A distinctive feature of private housing construction is the ability to choose the type of foundation. Very often, the preferred foundation option is a columnar grillage foundation. Low production costs are the main advantage. If a strip foundation or foundation slab requires a significant amount of concrete, then for the above option the consumption is reduced many times (up to several tens of times).
The material of foundation pillars can be different. Reinforced concrete is considered one of the best, which is characterized by durability and high reliability. We will consider this option. A columnar foundation with a grillage is installed in stages according to the technological map:
- the base on the site is calculated and marked;
- earthworks are being carried out;
- formwork is installed;
- foundation pillars are reinforced;
- concrete is poured and soil is backfilled;
- a grillage is installed.
Return to content
Calculation of a columnar foundation
Calculation work is a very important stage, since structural elements with the obtained parameters must be guaranteed to ensure the reliability and stability of the entire structure.
First of all, the bearing capacity of the soil is determined through geological surveys. The indicator is expressed in kg/cm2 and depends on the type of soil, its density, moisture content and freezing depth. The exact numbers can be found in the table. Next, you need to calculate the approximate load of the future structure on the support area. To do this, the weight of building materials that will be used for construction is adjusted for additional load from snow and wind. The resulting figure is divided by the indicator from the soil bearing capacity table and the reference area is obtained. The load on the ground will be close to the maximum permissible, so 20-30% is added to the resulting area (in order to protect the structure from possible miscalculations).
You can find out complete information on how to build a foundation on marshy soil by reading the article. The article describes the conditions and features of the construction of such a foundation.
And this article is about reinforcing the foundation with fiberglass reinforcement.
By following the link - https://vse-postroim-sami.ru/building/fundament/3584_kak-sdelat-opalubku-dlya-fundamenta/ - you will learn how to make equipment for the foundation.
The required number of pillars is calculated by dividing the supporting area by the base area of one element (column). The cross-sectional area of the pile is done at your own discretion, but in practice the elements are made with a linear size of up to 60 cm.
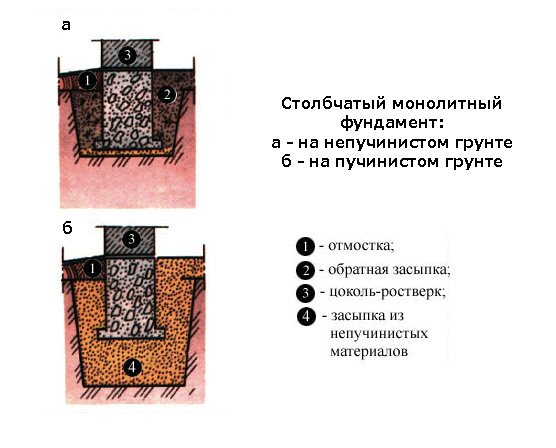
The calculation of a columnar foundation with a grillage is completed by marking the site. Places for columns are determined in the following positions and with a certain frequency:
- at all angles of the building;
- at the point of intersection of the walls;
- piles in straight sections are located in the range of 2.5-3.5 meters from each other. If you install supports less frequently, the grillage may become deformed and cracks may form on the walls. Installing the posts closer than recommended will not bring any benefit, but will require additional costs.
Return to content
Preparatory work
Pillar foundations are popular not only because of their financial benefits, but also because they can be built with your own hands without professional training. The volume of work is such that it can be handled alone or with 1-2 assistants without the involvement of heavy construction equipment. But for everything to work out, you need not only to purchase materials and allocate free time, but to plan everything correctly.
Calculation of a columnar foundation
In order for the foundation to be durable and able to withstand the weight of the house frame, it is necessary to carry out careful calculations. We present a variant of calculating a columnar monolithic foundation made of reinforced concrete using the example of a house with walls 3x5 m and a height of 3 m.
