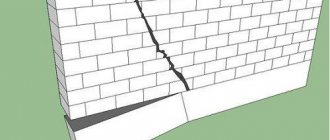
One of the most reliable foundations is strip foundation. A monolithic strip foundation takes a long time to build: assembling the formwork takes three days, and you still have to knit the reinforcement, then pour it with concrete and wait 21 days until it gains primary strength. It is easier and faster to make a foundation from concrete blocks - FBS, which is called a prefabricated strip foundation. You can make a foundation from FBS yourself.
With this technology, the foundation is assembled from reinforced concrete blocks of different types and sizes. That is why it is called block or prefabricated. These are all the same type.
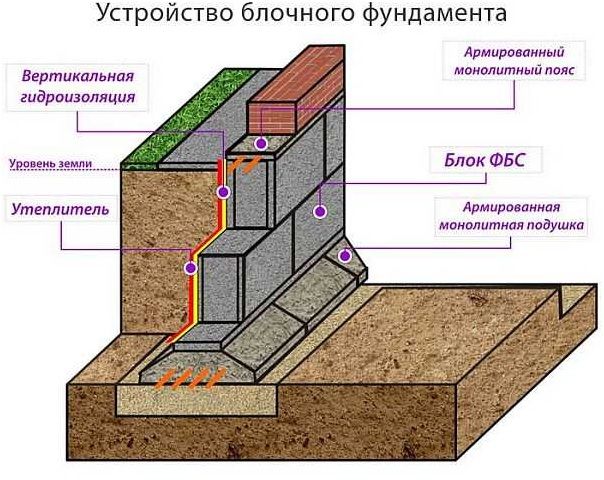
Strip foundation structure
The name “strip foundation” refers to the configuration of this type of load-bearing foundation. The foundation has the form of a continuous strip located around the perimeter to support the external and internal load-bearing walls of the building. The strip type of supporting structure can be made in the form of a concrete monolithic mass or in the form of prefabricated reinforced concrete or lightweight concrete elements. Since the construction season covers a short spring-summer period, during which it is desirable to complete the construction of the entire building, the best option to reduce time would be to use a prefabricated strip foundation.
Prefabricated monolithic base
The construction combines constructiveness and efficiency. Choosing the width of the tape for a prefabricated monolithic foundation allows you to choose the best option and wisely save financial investments.
During construction, standard monolithic blocks are used. Reinforcement technology allows you to strengthen the base in the last and first row, or in each row of masonry. To carry out the work you will need:
- Order special equipment for lifting foundation cushions (FL) and monolithic blocks (FSB).
- Buy a construction mixer for pouring concrete.
The work is performed in the following sequence:
- Site marking.
- Excavation.
- Preparing the base.
- Concreting.
- Laying waterproofing.
- Layout of fundamental pillows.
- Installation of monolithic blocks.
- Filling of the reinforced belt.
- Waterproofing.
Application area
Prefabricated foundations can be used for the following types of construction:
- For the construction of buildings made of brick, cinder block, foam concrete, monolithic concrete and other similar building materials. The main thing when choosing wall materials is their density, which does not exceed 1300 kg/m3.
- If there are heterogeneous soils on the building site. In this case, there may be risks of uneven distribution of load forces on the foundation, as a result of which the building may shrink and may become deformed. The strip foundation eliminates the occurrence of such destructive deformations.
- When planning the construction of a basement or basement. If during the construction stage the construction of doorways is provided, then the walls of the strip foundation will serve as the walls of the basement.
It should be noted that the key to a solid foundation will be not only the consistent implementation of all technological processes, but also the use of high-quality building materials of the appropriate brands. For example, when making cement-sand mortars for laying prefabricated foundation elements, the use of low-quality, low-grade cement is unacceptable.
Cheap and damaged building material is not suitable for constructing foundations.
Prefabricated columnar base
A prefabricated columnar foundation is a system of supports arranged in a certain order. The structure is mounted under light objects (frame, panel, wooden) without a basement. It is not recommended to build on a site with the following characteristics:
- On soil that is moving in a horizontal plane. To eliminate the influencing factors, an increase in labor intensity and financial investments will be required.
- If you plan to build an object made of brick or reinforced concrete.
