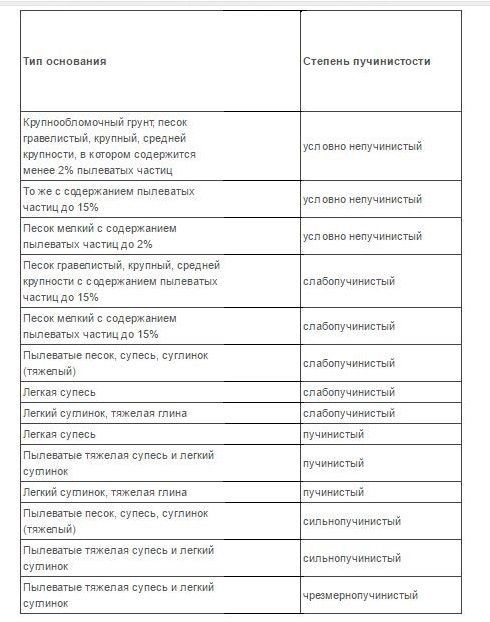
For a more accurate assessment of heaving on supposedly heaving soils, special data collected during experimental assessments are used (Table 1).
Table 1 – Degree of heaving of various soils
How to determine the nature of the soil on the site?
When inspecting the site, you need to distinguish between the soil and the bulk layer of earth. Buildings are built only on strong soil, so the bulk layer is not taken into account when calculating the load of the structure. It is necessary to select the best soil for construction with the involvement of specialists, but a preliminary assessment of the land on a specific site can be done independently. To do this, take a soil sample and soak it until it is suitable for sculpting. Next, roll a sausage out of the ground, connect its ends together and see how it behaves:
- It falls apart, but does not stain your hands - the soil is loose sand.
- Easily rolls and joins into a ring - clayey.
- Rolls easily, but falls apart when you try to connect the ends - loam.
- Does not roll down and leaves soil particles on your hands - sandy.
To obtain more accurate assessment results, soil samples should be taken from different places on the construction site. It wouldn’t even hurt to dig the soil with a shovel and make a fence from different depths.
Engineering-geological characteristics
Before constructing any object, the question arises: how to determine what kind of foundation is needed? The right decision depends on many factors. The most important of them is the engineering-geological characteristics of the land plot, which consists of a complex of engineering-geological surveys: relief, condition, composition and properties of soils, geological structure, seismotectonic, geomorphological and hydrogeological conditions, geological and engineering-geological processes and forecast of their changes during construction.
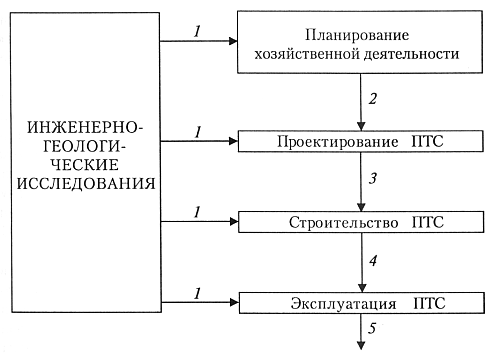
Table of engineering and geological surveys when choosing a site for construction.
To carry out the above studies, you can contact a number of specialized organizations or do everything yourself - it all depends on the type and complexity of the future structure. It’s good if there are pits and built houses nearby, because their condition relative to the selected type can give an idea of the soil. If the site is in an open field, then we will examine the soil ourselves.
The easiest way is to dig test wells or dig pits about 2-3 m deep at several points in the area where there is a depression in the topography or where water-loving plants grow. Every half a meter as you go deeper, you need to take soil samples, which are marked and placed in closed containers so that the samples do not dry out or absorb moisture. Using the samples, you can determine the soil moisture and conduct a simple test for the type of soil: take a sample, moisten it with water and roll it into a cord, which is bent into a ring. The thickness of the cord is 10-15 mm, the length is 10-15 cm. A ring made of clay will remain intact, one made from loam will break into 2-3 parts, and one made from sandy loam will crumble into small fragments. Based on the samples, you can draw a drawing of a vertical section of the land.
What soil is best?
