It is impossible to imagine a modern construction site without the use of concrete. The correct technological process for producing the mixture and the proportion of its components, professional pouring of concrete guarantee a solid foundation. The most popular is a solution based on cement, crushed stone, water and sand.
Modern durable structures in building construction are made using monolithic technologies, gradually eliminating the use of reinforced concrete products. The reasons why concrete pouring has become widespread are strength, stability, high level of waterproofing, reliability under seismic influences, and minimizing the use of special equipment.
Work with mortar is carried out when pouring the foundation of a house, floor and screeds, installing columns and constructing walls, erecting outbuildings and fences.
At what temperature can the foundation be poured?
When planning the construction of a supporting structure, it is necessary to take into account weather conditions, the brand and quality of cement. An important role in ensuring the strength of concrete is played by special additives that reduce the crystallization temperature of water, as well as maintaining optimal operating conditions during the period of foundation hardening. After pouring, the base sets within 24 hours and then gains strength in 28 days. The standard temperature range for creating a base is considered to be from + 3 to + 25 °C. It is known that the warmer it is outside, the faster the solution dries, but the heat can be dangerous for fresh concrete.
If at temperatures from + 5 to 15 ° C the composition sets naturally, giving off heat to the environment, then this does not happen in too hot weather. Under such conditions, a concrete frame can begin to form when the volume of material is further increased. As it cools, the surface begins to settle, and the already formed crystalline structure prevents this process. As a result, due to internal stress, the foundation may develop shrinkage cracks 4–12 hours after pouring. To prevent the base from crumbling at temperatures above + 25 °C, it is worth using quick-hardening Portland cement, which after 5-6 hours of pouring should be watered and shaded with old rags, cardboard or sawdust. To slow down hydration, it is permissible to introduce modifying additives and plasticizers. If cracks appear, repeated compaction is required.
In hot weather, the foundation may become cracked
Hardening of concrete
Immediately after pouring the foundation, two processes occur: setting and hardening of the concrete. Setting will not take more than one day; during this process the material will change from a liquid to a solid state. However, the strength will be low.
Then the hardening process will begin, it will take much more time. The main factors influencing the hardening time of concrete are:
- brand of material and its manufacturer;
- composition of the solution;
- the presence of special additives;
- temperature of the structure and its moisture content.
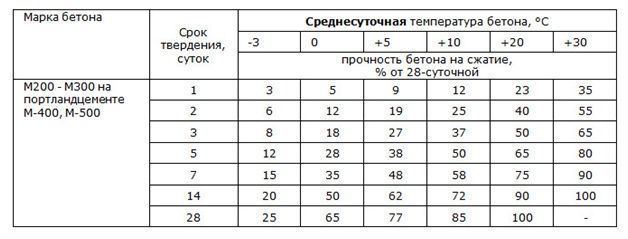
The optimal temperature for setting concrete is between 3° and 25°. The rate of hardening directly depends on the temperature: the warmer it is, the faster the concrete sets and hardens.
This table shows the relative strength of concrete at different curing times at different temperatures.
Is it possible to pour a foundation in winter?
The most favorable time for constructing a load-bearing structure is considered to be the period from April to November. However, the situation may turn out to be such that filling will need to be done in winter, because in some regions of Russia there is practically no summer. Modern construction technologies make it possible to create durable foundations even in cold weather. Building a foundation in winter is especially important on shaky soils. After waiting for them to freeze, you can dig an excellent pit. In addition, you can save a certain amount on purchasing building materials out of season. Most often in winter, strip foundations are erected using concrete blocks and structures made of concrete piles intended for light wooden objects.
According to various estimates over the past five years, the share of winter concreting in the total volume of construction ranges from 10 to 17%. This is a solid jackpot for manufacturers and suppliers of construction chemicals, and, in particular, those additives that should ensure the efficiency of the process at subzero temperatures. On the other hand, it was manufacturers who influenced the growth of winter construction. The interest here is mutual.
How does cement mortar behave in cold weather?
When planning winter work, it is worth remembering that ordinary concrete is not suitable for it. In cold weather, it is permissible to use only cement with special additives and modifying additives. The latter reduce water consumption by about 10–15%. When air humidity is 60% or higher, it is not recommended to use modifiers; moreover, it is worth remembering that they can react with some metals. To ensure structural strength, concrete must be heated in the first two days after pouring. The desired temperature regime of the mixture can be maintained using:
- thermal guns;
- special heating wire laid when pouring concrete;
- electrodes (reinforcing bars) to which voltage is applied.
