Combined options have the highest load-bearing capacity among all types of foundations. They combine the best characteristics of different types of foundations and qualify as bases with increased reliability. For this reason, a foundation on bored piles with a monolithic grillage rightfully occupies one of the first places in construction ratings. Due to the piles buried in the ground, it is qualitatively fixed in stable layers of soil, and the reinforced concrete grillage makes it possible to evenly distribute the load on the supports.
Types of pile-strip foundation
Depending on the type of piles that are used in the construction of the foundation, the latter is divided into:
- screw;
- bored.
The peculiarity of the first is that the piles in it are made of a metal pipe, the end of which is made in the shape of a screw.
If you look from the outside, it resembles a large screw, but only for screwing into the ground.
Thanks to this design, the support area of the pile increases, which increases its rigidity and, as a result, increases the reliability of the entire building.
Depending on the characteristics of the site where the house is being built, different screw diameters are used:
- for marshy and clayey areas its diameter can reach up to 850 mm;
- for frozen areas of soil, thinner piles are used - with a diameter of 300-400 mm.
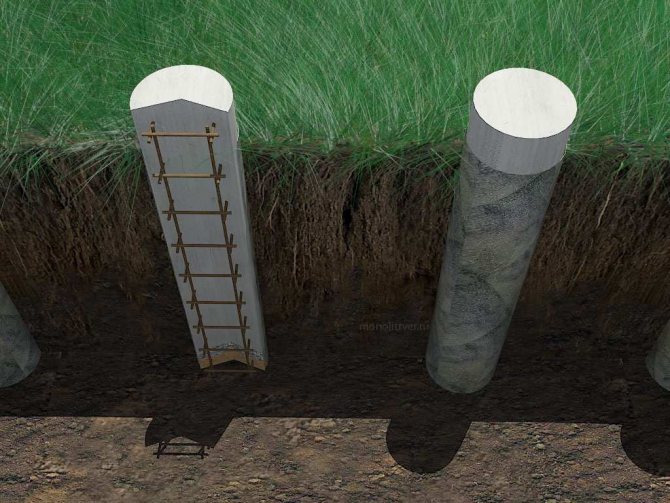
A bored foundation with a grillage differs from the previous one in that in this case ready-made metal structures are not used, and the piles are made immediately on the site. Using a drill, holes are made around the entire perimeter; their depth depends on the properties of the soil.
It is recommended to drill until the well penetrates at least 60 cm into the solid horizon. After that, wet sand is poured into the hole and compacted.
Next, reinforcement is installed and the well is filled with concrete.
Advantages and disadvantages

A slab foundation on piles has the following advantages:
- technical conditions are provided for construction in problem or wetlands;
- the impact of heaving loads disappears or decreases;
- the volume of excavation work is reduced, which in some cases is not carried out at all;
- it becomes possible to build on slopes or folds;
- construction adjacent to existing buildings or structures is allowed;
- the influence of hydrogeological factors is reduced.
A slab foundation on piles has the following disadvantages:
- there is no possibility of building a basement;
- large volumes of concrete work;
- construction requires certain weather conditions, which requires a preliminary calculation of the duration of the preparation and taking into account the hardening time of the concrete;
- material consumption increases;
- high requirements for waterproofing the base.
Despite the existence of serious disadvantages, foundation slabs on piles are widely used in construction on problematic soils, since there are no alternative options in such conditions.
Construction of a pile-strip foundation with bored piles