The ideal soil is one that has a slight and uniform compression that prevents severe subsidence of the foundation. It’s good if it can resist swelling, that is, it can increase in size when it freezes and shrink when the weather is warm. High load-bearing capacity and immobility are also important characteristics of the ground that will ensure the stability of the building.
The best soil for building a house is solid and clastic rocky soil. Tightly packed clay or coarse sandy soils are also suitable for construction. Peat, plant soil, and bulk or alluvial soils are considered completely unsuitable for construction work.
Constructions
Foundations can be strip, columnar, monolithic in the form of a reinforced concrete slab, or pile.
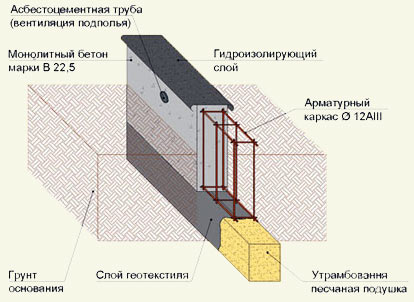
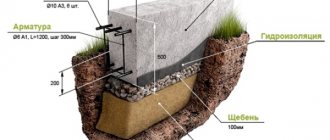
Strip foundation - detailed diagram.
Tape has a high load-bearing capacity; it is erected for buildings made of stone, brick and concrete. Such a foundation can be made during the construction of a basement and ground floor. Its feasibility should be indicated by the geological features of the land plot. The width directly depends on the thickness of the walls. Often it is monolithic from rubble concrete, reinforced concrete, and prefabricated (from blocks and slabs).
Rubble concrete is a mixture of sand, cement and large stones. It is used to construct buildings located on rocky or sandy foundations.
To avoid cracks or ruptures, it is not recommended to make a strip foundation of rubble concrete on a clay area.
Reinforced concrete is a mixture of crushed stone, cement and sand, which is reinforced with a special mesh or reinforcement. This material is affordable, durable, and most suitable for sandy soil.
Choosing a foundation based on the nature of the soil
Of great importance when constructing a building is the correct choice of the type of foundation for the house, taking into account the composition and nature of the soil in a particular area. The strip foundation is universal and can be used on almost all types of soil. The only condition is that it be laid to a depth of at least 30 cm below the freezing level of the ground.
On soft soils, it is recommended to use a slab foundation with the preliminary organization of a sand-crushed stone cushion. If the ground is heaving, it is advisable to install pile or screw foundations that can withstand almost any load.
Real Stroy-M specialists are ready to help you in choosing a construction site. We will conduct a thorough assessment of the soil and provide a full range of services for the construction of a building in Vladimir and throughout the Central region.
Types and characteristics of soils
The earth supports the load of the house, while the foundation correctly distributes the load from the structure, thereby creating conditions for the long-term operation of the building.
Different types of soil have different load-bearing characteristics, so careful analysis is necessary for the selected site.
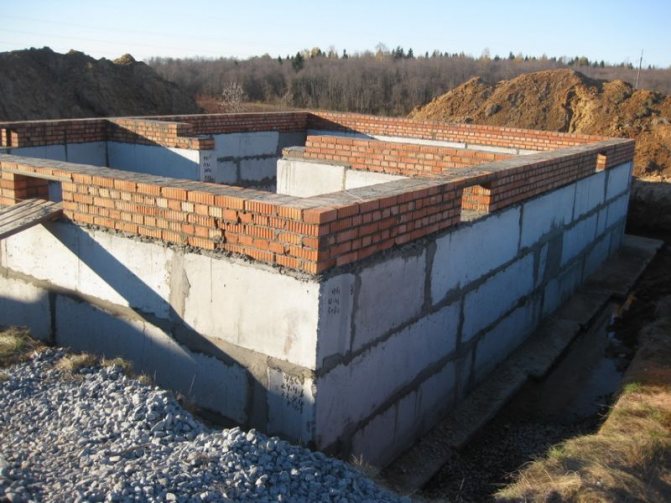

The choice of the type of foundation for the house is made after establishing the type and dimensions of the building, the properties of the soil, the amount of groundwater, weather conditions, the degree of heaving, and the relief.
The soils on which buildings are erected are of the following types:
- rocky;
- rocky;
- cartilaginous;
- clayey;
- loamy;
- sandy;
- sandy loam;
- peat;
- water-saturated or marshy.
