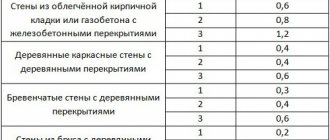
The strength and durability of a building depends on the foundation. Mistakes made during the selection and construction of the foundation will cost the developer dearly. The type of foundation should be selected depending on the geological conditions of the site and the expected loads on the foundation.
In private construction, the strip type of foundation is in demand. Developers are confident that it can withstand heavy loads and is easy to implement. In addition, it will cost less than a stove. Is it so? Let's compare two types of foundation.
Strip foundation
It is a reinforced concrete strip around the perimeter of the house and under the internal load-bearing walls.
Based on depth, it is divided into:
- not buried;
- shallow;
- recessed
By construction method:
The buried monolithic strip foundation rests on the deep layers of soil, and therefore withstands frost heaving. A shallow foundation is also resistant to heaving if special measures are taken - insulation, cushion, possibly drainage. However, it is not suitable for buildings made of heavy materials or buildings with several floors.
Advantages of strip foundation:
- Reliability. Resistance to soil heaving, subject to certain conditions (either below the foundation depth, or both the base and the soil around the house are insulated).
- Durability - if the technology is followed, a house on such a foundation will last up to 150 years.
- The construction technology is simple and does not require highly qualified workers.
- The construction of a strip foundation is possible with uneven soil density.
- A strip foundation, unlike a slab foundation, can also be erected on slopes.
- Possibility of installing a basement or underground. In a building on a strip foundation, it is easy to install (and subsequently maintain) engineering communications.
- Allows you to build houses with weighted floors.
- The ability to combine different types of strip foundations on one site.
- There are no strict requirements for the reinforcement of the base, because the structure itself is strong. With good soil characteristics and compliance with construction technology, buildings without reinforcement last for decades.
Flaws:
- Large labor costs (excavation work, reinforcement, formwork installation, soil removal).
- Unlike a slab, a strip foundation does not fill the entire area under the house, which means that additional floors or floors will need to be built on the ground.
- The construction of a strip foundation requires a large amount of materials.
- Building on your own takes a lot of time.
Basic information
The main document defining the requirements for strip foundations is GOST 13580-85. The standard was developed in 1985, changes and amendments were regularly made to it, the latest in 2004, and at the moment it is the one that is relevant. The standard specifies:
- scope of FL ;
- temperature conditions at which the products can be used;
- seismicity limit;
- dimensions and geometric parameters;
- reinforcement features;
- methods of quality control, transportation and storage.
Slab foundation
Slab (solid) base - a concrete platform located under the entire area of the building. It can be buried in the soil or simply built on a leveled surface.

Solid foundation options:
- flat;
- box-shaped;
- ribbed;
- prefabricated (from road reinforced concrete slabs);
- monolithic;
- with extensions at the corners;
- with and without reinforcement;
- cold or insulated.
In private construction, a flat monolithic foundation 20-40 cm thick with insulation is mainly used. A well-designed monolithic platform is suitable for construction on any type of soil. It does not sag in certain places, as happens with other foundations.
Advantages:
- Versatility. The slab foundation is suitable for any terrain, for all types of soil. The exception is for areas located on a slope. But modern technologies make it possible to combine them with high monolithic strips or pile foundations.
- The pressure on the ground is low due to the large area of the foundation. This allows you to build houses on several floors without fear of heavy load.
- Aerated concrete, brick, cinder block walls can crack from the slightest soil movement. The slab base is solid, so this danger is minimized.
- Excellent insulating qualities: heat loss from the house and moisture penetration inside are minimized. With appropriate insulation and waterproofing.
- Easy construction technology, minimum excavation work, on a flat site.
Flaws:
- It is impossible to arrange a basement or underground.
- Increased requirements for reinforcement.
- It is advisable to pour the foundation in favorable weather. While the concrete is setting after pouring, there should be no rain, because covering it will be problematic, and water that gets in can significantly reduce the grade of concrete.
- High cost due to large number of materials.
The last mentioned disadvantage can be called conditional, because on some points costs are reduced. What are the savings?
- There is no need to make ceilings or install a subfloor - it is already ready.
- Less material is spent on formwork, because It is enough to fence off the area of the future slab, while for a strip foundation you need formwork around the perimeter in two rows and where there will be internal load-bearing walls.
- There is not as much soil left as after the construction of a strip foundation, which means there are no costs for its removal.