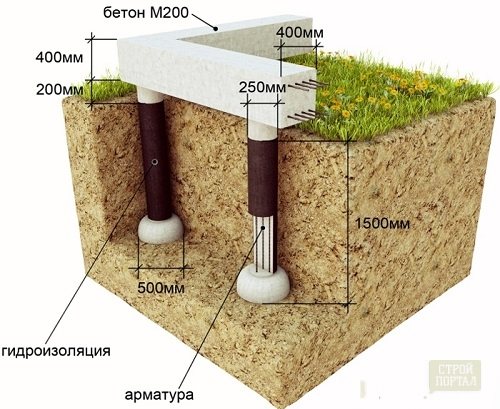
Progress:
- For such a house you will need square pillars 50 cm long and 100 cm high.
- The grillage for such a foundation will be 30 cm wide and 20 cm high.
- A house made of blocks with a roof on a wooden frame covered with slate. The floors and attic are wooden. In total, the construction will take about 5 cubic meters of wood and 23 sheets of slate.
- Let's say the soil resistance is 3. Under this condition, you will need to install 4 corner pillars and the same number of pillars located in the center under each wall.
- Since the length and width are 50 cm, and the height is 100 cm, we calculate the volume of the column: 0.5 * 0.5 * 1 = 0.25 cubic meters. It follows from this that the total volume of all 8 pillars will be 2 cubic meters (0.25 * 8).
- The average density of concrete is 2,500 t/1 cubic meter. The total weight of the pillars is 5 tons (2500*2).
- To calculate the grillage, you need to find out the sum of the lengths of all the walls of the house: 5*2+3*2=16 m.
- We calculate the volume of the grillage: 0.2*0.3*16=0.96 cubic meters.
- Grillage weight: 0.95*2500=2400 kg.
- To calculate the volume and mass of the walls, you will need to know the area of the end of one block when it lies on an edge - 0.18 square meters. m. Let's say the total area is 48 square meters. m, which means you can find out the number of blocks required for construction: 48/0.18 = 266.6 (rounded to 267) blocks.
- The mass of one block is 30 kg, which means you can find out the mass of the walls: 30*267=8010 kg.
- The mass of 5 cubic meters of wood is 4 tons, slate weighs 598 kg. We add up all the data and get the weight of the house box - 20 tons.
- We add the mass of all internal walls and partitions, calculated in a similar way, and find out the support area of the pillars using the formula: 2.5t*8=20000 sq. cm.
- To calculate the mass of a tree, multiply the density of the selected wood by the total volume. Since in our example there are 5 cubic meters of pine, we make the calculation: 2500*8=20000 sq. cm.
- Divide the mass of the tree by the area of the house support: 20000/20000 = 1 kg per 1 sq. cm. Provided that the soil has a resistance of 3, the number of pillars corresponds to the norm.
Foundation plan
Not a single foundation, even the simplest one, is built without a plan. It is depicted as a horizontally dissected plane, where the cut passes above the base of the pillars, but below the surface of the soil. The plan should clearly show the base of the foundation - the layout of the blocks, rubble or rubble concrete pad, etc. If you plan to make a basement in the house, you need to show its outline on the drawing so that the walls rest on the foundation. The basement is marked on the diagram with a line thinner than the pillow line.
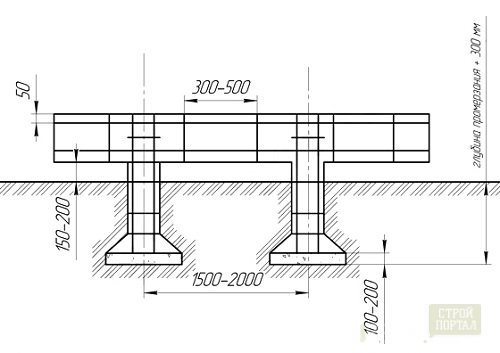
The drawing must contain coordinate axes and dimensions by which you can determine the distance between the pillars, the binding of the elements, the marks of the level of the cushion, as well as the marks of the elements of prefabricated structures.
If you doubt that you can calculate the pile foundation grillage yourself, it is better to entrust this matter to specialists. And if you can save money on hiring workers to build the foundation, then it is better to create a plan as efficiently as possible.
After drawing up the drawing, break down the plan. Roughly speaking, this is the transfer of basic dimensions from the drawing “to the field.” To do this, measurements are taken to determine the area of the future house, the fertile layer of soil is removed, pegs are inserted at the construction sites of pillars and walls, and a rope is pulled between them.