- The composition of the rocks includes weak-bearing soils: peat, clay.
- Uneven area, the difference is more than 2 meters.
The material of the foundation pillars is chosen depending on the plan and weight of the house:
- reinforced concrete and concrete blocks;
- pipes made of metal or asbestos cement;
- monolithic reinforced concrete;
- rubble stone;
- high quality red brick;
- hardwood;
- combination of bitumen and concrete.

Mounting locations for supports are determined according to the following criteria:
- corners of the structure;
- boundary along the perimeter of the object;
- wall intersection area;
- under external and load-bearing walls;
- at points of increased load.
The pressure on the ground is reduced due to the expansion of the lower part of the pillars. Stability is ensured by a grillage that connects the supports.
Advantages of a prefabricated columnar foundation: low financial investment, cost-effectiveness.
Types of prefabricated strip foundations
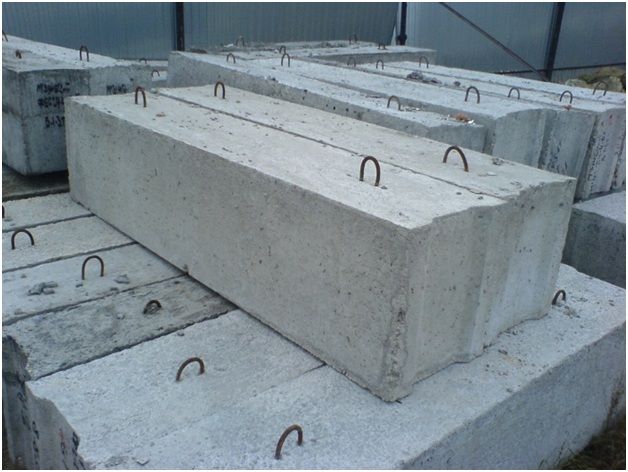

Belt-type support structures can be made from building materials such as:
- A solid cinder block, which many builders know as “concrete”.
- Reinforced concrete blocks called "FBS".
- Natural or rubble stone.
For shallow foundations on dry and strong soils of auxiliary buildings and outbuildings, the use of high grade solid bricks is allowed. An exception is the use of white sand-lime brick, which is susceptible to destruction in an earthen trench.
The foundation strip configuration can be continuous or discontinuous and has a rectangular or square appearance.
According to building codes and regulations, the width of the strip foundation should be 100 -200 mm greater than the thickness of the supporting walls.
Precast concrete base
To install the base, hollow or monolithic blocks reinforced inside are used. When constructing massive objects, a prefabricated reinforced concrete foundation is made from integral products, and for light structures - hollow slabs.
The plan for a prefabricated reinforced concrete foundation is carried out only by a specialist on a scale of 1:200 or 1:400. In the drawing, the reference is made along the center lines of the building, and the following parameters must be indicated:
- Cushion configuration and width.
- Laying depth of structural elements.
- Section of the foundation, clearly showing: laying depth, type of waterproofing, backfill thickness, base height, number and sizes of blocks.
- The location of communications and the necessary holes for them are indicated.
- The base plan indicates the layout of foundation pads (FL) and monolithic blocks (FBS).
- An explanatory note and specification are attached to the drawings.
For massive buildings, monolithic blocks (FBS) should be chosen; for lightweight structures, it is better to use hollow foundation blocks (FBP).
Device Features
When choosing a foundation design, the following factors must be considered:
- Depth of soil freezing on a building site. According to building codes, the base of the foundation must be located below the frost line, otherwise deformations may occur during the alternating cycle of freezing and thawing of the soil base.
- Groundwater line. In practice, the level of the groundwater horizon is determined by drilling wells and measuring the depth of water appearance.
- Terrain. On steep slopes or marshy areas, advice from specialist designers will be required to select the type of foundation.
- Categories of soils and their condition, which is assessed by indicators of strength, settlement and heaving.
What is taken into account when choosing the type of base
The following factors influence the decision-making of a pressing issue:
- Conclusions of geodetic studies on soil characteristics.
- Load from the selected structure.
- Availability of groundwater at the construction site.
- Technical characteristics of underground communications.
- Presence of basements in the house.
- Quality and type of building materials.
- Estimated service life of the future home.