In addition, with proper calculations, it is possible to build a monolithic foundation 15–18 cm in height. Thickening must be done at the junction of load-bearing walls, in the corners and around the perimeter. That is, a slab foundation may not be so expensive if you think about and calculate the loads in advance, identify problem areas on the site, and the costs of materials. To do this, you should turn to professionals
Ribbon
A strip foundation is a buried reinforced concrete structure that is laid under the external and load-bearing walls of a building. The width, height and depth of depth may vary. The strength, stability and reliability of the foundation depend on these indicators.
Advantages and disadvantages
The strip foundation is considered universal. It is suitable for construction on different soils and for various architectural structures.

It has the following advantages:
- high construction speed;
- the ability to build the foundation of a house without the use of special construction equipment;
- efficiency (due to the fact that the foundation is laid only under the walls, and not under the entire building);
- possibility to build a ground floor or basement;
- high strength (a massive tape can become a reliable support for a three-story brick house).
This foundation option also has its disadvantages:
- This option is not suitable for construction on peat and subsidence soils;
- accurate preliminary calculations are required.
Area and conditions of application
This base option is suitable for the construction of buildings made of any materials up to 3 floors high. Moreover, it is possible to build using it under almost any site conditions. Tapes are used on sites with pronounced relief, with a predominance of rocks, with high occurrence of underground flows and increased heaving of the soil.
In some cases, for example, when the water level is high, the strip structure is supplemented with pile supports, which are buried to the level of stable soil. Thus, the characteristics of the strip base are improved and the scope of its application is expanded.
According to the standards laid down in SNIP, classic strip foundations can be used without restrictions on coarse clastic and rocky soils. When erecting buildings on other, less stable soils, careful calculations are required, and sometimes reinforcement of the structure is required.
On biogenic soils, the construction of a strip foundation is considered irrational. However, even in these cases it applies. But certain preparatory work is needed - strengthening the soil using bulk methods, replacing weak soils with dense bulk materials, installing piles under the belt.
Which is better: monolithic slab or strip foundation
This depends on the type of soil and expected loads. In an area with deep groundwater, slight freezing of the soil and for the construction of a one-story building, a shallow strip foundation is suitable. In this case, it is inappropriate to build a monolithic slab.
Considering two types of foundations under equal conditions, builders disagree. There are those who claim that a properly constructed monolithic foundation is universal and therefore will not cause damage under any loads and operating conditions.
But here one can argue: a slab foundation is very inconvenient to maintain due to the lack of a basement or underground space for communications. In addition, the absence of a plinth can reduce the lifespan of the building. This applies to wooden structures. It is easier for rodents to get into such a house. The strip foundation is higher than the slab, so it better protects the building from bad weather and from rodents.
There are so many specialists, so many opinions on this matter. To make the right decision, you need to: do a soil analysis, evaluate the relief, calculate financial costs.
Advice! If you need builders to build a foundation, there is a very convenient service for selecting specialists from PROFI.RU. Just fill out the order details, the experts will respond and you can choose who to collaborate with. Each specialist in the system has a rating, reviews and examples of work, which will help with the choice. Looks like a mini tender. Placing an application is FREE and does not oblige you to anything. Works in almost all cities of Russia.
If you are a master, follow this link, register in the system and be able to accept orders.
Good morning everyone))) we are planning to build a house measuring 10x15m, the first floor is foam blocks (thickness 30-40cm), the second floor is attic, on the second floor there will most likely be plasterboard partitions, the roof is planned from the profiles of quickly erected houses, the soil is clay. I’m racking my brains as to whether it would be easier and cheaper to pour a monolithic slab or strip foundation in the Tyumen region, heating warm water floors on the 1st and 2nd floors, I drew an approximate design for the layout of the house))))
Slab pouring technology
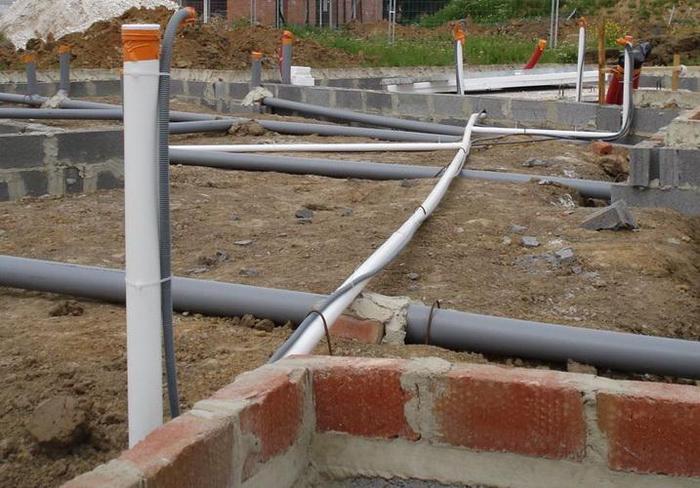

Before pouring the solution, it is necessary to carefully check the functionality of all installed communications.