There is also a method of heating the concrete mixture using a welding machine, but it essentially boils down to the use of electrodes and is applicable only for small volumes of pouring.
Only water and fillers are allowed to be heated, but not cement, otherwise it will lose its qualities.
For winter work, concrete with special additives is required.
Typically, in regions of the Russian Federation, a solution with a temperature above 21 ºC is not used, taking into account the fact that 4.5–5 ºC will be released into the atmosphere. Therefore, for the working composition, the liquid is heated to 32 ºC. Hotter water is first mixed with fillers, and then portionwise with cement.
Is it possible to pour concrete in cold weather without heating?
Whether it is possible to pour a foundation in cold weather without heating should be discussed separately. Even temperature fluctuations from +5 to 0 °C for concrete mortar are considered winter. During the cold season, when concreting, it is important to ensure smooth hardening of the solution by at least 60%. This guarantees the preservation of the structure of the base and its ripening when the thaw arrives.
However, the foundation will gain strength only when the temperature of the solution is above zero, so without artificial heating, you need to choose a fine winter day for construction work. The composition of the cement is also important: the so-called cold concrete contains antifreeze additives that lower the freezing point of water. For these purposes, potassium and sodium chloride are used in concentrations from 2 to 15%. Using anti-frost modifiers, it is possible to dismantle formwork with M200 mortar at 40% strength, M400 at 20% and M300 at 30%.
Video: warming up foundation concrete in winter
The effect of frost on concrete hardening
Of course, the weather affects construction, including the laying of concrete and its hardening. It is important to approach the work correctly and follow technological norms and rules, otherwise you will only ruin the foundation.
Here are some features of pouring a foundation in the fall:
- Hardening of concrete slows down in autumn, so 15-25 degrees is the most optimal temperature;
- A sufficient level of humidity is necessary, since rains will adversely affect not only the progress of work (flooding of wells and trenches), but also the composition of cement itself (reduction of cement laitance due to rain).
The most favorable period for construction and pouring concrete is considered to be the beginning of autumn, since there is neither heat nor frost with rainy weather. Concrete gains strength within 28 days, so the ideal option would be to start laying the foundation in early autumn so that it has time to harden before the onset of cold weather. However, the possibility cannot be ruled out that rainy weather will still occur within a month, but one should not be afraid for this, since precipitation can only affect the foundation for the first two days, because then, when the solution sets, it only has a beneficial effect, helping the concrete dry out. Accordingly, it is important not to miscalculate the weather and have time to complete construction work in good weather.
You should also think about protecting the underground part of the building from frost. Here everything is much more complicated in terms of technological conditions and more costs are required. If the concrete freezes, the strength of the foundation will decrease to a critical state, which threatens the destruction of the building. Another disadvantage is the frozen soil, which complicates the process of digging trenches and pits, and the cost of such work increases.
Based on what was written above, we will draw a small conclusion that it is best to carry out work with the underground structure in September, since it is cheap and can be done in simple ways. But if the work is delayed, special technologies should be used, the correct implementation of which will ensure a good and high-quality foundation.
Here are some methods to make foundation construction easier in sub-zero temperatures.
- Covering the foundation. This is one of the simplest and most inexpensive ways. However, it is far from the most reliable. It consists of covering the foundation with a thermal insulating material that helps retain heat. Mineral wool and sawdust are often used as insulation materials.
- Special additives. This method consists of adding components, plasticizers, due to which the concrete gains strength. The disadvantages of this method lie in the high price and in the application with other technologies.
- Heating the concrete mixture. It is best not to do heating the concrete mixture yourself, as it is technically complex. First, the power of the cables that are laid on the foundation is calculated, and the appropriate temperature is determined to avoid overheating of the solution.
- Construction of thermal formwork. Here you will also need the help of specialists, since the method is very difficult to implement. Basically, formwork is used only by construction companies in emergency situations.
- Drying concrete. An important condition to comply with is the absence of moisture. To avoid this problem, guns are placed under the awning, which fill the space underneath with warm air. Therefore, it is possible to dry the foundation of a future building even in the lowest sub-zero temperatures.
When can you pour the foundation in the spring?
Those who decide to start building a foundation in early spring (before April) should exercise caution. First you need to wait for the soil to thaw and warm up, when the temperature at night does not drop below 0 °C. It is also necessary to take into account the “drying out” of roads, which lasts one to two months, during which heavy equipment (concrete pumps, scows, toners and other vehicles) are restricted from moving on regional roads. Without the listed transport, it is impossible to build a monolithic foundation. From April, the cost of consumables begins to rise.
In the spring, the roads wash out, so heavy equipment cannot pass along them.