A standard strip foundation consists of a simple monolithic base, which is placed around the entire perimeter of the future structure.
The pile-strip foundation, in contrast to the previous one, does not rest on a simple sand cushion, but consists of free-standing piles with a monolithic or beam grillage.
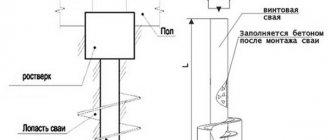
The grillage is the upper part of the foundation, which evenly distributes the mass of the building onto the piles.
Depending on its location, structures with a hanging or recessed grillage are distinguished.
The first is a foundation that is several centimeters above ground level, while in the second case it is in direct contact with the ground.
Pouring the grillage
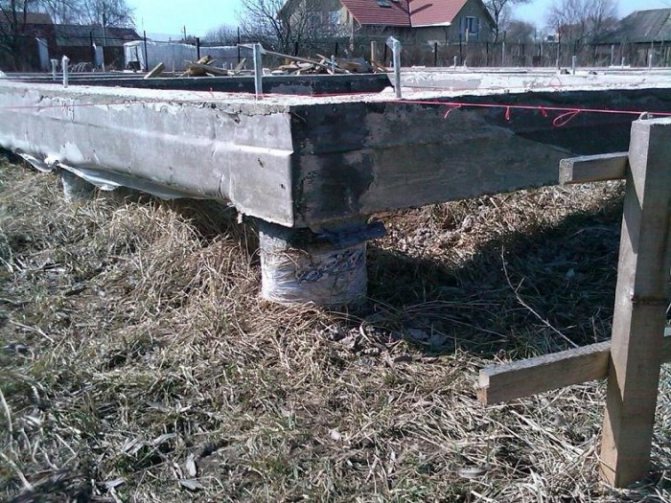

Pre-prepared piles are cut to an even horizontal level, then the grillage is poured:
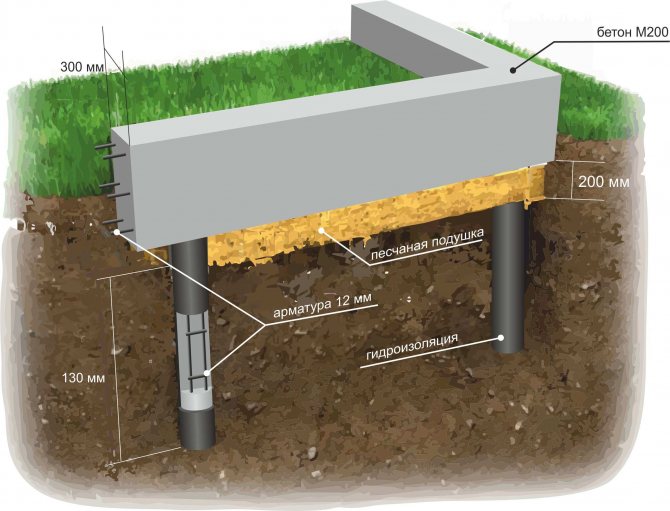
- installation of formwork and reinforcement cage made of rods with a diameter of 12 mm inside the formwork;
- pouring a concrete solution, the technology is followed as when pouring a strip foundation: the mixture is laid out in layers with tamping and compaction - the process is carried out in one day.
According to dimensional gradations, the grillage must be at least 30 cm in height and 40 cm in width. The grillage may be made monolithic or block. A foundation with a monolithic grillage has greater strength and bending rigidity. In addition, a monolithic grillage is more convenient for DIY construction, since the installation of ready-made block elements may require the use of special equipment.
Types and advantages of pile-column foundations
The grillage can be suspended or recessed. Suspended grillages are good for light buildings made of timber or made using frame technology. The pile foundation of a drilling rig with a buried grillage is indicated for construction on soils with increased heaving rates.
The technology for constructing a recessed grillage requires the following work:
- the soil is cut from the upper end of the finished pile body so that the head is at least 25-30 cm high;
- formwork with reinforcement is constructed;
- the grillage is poured over the cap.
Important! The distance from the ground to the grillage must be at least 10 mm to avoid possible deformations in the event of natural soil movements or heaving.
List of necessary tools and materials

In order to independently make a bored foundation with a grillage, you will need the following tools and materials:
- cement, sand, gravel;
- fittings;
- wooden beams;
- boards;
- roofing felt or other material for waterproofing;
- hammer, shovel, construction mixer or concrete mixer, drill;
- wire and nails.
Calculation
The procedure for calculating TPF is complex; for an unprepared person, this procedure represents an insurmountable task. A pile-slab foundation, the design of which consists of two units, requires parallel calculation of the bearing capacity of the underground and above-ground parts of the foundation. It is necessary to determine:
- pile field configuration;
- type of piles;
- number of vertical supports;