The installation diagram of a monolithic base inside a strip frame is as follows:
- First, a layer of soil is removed along the entire perimeter of the closed loop to a depth of approximately 30 cm. In this case, there is no need to remove the soil from the site yet.
- The bottom of the prepared pit is covered with geotextile so that the edges overlap, and the walls of the pit are also protected by the material.
- The next layer of the pie is sand and crushed stone with a total thickness of 20 cm. The loose ones need to be slightly moistened and compacted well.
- Next, according to the building design, all plumbing communications are laid out, leaving pipe protrusions above the level of the future slab. The pipes can be properly insulated.
Important: before pouring the solution into the formwork, you must carefully check the functionality of all installed communications. Otherwise it will be too late later.
- Wooden panels are used to make formwork for pouring mortar.
- The next step is to reinforce the structure.
Tags: foundation, house, monolithic, strip
Comments 42
a pile foundation should be cheaper if done in compliance with building codes.
If you don’t know which foundation to take. Do geology, you need to find out the physical and chemical properties of the soil. There was an experience - I had to plant a one-story house on stilts! very bad soils. Do not risk!
I have the first option
Wood floors suck. Make a stove and warm floors right away. In one pour, you can install the floors, foundation, plumbing and some electrical work. All you need is a project.
Where in Tyumen are you building?
I don’t know how it is there, I know from the Starotobol highway)
What do you know about the Starotobolsky tract?)
What kind of soil and groundwater level)
This year I will be making a foundation in Malkova for a one-story house with a monsarda made of porevit, I’m thinking what kind of foundation, will a strip one be enough?
Enough, dig up to the clay and good, I have a garage 17 by 6 and an attic roof with expanded clay blocks in one block and brick cladding, 700 by 300 tape foundation. 7 years no cracks. I haven’t reached the house yet, there are a lot of people in Yakusha the tape is made on a shallow one, no one complained
The first thing you need, sir, is to ask the right question. Secondly, if it’s clay, then you need to decide on the dimensions in advance and absolutely precisely. The extensions will not work, because such soil is unstable and when the seasons change, winter and summer, the building bulges. Most likely, the previous speakers are right - we need to make a tape. Columnar will play. Walls. Foam block is warm and inexpensive, but there is such a thing as hygroscopicity - it must be strongly protected from precipitation. Aerated concrete too. On a budget, I would recommend expanded clay concrete. It has better “nailability” and is cheaper. 400 mm blocks are quite sufficient, but with such dimensions an armored belt is needed, so get ready to buy a couple of brick cubes, or even more.
for the armored belt there are special blocks for reinforcement in which the reinforcement is laid and poured))) here in the Yamal-Nenets Autonomous Okrug where there is a swamp all around they often make slabs and foam blocks
It’s very correctly said about brick - it’s just that its total weight on the foundation is large compared to a foam block, and laying a foam block is easier and faster compared to brick. Now for some reason many are obsessed with foam blocks and similar materials. Of course, it’s not good to contradict yourself, but for me the second floor in the garage you will have to make it with lightweight blocks - the foundation is different from the neighbors and there is generally a curb under the gate, so I don’t know...
I don’t recommend foam block, it’s complete crap. It cracks anywhere, you can’t hang anything normally, it lives on its own, expands and contracts. Best of all, this is a “collective farm” brick, environmentally friendly, durable, where you want to screw what you need.
I would rather do normal geology with a study of the bearing capacity of soils and hire a PGS engineer to calculate the foundation. Otherwise, the savings will go sideways
to follow up: with a floor height of 3 meters, an ideally comfortable staircase needs 20 rises of 15 cm each, which with a normal step of 300 (250) * 150 mm comes out to 5-6 meters in length, and you have drawn 14 rises for an approximate length of 3 meters, i.e. step 215 mm. for this question: uncle, are you a climber?