The pillars are installed 1-2 m from the main building. From the intended walls of the building to the pillars there should be parallel nailed boards or slats, on which the dimensions of the holes for the pillars and trenches for the walls should be indicated.
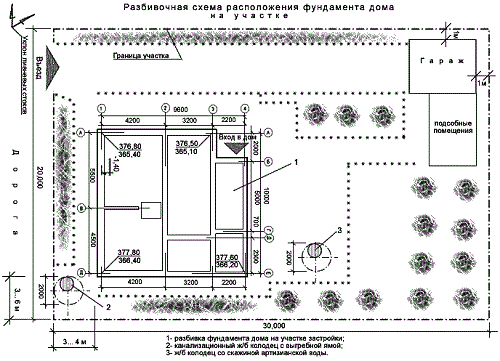
Be sure to check the evenness of the corners of the rectangular base. Using a theodolite, check the markings at the bottom of the trench, paying special attention to the corners of the house and where the tapes intersect. The markings on the site must completely coincide with the drawing, and the distance between the pillars should not be more than 1.5-2.5 m.
When drawing up a foundation plan, it is absolutely necessary to find out the depth of soil freezing, as well as the level of groundwater. The nature of the soil plays a big role, since columnar foundations are recommended to be installed on problematic and unstable soils (they give less load).
Land works

The work boils down to removing the plant layer. A shallow ditch is dug along the entire perimeter of the marking, and recesses are prepared for the foundation pillars at established points. The recesses are made to the full depth of soil freezing (data are taken for the region) plus an additional 20 cm for the cushion. The column corresponds to the thickness of the wall, so the pit should have a similar transverse size and an additional 20 cm on each side. These additional indentations will allow you to easily install the formwork and spacers
A cushion (a mixture of crushed stone and sand) is placed in the hole over the entire bottom area, that is, around the pile there will be a free part of the cushion protruding beyond the base by 10-20 cm. Then tamping is done with the addition of a decent volume of water. The top of the filling is covered with a gasket (polyethylene or roofing felt), which, when filling the prepared depression, will retain water and will not allow it to escape into the concrete soil. Otherwise, the strength of the pillar will decrease.
Return to content
Installation of formwork for foundation pillars
The formwork is made from metal, wooden boards, and derivatives of sawmill materials. The latter material is used most often. Boards are only suitable with a thickness of 20 mm or more. The choice of material is justified by its low cost and low weight compared to other options.
The boards are assembled into panels, and boxes are made from them. The structure is installed in a prepared pit. To prevent the formwork from absorbing moisture from the concrete, it is well moistened with water. This operation will also make it easier to dismantle once the concrete mixture has hardened sufficiently.
The formwork can be ready-made pipes of the required diameter made of ceramics, asbestos, or iron. There is no need to remove them from the pit upon completion of work.
If the hole in the ground is dry and its walls are dense (without the risk of collapse), you can do without formwork, but the hole must correspond to the calculated size of the base of the pillar. The walls are lined with polyethylene, preventing the premature loss of moisture from the concrete solution.
Return to content
Assembly and installation of formwork and reinforcement cage
To construct a columnar-grillage foundation, it is necessary to assemble and then install the formwork and reinforcement cage.
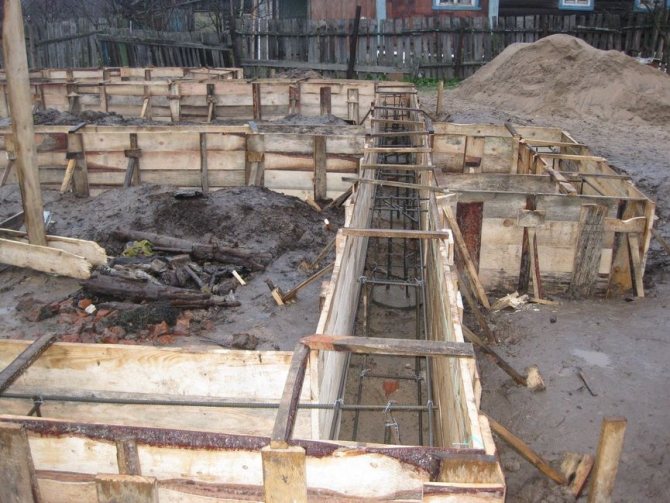

Formwork with assembled reinforcement cage
The material for panel structures is often boards more than 2 cm thick, as well as plywood. This is due to their accessibility and ease of working with them. Metal analogues are expensive, so it is not advisable to purchase them just once.