Unexpected frosts can cause irreparable damage to the structure, so when the weather forecast is unstable and work has already been planned, it is recommended to insure yourself by purchasing anti-frost fillers. Even at an air temperature of +23 °C, concrete gains standard strength only after three weeks. At lower temperatures, the time period increases noticeably; as a result, you cannot rush to lay the walls after pouring.
As practice shows, a house built on bare ground lasts for a few years. In the absence of a foundation, the lower blocks or wooden crowns are destroyed due to soil deformation.
What is the connection between the foundation and the time of year?
This connection is relevant for foundations based on concrete, and it is connected with the cycle of formation of artificial stone from mortar. Concrete gains strength gradually as it dries. Further work at this time is limited to tasks not related to the foundation.
The formwork can be removed and construction can continue only after the concrete has gained a certain proportion of its nominal strength (usually 50-70%).
The bottom line is that the installation time of the foundation affects the rate of strength gain, and therefore the amount of forced downtime.
The higher the air temperature, the faster the foundation dries. Therefore, in the summer, when it’s below 30 degrees outside, the formwork from the foundation can be removed in just a couple of days, and construction can continue in a week.
In winter, such a maneuver will not work. At sub-zero temperatures, even after a month the solution will not gain the required strength.
Likewise, the rate of formation of artificial stone is negatively affected by high humidity and precipitation.
Is it possible to pour a foundation in the rain?
Nowadays, rain is not a reason to stop concreting, as it was in the recent past. Using simple equipment and a suitable brand of cement, you can pour the foundation even in wet weather. Water itself does not have a negative effect on the solution; it’s just that before it hardens, erosion and an imbalance in proportions may occur. Therefore, everything depends on the strength of precipitation.
If the site is not flooded by rain, then a canopy will be enough to continue work. Ordinary polyethylene film will protect from light rain, which must be used with caution, because concrete hardens only in fresh air. Of course, in warm and sunny weather, the solution is better saturated with carbonic acid and hardens faster, forming a solid base. But building foundations in the rain also has its advantages, since the concrete mixture becomes stronger at 80% humidity.
Polyethylene film cannot be kept on the surface for a long time, since concrete does not harden without an influx of fresh air.
Is it possible to get rid of seasonality?
Yes, and there are 2 approaches for this:
The first is that you choose a type of foundation that does not involve concrete, such as screw piles. This foundation design is characterized by indifference to climatic conditions during work. Piles are also installed in winter, but in this case difficulties arise with screwing the products into frozen soil.
The second approach involves the use of auxiliary technological means to create ideal climatic conditions on a local scale. An example of such means: heating systems, air guns, insulation of a construction site, the use of special additives to the solution, and so on.
Thus, the answer to the question of what time of year can a foundation be made depends on the type of foundation and the equipment used. For strip foundations in limited conditions of individual construction, it is recommended to carry out work in late summer or early autumn.
How to increase the frost resistance of concrete without plasticizers
Considering the temperatures at which concrete can be poured without plasticizing additives, in frosty weather it is extremely difficult to obtain a monolith of the required strength. However, there are several alternative ways to help insulate the solution:
- "Thermos". This inexpensive method allows you to protect the foundation from heat loss. To do this, it is necessary to fill the formwork with heated concrete mortar as quickly as possible and promptly cover it with heat and vapor barrier material. Thanks to such insulation, the monolith will not lose heat, and the 80 kcal of thermal energy it generates will be enough to fully gain strength.
- Teplyaki. Some builders build a kind of greenhouse over a concrete structure. To do this, it is necessary to install tubular frames around the formwork and attach polyethylene to them. Heat guns are installed inside the resulting tent. However, this method is characterized by its high cost. Another type of greenhouse is a structure made of a frame and tarpaulin, which more reliably protects the foundation from low temperatures. In this case, heat guns are also used.