- their placement diagram;
- depth and method of diving.
No less complex is the calculation of the slab, in which the following parameters must be determined:
- the degree of settlement of both the slab itself and the entire base as a whole;
- plane roll level;
- slab configuration taking into account the uneven arrangement of piles.
In addition, the calculation of the load on the base is carried out based on the weight of the building. It consists of two quantities - building structures and payload, consisting of the weight of finishing materials, furniture, people, other objects and materials. To this is added the snow load on the roof in winter, the degree of exposure to wind and other external factors. It is especially difficult to calculate a slab-pile foundation for a high-rise building experiencing increased external loads in combination with operational impacts.
To perform a correct and accurate calculation, it is necessary to involve a competent and experienced designer specializing in foundations of this type. Attempts to independently resolve the issue are doomed to failure, since, in addition to mathematical formulas, geological exploration data, seasonal fluctuations in groundwater levels, soil freezing depths and other special indicators will be required. As an option, online calculators can be used, of which there are a considerable number on the Internet.

More accurate calculation results can be obtained by using the GeoPlate program, created specifically for design work with slab foundations.
Main stages of work
Let's look at the main stages of constructing a bored pile foundation
Initial
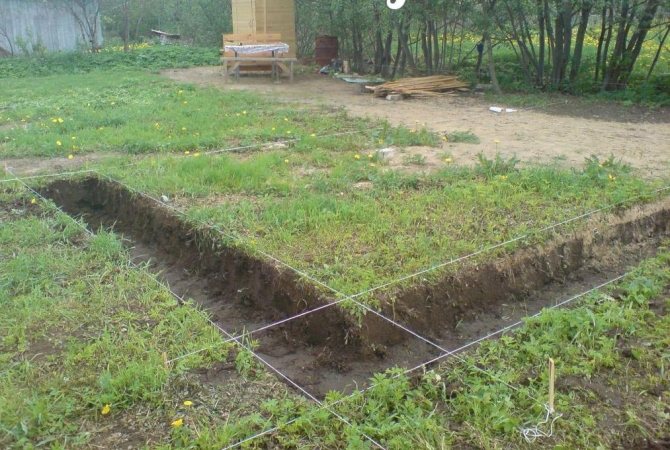
First, before the active phase, it is necessary to clear the area of debris and level it. Next, using cast-offs and cords, the territory is marked - the location of the axes, the width of the tape, and the installation locations of the piles are noted.
Excavation
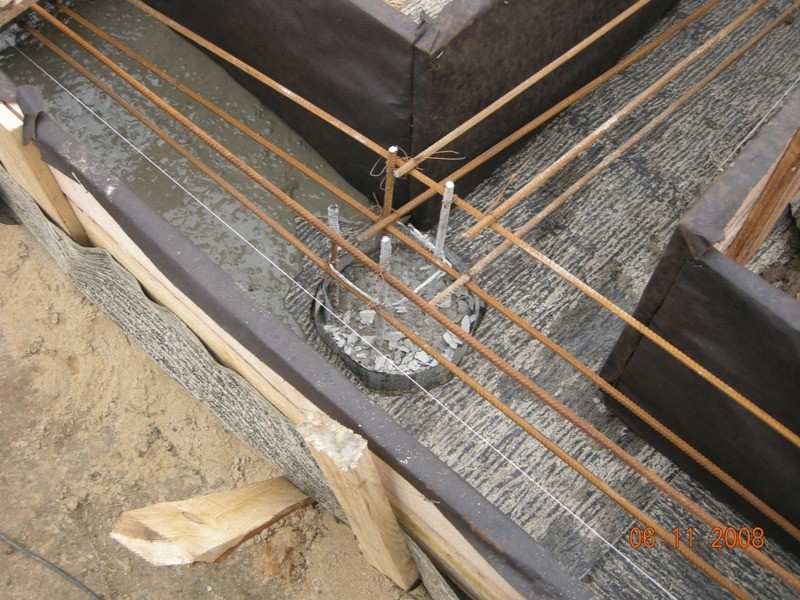

