Blocks for foundation construction are a modern building material that is popular due to its successful combination of affordability and impressive technical characteristics.
Manufacturers offer a wide range of blocks with different operating parameters, which allows you to select a material based on individual requirements.
Before constructing such a foundation, it is recommended that you familiarize yourself with the main positive and negative aspects of this option, as well as the specifics of installation. All these features are discussed in detail in this article.
Advantages, disadvantages and features of the device
A shallow foundation is a not too deep foundation for a building. The average depth is about 0.2-0.5 m. The need to use this type of house foundation is due to the fact that construction is planned on heaving soils. The advantage of a shallow foundation is obvious, since with a buried foundation, the tangential heaving forces acting along the side surface of the reinforced concrete structure of the foundation for construction significantly exceed the load created by light houses. And in the case when a shallow foundation is used on heaving soils, this problem is eliminated.
In addition to everything, this version of the foundation for construction allows you to do the construction yourself. Firstly, when laying this type of foundation, it is enough to use half the amount of materials that would be needed if a buried foundation were being built. Secondly, a shallow foundation with your own hands does not require much effort to prepare a very deep trench, since sometimes you can get by with a depth of 20 cm.
However, there is also a drawback to this type of foundation for construction. So, the degree of soil heaving plays a role. In case of increased heaving, it is necessary to use reinforcing mesh, and weak heaving soils allow you to make do with a concrete base. There is also another variety - a shallow columnar foundation. Its use is quite limited due to the small loads it can withstand, which is explained by the small supporting area. And this parameter, in turn, characterizes the bearing capacity of the foundation for construction. But a shallow columnar foundation with your own hands is also much easier to create and much more economical.
If you do not have qualifications or basic skills in construction, you can choose an alternative option. Considering that for any foundation for construction it is necessary to prepare a concrete mixture, make formwork, and, if necessary, strengthen it with reinforcement, a lot of time and effort is required. But there is a simplified option - a shallow foundation made of FBS blocks (foundation building blocks).
What is this material? These are ready-made blocks, which will cost approximately the same amount as completing the foundation for construction completely independently. However, their strength is high enough to withstand even multi-story buildings. Therefore, a shallow foundation for a brick house can be made from such material.
Building a foundation in winter: conclusions
1. Construction of foundations for country houses on heaving soils is recommended to be carried out in the warm season. Only in this case can the quality and efficiency of construction and the reliability of foundations be ensured.
When making buried foundations on heaving soils in winter, deformations are possible, which leads to a violation of the integrity of the foundations themselves. The manufacturing reliability of such foundations is low.
2. It is permissible to install buried foundations for wooden houses in winter on non-heaving soils, as well as on slightly heaving soils, subject to all the requirements of the work technology.
3. Regardless of the degree of soil heaving, it is permissible to erect wooden houses in winter on shallow foundations made before the onset of frost.
4. Making foundations in winter significantly increases the cost of construction.
AN INTERESTING RECIPE FOR ANTI-FROST ADDITIVE WAS USED BY THE ARCHITECT MONTFERRAND WHILE CONSTRUCTING THE FOUNDATION OF THE ALEXANDRIAN COLUMN ON PALACE SQUARE IN ST. PETERSBURG (CONCRETE WORK WAS CARRIED OUT AT NEGATIVE AIR TEMPERATURES): HE I MIXED CEMENT WITH VODKA AND ADDED A TENTH OF SOAP.
How to calculate the amount of material
To find out the required amount of building material that is supposed to be used, it is necessary to calculate the depth of the foundation for the building. The main parameter that is taken into account is the depth of soil freezing. The calculation of a shallow foundation is also influenced by the degree of soil heaving, as well as the height of the groundwater.
For example, if the freezing level of slightly heaving soil is 1 m, a foundation depth for construction of 0.5 m will be sufficient. In addition to these parameters, the load level should also be taken into account. Thus, a shallow foundation for a frame house, due to its lightness, can be made with a shallower depth at the same level of soil freezing. Next you need to calculate the total volume of the concrete mixture. Why is the value of the perimeter of the future house and the length of all internal walls summed up? The volume of the trenches is then calculated.
To calculate the mass of the concrete mixture, you need to multiply the resulting figure by 2,500 kg/cubic meter. m. It is quite possible to calculate the amount of cement if you divide the volume of the concrete mixture into five parts, which are cement, sand and water.
Step-by-step instructions for performing construction work
The construction of shallow foundations is a combination of basic materials: a concrete slab and a sand cushion. If the first of them takes on the load transmitted by the building, then sand is an excellent way to maximally smooth out the uneven distribution of base deformations. A shallow foundation for a wooden house also needs a sand cushion, despite the lightweight type of construction. The thickness of the sand layer under the base is determined by the level of load transmitted by the object.
After the site has been marked, trenches can be dug. It is important to first perform the necessary calculations to determine the sufficient depth of the foundation for construction. At one stage of construction, a blind area for a shallow foundation is constructed. If in any other case this is done in order to avoid the negative impact of wastewater on the concrete foundation of the house, that is, the blind area plays the role of waterproofing, then with a shallow foundation it additionally helps to negate the effect of soil heaving in frosty times.
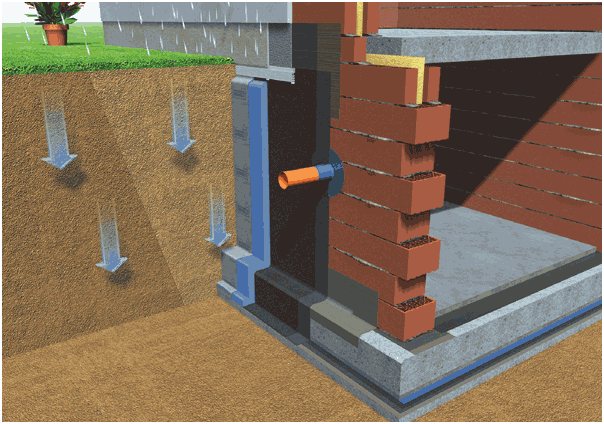
Returning to the step-by-step execution of the work, it should be noted that after sand has been laid at the bottom of the trench as a cushion, you need to take care of waterproofing. For this purpose, bitumen-polymer roll materials are used. Then the formwork is built, if necessary, the reinforcement frame is fixed and concrete is poured. At the next stage, the shallow foundation is insulated with polystyrene foam. This is done on the outside of the foundation for the building in order to protect the basement floor, if there is one, or the residential building itself from cooling.
Insulation of a shallow foundation can be carried out not only on the outside of the concrete foundation of the house. In areas of more severe climates, a different insulation scheme is used, in which the heat-insulating material is laid horizontally directly under the base of the foundation. This is done before pouring the concrete mixture. There is another insulation scheme, which is a combined version of the two methods described. That is, the thermal insulation is located both in the vertical and horizontal planes, maximally protecting the foundation from the effects of low temperatures.
Foundation for a house made of FBS blocks
A house made of FBS blocks is a very popular type of construction. This material is used to create load-bearing elements of buildings that can be used at temperatures from -70 to +50 degrees. Their most relevant use is for the construction of basement and basement surfaces and laying strip foundations. It is worth noting that such blocks are perfectly combined with all types of soil and climatic conditions. In our article we will find out how to build a building from FBS correctly and independently.
Pros and cons of the material
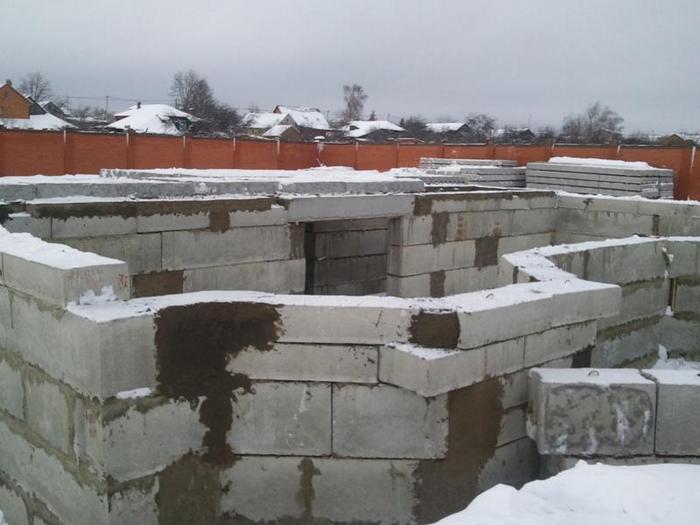