There are also fertile black soils, but construction in areas with such soil is often not carried out.
Features of rocky, stony and cartilaginous surfaces
Rocky and rocky soil is ground with varying degrees of inclusions of small and large stones.
On such land there is practically no phenomenon of heaving, since it contains a very small amount of water.
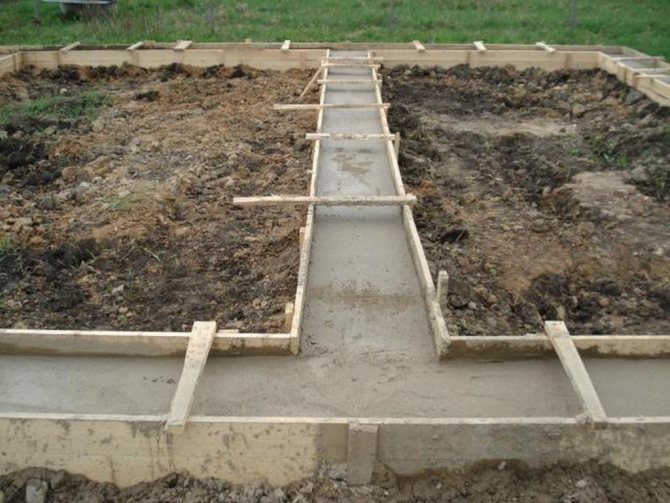

It is advisable to build a shallow strip foundation or a foundation with a foundation slab on such soil. Such a foundation on rocky ground will be very reliable and, if built correctly, will last a long time.
Cartilaginous soil includes rock, sand and clay. Just like rocky soil, such soil is perfect for a shallow foundation that will last for decades. There is no heaving, so subsidence of the base is excluded.
Laying a foundation on such soil can be quite labor-intensive, which is a disadvantage due to the large presence of fairly large stones. Additional effort and time may be required when manually or mechanically digging trenches or pits.
Features of clay and sandy surfaces

Grain sand is the main component of sandy soil. Such soil perfectly permeates water and is prone to compaction, so the construction of a foundation in this area is limited. Sand in the soil can be fine-grained or coarse-grained, which affects the freezing depth. The average freezing depth is about 1 m.
Clay-based soils are even more susceptible to heaving and soaking, so construction on such soil cannot be carried out without pre-treatment. The freezing depth of clay soil is about 1.5 meters.
Loam and sandy loam consist of mixtures containing sand and clay with a predominance of one or another component. Loam differs from sandy loam in its characteristics only in the degree of soaking, which increases with increasing clay content.
A certain area with sandy or clay soil or mixtures thereof must undergo soil replacement or the installation of a special foundation cushion in order to obtain a high-quality structure in the future.
In the presence of special preparatory work, deep-buried strip foundations, columnar or pile-type foundations are used.
Features of peat and marshy surfaces

The peat type of soil, which determines the use of a pile foundation, is found in areas after the drainage of swamps. The water saturation of such soil is high due to the shallow depth of groundwater.
If constructed incorrectly, such a surface can tighten the foundation.
Foundations on subsidence soils must be of the pile type with a sufficiently large pile driving depth.
Marshy surfaces are quite heterogeneous, with different densities of individual areas. Density depends on the composition of the soil and the amount of moisture. The composition is dominated by peat, clay and sandstone.
The foundation on complex soils, such as swamps, is built after a thorough analysis of the composition and geological research. Such a foundation usually involves the use of screw piles.
On such heaving surfaces, the freezing depth can average up to 2 m.
Geological study of the soil under the foundation
Before planning the location of the foundation and determining its type, first of all, it is necessary to carry out a geological study of the soil . After all, foundations on different soils will be completely different from each other. What will be good on sandy soil will be completely unacceptable on heaving or clayey soil. And if you build a house without taking into account all these nuances, then over time the building may “settle” or warp, breaking the walls and roof.
You can entrust geotechnical analysis to specialists, or you can save money by doing it yourself. This can be done using two methods : determining the percentage of sand, clay and silt or using visual-tactile assessment. Let's consider the second, simplest, method.
Use of rocky soil for road work
Rocky soil is widely used in road construction.