After marking, you can begin to directly dig the trench. Its depth depends on the type of soil, but, as a rule, no more than 40 cm. Regarding the width, it should correspond to the width of the monolithic tape.
Next, wells are drilled in the corners and the entire perimeter of the area, and it is recommended that the step between them be no more than 2 meters.
Regarding their depth, it all depends on the type of soil - each well must penetrate into a solid horizon at least 60 cm.
According to information from builders, the average depth of a well is from 1.6 to 1.8 m. The diameter of its hole should correspond to a third of the width of the trench.
Preparatory work
At this stage, it is necessary to waterproof future piles in order to improve performance characteristics and increase their service life. To do this, you simply need to place layers of roofing felt or other waterproofing material in the holes.
You can also use asbestos-cement or plastic pipes, but then you need to take into account their diameter. Then the area of the future foundation with a grillage is covered with sand to a height of about 30 cm and the formwork is prepared.
Reinforcement
To create a monolithic concrete structure, it is necessary to reinforce not only the tape, but also all the piles. 12-15 mm rods are used as a reinforcing belt.
For piles, it is recommended to use at least 4 pieces of reinforcement. All reinforcement bars are twisted together using wire and welded.
Fill
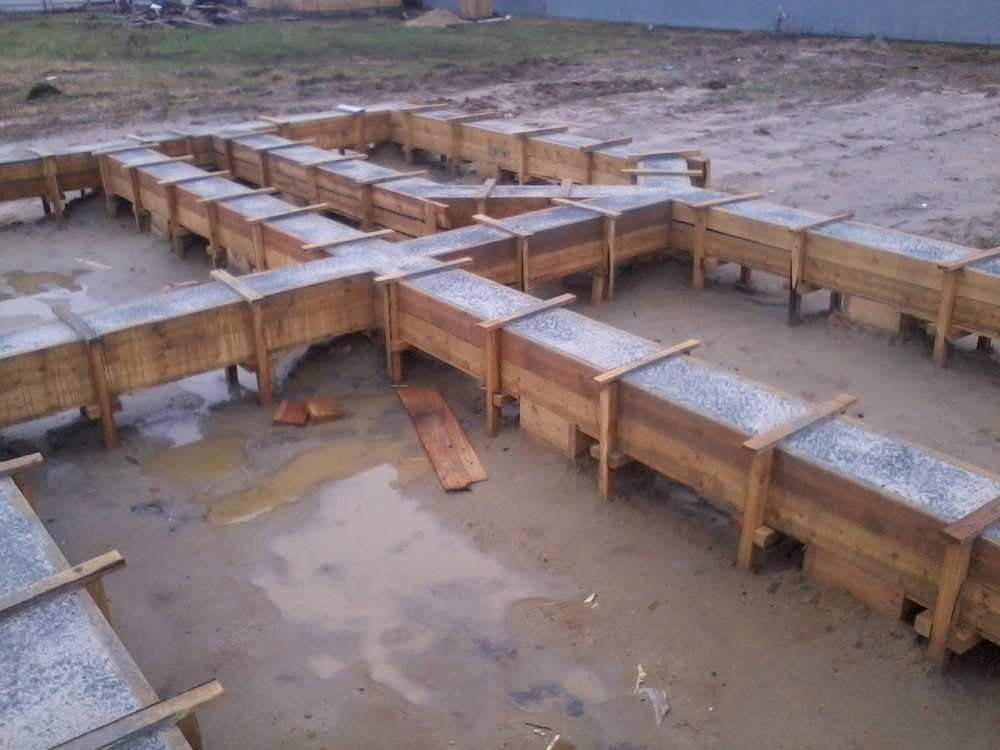