Before choosing blocks for installation work, you need to familiarize yourself with the advantages and disadvantages of the FBS material. Namely these:
- Good strength;
- Durability;
- Resistance to mechanical and biological influences;
- High level of thermal insulation;
- Environmental Safety;
- Wide range of block models.
Such advantages expand the range of applications of FBS products, allowing them to be used in the most uncomfortable conditions. Construction specialists strongly recommend using such material for laying basements, as this will reduce the time it takes to build a house. Of course, such blocks have a huge number of advantages, but we must also consider the disadvantages of these products:
- It is worth noting that the blocks have a high cost, but it is lower than that of a monolith;
- In addition, in most cases it is not possible to obtain maximum sealing at the joints. If you install a self-leveling foundation and a plinth, you can get a more reliable structure. This design is especially relevant in difficult climatic conditions.
- For construction work on the construction of the plinth, it is necessary to use the services of special machines.
Attention! FBS products are more expensive than other materials, and require additional waterproofing treatment of the base or basement.
Concrete works
When installing formwork and installing reinforcement, snow and ice should not fall on the poured base.
To ensure that concrete does not freeze in cold weather when laying and curing, the following measures must be taken: transport concrete in vehicles equipped with heating; use concrete with antifreeze additives that reduce its freezing point; use electric heating of laid concrete; cover concrete with insulation.
Currently, there are many effective antifreeze additives, including additives S-ZM-15, sodium formate, sodium nitrite, etc.
It should be borne in mind that at low positive temperatures the rate at which concrete gains strength decreases by 2 or more times compared to summer, and at negative temperatures - up to 5 times.
The grade of concrete in terms of frost resistance and water resistance should not be lower than F50 and W2, respectively.
When concreting in winter, it is absolutely unacceptable to use liquid concrete with an impaired water-cement ratio. The required amount of water reacts with the cement. Excess water remaining in concrete, when frozen, can cause the destruction of the foundation or reduce its strength.
To ensure high-quality laying of rigid concrete, plasticizers are usually added, for example Superplasticizer S-3. Electrical heating of concrete requires special equipment and skilled workers, which the vast majority of construction companies do not have.
Selecting blocks for installation

When choosing a building material for a house, namely FBS blocks, first of all, you need to check the product documentation and the availability of a passport. The official product certification must contain the following information:
- Contact information of the manufacturer;
- Serial code and lot number;
- Dimensions, brand, weight;
- Indicator of strength during compression;
- Resistance to frost and moisture;
- Basic operating rules.
We make the foundation from blocks with our own hands
The construction process using FBS products is no different, but the work must be performed in strict accordance with the instructions. So, the first thing you need is to calculate all the values. Let's talk about this in more detail.
Calculation of the quantity of materials
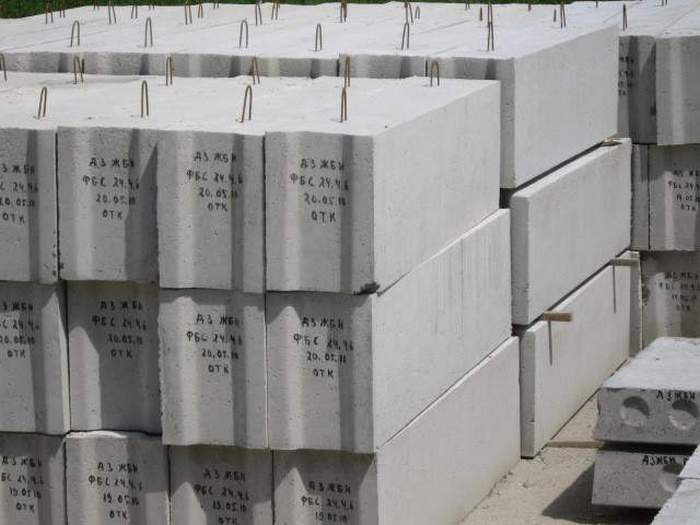

Before you go shopping. We need to know how much material we need to complete the construction. The volume of load-bearing masonry is calculated using the following formula:
V= l by a by h, that is, length multiplied by thickness and height. Next, the resulting value is divided into indicators of one block. If the building has the shape of a parallelepiped, then the calculation is complete, the resulting amount will be the amount of material needed.
Attention! Here it is very important not to forget that FBS elements have a lot of weight, so you should use the services of specialized equipment to carry out the work. Based on this fact, professionals recommend performing calculations for middle blocks, since they will be easier to install.
Today, manufacturers produce several standard parameters for block products. Such values simplify construction work. Usually the block has a height of 58 cm, but for calculations you need to use the number 60. The side walls may be slightly convex, but this is not a mandatory norm, so most blocks are even. Design features are based on the financial capabilities of the owner.
Attention! Of the main requirements, we must not forget that construction should begin by creating a sand and gravel cushion for the foundation. All work is done easily, the main thing is to do everything accurately and correctly.
Tools and materials for performing work
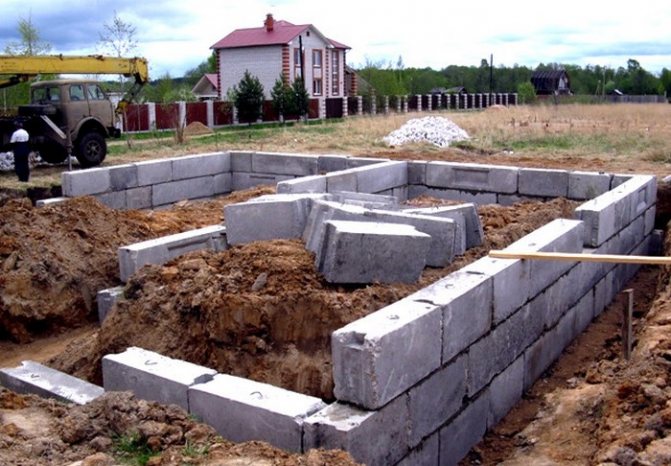