After a thorough analysis of all the information, the issue of choosing the type is resolved.
Positive sides
The prefabricated strip foundation gained its popularity due to its technical and economic indicators:
- The speed and speed of construction work on the construction of the structure. After laying the prefabricated elements, the construction of the external and internal walls of the building can begin virtually the next day.
- Guaranteed quality of most of the materials used, which are manufactured in the factory and have a certificate of quality for the finished product.
- Availability of construction technology by analogy with brickwork, the main rule of which is compliance with the correct ligation of masonry rows.
Parameter calculation method
A prefabricated foundation is a part of a construction project that takes on loads and transfers them to the soil. The technology for constructing a prefabricated foundation includes a whole range of works. There are certain GOSTs, according to which the construction of the structure is carried out taking into account all operating conditions.
Preparatory work is carried out in accordance with developed and approved drawings. According to regulatory documents, a certain depth value is recommended for different types of soil. The table shows values for non-heaving soils.
| Freezing depth, meter | Laying depth, meter |
| 1 | 0,5 |
| 1,5 | 0,75 |
| from 1.5 to 2.5 | 1 |
When creating a foundation plan, it is necessary to take into account the drainage of atmospheric and surface water. This affects the service life of the structure.
The technical parameters of the future facility are also analyzed: wall thickness, height, total area, building material.
Calculation, preparation and installation of a building is an expensive and lengthy process, the quality of which determines the result.
Flaws
Prefabricated strip foundations have a number of disadvantages, which are recommended to be familiar with when choosing foundation structures:
- Mandatory implementation of protective measures for reliable waterproofing of the base and side surfaces of the foundation.
- When delivering and installing prefabricated reinforced concrete blocks, it is impossible to do without the use of expensive construction lifting equipment.
- Any prefabricated structure has less strength than a single monolithic mass.
After a comparative assessment of the advantages and disadvantages of prefabricated strip foundation structures, we can conclude that it is advisable to use this type of foundation.
Prefabricated slab base
If the site has complex soil (water-saturated, weak-bearing), it is better to choose a prefabricated slab foundation. It is made of reinforced concrete slabs. A leveling cement screed must be applied to the base. To perform the work you will need special lifting equipment (crane).

The main thing is to correctly calculate the thickness of the slab. Floors that are too thin may not be able to withstand the loads, and floors that are too thick may result in unnecessary financial investments. For proper calculation, you can use a special program or seek help from a specialist.
The disadvantage of a prefabricated slab foundation is the high price.
Material
The most common building material for prefabricated strip foundation structures is reinforced concrete structures.
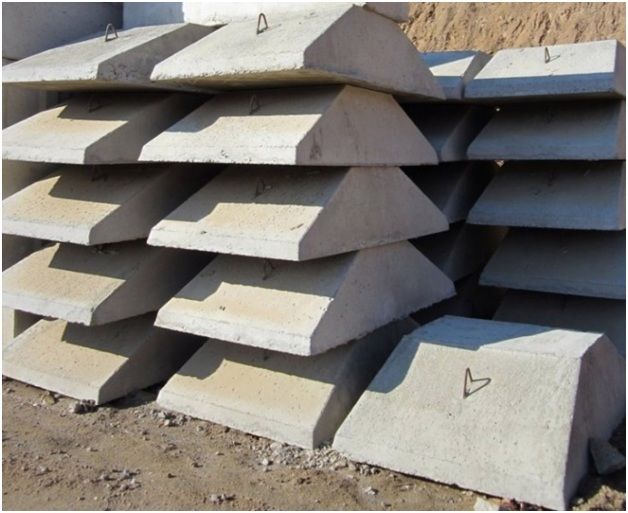

Foundation slabs
To understand why these elements are so popular, you need to take a closer look at their variety:
- Foundation pads in a strip foundation perform the function of a base - a sole that receives the load from the entire structure for transmission directly to the ground. In appearance it resembles a volumetric trapezoid made of reinforced concrete. Manufacturers, in accordance with GOST 13580-85, mark the slabs with the “FL” sign. The dimensions of the foundation pads are standardized: the width of the slabs ranges from 600 to 3200 mm, the length of the products is 800 – 2400 mm and the height is 300 – 500 mm. Foundation pads are made of heavy concrete of a class no less than. B 12.5 with internal spatial metal reinforcement frame.