Concrete pouring begins from the wells. During this process, it is necessary to reduce the risk of voids.
To do this, after every 20-30 cm of concrete pouring, it is compacted.
After filling all the wells, the foundation with a grillage is poured directly.
A few days after the structure has dried, the formwork can be removed.
Feasibility of application

Pile-slab foundations are erected on heaving soils prone to flooding
A common problem for all developers is to achieve the required degree of stability of buildings in unstable soils. In addition, engineers need to know and take into account the freezing depth of the ground in their calculations. In some cases, when choosing a technology, a slab on piles foundation equally successfully withstands changes in soil moisture and its freezing-thawing cycles.
Based on this, it is advisable to use this design in the following conditions:
- loose and weak soils;
- high level of groundwater;
- swamps and peat bogs;
- high degree of frost heaving;
- real risk of seasonal flooding;
- severe freezing of the ground during long winters;
- impossibility of excavating a pit due to dense underground infrastructure;
- complex terrain of the site;
- creating an extension to the building on a strip foundation;
- seismic activity of the region;
- conducting low-rise construction in unexplored areas.
The lower part of the piles rests on dense layers of soil, transferring the vertical load from the building to them. At the same time, single products tend to vibrate noticeably, entering a state of resonance with the house. The foundation slab acts as an enlarged grillage, connecting all the supports into a single system and damping all vibrations.
Arrangement of bored piles and footings
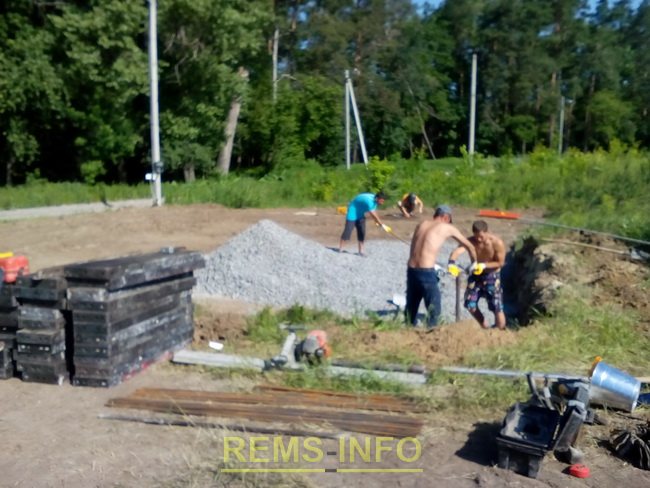
The next step, using a hand drill (two people worked), boreholes were drilled for the piles, each depth 2 meters (minimum depth 1.5 meters). The piles are designed at the corners of the foundation and the middle of the sides, eight in total.

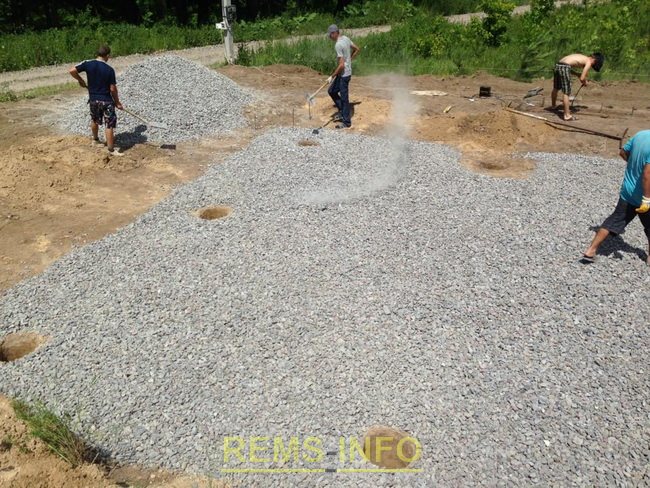
Afterwards, 15 cm of crushed stone was poured over the plane, which was leveled and then carefully compacted with an electric rammer. Crushed stone is the most important element of foundation drainage.