As we have already found out, installation of the foundation for the house is carried out without any particular difficulties. The duration of the process depends on the characteristics of the soil on the site and the total weight of the building. But, you should not forget that the blocks need to be mounted on a prepared surface, which takes most of the time. To perform installation you need the following tools:
- Level of construction purpose;
- A special level, a clamp and a long rope;
- Compact excavator or shovel. The choice of this tool depends on the dimensions of the house.
- Sand and crushed stone;
- Vibrating mechanism for compaction;
- FBS blocks;
- Wooden board for creating formwork;
- Concrete solution.
The materials for creating a prefabricated base are FBS blocks, with a length from 120 to 240 cm, and a height of 40 and 60 cm. These values are standard, but nowadays experts use other options.
Attention! Before you buy blocks you must decide for yourself. Which blocks will be more profitable for you to install?
Preliminary construction stage
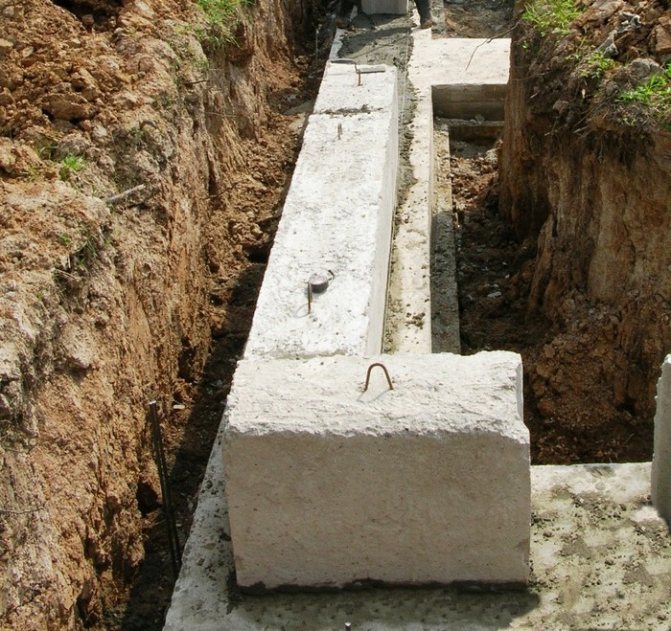

When you need to lay blocks, you must not forget about the most important work - preparatory work. This stage includes the following sequential actions:
- We prepare the area for work. To do this, you need to level the soil, remove large grass and bulges in the area. Next, we determine the type of soil by deep shunting. The type of finish will depend on this factor.
- If the construction is carried out on clay soil. For such conditions it is necessary to dig a ditch of a certain depth. Sand and gravel 30 cm wide need to be laid at the bottom. Such a layer can be created in several ways, which are selected according to the availability of materials for construction. The compaction of the pillow should be done with a special vibrating tool.
- After completing the layer of sand and gravel, trapezoidal slabs should be laid on the cushion. FBS products are used to increase the area of load on the soil. This process increases the overall strength and stability of the building. It is recommended to lay the blocks one at a time, in the form of a chessboard.
- If the site has sandy soil, the process is slightly different. To perform installation, it is recommended to use a different method. First. What needs to be done is to prepare a trench. It is worth noting that for such soil there is no need to make a sand cushion. We compact the bottom, install the slab and fill it with a thickness of 10 cm.
Attention! For a sandy type of site, it is cheaper to install a strip base.
The main stage of the construction process
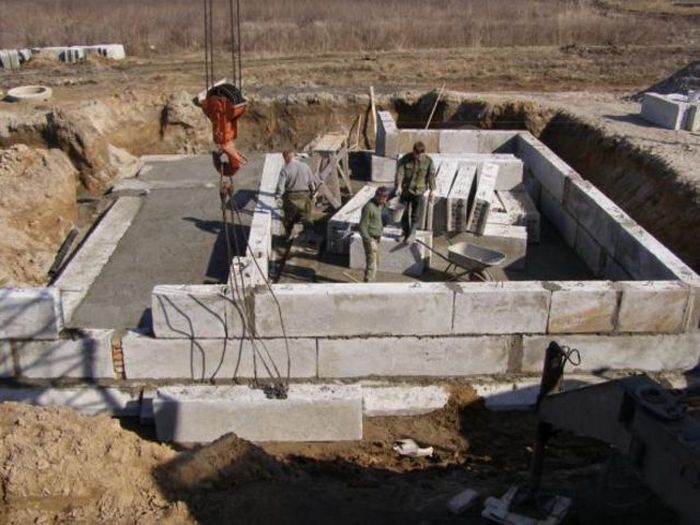

This stage is called the main stage, since it is now that the blocks are being laid. There are some rules for performing this task. FSB products should be laid from corner to corner and diagonally. We begin work by completing the first layer of construction. The blocks must be installed on a prepared concrete layer, which must be durable and free of gravel and crushed stone. It is worth noting that this principle is reminiscent of brickwork.
Installation of block elements must be carried out with bandaging in the corners of the building. In this case, there should be no seams between adjacent blocks. Each layer of the structure must be protected from water and moisture. Suitable materials for waterproofing include rubber, liquid resin and roofing felt.
The position of the structure plays an equally important role in the quality of construction. It is worth noting that it can be performed vertically and horizontally. The second method is characterized by checking using special beacons, a rope and a building level. Deviation from the norm of the angle can be the following values: horizontally - 2 degrees, vertically - 3.
Attention! It is impossible to create voids when installing block devices, as they can quickly deform or lead to the destruction of the building.
The final stage of construction
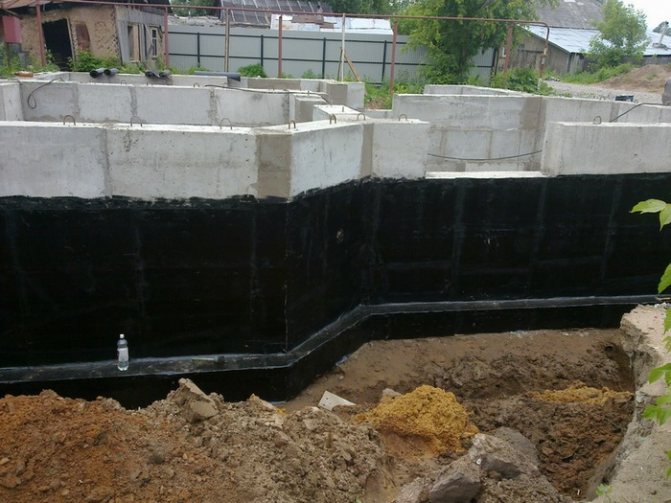