The formwork is knocked down from the boards, which is then installed around the perimeter of the base with a shallow grillage. If the latter is raised above the ground surface, then horizontal shields will also be needed.
Pipes made of different materials, roofing felt, cardboard, and polyethylene are also used as formwork for pillars. These are cheap options. Ruberoid or polyethylene are used only on dense types of soil. The integrity of the form is supported by the walls of the pit.
Installation of the foundation reinforcement frame begins with the connection of transverse reinforcement with longitudinal wire or by welding. Choose rods with a thickness of 10 to 14 mm. The shape and dimensions of the frame correspond to the same parameters of the pillars. It is taken into account that the minimum distance from it to the walls of the shields should be 5 cm.
The longitudinal rods are taken of such length that they can be connected to the grillage frame. Its shallow-depth version is reinforced after the pillars; the version located above the ground (at a height of at least 15 cm) is when the supports harden and the formwork is mounted on them.
The structure is made on the ground, and then installed in the prepared recesses. Tying the rods with wire will speed up the use of the gun. Welding in operation is available if the marking of the fittings contains the letter “C”. Plastic clamps are also used to assemble the frame.
Reinforcement of columnar foundation supports
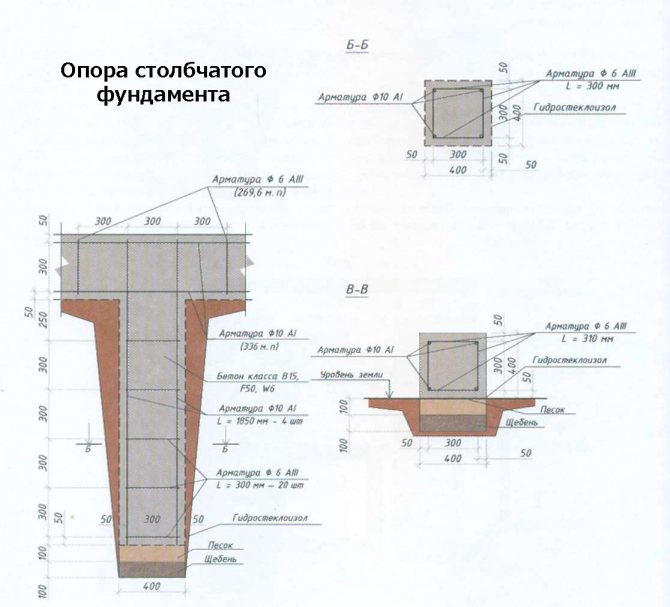
To reinforce a columnar foundation with a grillage, rods with a cross-section of 10-14 mm are used. The elements are assembled into a frame (mesh) of such a size that when placed in the recesses under the column there is a gap of at least 5 cm to the edge of the formwork. Assembly is carried out on the surface. The longitudinal rods are fastened to horizontal jumpers by welding or simply tied (this option is preferable). In cross-section, the frame should follow the shape of the pillar. The diameter of the horizontal bars is 6 mm, and the frequency of their installation is every 30-40 cm. The vertical reinforcement elements will then be connected to the reinforced mesh of the grillage, so the first ones must rise above the head of the column: 30-40 cm is enough. After assembly, the finished frame is installed in the recess under the future column.
Return to content
Grillage: what is it?
The grillage is part of the columnar foundation, located at the top and distributing the entire load. In addition, it is a kind of support for the entire structure. In appearance, it looks like beams connecting the heads of the pillars.
Foundations with a grillage can be of the following types:
- tape;
- solid.