- Concrete prefabricated foundation blocks (FBS) are produced in accordance with GOST 13579-78, they have the form of a massive parallelepiped made of class B 7.5 -15 concrete with internal reinforcement with a metal reinforcing cage. The design of the blocks has grooves at the ends that are filled with cement-sand mortar during installation. For ease of installation of the foundation tape, FBS blocks are produced in lengths from 800 to 2400 mm, width can be from 300 to 600 mm with a height of 600 mm.
Features of manufacturing reinforced concrete foundations
The production of reliable reinforced concrete foundations is subject to strict technological regulations and specialized SNiP. The key importance in them is given to the selection of structural materials.
Cement

Types of cements most often used in private construction:
- Portland cements (PC) – suitable for installation of monolithic foundations located in areas of difficult climatic influences;
- slag Portland cements (SPC) - work well in wet soils, although they gain strength more slowly and tolerate low temperatures less well;
- pozzolanic Portland cement (PPC) - ideal for conditions close to groundwater foundations or in flooded areas.
Visually determining the brand and quality of the binder is quite difficult, even for an experienced builder. At the same time, different manufacturers may classify cement according to GOST standards:
- 10178-1985;
- 31108-2003;
- 57293-2016, corresponding to the European standard EN 197–1.
Regardless of the production standard used, cement of at least M 400 should be used for the foundation. Grade (M) - shows what minimum compressive load (kg/1 cm2) after a 28-day hydration period the formed cement stone can withstand. The higher the number, the better.
Filler
Mostly it is a mixture of sand and gravel (the amount of impurities in the form of clay, earth or silt is no more than 5%). Its fractional composition should ensure that the solution fills the formwork uniformly (emptiness-free). In addition, the filler particles should be placed as closely as possible relative to each other. Otherwise, the volume of free zones will be taken up by cement, which will significantly increase the estimate. Therefore, gravel should be taken in several fractions with a particle diameter from 10 to 80 mm, and sand with an average fraction of 2.35 (± 1.15 mm).
Armature
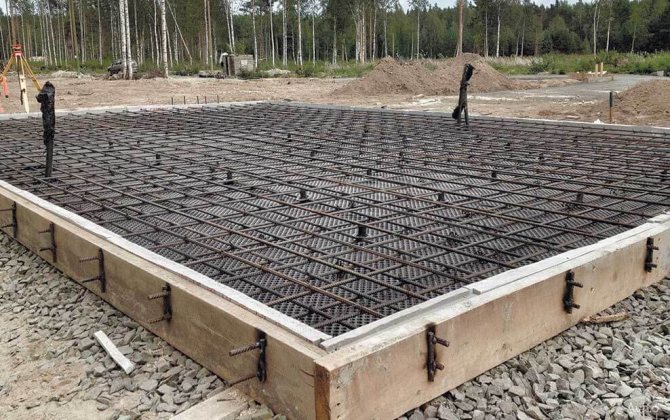

The resistance of a reinforced concrete foundation to bending, tearing, and shear loads is ensured by the reinforcement skeleton. It is often made from steel rods. However, recently, reinforcement made of durable fiberglass has become increasingly popular. Due to its resistance to corrosion, it is especially recommended for use in molding monoliths in wetlands or flooded areas.
According to SNiP 52-01-2003, the calculation of reinforcement is carried out based on the condition that it covers at least 0.1% of the cross-sectional area of the foundation. Therefore, taking into account market prices for reinforcing materials, it is more economical to reinforce concrete with thicker rods taken in smaller quantities.
As for the profile and thickness of the reinforcement, they depend on the purpose of the foundation. For example, some of them are shown in the table:
| Reinforcement profile | Ø fittings, mm | Application area |
| Smooth | 6 | Clamps |
| -//- | 8 | Clamps, bored piles |
| -//- | 10 | Foundations for light private buildings |
| Fluted | 12–14 | Strip and slab foundations |
| -//- | 16 | Foundations for massive buildings or on difficult soils |
Hot-rolled reinforcement used for the foundation must be of class A 400 or higher. It is better to use products marked “K” - corrosion-resistant.