When creating a building on any type of soil, with the exception of the sandy type, the last stage consists of performing the following mandatory work:
- Waterproof the material. This task can be accomplished using roofing felt, liquid rubber, and bitumen.
- When the waterproofing agent has dried, it is necessary to fill the area near the walls with sand from the inside and outside. It is worth noting. That all layers need to be compacted with a vibrating block.
Attention! A prerequisite for such a construction is the need to install a drainage system and a concrete blind area.
So we got acquainted with all the nuances and features of installing houses from FBS blocks with our own hands. Now you can build the desired building yourself.
Installation of the foundation on site
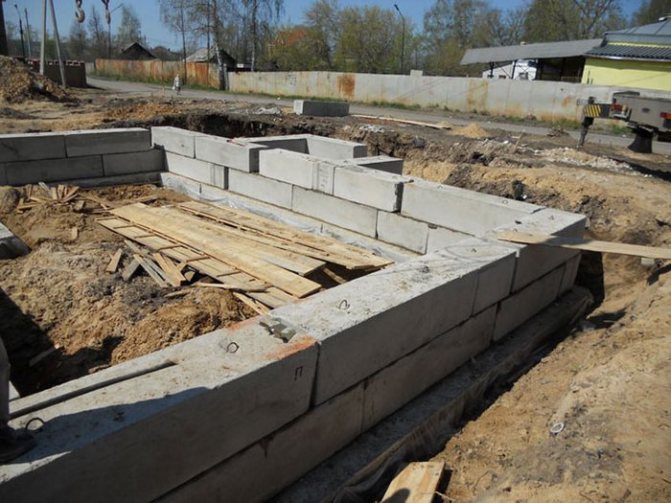

