Conducting a soil study to select the type of building foundation The best foundation for a foundation is rock. However, even in its absence you can make a good solid foundation. In our latitudes, most developers have to build a foundation on sandy soil. This is an excellent building material for building a foundation. To understand which foundation to choose for a specific building site, it is important to know the difference between sands and the technology for working with them, as well as make all the necessary calculations.
Types of sandy soils and their features
Sandy soils are divided into types:
- Coarse-grained sands are sands consisting mainly of particles of large fractions. These are the best sand bases for the construction of surface foundations. They are distinguished by good water throughput, load-bearing capacity and the absence of frost heaving.
- Fine-grained sands, mainly consisting of fine and dusty particles. Working with such soil is difficult, as it is difficult to compact. The permeability of such sand is extremely low; when moistened, it becomes plastic and turns into mud. If the groundwater level is located close to the surface, then such a foundation may become quicksand. When working with this foundation, you should carefully carry out calculations, because altering the structure can be more expensive than building it.
- Sandy loam and loam. Such foundations are not suitable for constructing a foundation, since they are loose, unstable, and it is almost impossible to compact them to the required level.
To find out what kind of soil the building site is made of, you need to contact the geological service.
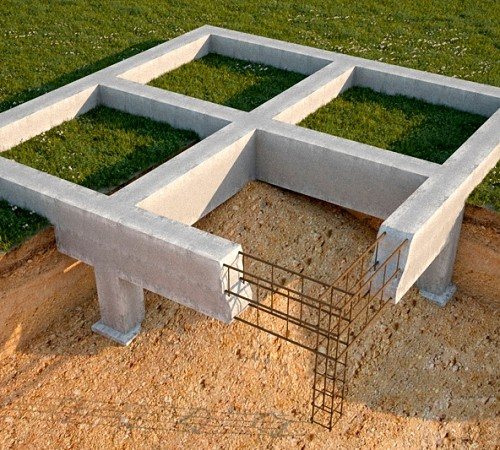
Positive aspects of a slab foundation
The advantage of a monolithic slab is its large support area, which significantly reduces the pressure on the soil. Uneven shrinkage and the risk of wall deformation are completely eliminated.
Advantages:
- ease of installation;
- long-term operation;
- safety;
- strength;
- preventing ground movement;
- resistance to ground and surface waters;
- possibility of creating a base;
- using the slab as a base for the floor on the first floor.

Characteristics of the slab base
Negative qualities
A significant disadvantage of the slab is that the cost of the base is very high compared to similar methods. But it is completely justified, thanks to guarantees of reliability in the face of adverse environmental conditions.
Coarse sands

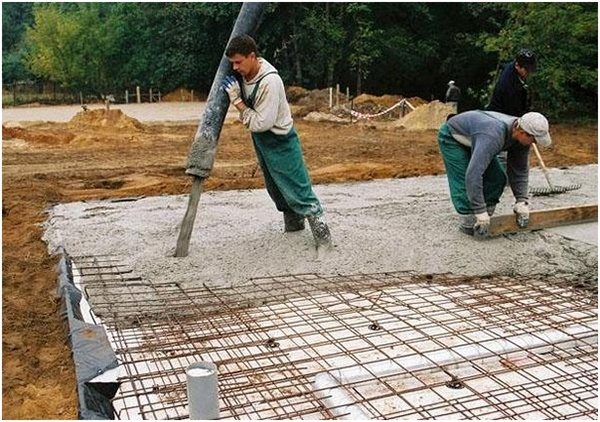
It is quite simple to build a foundation on sandy soil, consisting of particles of large fractions. On this basis, strip and column foundations are usually installed. In this case, additional work is reduced to a minimum - clearing the site, removing the fertile soil layer and digging shallow trenches for formwork.
It should be noted that when constructing a light building, such as a bathhouse, barn or wooden house, you can get by with a columnar foundation. You can lay it out of brick or make it monolithic. The columnar blocks need to be placed along the perimeter of the future walls of the building, as well as at the intersection of the walls. This will be enough to withstand the load of the entire structure. No additional calculations are required.
When working with coarse sand, you only need to dig trenches for installing the formwork, level the bottom and compact it. In most cases, no addition of other materials is required, unless it is a massive multi-story building - then it will be necessary to make calculations, including the load-bearing capacity of the sand base.
We determine the properties of soils at the construction site.