Concrete mortar
The characteristics of concrete that has reached the design strength, whether factory-made or home-made, are determined by a number of indicators. The main ones:
- Class (B) – compressive strength. Similar to the brand, the higher the number, the better, adjusted for price, of course. For example, B 15 corresponds to M 200, B 22.5 to M 300, and B 30 to M 400.
- Frost resistance (F) - measured in units from 25 to 1000. The number means the number of freezing and defrosting cycles that concrete can tolerate without significant loss of performance characteristics. For the construction of foundations in most regions of the Russian Federation, the following are suitable: F 50–F150, in the most severe regions – F 150–F300, in areas with waterlogged soil and frosty winters – F 300–F500.
- Water resistance (W) – measured by a numerical index from 2 to 20. It is of particular importance for reinforced concrete structures located in areas with high groundwater levels. To form them, it is worth choosing solutions with an indicator close to W 20, not forgetting about subsequent reliable waterproofing.
- Solution mobility (P) – index from 1 to 5. The higher the index value, the more fluid the solution. Mainly for forming reinforced concrete foundations, the optimal indicator is P 2 or P 3. With dense placement of reinforcement cage bars - up to P 5.
Work production technology
The technological process for installing a prefabricated strip foundation consists of the step-by-step implementation of all stages of construction, starting from marking and ending with the care of the finished strip foundation structure.
Preparatory stage
At the initial stage of laying the foundation, it is necessary to prepare the construction site: clear the area and carry out the necessary markings according to the executive working diagram of the foundations. Using rope and pegs, the linear dimensions of the foundations are fixed directly to the soil. You should pay attention to the correctness of the marking angles. A control check for the correctness of the layout is to check the diagonals of the linear configuration of the foundation: all diagonals of the rectangular sections must have the same value.
Excavation
Excavation work consists of preparing a trench for laying prefabricated elements. For large volumes of excavation, it is best to use construction earthmoving equipment - an excavator.
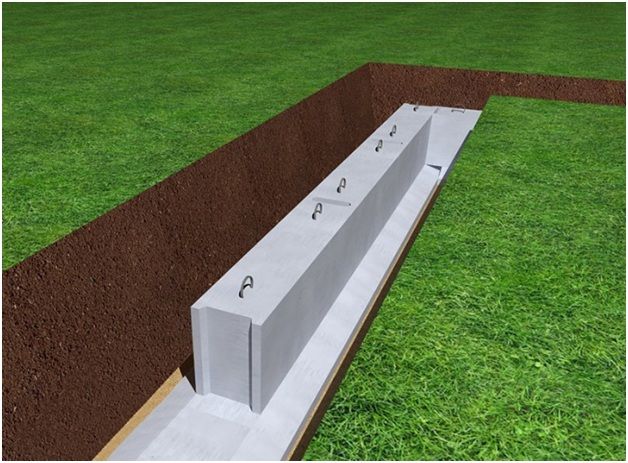

Scheme of laying FBS blocks
With small volumes of earth and a shallow foundation depth, you can prepare a trench yourself with your own hands. The working width of the trench is slightly larger than the calculated width of the foundation blocks. This difference is necessary for the convenience of installation and waterproofing work. The bottom of the trench is cleaned and leveled to the building level.
Preparing the base
It is necessary to lay a sand preparation with a thickness of 50 - 100 mm on the prepared, cleaned bottom. The filled sand is leveled and compacted using manual or electric vibration tampers. After this, the sand cushion is spilled with water. A waterproofing layer of rolled roofing material is laid on the finished sand floor. The waterproofing is filled with cement-sand mortar; after drying, the base is considered ready for installation of foundation blocks.
Installation of prefabricated elements
To correctly lay prefabricated blocks, it is necessary to transfer the center lines of the diagram or drawing of the building to the edge and bottom of the trench. Beacons are placed along these lines along which the corner foundation elements will be laid.