In case of moving blocks to align them and forming cracks, all openings are filled with mortar
After digging the trenches, all that remains is to assemble the entire structure. It happens like this:
- Pillows under the foundation are installed on a sand base, and first you need to set the corners, and then the intermediate elements. If you pull the mooring 5 cm from the edges of the corner blocks, this will help mount all the other elements quite evenly.
- It is necessary to constantly monitor the height marks and horizontal position of the pillows.
Important! Remember that the distance from the edge of the reinforcement bar to the outer edge of the foundation block cannot be less than 0.3 cm.
- Connect the reinforcing bars by welding or overlapping, keeping the length of the weld no more than 10 diameters, and the overlap no more than 350 diameters.
- Fill the reinforcement structure with a screed no thicker than the size of the blocks.
- Leave technological openings for drainage of sewage and water. Fill the openings for installing bushings with concrete.
- Perform external waterproofing, backfilling and compaction.
If the blocks are moved to align them and cracks form, all openings are filled with mortar. The width of the layer cannot exceed 0.3 cm, so as not to disrupt the density and bearing capacity of the foundation. And special attention must be paid to the evenness and correct installation of the top row of blocks. Any shift guarantees uneven walls and lopsidedness of the entire structure.
Installation instructions for foundations made of FBS blocks
FBS building blocks are rectangular concrete blanks used for the rapid construction of walls, foundations, and basement sections. They are easy to install due to their simple geometric shape; compared to pouring mortar, the labor intensity of the process is minimal; an additional advantage is the independence of installation from the time of year. The strength and reliability of reinforced blocks make it possible to create a durable base that is resistant to mechanical loads.
The use of FBS is a proven construction technology; thanks to factory quality tests, the workpieces have no defects and are not subject to temperature changes. Disadvantages include the need to rent lifting equipment, high requirements for waterproofing and the risk of subsidence of sections of the structure (minimal if construction standards are observed). The work does not require special skills, but it is advisable to study video instructions on the topic: how to correctly lay blocks with your own hands and carry out calculations.
Calculation of masonry parameters
The depth of the structure depends on the characteristics of the soil and the expected load. On average, to build a base, 2 to 5 rows of FBS are laid (up to 2.5 m). The use of a shallow strip foundation (1 block) is allowed only during the construction of utility rooms, garages or bathhouses.
In this case, the masonry is the protruding part of the base. Calculating the required number of blocks is easy to do, thanks to their standard dimensions (the length and width are different, in contrast to the height - 58 cm). After calculating the volume of the masonry, the resulting value is divided by the parameters of one workpiece and their required number is obtained.
Device and design features
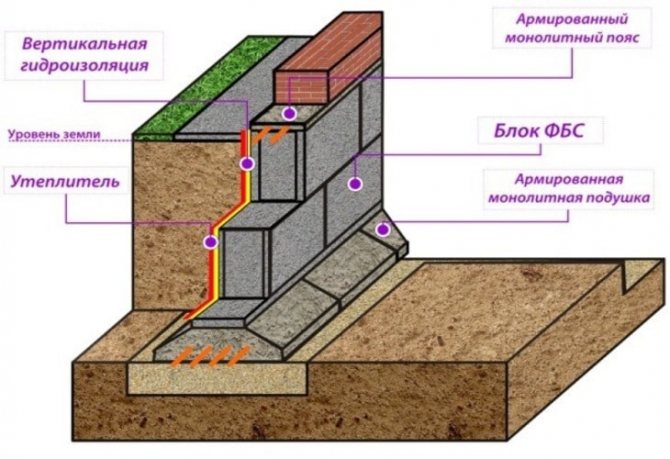
The design of reinforced concrete foundations of this type consists of several elements in addition to the FBS blocks themselves:
- Sand and gravel cushion. Located at the bottom of the trench, it serves to evenly distribute the load and provide high-quality drainage;
- Reinforced concrete base. Prefabricated structures have a trapezoidal cross-section and an increased base area in comparison with FBS blocks. Used to increase the bearing capacity of the foundation and protect against subsidence.
- Reinforced belt. It is a layer of concrete in the upper parts of the FBS foundation. The load-bearing walls of the building are subsequently erected directly on the armored belt.
- Thermal and waterproofing. These materials are laid along the sides of reinforced concrete blocks. Their main functions are to prevent the destruction of structures due to exposure to groundwater, precipitation and sudden temperature changes.
Main stages
Standard step-by-step instructions for laying a strip foundation include:
- Preparatory work: marking, digging a trench.
- Laying and compacting the sand cushion.
- Arrangement of the base: installation of wide FBS slabs or monolithic concrete screed.
- Laying foundation blocks.
- Waterproofing and, if necessary, insulation.
The construction of a columnar foundation from FBS is almost no different, with the exception of pouring bitumen mastic under piles or pedestals instead of a concrete monolith. Conventionally, all work can be divided into two stages: preparatory and direct laying of the blocks. It is important to make the placement scheme in advance; filling the cracks with brick or concrete is allowed, but this leads to a decrease in the strength of the structure. After determining and marking the main axes, rigid reinforcement is driven into the required points, which is checked as the trench is dug for vertical deviation with plumb lines.
The base cushion is standard: at least 10 cm of crushed stone and 5 cm of sand (for clay soils it is three-layer, up to 60 cm, coarse filler is poured as the middle layer). A prerequisite for proper preparation of the pillow is abundant moistening and compaction. The walls of trenches dug in loose soils need protection from collapse. Next, a thin layer of concrete (2–3 cm) is poured onto the compacted sand, and a certain period of time is waited until the minimum strength is achieved. As an alternative to cement screed, masonry mesh can be used under foundation building blocks. Laying the first row is allowed only after the cushion and concrete layer have dried.
First, the base is formed: wider slabs (specially purchased flat or simply inverted) are placed. Laying FBS begins from the corner and the axes marked with reinforcement. For fastening, a high-quality cement-sand mortar of medium thickness or construction glue is used (the latter option is preferable, but will be more expensive). All cracks and contact points, including vertical seams, are coated without exception, and the horizontal level is checked. Free space (if any remains) is filled with brick or concrete. The exception is the gaps for pipes and communications; it is advisable to think through their placement scheme without damaging the wall foundation blocks.
Each subsequent row must be laid offset, according to the principle of brickwork. That is, the vertical seam of the upper block is located strictly in the middle of the lower one; for corner elements, the overlap method is used. The thickness of the cement mortar between the rows is 1.5 cm; if the dressing is insufficient, reinforcement is carried out with mesh or rods.
It is also recommended to reinforce the foundation of blocks with metal when building on heaving soil. By analogy with the first row, each subsequent row is checked for level deviation horizontally and vertically, all voids are filled with solution (the latter is the most important nuance of the technology).
In some cases, the construction of an intermittent foundation is permitted (subject to suitable soil conditions, lightweight masonry and the absence of a basement). But the maximum permissible gap between FBS should not exceed 70 cm. This option allows you to save up to 20% of building materials, but it cannot be used when constructing a building with more than 2 floors.
Ideally, choose long blocks that match the foundation layout. After the solution has hardened, they begin waterproofing work, in this case coating, the top row is covered with roofing felt. In case of intense freezing of the soil, additional insulation of the base is required, most often with polystyrene foam or extruded polystyrene foam; it is allowed to start building walls after 1 month.
How to properly lay a single-row structure?
For light buildings, a simple shallow foundation made of FBS is sufficient, but if there is a risk of displacement (in heaving soil conditions), it should be strengthened. For this purpose, the trench is deepened by 40 cm, and a 30 cm cushion of crushed hard rock and sand is poured onto the bottom. Then a concrete screed, at least 10 cm thick, with reinforcement is poured.
Laying foundation blocks is allowed only after the mortar has hardened; they are coated with bitumen on the sides, and another concrete monolith with a reinforcing frame is installed on top. A prerequisite for the construction of a single-row foundation is the insulation of the blind area.
- Purchasing from an unverified manufacturer.
- Lack of coating waterproofing.
- Construction of discontinuous foundations in buildings with basements.
- Construction of a structure without taking into account future communications.
Tips and tricks
The main advantage of FBS is associated with the high speed of foundation construction; the use of the longest blocks is considered optimal (up to 2.38 m). In this case, the structure becomes more monolithic and the time required to use expensive lifting equipment is reduced.
The foundation should be compacted in stages; river sand is well suited for backfilling; each layer is recommended to be wetted and compacted. On heaving soils, it is not advisable to deepen the structure, but its thermal insulation properties are strengthened in every possible way (by reinforcement, insulation of the base and blind area).
Disadvantages of blocks
Considering this building structure, one cannot help but dwell on its shortcomings. As with any other material, it has both positive and negative sides.
- When erecting a structure from large blocks, it becomes necessary to use additional special equipment.
- Moisture can get into the partitions between structures. It will gradually destroy the foundation. To prevent this from happening, it is recommended to treat them with waterproofing materials.
- Cold air can penetrate into the room through the cracks between the blocks. This leads to an overall decrease in thermal conductivity. The problem can be solved by taking measures to additionally insulate the room.
- The base itself can be compared to assembling a construction set from individual cubes. Therefore, this type of base cannot be called the most durable. Its strength is much lower than the strength of a monolithic foundation, which is a single flat surface.
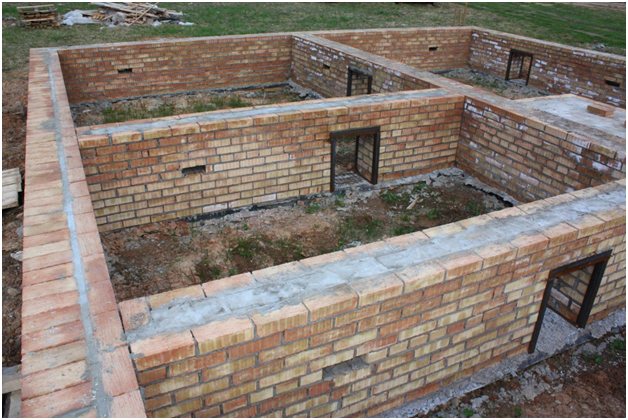
Strip foundation made of FBS concrete blocks for a bathhouse
It is faster to install a strip foundation under main walls using FBS blocks
In construction, the design of a prefabricated strip foundation made from FBS brand blocks is very common.
The foundation design of FBS blocks was previously used everywhere in the construction of multi-storey residential buildings. Convenient, fast. Therefore, the industry for the production of such blocks in Soviet times very quickly occupied its niche.
During the construction of multi-storey buildings on a construction site, construction equipment was necessarily used and construction cranes were assigned to this construction site for the period of construction of the facility. Unlike the modern construction organization, now not all contracting organizations have construction equipment and often the necessary construction machines are rented on an hourly basis.
Why is the issue of the cost of construction machines so acute when building a foundation made of blocks? Because FBS blocks, although they have several standard sizes, all of them require the use of equipment during their installation. And the cost of renting a crane per hour of work is not small.
Brick LF technology
To reduce the construction budget, brickwork can be used instead of monolithic structures and prefabricated FBS strips. In this case, it is necessary to take into account:
- tape made from small-format material is more resistant to ground movements
- no special equipment required, individual masonry fragments can be easily repaired
- without formwork it is possible to produce complex façade configurations
- however, the resource of this structural material is noticeably lower than that of concrete
- It is more difficult to waterproof masonry with coating and lining materials; it is better to use penetrating impregnating mixtures
The laying technology is no different from the construction of walls - bandaging corners and adjacent rows with an offset of ¼ - ½ brick. Marking and digging trenches/pits are completely similar to the previous options. To supply large volumes of building material inside the pit or trenches, it is necessary to provide transportation ladders - boards with bars stuffed on them.
For underground structures it is prohibited to use silicate bricks made by semi-dry pressing. Only ceramics with maximum moisture resistance, strength, and frost resistance are allowed. Hollow, slotted block, stone is not recommended.
Preparing the base
Regardless of the material used for the strip foundation , the set of measures to protect against soil swelling remains unchanged:
- drains around the perimeter from perforated corrugated pipes - slope to the underground reservoir 4 - 7 degrees for gravity flow, wells in the corners for inspection, sewer cleaning
- foundation cushion - 20 cm of sand, 20 cm of crushed stone, compacted layer by layer with a vibrating plate
- waterproofing of the sole - over a layer of concrete (5 cm screed) or over sand in 2 - 3 layers with rolled material (gidrostekloizol, Bikrost, TechnoNIKOL) with sealing 10 cm of overlapping sheets