Without this data, it is impossible, first of all, to make a high-quality and moderately economical foundation and, therefore, to build a reliable and durable house. This article will talk about how you can independently determine the physical and mechanical properties of soils. It is no secret that the best way to study a development site is geological and geodetic surveys conducted by specialized organizations. Using a drilling machine, several wells are made, soil samples are taken at different depths, and then the necessary physical and mechanical properties are determined in the laboratory.
Due to the high cost of this procedure, people who build a house on their own often refuse it. The construction of the foundation is carried out either on the basis of the experience of the neighbors on the site, or relying on our almighty “Russian maybe”. This can lead, at best, to the laying of an excessively massive foundation with excessive monetary costs for it, and in the worst case, on the contrary, to the construction of a foundation that is too weak and to its subsequent destruction.
Below we will look at how you can determine for yourself the basic properties of the soil necessary for a more or less accurate selection of the parameters of the future foundation of the house. If, when determining any characteristic, you are considering two options and do not know which one to choose, always take the option with the worst conditions. A slightly excessive margin of safety of the foundation is not so terrible as its lack.
So, to begin with, you need to make at least two, and preferably four (in the corners of the future house) wells on the site. Their depth depends on the type of foundation, the number of storeys of the house and the material from which it will be built. For example, if a specialized organization is doing research for a two-story brick house, then wells will be drilled to a depth of about 10 meters. Obviously, doing this manually yourself is problematic (although possible). In this regard, you need to try to make the well as deep as possible, at least to two freezing depths. It is most convenient to use a regular garden auger. Also, if necessary and possible, you can immediately dig a hole for a septic tank before building a house. This makes it even easier to study the soil.
Using wells, the type of load-bearing soil, the thickness of the fertile soil layer and the groundwater level are determined.
I. Type of load-bearing soil
As you go deeper into the ground, first comes the fertile layer of soil, then the load-bearing soil. The foundation must rest on it. There are four main classes of load-bearing soils:
- rocky;
- dispersed;
— frozen (containing ice);
— technogenic (bulk, alluvial, etc.)
Most often, especially in central Russia, you have to deal with dispersed soils. There are several types of them: clayey, sandy, silty and peat. Of these, clay and sand are suitable for low-rise construction. It is better not to build anything on muddy and peaty soils on your own without special knowledge.
Let's consider two ways to determine the type of dispersed load-bearing soil.
Method 1: Take some soil in your hand, moisten it with water and squeeze until water stops dripping from it. Then roll the soil with your palms into a rope with a diameter of about a centimeter and bend it into a ring. Depending on how you succeed, you can distinguish the following types of soil:
— if you can’t roll a rope at all, it means you have sandy soil (sand) in your hands;
— if the rope still rolls up, but turns out to be very fragile and easily crumbles, it’s sandy loam;
- if the tourniquet rolls up, but when you try to bend it into a ring it immediately breaks - it is light loam;
- if the rope bends into a ring and cracks appear on its surface, this is a sign of heavy loam, similar in properties to clay;
- if the rope is sticky, rolls out easily and remains smooth without cracks when bent, then you are holding clay.
Method 2: Take a transparent glass jar, for example a liter one, and fill it halfway with the soil being tested, having first cleared it of roots and stones. Then add water to the top and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous suspension is obtained. Place the jar and do not touch it until all the particles have settled and the water becomes clear. Depending on the composition of the soil, this can take from a couple of hours to two to three days.
Due to the different settling rates of sand, silt and clay particles in the jar, the boundary between the layers will be visible. Below is sand, above is silt (silt particles) and above is clay. The height of the layers must be measured with a ruler and converted into a percentage.
Using the triangular diagram below, you can determine the type of soil being tested:
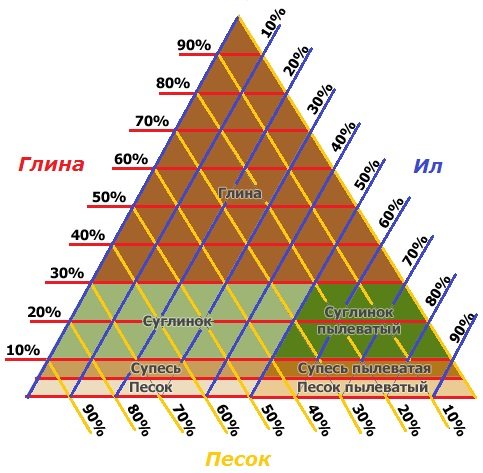
The percentage of sand is shown in yellow lines, clay in red, and silt in blue. The intersection point of these lines shows what type of soil sample this is.
II. Ground water level
Before starting any construction, you must know the groundwater level on the site. After drilling the holes, after 2-3 hours, lower the wooden slats into them. If there is water, it will be visible, and it will be possible to determine at what depth it is. Measurements should be taken in the spring, when the level rises.
If there is a well in the immediate vicinity of the site, it is also not difficult to determine the groundwater level from it.
III. Soil freezing depth
The depth of soil freezing is an important characteristic, without which it is impossible to correctly calculate the foundation. To begin with, you can roughly determine its standard value using the freezing depth map:
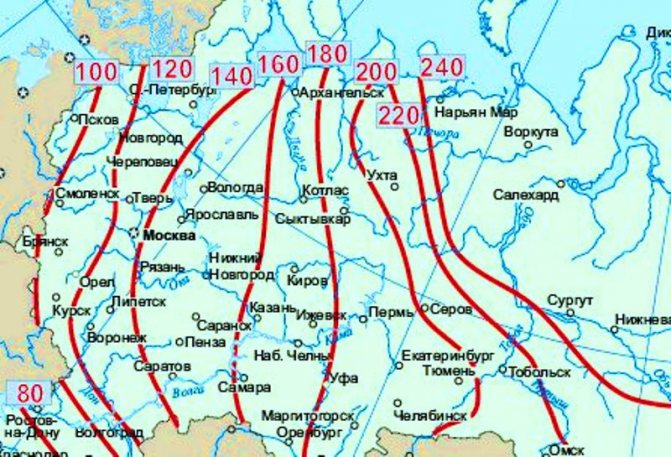
This map (click on the image to enlarge) shows the dependence of freezing depth on climatic conditions in a certain area. But in addition to climate, freezing also depends on the type of soil on the site, on the construction of the floor in the house, on the presence of a basement and on the average daily temperature indoors. You can more accurately determine to what depth the soil will freeze under given specific conditions using a simple and convenient calculator located here... It is very simple to use: find your city (or the nearest one) and select the value with the appropriate conditions in the tables below.
IV. Degree of soil heaving
Sometimes when calculating a foundation, for example, a shallow foundation, with limited data on the physical and mechanical properties of the load-bearing soil, the degree of its heaving is determined. This is done as follows:
- the indicator Z = dw - df is calculated, where dw is the depth of groundwater, m; df—estimated freezing depth, m (defined above).
— depending on the Z value, the degree of heaving is determined from the table below:
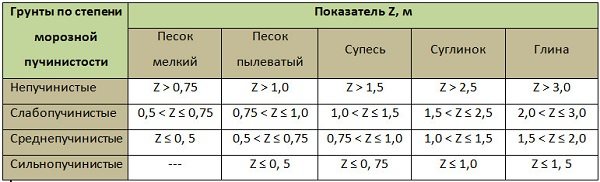
Non-heaving soils also include rocky and coarse-grained soils, as well as coarse and medium-sized sands that do not contain clay inclusions.
In the comments to this article, you can share with readers your experience in studying the properties of soils, or ask questions that interest you.
If the article was useful to you, please click on one or more social buttons. This will greatly help the further development of our site. Thanks a lot!!!
Fine sands