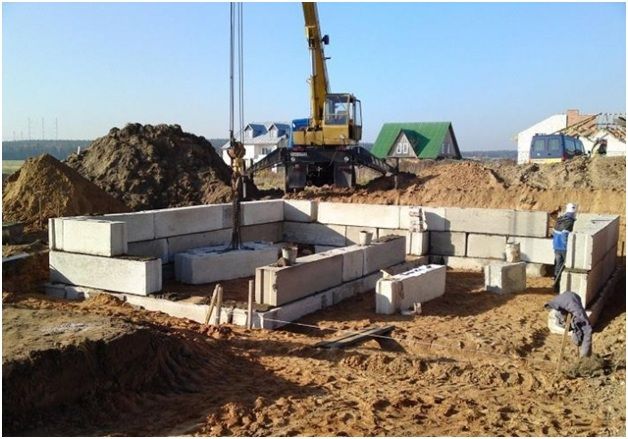

Laying foundation elements
Using lifting construction equipment, prefabricated foundation elements are laid on the concrete mixture and the horizontalness is checked with a building level. The grooves of the blocks are filled with cement mortar.
The final stage of foundation assembly
After finishing laying the foundation blocks, it is recommended to carefully fill the seams between the blocks with cement mortar and after they have completely dried, it is necessary to perform protective coating or adhesive waterproofing of the side surface of the strip foundation. Such an insulating coating will reliably protect the foundation structure from capillary and atmospheric moisture. Properly performed waterproofing creates a comfortable microclimate for living in the house.
It is necessary to prepare a trench for the foundation immediately before starting work. In the event of precipitation, the walls of the trench may collapse and all work will have to be redone.
Video example of laying FBS blocks:
To lay utility lines, installation holes should be provided in advance in the foundation strip. The installation of such holes will make it possible to easily lay all the necessary pipelines and cable products into the basement of the foundation for further wiring throughout the house.
Kinds
The prefabricated strip foundation is divided into several types:
- Shallow without a cushion.
- Recessed without cushion.
- Shallowly buried with a supporting layer.
- Recessed with a supporting layer.
These types differ from each other in the height of the masonry level, depending on the degree of soil freezing in a particular climatic zone. A support cushion is needed if the soil has high humidity, for example clay and loam. Increased humidity gradually rises to the joints between blocks and walls, resulting in displacement of prefabricated elements and cracks in the building. A special layer allows you to avoid destruction of the building from the base.
The degree of depth is determined by the magnitude of the expected loads, the number of storeys of the building, and the need to arrange a ground or basement floor.
Return to contents
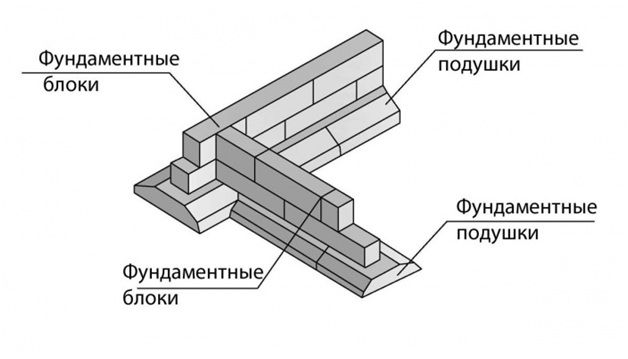
Foundation using blocks
To lay strips of individual blocks, building materials are placed perpendicular to the alignment axes. You will first need to install beacons from the same blocks at the corners and intersections of axes. The level is set by a level. The laying of the remaining blocks is carried out both along the edge of the bottom row and along the alignment axis. A concrete solution is placed in the vertical space between the blocks, reinforced with reinforcement bars 20 mm thick. Excess steel and mortar are removed immediately so that they do not interfere with further installation of waterproofing.
In places provided for communications, gaps are left between the blocks. Pipes made of plastic or metal are immediately filled with solution and covered with waterproofing on the outside. As a waterproofing layer, you can use bitumen mastic or roofing felt. A concrete belt made of reinforcement is laid on the blocks, which will make it possible to achieve a flat surface of the belts and avoid bevel of the building. The foundation of the prefabricated type can be hollow, monolithic blocks without grooves or with them.