If necessary, the widening of the sole is made of the same material, for which it is enough to increase the width of the masonry. The holes for entering communications immediately have the required size, sleeves can be embedded in them, and minimal gaps can be provided through which soil can fall into the underground level.
Brickwork, waterproofing
Depending on the configuration of the walls, the consistency of cement-sand mortar is used (1/4, respectively + 3 drops of Fairy per 100 liters of concrete mixer) sour cream - cottage cheese. Liquid soap gives the mixture plasticity; by wetting the stones before laying, you can increase the time for adjusting the bricks in the rows. Standard technology:
- corners for 4 rows - ligation of vertical seams
- filling the rows - displacement of the butt/spoon in each adjacent row, backfilling in the foundation is prohibited
- reinforcement - mesh with longitudinal bars 4 - 6 mm of periodic section, transverse wire 2 - 4 mm

In reinforced rows, the thickness of the seam increases, which must be taken into account when adjusting the design level. In the underground part, all seams are filled completely without jointing (trimming with a trowel). In the basement part, the seams are either expanded (facing bricks) or not completely filled (empty brick) for better adhesion to the plaster mortar. If the project includes tape insulation, the seams are filled completely along the entire height of the masonry.
Unlike concrete reinforcement, the protective layer in brickwork increases to a minimum of 4 cm. When using meshes of 5 mm wire in the transverse and longitudinal direction, it is better to choose zigzag cells instead of square ones.
Waterproofing masonry is practically no different from protecting concrete tape. If you add the penetrating composition Admix from the manufacturer Penetron to the solution and treat a brick wall with the same impregnating composition, at least from the outside, the service life of the foundation will double. When using coating bitumen mastics in combination with TechnoNIKOL rolled waterproofing, the service life will be 30 - 70 years, depending on the geological conditions in the building area.
For the convenience of individual developers, all options for prefabricated strip foundations with step-by-step production are given. This will allow you to choose the optimal option for specific conditions and ensure a 70-100 year lifespan of the building.
Concrete blocks for foundation
For some reason, concrete blocks for foundations of the FBS brand are always called concrete, although little reinforcement is used in their manufacture.
The abbreviation FBS stands for foundation wall blocks. They are intended for basement walls, because often such a foundation is laid to the depth of soil freezing or immediately for the purpose of constructing a basement under the building. Therefore, walls made of FBS blocks are also the foundation and walls of the basement of a residential building or building for any other purpose.
Building a foundation in winter - video
Winter construction and foundation in winter
TOOLS FOR CRAFTSMAN AND CRAFTSMAN, AND HOUSEHOLD GOODS VERY CHEAP. FREE SHIPPING. THERE ARE REVIEWS.
Below are other entries on the topic “How to do it yourself - for a homeowner!”
- Repair of slab and strip foundations HOW TO FIX THE FOUNDATION? WE ALREADY TOLD...
- Do-it-yourself pile foundation for a shed, toilet, bathhouse SECRETS OF A RELIABLE PILE FOUNDATION FOR…
- Foundation project Why do you need a foundation project and...
- Do-it-yourself foundation insulation, how and with what Foundation insulation: technology and materials Insulation…
- Do-it-yourself insulated Swedish slab (USP) - pouring scheme using Do-it-yourself warm foundation technology or...
- Shallow foundation slab with your own hands - diagrams, design options SHALLOWED FOUNDATION - OWN PLATE...
- How to properly make a basement ceiling yourself View the full album Making a basement ceiling...
Subscribe to updates in our groups and share.
Let's be friends!
With your own hands › Construction › Building a foundation in winter - is it possible or not (detailed description of the technology)
Strip foundation made of blocks
A strip foundation made of blocks in private construction is arranged:
- for a low-rise building with solid walls (brick, gas block) with the base of the foundation laid to the depth of soil freezing
- for a low-rise wooden house or bathhouse with or without a basement, with the base of the foundation laid to the depth of soil freezing
- for any one-story building (house, bathhouse, garage) without a basement, like a shallow foundation
When building any foundation structure, it is necessary to build on the soil.
A strip foundation from FBS blocks can be made for any type of soil, it will only be necessary to apply appropriate structural measures depending on the type of soil and groundwater level.
For example, you want to build a wooden house with a bathhouse, and even a basement. This is a fairly large building.
If you have sandy or rocky (with crushed stone, gravel) soils and the groundwater level is below -3m, then no problem, the design of a strip foundation made of blocks is your most optimal solution.
These soils are not heaving, so under such soil conditions it is possible to construct a full-fledged basement from FBS blocks, which will always be dry.
If you have clayey or loamy soils and a high groundwater level, for example, at 1 m below ground level, then you need to think very carefully before making foundations from FBS, since the basement will have to be waterproofed against groundwater seepage. And clayey soils are heaving and therefore you will have to do:
- monolithic belts along the base of the foundation and along the top of the foundation to strengthen the FBS masonry located in the middle between the monolithic belts.
- fill all foundation cavities around the perimeter of the building with medium-grained sand, which is a non-heaving soil
- coat the side surface of the foundation in contact with the ground with bitumen, thereby reducing lateral buckling forces
- in modern construction, another design solution is used to reduce soil freezing by installing an insulated blind area around the perimeter of the structure
Foundation strip design
Until recently, the most popular foundations among individual developers were slab and strip foundations. Therefore, the technologies have been developed and have been supplemented with options for various operating conditions. Currently, there are several modifications of strip foundation :
- monolithic – concreting into locally installed formwork
- prefabricated - FBS blocks on FL slabs, less often masonry with wall blocks 20 x 20 x 40 cm or brick
- deep - the sole is located below the freezing mark, there are no heaving forces underneath it
- shallow-depth MZLF - under the base the soil is replaced with non-metallic material to a depth of 40 - 60 cm, tangential forces from soil swelling are reduced due to the minimum depth of the tape (30 - 70 cm)
- T-shaped – due to the widening of the sole, the load-bearing capacity of the belt is increased
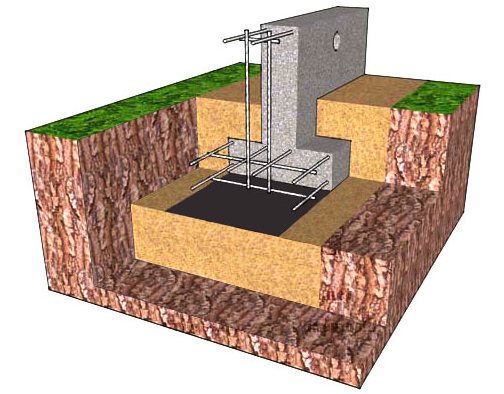
- not buried - only the fertile layer is removed under the foundation, the base starts from the ground level
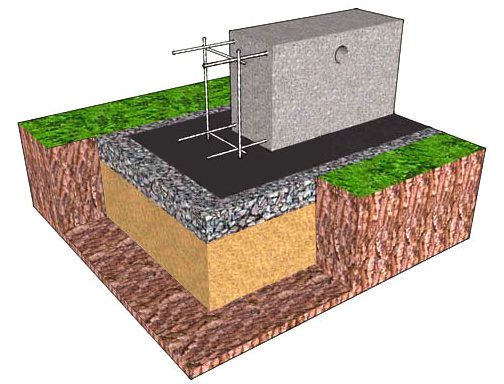
- monolithic belt - similar to the previous case, the width of the belt is greater than its height to increase the supporting plane
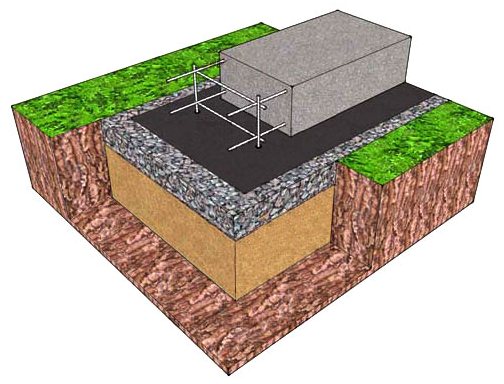
Prefabricated LFs can have any depth, but are mainly suitable for light buildings (frame, panel, half-timbered, log, panel cottages). For brick walls, an MZLF is usually built with insulation of the sole, blind area, or a recessed LF.
Monolithic foundation LF
Monolithic tapes with two to three reinforcement belts with bars of periodic cross-section 10–14 mm have the maximum service life and spatial rigidity. They are poured into formwork, the concrete laying technology