We assembled the metal formwork. In general, you can make homemade formwork from boards, but metal formwork is better and more convenient. It is easy to rent for several days.
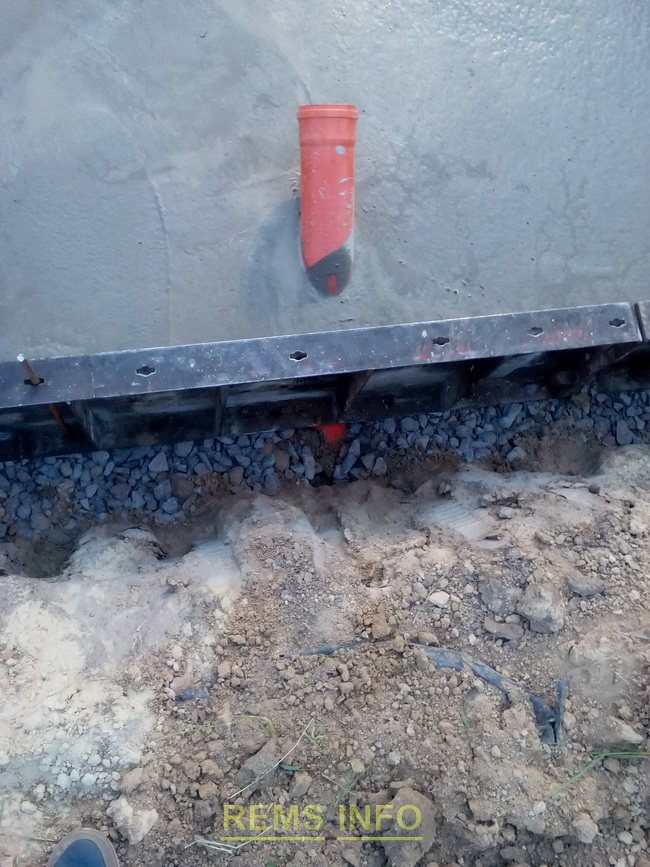

When pouring a monolithic slab foundation, you need to design some communications in advance. So, even before pouring the concrete base, a box was installed for the water inlet into the house and the sewer outlet using an external sewer pipe.
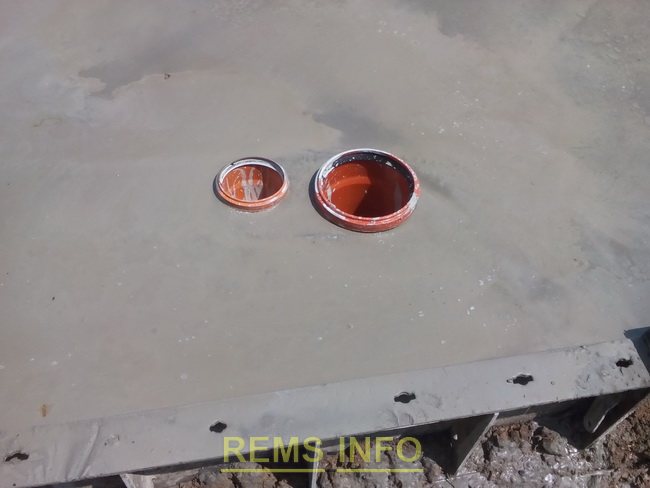

They tied the reinforcement poles - the reinforcement frame of the piles, and placed them in the prepared wells, covered them with crushed stone
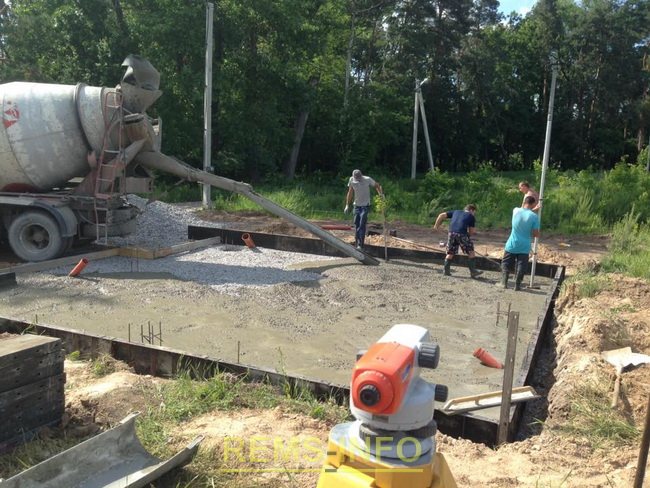