Return to contents
Foundation using slabs
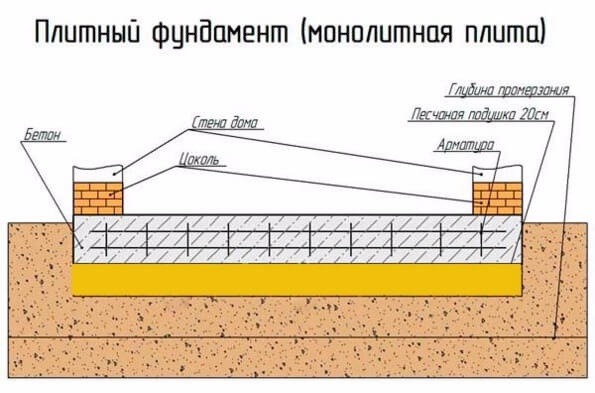
As an alternative, monolithic reinforced concrete slabs can be used instead of blocks to construct a strip base. The technology of their laying is somewhat different. A cushion of crushed stone and sand with a layer of 100 mm is placed in a pre-dug pit. Formwork is installed along the contour of the future concrete pouring. It and the soil should be moistened before filling with cement mortar. The concrete pouring height is 150 mm.
It is necessary to strengthen the support areas of the walls using reinforcing mesh with 10 x 10 cells. This will strengthen the structure. The poured solution is compacted and left for two weeks to harden. Afterwards, you can remove the formwork, dry and prime the surface. At the last stage, waterproofing is carried out. The screed is poured on top.
Return to contents
Technology of construction of reinforced concrete foundations
Let us consider in general terms the technology for constructing each type of reinforced concrete foundation.
Strip foundation
The construction of a strip foundation is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- Preparatory work is carried out - the construction site is prepared, the top layer of soil is removed, the design markings of the foundation are transferred to the site;
- A trench is dug to a depth of 20-30 centimeters greater than the depth of the foundation;
- A compacting layer of sand and crushed stone is installed in the trench;
- A formwork is created from planed boards, into which the concrete mixture will later be poured. The formwork is installed around the perimeter of the trench, and the inside is covered with waterproofing material;
- A reinforcement frame is tied from reinforcing bars, which is laid inside the trench;
- The foundation is poured with concrete mixture;
- The formwork is covered with oilcloth; during the hardening period (28-30 days), the concrete is regularly moistened.

Slab foundation
The stages of constructing a slab foundation are essentially similar to the construction of a strip foundation, the differences are only in the volume of work - while for a strip foundation a trench is dug, following the contours of the walls, and formwork and a reinforced frame of the appropriate shape are created for it, for a slab foundation a pit is dug, the area of which is identical area of the house.
The sequence of work is as follows:
- A compacting cushion is installed in the pit;
- Formwork is assembled along the perimeter of the pit from flat boards;
- The footing is poured - a layer of liquid mortar 2-3 centimeters thick, which, after hardening, will prevent the leakage of cement laitance from the main layer of concrete;
- A double-circuit reinforced frame is formed on the hardened concrete base;
- The formwork is filled with concrete.

Expert advice! Dismantling of the formwork is carried out after the concrete reaches its design strength of 60-70% of the maximum (on the 15-20th day of hardening).
Pile foundation
The technology for constructing foundations from driven reinforced concrete piles is implemented using special pile-driving machines - pile drivers. The sequence of work is as follows:
- Piles are brought to the construction site;
- The pile field is marked according to the design data;
- The pile driver begins driving piles - with the help of winches, the machine pulls the pile towards itself from the storage site;
- A cap is placed on the pile, it is lifted into the air and placed vertically at the immersion point;
- The verticality of its position is verified and the driving direction is driven (the blows with a diesel hammer are not applied at full force);
- After the direction of immersion of the pillar is set, the pile is driven to the design depth;
- The pile driver detaches the head from the pile and moves to the next driving point;
- After installing all the pillars, the piles are tied with a reinforced concrete grillage.

Rice. 1.8 : The process of driving a pile field
Bored piles are installed according to the following algorithm:
- The leader well is drilled to the designed depth;
- A casing pipe is immersed into the well, acting as formwork for pouring concrete;
- A reinforcement frame made of longitudinal-transverse reinforcing bars is placed in the casing pipe;
- The well is filled with concrete mixture.

Rice. 1.9 : Creating bored piles with your own hands
Expert advice! After hardening, the concrete forms a full-fledged pile support that is resistant to buoyancy and bending loads.