The disadvantage of the technique is the increase in construction time. Concrete takes time to gain strength; the formwork must first be installed and then dismantled.
Prefabricated foundation LF
When using ready-made FBS blocks made industrially, work time is reduced. However, reinforced concrete products are laid exclusively using special equipment, which increases the construction budget. There is a strip foundation technology using brick and concrete masonry.
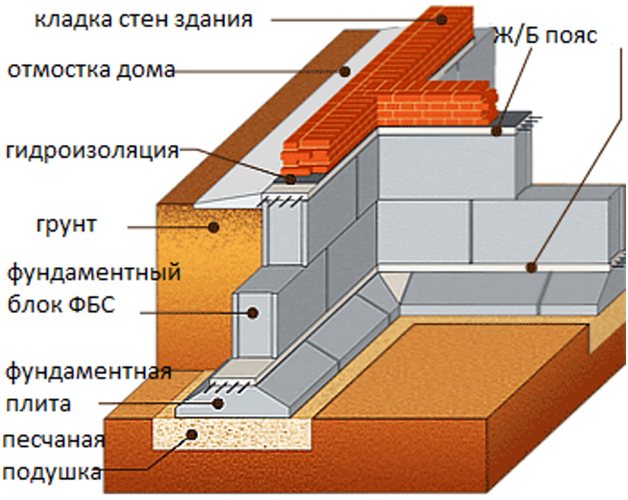
The disadvantage is the maximum number of mortar joints, which are much more difficult to waterproof than the homogeneous concrete surface of a monolithic structure.
Shallow foundation MZLF
The service life of any foundation depends on its load-bearing capacity and heaving forces tending to disrupt the geometry and integrity of the structure. In MZLF, strip foundation technology solves the latter problem in several ways:
- a layer of non-metallic material under the base - 40 - 60 cm of sand, ASG or crushed stone, in which swelling is guaranteed to be absent
- drainage at the sole level – prevents saturation of clay soils with moisture, heaving forces are reduced to an acceptable level
- insulation - blind area or sole (5 cm polystyrene foam) + side walls of the tape (5 - 8 cm layer), heat insulator retains the heat of the subsoil, the soil does not freeze in any frost
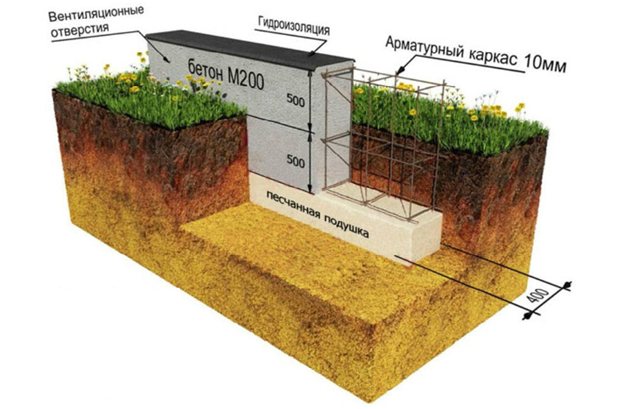
The complex of these measures makes it possible to produce a LF from brickwork or FBS blocks without reducing the service life of the foundation.
Deep laying tape
The most expensive of all existing LF strip foundations is a strip buried below the freezing mark. Therefore, it is chosen exclusively for projects with a basement. the construction time of a strip foundation .

It is very difficult to pour formwork 2.5 m high and 50–60 cm wide in one go, even when ordering mixers. Therefore, lifting equipment is rented, FL slabs are laid, on which FBS blocks are mounted.
In the absence of backfilling inside the perimeter of the LF (basement floor, underground), the soil, when heaving, exerts serious pressure on the foundation walls. Therefore, massive blocks are used, laid on cement-sand mortar.
Foundation for a bathhouse made of blocks
- sand and gravel pad 300mm thick
- preparation for 100mm thick blocks of monolithic concrete with reinforcement
- laying concrete blocks on a layer of cement mortar and filling the vertical joints between the blocks with mortar
- monolithic reinforced belt on top of a row of blocks 100-200mm high
- Coating the sides with bitumen
- filling the foundation cavities with sand 100-300mm wide
- insulated blind area
- Less likelihood of deformation under the influence of soil heaving forces
- Greater structural rigidity of the foundation
Foundation blocks: types, sizes, markings
In private construction, several types of blocks are used. To construct a prefabricated strip foundation, only two types are most often used:
- FBS is a solid foundation block. When they talk about this type of block, they mean a reinforced concrete (with reinforcement) element without voids. These are rectangular blocks of different sizes with mounting steel loops on the top surface. Sometimes vertical channels are formed in the side edges, which are filled with mortar during construction. The foundation strip is made from these blocks.
- FL - pillow blocks. They look like a trapezoid. They are laid on a prepared base and serve to increase the bearing capacity of the foundation.
Types of foundation blocks that will be needed for a prefabricated strip foundation