The choice depends on:
- soil;
- materials used;
- device methods.
Wooden grillage for columnar foundations has become widespread in country house construction. This is an ideal type of foundation for building a wooden house, bathhouse, veranda, etc. But it can be made not only from wood, but also from other materials. Although, naturally, its price will be much higher.
Pouring concrete and backfilling soil
The prepared pit (with formwork and reinforcing mesh) is filled with concrete. Having selected the required grade of concrete, layer-by-layer laying begins. The poured layer, the thickness of which is 20-30 cm, must be pinned or leveled with a vibrator. This operation will eliminate air pockets (if any have formed) that could reduce the strength of the post.
All layers of concrete are laid one after another in a conveyor mode: a layer is poured, pierced, a new one is poured, pierced... The cycle is repeated until the top. Otherwise, the layers will dry unevenly, and a seam will form at the joint, which weakens the bearing capacity of the column. If the formwork was planned to be removed, then this can be done 3-4 days after pouring. And although the solution will dry completely in a month, it is allowed to continue work after removing the formwork.
The head of the pillar is waterproofed with special compounds (hydroglass insulation or bitumen resin is suitable). Further, according to the technology, the soil removed from the pit must be returned to the remaining space. If the soil is not heaving, it is covered with it, otherwise it is necessary to use sand or other non-heaving material. After backfilling, the area around the post is compacted. Backfilling, if necessary, can be preceded by insulating the foundation with slabs of extruded polystyrene foam.
Important points of the stage: pouring within one day to prevent the formation of seams; All posts after pouring should be at the same level above the ground.
It is advisable to carry out work on pouring a columnar foundation when it is warm. In order to preserve the integrity and structure of the structure, it should not be left unloaded during the winter.
Return to content
How is a columnar grillage foundation constructed?
The construction of a columnar grillage foundation is not that complicated. The main elements of the foundation are load-bearing supports (pillars), which can be made of various materials: concrete, rubble stone, brick, metal pipes.
As mentioned above, the pillars are installed in the corners and at the intersections of walls, and the step of their installation depends on the design and expected load of the building.
Calculations of the diameter of each support are made for each building individually. The burial depth should be below the soil freezing level, and the lower support point should be placed in a stable layer of soil. A prerequisite is the presence of grillages for connecting pillars to distribute the load on all existing structural elements of the building.
Arrangement of a grillage for a columnar foundation

The construction material is usually monolithic reinforced concrete or prefabricated concrete. The level of the grillage above the ground can vary, being directly on the soil, hovering in the air, or going slightly deeper into the ground. There is no consensus on the best option. A high grillage is located above the soil surface, which prevents heaving forces from acting on it and deforming or breaking the structure.
The manufacturing process follows a certain pattern. It is necessary to install continuous formwork between the pile elements along the entire perimeter of the foundation. The first layer in the formwork will serve to raise the future concrete structure to a height. Sand is used as such a support; its layer should correspond to the gap between the soil surface and the bottom of the future grillage. The sand is covered with a polyethylene film.
Next in the formwork you need to tie and install the frame (rods 12-14 mm). The elements of the frame mesh should not be closer than 5 cm to the edge of the box. Then, by welding or tying, the rods from the piles are connected into one whole with the grillage mesh. The entire process of pouring formwork is carried out once; it is impossible to split the process over several days. The requirements are related to the possible formation of seams during a break. To remove air bubbles from the poured concrete solution, use a vibrator or pierce the solution with reinforcement.
You will learn how to knit reinforcement for the foundation by reading this article.
And here is an article about building a foundation for a greenhouse.
Read our website and you will learn a lot of useful information about construction and renovation.
The formwork can be removed as soon as the concrete has set (waiting time 3-4 days). The sand layer is also removed. Thus, the grillage “hangs” above the ground. For the future grillage, instead of sand, you can use an inverted box (reminiscent of the letter “p”) as a raising link for the structure. Several temporary brick supports are installed along the line of the columnar supports for mounting wooden formwork on them. After 3-4 days after pouring the grillage with a pre-installed frame mesh, the bricks and wooden structure are removed.