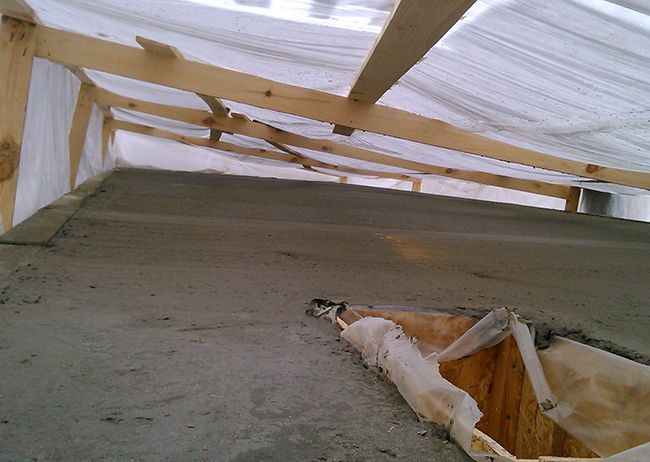

In addition, you can warm up the concrete using electric heating. In this case, you can use one of two methods:
- Pass live electrodes through the concrete. This method is relatively easy to implement, since the fittings conduct electricity well and can act as electrodes. However, it is worth considering that for such heating you will have to use specialized equipment. If you increase the hardening speed of the monolith with the help of reinforcement, then the current must be supplied at a voltage of 127 volts; if there is no reinforcing frame, then the current increases to 380 volts.
- Pass current through a wire laid in the middle of the concrete mass. In this case, the heating cable is laid along the reinforcing frame before pouring the concrete. Afterwards, the solution is laid, and the wire is connected to the substation. The efficiency of this method is much higher, but the cost of equipment will hit your pocket hard. In addition, when using a heating cable, it is necessary to constantly monitor the temperature level so that the cement-sand mass does not dry out.
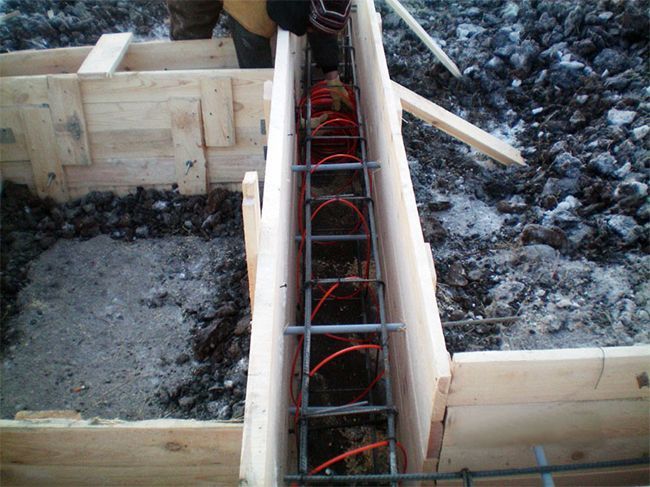

In addition, you can use simpler insulation methods. For example, you can insulate only the visible part of the formwork. Anything is suitable for this, from sawdust to polystyrene foam.
Pouring the foundation without formwork
Many developers are interested in the question of the possibility of laying concrete in a trench without formwork. According to the requirements of SNiP, this cannot be done, since the formwork not only gives the foundation the desired shape, but also protects the concrete from soil contamination.
In addition, it prevents the loss of laitance, the main binder of the concrete mixture. Without formwork, it is impossible to perform lateral waterproofing of the foundation, and without it, groundwater will freely penetrate into the concrete. When it freezes, it can destroy the foundation.
Pouring without formwork, which builders call “by surprise” concreting, can be done only for light foundations of outbuildings, garages, gazebos or bathhouses. Such work can only be done in dense clay soils that do not crumble into the trench after digging it.
Pouring the foundation in separate sections
Many developers are interested in the question of whether it is possible to fill the foundation in parts, since it is not always possible to prepare concrete in such quantities that it is enough to fill the entire formwork.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with what the entrance door to the bathhouse should be like
Let's see what SNiP says about this. The best method of installation, according to building regulations, is concreting in horizontal layers without interruptions.
If the volume of the foundation is large and does not allow laying in a continuous layer, then laying in inclined layers is allowed. In this case, the length of the joint on which fresh concrete will be laid must be at least 1.5 meters, and its slope no more than 30 degrees.
When pouring the foundation layer by layer, it is important to follow one more rule. Fresh concrete must be laid on the top layer before it sets to ensure the solidity of the entire structure.
If several days have passed after pouring and the concrete has hardened, before laying fresh concrete mixture it must not only be rinsed well with water, but also the cement film must be removed from the surface. It forms the interface along which the foundation fails under load.
Dependence of the cost of work on the weather - how to save on the foundation?
Laying concrete during rain requires a basic rule: do not allow excess water to get into the fresh concrete. Therefore, after placing the concrete mixture in the formwork, it must be immediately covered with plastic film so that water does not wash out the cement and reduce the strength of the foundation.

After the concrete has set (1-2 days), rainwater can no longer have a negative effect on it. On the contrary, during the hot period of the year it contributes to the hardening of concrete, since it protects it from drying out.