When constructing a strip foundation, it is necessary to provide routes for laying and supplying engineering systems: water supply, sewerage, electricity, heating. You must not forget about the ventilation system and leave holes for vents to ventilate the underground space or basement. For this purpose, blocks with a channel for laying communications may be useful: FBV.
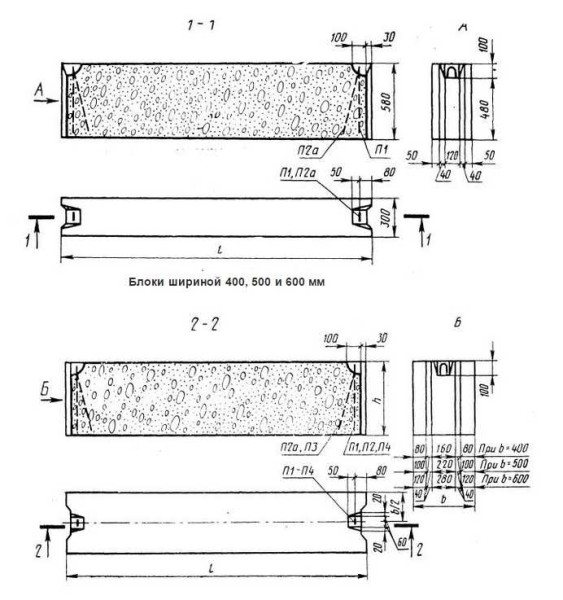
The sizes and types of blocks are regulated by GOST 13579-78. For a private developer, size and performance characteristics are mainly important. The photo below shows part of the standard, which defines the types and sizes of blocks.
Excerpt from GOST standardizing the dimensions of foundation blocks
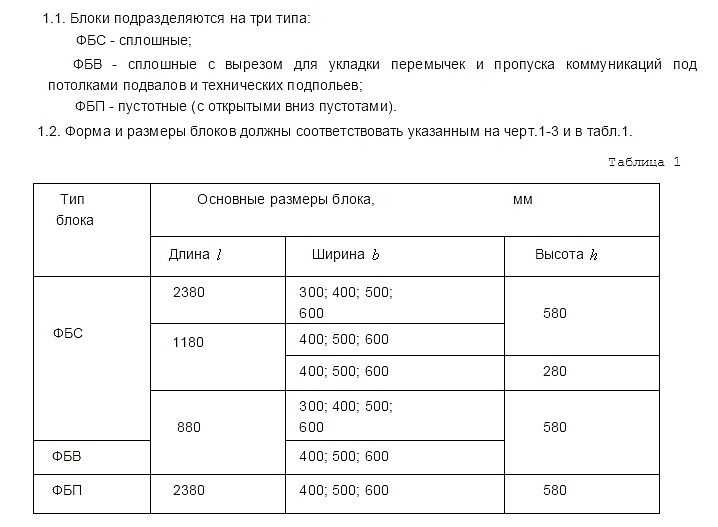
Marking according to GOST
To make it easier to navigate the specifications, the names of the blocks, by the same GOST, contain information about their size and type.
First comes the title. Next are numbers describing the geometry in decimeters;
- the first is length (9, 12,24);
- the second (through a dash or dot) - width (3,4,5,6);
- third - height (3.6);
Marking of concrete foundation blocks

If there are any lengths and widths, then the FBS height is usually made 580 mm (marked “6”). Blocks with a height of 280 mm can be made to order.
Next, after the numbers there is a letter designation of the type of concrete used:
- T - heavy (cement-sand mixture with crushed stone). The heaviest high density block. This type is used in the construction of foundations.
- P - porous with expanded clay concrete filler. They have less weight, but also less strength, and are also more hygroscopic.
- C - made of silicate concrete (the main binder is lime). This type of blocks is afraid of getting wet, therefore it is not used in the construction of foundations.
For example, FBS 24.4.6 -T stands for: rectangular block of high-density reinforced concrete. Length 2380 mm, width 400 mm, height 580 mm. By analogy, you can decipher other symbols.
Dimensions of FBS blocks according to GOST
Construction of foundations from FBS blocks
FBS concrete blocks are laid with ligation of vertical seams
To construct foundations from FBS blocks, it is best to hire professionals who have construction equipment.
The technology for constructing foundations from FBS blocks is as follows:
- digging a pit to the depth of soil freezing or to the depth of the basement height with the addition of the height of the basement floor structure. The width of the pit should be larger than the dimensions of the foundation so that the blocks can be comfortably mounted.
- cleaning the bottom of a pit or cleaning the bottom of trenches for foundation blocks with horizontal leveling and measuring the design elevation of the foundation base.
- foundation preparation device: sandy or monolithic, depending on the type of soil, its bearing capacity and groundwater level.
- laying foundation slabs (FL pads) under FBS, which increase the base area of the foundation. They can be laid as a continuous strip or intermittently, depending on the overhead load on the foundation. For low-rise construction, foundation slabs can be replaced with a monolithic slab with reinforcement. It is possible for low-rise construction to construct a foundation from FBS blocks without widening the base, that is, without the use of foundation slabs. Everything is determined by calculations and ground conditions.
- Installation of FBS foundation blocks according to drawings and layout diagrams with ligation of vertical seams (in the middle of the blocks). The blocks are laid using cement mortar and filling the vertical joints.
- Construction of monolithic sections between blocks according to the drawings and laying sleeves for communications.
- Installation of roofing felt waterproofing on the horizontal surface of the top row blocks
- Coating with bitumen 2 times all the side surfaces of the foundation, which will later be backfilled and come into contact with the ground
- Backfilling of foundation cavities with local soil or sand, depending on the heaving of the soil and design decisions.
What materials should I use to build walls in the basement?
For the construction of basement walls, mainly FBS concrete blocks, hollow facade blocks and concrete poured into formwork are used. Hollow blocks for the plinth are used when the walls require additional reinforcement and you ultimately need to get the thinnest possible walls with good thermal insulation. After laying the hollow blocks, vertical channels are formed in the wall into which reinforcement can be inserted. Then the channels are filled with concrete or expanded clay. This method is quite expensive and time-consuming.
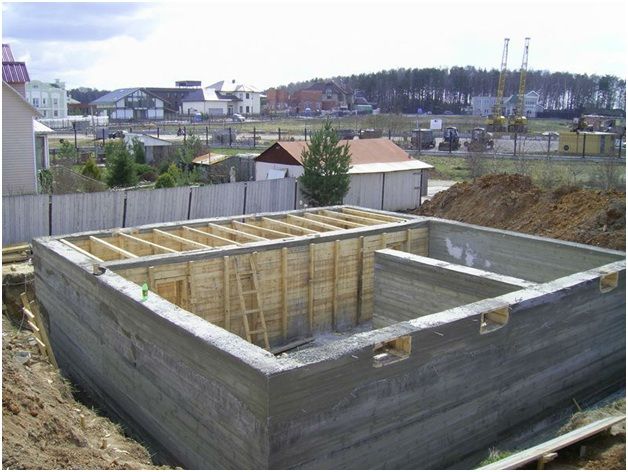

Monolithic ground floor
Monolithic (solid) basement walls should be installed when it is possible to rent high-quality reusable formwork. Specialists will install it very quickly, and the resulting wall surface will be even and smooth. In an ordinary private house, installing such formwork and pouring it with concrete takes no more than two days, and after another 3-4 days the formwork can be dismantled, but such work must be carried out by highly qualified specialists. Preparing formwork is very labor-intensive, and its insufficient rigidity often leads to unexpected deformation of the walls.
You should not try to build monolithic walls yourself (without experience) using traditional plank formwork. The result will almost certainly be unsatisfactory.
Both of these solutions are significantly more expensive than using the traditional method - building a basement floor from FBS. Walls made of concrete blocks are the most popular due to their relatively low price and ease of implementation.