We set up the formwork and a mixer with concrete B 15 P3 poured the spot on the house (to a height of 10 cm) and the piles.
The formwork was metal; thanks to this formwork, the walls of the slab were smooth, without visible joints, and the installation speed of such formwork was higher.
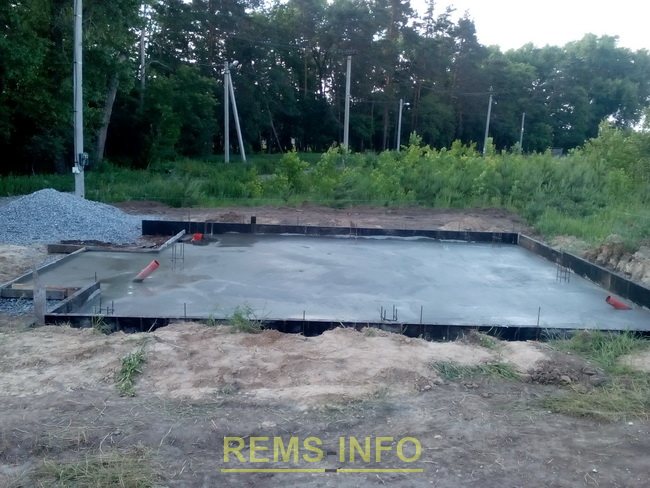

It must be said that the footing is required in accordance with the standards SNiP 52-01, SP 52-101/2003 and SP 50-101/2004 and performs a number of functions:
- levels the surface for subsequent laying of the reinforcement cage;
- serves as additional waterproofing;
- evenly distributes forces arising in the soil.
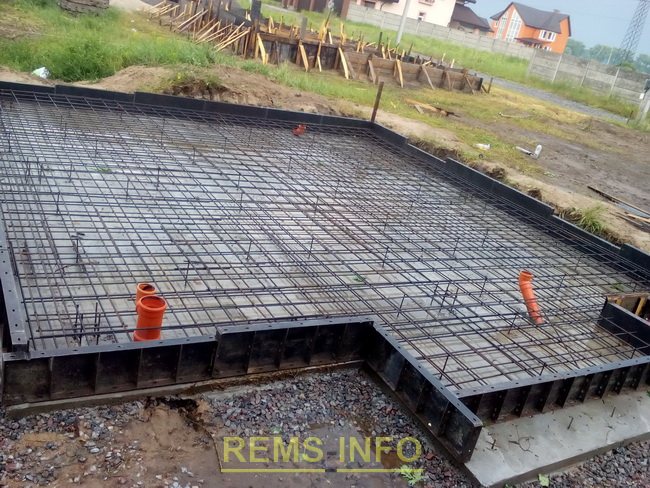

Preparation and marking of the site
The construction site is cleared of debris, the top layer of soil with vegetation is cut off. If there are holes in the area, small drops, or the soil has subsided, then it is recommended to make a backfill followed by compaction.
Marking the future foundation is a must! It will help you position the supports correctly and fill the tape. It is best to mark using a laser range finder and a building level. The locations for drilling future wells for piles are marked with stakes. Base tapes - with cables or ropes. Corners can be marked with boards or pipe scraps.
For a shallow foundation, a trench is dug, equal in width to the monolithic tape. The depth of the trench should be 10-20 cm greater than the depth. This is necessary to add a gravel-sand cushion under the base.