It is used in the following works:
- Creating a base under the road surface
- Construction of temporary roads and underground tracks
- Construction of dirt roads
- Road repairs
- Creation of embankments and shoulders
Next we will talk in more detail about each type of work.
Creating a base under the road surface
The stronger the foundation, the longer the road will last. Potholes and cracks will appear on it less often. Often the bases are made of crushed stone, but to save money without losing quality, you can use rocky soil. According to its characteristics, it must comply with the requirements of SNiP 3.06.03-85 dated 1986-01-01 (Highways).
For bases, take a large fraction, 0-500. If a highway with a lot of traffic is being built, it is best to use explosive soil made from igneous rocks. For small roads, collapsible, metamorphic or sedimentary ones are also suitable.
The soil for foundations must have sufficiently high unilateral compressive and shear strength, a crushability grade of at least M400-M600, and high frost resistance. It is undesirable to use heavily weathered rocks for such purposes.
Construction of temporary roads and underground tracks
For a temporary road, you can use explosive and collapsible rock soil of any origin. The choice largely depends on the number and weight of cars that will drive on the surface throughout its entire service life. If intensive use of the driveway is expected, you need to use durable explosive soil of igneous origin. When you want to build an entrance to a private construction site, it is better to focus on the price; cheaper material is suitable here.
So that the road does not have to be repaired, the coating is made in 2-3 layers, each 10 cm thick. For the lower one, use small rock of fraction 0-200. The top layer is filled with 40-70 mm crushed stone (for information on how to choose it, read the article Crushed stone for dirt roads).
Rocky soil for a temporary road not only saves money. It contains particles of different sizes that are used for decluttering. The fabric can also be strengthened with inexpensive binding materials. Remains of Portland cement, slag from ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy, lime, bitumen, and tar are suitable for this. But at the entrances to small areas where there is no heavy traffic of heavy vehicles, it is not necessary to use binders.
Construction of dirt roads
The bases of dirt roads made of rock are of quite high quality. It is also used to strengthen weak soils (sandy, sandy loam, loess), where road construction is planned in the future. The material is cheaper than crushed stone, but at the same time stronger than this material.
When purchasing, you need to pay attention to the strength and grade of crushability. It is desirable that the first indicator be no lower than 50 MPa, and the second – M400 and higher. It is also important to check the brand for abrasion of the rock. It should be from I1 to I3. With these parameters, the canvas will deteriorate more slowly under the load of vehicles.
To strengthen the soil, drain the site and equip the lower layers of the road, large and medium fractions are used. When compacting, small stones and sand fill the voids, creating a wedging effect. The thickness of the coating should be 20-30 cm. It is covered and compacted in layers of 10 cm.
As for the top layer, the rock is not suitable here due to its heterogeneous composition. It will be very difficult to level the coating, so it is more logical to pay attention to smaller materials - for example, ASG.
When constructing a permanent primer, it is advisable to strengthen the road surface with binders (bitumen, lime, cement, tar). Then the road will last longer and will have to be repaired less often.
You can read more about how to equip a dirt road in the article “Construction of dirt roads.”
Creation of embankments and shoulders
Rock soil is a universal material for creating embankments. It can be used in the construction of roads of any class. Restrictions exist only for materials from sedimentary rocks, which contain many soluble inclusions (sulfates, more than 30-40% gypsum, chalk, opoka), as well as impurities of fine sand and swelling types of clay. Rocky soils made from easily softened and highly weathered rocks are not used. For roads with high traffic, as well as railway tracks, it is better to take an explosive type of material rather than a collapsible one.
For the bottom layer of the embankment, coarse soil is suitable. The top layers are made from fine or medium. The roadsides are covered with fine rocky soil. Large particles whose diameter exceeds 40-70 mm are first removed from it.
Road repairs
For road repairs, rocky soil is used less frequently than for other works. The fact is that it is better to fill holes and cracks with small material. Crushed stone, gravel, gruss or asphalt cuttings are more suitable for such purposes.
If you decide to use rock soil, buy a fine fraction. The material must be sifted to separate particles that are too large (with a diameter of 50-70 mm). To improve the quality of repair work, rock soil is mixed with binders.