Return to content
Arrangement of grillages
To install them, you can use ready-made reinforced concrete products or fill them with concrete. Regardless of the type of deepening of a monolithic grillage, the main stages of their construction are the same:
- installation of formwork around the perimeter;
- installation of fittings;
- connection of the reinforcement frame of the grillage and the pillar;
- waterproofing walls with roofing felt or mastic;
- laying the concrete mixture followed by compaction.
The formwork is removed two weeks after completion of the work. The space between the pillars is sealed or left open.
Insulation and waterproofing of the foundation
The space between the ground and the base of the building is exposed to cold and moisture. To protect it from the influence of negative factors, it is necessary to install a base. The material can be boards, bricks, timber, foam blocks or polystyrene foam. The inner surface of the foundation will be protected from the cold; the floor will not freeze in cold weather. To prevent the interior space of the base from becoming damp, ventilation holes are installed (size from 100 mm). Plugs will help keep warm in winter.
Attention! The outer surface of the foundation must be waterproofed to prevent rapid collapse of the structure. Before applying rubber-bitumen mastic, you should get rid of dust and dirt on the surface and prime it.
It is quite easy to build a columnar foundation from the point of view of physical effort. Combined with low costs, this type of foundation looks like a very suitable option. It is important that when constructing it, calculations and work are carried out taking into account geological surveys, there is strict compliance with the building design and adherence to technology. Then the future house will receive a guaranteed reliable foundation in the form of a columnar foundation with a grillage.
Return to content
Types of foundations with grillage
Foundations with a grillage belong to the category of structures, in the classification of which great importance is attached to the method of forming the upper part that combines the heads of the pillar supports. In accordance with this feature, they are all divided into the following types:
- Prefabricated structures.
- Monolithic foundations.
- Prefabricated monolithic structures.

Let's look at each of these varieties in more detail.
Prefabricated
Columnar foundations of this type are industrial designs of foundations with a supporting part designed in the form of a prefabricated grillage. In their design, they resemble a construction set, sequentially assembled based on ready-made parts. Some of its elements are equipped with locking clutches and special fastenings. Prefabricated samples include a grillage made of timber mounted on a columnar foundation.
Due to the complexity of the design and labor-intensive assembly, this type of columnar foundations is very expensive to manufacture and is most often not suitable for private construction. It guarantees high quality foundation construction and is usually used in the construction of industrial facilities, where expenses within the budgeted amount are not given much importance.
Monolithic
The monolithic type of foundation with a grillage is in reality a solid beam or a solid concrete slab. Through such structures, all support pillars are combined into a single whole.
In individual construction, it is quite possible to make a columnar foundation with a grillage with your own hands, since no special equipment is required for this.

There are several modifications of such structures that differ in height relative to ground level. In accordance with this feature, they are divided into high, low, and recessed bases. Each of these options will be discussed in the following sections.
Prefabricated monolithic
Prefabricated monolithic grillages are a combination of the two previously discussed options, implemented through the use of an entire system of steel beams or metal channels. The resulting structure is characterized by increased strength, but its independent production faces certain difficulties. When arranging it, it will be necessary to move large workpieces of significant weight, which is almost impossible to do without special equipment.
In addition, assembly will require special welding equipment, which not every private owner has. And even if you have everything you need, this method of assembling a grillage is not very reliable, which is explained by the low strength of the welded joints. It is usually used in the construction of temporary objects with a guaranteed service life of no more than 15-20 years.
Types of monolithic grillage
Since monolithic structures are the only type of foundation with a grillage suitable for private construction, a little more attention will be paid to its consideration.
Particularly common in construction are the so-called “high” monolithic grillages, rising above ground level by at least 100 mm. This design is in demand in places where there is severe soil heaving. Its disadvantage is the impossibility of high-quality insulation of the space under the grillage and the arrangement of a basement in this place.
Low bases are usually made flush with the ground. Thanks to this, the grillage beams slightly overhang it, forming an artificial air cushion. Recessed foundations are prepared in accordance with their name, that is, they are recessed into the ground to a greater depth than low ones.