To determine which foundation is suitable for sandy soil, you must carefully examine the soil itself. Sand, as you know, can have different particle sizes: from large ones, up to a millimeter, to very small ones, more like dust.
Coarse sand is an excellent basis for any type of foundation; it drains water well, is practically not susceptible to frost heaving, and is resistant to seasonal movements. Sand with small particle sizes is dust when dry, and when moistened, it does not allow water to pass through, like coarse sand, but absorbs and retains it. Dirt is formed, which when frozen due to the high water content greatly increases in size. Therefore, fine-grained silty sands are very susceptible to frost heaving, and this must be taken into account when calculating the foundation.
Construction of a foundation on sandy soil
The second factor that complicates construction on fine-grained sands and sandy loams is their tendency to form quicksand in areas with close groundwater. Before starting construction, you need to order a geodetic study of the soil from companies specializing in this, otherwise the costs of correcting errors may exceed the costs of the foundation itself.
Types of sandy soil
Sand varies in the size of the particles in its composition, as well as their number. Depending on this, four groups of sandy soils are distinguished:
Types of sandy soil
- Dusty sand. Construction on such soil can lead to many troubles. The fact is that this type of soil has low load-bearing characteristics when dry, but when moist it is more like clay.
- Fine sandy soil contains over 75% of particles whose size is greater than 0.1 mm. The bearing capacity of this type of soil is inversely proportional to the degree of moisture. That is, with increasing humidity, the load-bearing characteristics of the soil decrease. Additional waterproofing using polyethylene film helps solve the problem.
- Medium and high soil coarseness is provided by particles whose size exceeds 0.5 mm. Moreover, their content in the composition is more than 50%. This type of soil has a high load-bearing capacity, so it causes almost no problems during the construction of a house and its foundation.
- In gravelly sandy soil, more than 25% of particles larger than 2 mm are observed. An area with a predominance of such soil is an ideal place for arranging various foundations.
Device and thickness
It is individual for each project, and for correct calculation several factors should be taken into account:
- What type of foundation is planned to be used?
- Dimensions and weight of the building.
- The soil on which the building is erected.
- Soil freezing depth.
- Presence and proximity of groundwater to the soil surface.
Many publications say that the thicker the sand layer, the better it resists various deformations of the structure. Experts strongly disagree with this opinion.
Important! The maximum thickness of the sand cushion for strip foundations is three strip widths.
For strip foundation

Strip foundation is the most common type of foundation used in the construction of low-rise buildings.
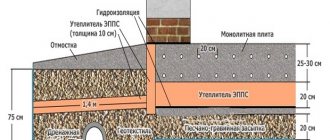
The thickness of the sand cushion under this type of foundation is determined based on the specific construction conditions. But for a small building, as a rule, they take an average value of 15-25 cm.
Experts recommend that the width of the sand cushion be 10-20 cm larger than the width of the tape.
A layer is made between the strip foundation and the soil as follows: the recommended layer of sand is poured onto the bottom of the trench and carefully leveled. After which the sand is moderately moistened with water for better shrinkage and subsequent compaction.
The process of compacting the layer is best done using a vibrating plate, but this can also be done with improvised means.
The degree of readiness can be determined as follows: there should be no traces of shoes left on the surface after the passage of an adult. After compaction, the stage of carefully leveling the pillow and laying a layer of waterproofing on it follows.
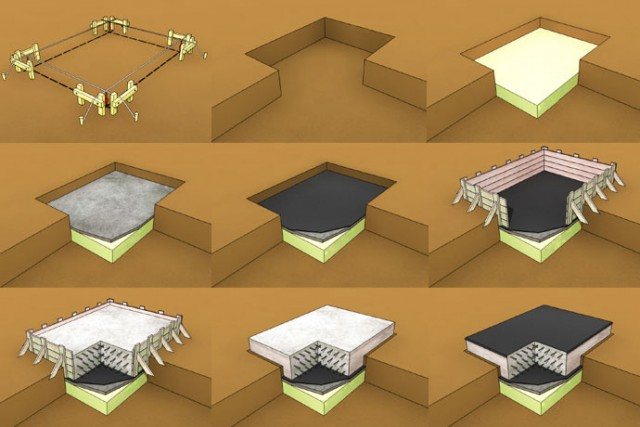
For a monolithic foundation
The arrangement of a sand layer under such a foundation is done in the same way as in a strip foundation, but over the entire area of the pit.
To make the correct layer for this type of foundation you need:
- Carefully level the bottom of the pit.
- Pour gravel or crushed stone 10-15 cm thick. This material serves to compensate for the low density of the soil and its heaving.
- A layer of sand is poured onto the crushed stone. For a small bathhouse or small cottage, a layer of 10 cm is enough. Sand will help to evenly distribute the load from the building on the soil.
- The next stage of the device will be thorough compaction. For this, experts recommend using a vibrating plate.
Before laying a foundation on it, the sand layer must be leveled and covered with a layer of waterproofing to prevent moisture from entering the foundation of the building.
For columnar and pile foundations
A columnar foundation also requires a sand layer underneath, or rather a sand and gravel layer.
The principle of its construction is the same as for other types of building foundations: first, a layer of gravel or crushed stone is poured, after which sand is poured, moistened and thoroughly compacted with a hand tamper.
For foundations of this type, the sand and gravel layer should be 20-30 cm thick. In addition, it should be 10-20 cm wider than the pillar on each side.
Afterwards, roofing felt or polyethylene is placed on the surface of the pillow to prevent water from being poured into it from being poured into the concrete.
Features of sand-dominated soil
Any type of soil has individual characteristics that influence future construction to varying degrees. Sandy soil is characterized by the following properties:

Features of sandy soil
- High load-bearing capacity. This property shows how much load the soil can withstand without any consequences. Sandy soil maintains its integrity even under pressure, preventing layers from shifting. Therefore, foundation subsidence in this case is minimal. The high density of the soil allows it to withstand high pressure, and the low water content of the soil reduces the risk of change and displacement.
- Low soil compressibility. This indicator characterizes the degree of soil compression under load. The foundation built on sandy soil does not settle for long, so construction time is significantly reduced.
- Low frost heave rate. Sandy soils do not retain water, so they do not change when temperatures drop seasonally. As a result, the pressure is reduced, therefore, the risk of deformation and destruction of the base is minimized.
Which foundation is better to build on sand?
The type of foundation for a house is selected depending on the type of sandy soil.
Ribbon base
Strip foundations are very often used in Russia. Laying a belt on sandy soil cannot provide high strength characteristics. Mistakes made when constructing structures on silty soils can lead to the formation of cracks and deformation of the base. As a result, both the foundation and the entire structure are destroyed.
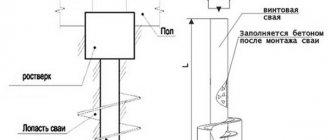
Columnar base
The main elements of such a foundation are separately placed columns. The strength of the base largely depends on their correct installation. Construction on dusty and shallow soil requires a large depth of the main elements of the foundation. If this condition is not met, the columns may diverge or become skewed, which can lead to the formation of cracks in the walls of the building. In addition, during frost heaving of the soil, pushing out of the foundation columns may occur, and during thawing, their lowering may occur. As a result, the structure is deformed and destroyed.
Monolithic slab base

Slab foundation on sandy soil
The slab foundation has a larger support area, which gives it high strength even when built on sandy soil. Additional reinforcement of the base slab increases its strength several times. Therefore, in areas with sandy soil, it is best to use a monolithic base in the form of a slab. However, the cost of such a foundation is quite high, so they resort to its arrangement only in rare cases.
Foundation on stilts
Arranging a pile foundation on sand is an ideal solution. This base is highly durable and reliable on any type of soil. However, when constructing massive structures, additional calculations are required.
Proper preparation of the base for the foundation
Any professional builder knows that the first half meter of soil has the lowest load-bearing capacity and is often not taken into account when designing foundations. To obtain the most stable and reliable position of the building box, it is necessary to get to the most stable and dense layers of rock, the condition of which and bearing capacity do not depend on air temperature and amount of precipitation. Therefore, preparing the base for the arrangement of the foundation requires a significant and materially costly amount of work:
- Planning the site of the future foundation, removing surface soil, and in the case of thick deposits of peat, loam, and water-logged clays, during preparation it is necessary to remove the surface layer by a meter or more;
- Arrangement of drainage systems with planning of future drainage slopes and storm sewers;
- Compacting the soil with vibratory rollers, filling cushions of crushed stone and sand;
- If necessary, laying concrete preparation under the base of the foundation and waterproofing.