Modern construction organizations carry out work on pouring concrete in the summer or at the end of spring or autumn before the onset of frost. The explanation is simple: it reduces the cost of construction. Construction of the foundation in the winter months leads to additional financial costs, and it is also necessary to take into account that:
- Even under the most favorable factors, a 25% increase in construction costs is inevitable;
- You cannot do without the use of expensive reagents;
- For private buildings, it will be necessary to use the services of mixers, since it is not possible to prepare the solution in winter.
- Home electrical wiring may not be able to withstand the load of heating the base, so the owner will need an additional source of electricity.
We suggest you read: How often can you go to an infrared sauna?
The only advantage of building a foundation in the winter months is that it allows you to begin construction work right away in early spring. However, you need to weigh the pros and cons and think about whether this opportunity is worth the financial resources spent.
If it rains a little while pouring the foundation, then this is rather a favorable factor. Indeed, in hot weather, the solution dries unevenly and as a result of drying out, serious defects may appear. When precipitation occurs, the water from the surface of the newly poured foundation does not evaporate. However, you need to ensure that water does not wash away the concrete from the formed structure and pay special attention to the quality of the cement mixture.
Why do most people choose spring?
In fact, even spring is not considered the best time to start construction work.
And there are a number of reasons for this:
- Increasing demand for building materials;
- A sharp increase in prices for construction services;
- Soil instability at the construction site;
- The time required for complete thawing of soil.
And the frequent start of construction is due to the impatience of the customer, who wants to get a high-quality result as quickly as possible. Therefore, some experts are inclined to believe that the best time for arranging the foundation (regardless of the type of building) is the summer-autumn period.
Arguments regarding pouring the foundation of a building in winter
Pouring concrete in the cold season is not prohibited, but this task will need to be performed in a non-traditional manner.
Features of performing the task in winter
The only way to prevent icing and destruction of the foundation poured in winter is to use heated concrete. The temperature of the solution components should be 30˚ C. It is recommended to heat the water to 70°C.
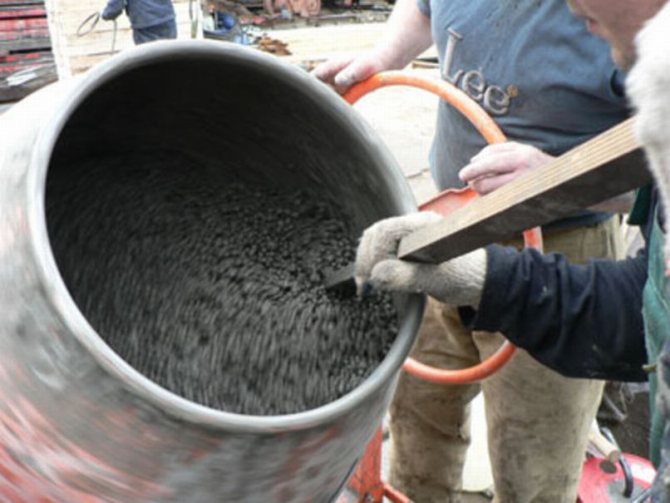

Hot water must be added to concrete that is being prepared for pouring in the cold.
To prepare cement mortar in winter, you first need to introduce hot water into the granular filler. After this, cement can be poured into the liquid composition.
The poured base of the building must be protected from the cold - covered with plastic film and heat-insulating material. Straw, peat, sawdust and even snow will do an excellent job of protecting concrete from frost.
Ways to pour concrete without heating
The simplest solution to insure against damage to concrete poured in winter is to choose dry cement of a higher grade. You can also avoid negative consequences by adding more of the main component to the solution.

To prepare concrete that will be poured in the cold season, it is better to use cement grade M-400 or M-500
Another way to solve the problem is to make liquid concrete from more than just conventional components. With the help of various additives and plasticizers, special properties can be imparted to cement. For example, they can turn concrete into a compound that hardens much faster than it should. These additives are usually introduced into water, and then into cement.
Table: additives to accelerate concrete hardening
| Additive | Description |
| Potassium carbonate | A white crystalline powder that makes the structure of concrete coarsely porous. Recommended amount of additive - up to 5% by weight of cement |
| Calcium chloride | White crystalline powder or aqueous solution. When exposed to air for a long time, the powdery substance spreads |
| Calcium nitrate | Colorless crystals that dissolve well in liquids |
| Sodium sulfate | Colorless crystals that decompose when heated, releasing oxygen |
| Sodium aluminate | Water solution. Dosage - 3% by weight of cement |
| Quicklime (calcium oxide) | Crystalline substance. Dosage - 2% by weight of cement. The product is aggressive towards steel fittings |