The most common reason for violating the bearing capacity of the foundation is the use of fill building materials that do not meet the requirements of the project. The completed acceptance document, protocol or act confirms the scope of work completed, the thickness of the laid crushed stone and sand, the presence of a geotextile base, but does not reflect the quality of the sand, which plays a major role in ensuring the bearing capacity of the foundation base.
To ensure the necessary strength of the surface layer of the rock, the soil is prepared, compacted and filled with crushed stone of different fractions, first coarse, then screenings and, finally, sand. A layer of crushed stone sealed into the ground dramatically increases the stability of the foundation, but due to its high rigidity and hardness, it is not able to evenly transfer the load from the weight of the building to the base of the foundation and to the surface of the earthen layer.
Self-arrangement of the foundation on the sand
When arranging the foundation of a house on sandy soil, you should follow a certain sequence and follow the recommendations of specialists.
Preparation and marking of the site
The area allocated for construction is cleared of excess vegetation and the top fertile layer is removed. When marking, use wooden pegs and nylon cord. First, mark the outer perimeter of the house, and then the internal load-bearing partitions. Pegs are driven in the corners of the building, and, if necessary, along the perimeter of the walls.
Carrying out excavation work
To arrange the foundation, it is necessary to make a recess, which depends on the type of foundation chosen. To lay a monolithic slab, you need to dig a pit, for a strip foundation, a trench is dug, and round or square holes are prepared for a columnar foundation. Before starting work, it is imperative to organize the drainage of surface water, which contributes to soil liquefaction and a decrease in its load-bearing characteristics. To solve the problem, it is enough to make grooves.
The depth of the foundation depends on the type of soil:
- No more than 1 meter - for coarse sandy and gravelly soils.
- No more than 1.25 meters - for sandy loam soils.
When removing excess soil, you cannot top up the excavated soil. This can lead to uneven shrinkage of the building and subsequent destruction. You can replace the missing soil with sand, crushed stone or gravel. They require careful compaction. You can compensate for soil overflow with concrete mortar.
If construction is delayed for a certain time, it is better not to dig a trench or foundation pit to the required depth. This will help protect the recesses from erosion during precipitation. The remaining soil must be removed immediately before construction begins.
Details
A good basis for any type of device
The bases are considered to be coarse-grained sand. It is not afraid of frosty influences, liquid does not stagnate in it and it withstands atmospheric conditions.
Fine sand is essentially dust, and if it gets wet, water will pass through it. Therefore, due to stagnation, dirt will form in it and, as it freezes, it will increase in size. Thus, fine-grained sandy soil is more susceptible to frost heaving. This is an important point when making calculations.
The formation of quicksand will further complicate the process of laying a foundation on such soil. Quicksands occur in places where groundwater is located closest to the surface.
Important: Before starting construction, you need to order a soil study from a special organization. Otherwise, you may encounter serious problems, the solution of which will require you to spend a large amount of extra money.
Technological features
If you are going to build a house on silty or fine-grained sand, then the foundation must be extremely strong. It would be appropriate to use a tiled foundation here. First, the fertile layer is removed, then concrete slabs are cast, which are made larger in size than the building. This type of foundation has the feature of moving along with the movement of the soil. Therefore, it is not afraid of seasonal soil changes. This type of foundation is also called floating.
The most common foundation used on fine sandy soils is considered to be a finely serrated strip type, which is made in a trapezoidal shape that widens towards the bottom. This expansion will help reduce external impacts on it.
Before pouring, a waterproofing layer is laid in the trench.
Important: For foundations built on fine sand, a drainage system is required.
For large buildings (for example, a two-story house) erected on fine sandy soils, pile-strip foundations are mainly used.
The construction of the foundation is carried out using the following technology:
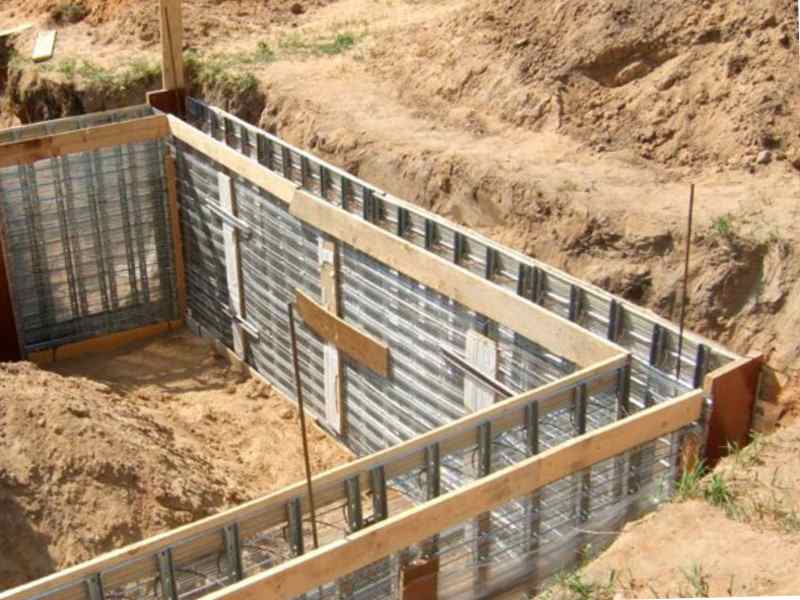

First, markings are made, a foundation pit is dug, and formwork is made;- where the foundation strip intersects, wells are drilled. Their depth should reach the level of a stable layer of earth;
- Asbestos concrete pipes are placed in these wells, the structure is leveled and strengthened with supports;
- Concrete solution is poured into the pipe, first one-third, and the pipe is raised to form a thickening at the bottom. Next, the pipe is filled completely.
Adviсe
Note: When pouring pipes, the fittings are lowered inside first.
Piles can be poured without installing pipes, if the wells in the given area are not filled with water:
- the well is expanded from below using a special device - a plow;
- The reinforcement is lowered into the well and the concrete mixture is poured;
- Once the pile structure has completely dried, the tape is poured.
Since coarse and gravelly sands are reliable, any type of foundation can be used for a one-story house.
If the house does not have a basement, then it would be more advisable to install a finely serrated strip base. If the structure is made of light material (frame, panel), then the base can be columnar.
For massive buildings with a plinth, it is better to use a recessed strip type base.