This type of soil has a number of features that will have to be taken into account when working with it. Due to the weak water throughput and the ability to increase the volume when moisture freezes, it is best to add a drainage layer to such a base, which will interrupt the capillary rise of moisture to the foundation.
The second way to protect the future foundation from the heaving ability of fine-grained sand is to install piles under a strip frame. They can be installed either manually or screwed in using a special machine.
Which method to choose is up to the developer to decide based on his financial capabilities. The piles should be installed so that their upper part protrudes at least 10 cm above the bottom of the trench. To save on the number of piles, it is better to make calculations so as not to install unnecessary ones. Before installing the formwork, it is necessary to backfill the base with coarse-grained material, and also lay a layer of rolled waterproofing.
Fine-grained sand is quite loose and does not compact well - in order to achieve the required compaction coefficient, you will have to add water during compaction, according to calculations.
If the developer does not want to do extra work with fine-grained sand, you can build a foundation on bulk soil, for which a layer of old soil is removed and coarse-grained material is laid. It should be noted that all inert materials are well compacted under their own weight, therefore, if you fill the new base with a layer of small thickness and leave it for a long time (for example, for a time when it will not be possible to carry out work due to seasonality), then later you won’t even need to add it thicken.
When is soil required?
Reasons for using embankment:
- It is necessary to change the terrain of the territory. When purchasing a suburban area that partially included fill soil, additional soil testing will be required. It will be completely unclear whether the compaction of the base was artificial or independent. The most dangerous thing is the heterogeneous composition of the soil; it is analyzed more carefully.
- Non-compliance of the soil at the construction site with the requirements for load-bearing characteristics. For example, you need to organize a base on peat. When the layer is small, it is replaced with sand and gravel.
Sandy loams and loams

It is not recommended to install foundations on such soils, but if there is no choice, then pile driving technologies and drainage systems will help. When constructing a pile field and grillage, under which the underlying and drainage layers will be located, you don’t have to worry about loam and sandy loam, since the calculation of such structures has a large margin of safety.
Such a foundation on bulk soil with a pile foundation is extremely expensive and is mainly used in the construction of industrial facilities and apartment buildings.
Foundation
The following types of base can be used on the embankment:
- pile;
- tape - monolithic, prefabricated;
- slab.
The main goal of the owner of a site with weak soil is to select the type of foundation for the house. When the choice is made correctly, the embankment will not affect the quality of the work. The construction of a base on weak soil is characterized by a wide base area; the heterogeneity of the surface structure should not affect the strength.
It is better to use a slab base on the embankment; it prevents shifts and deformations of the house. But we need to consider other options.
Monolithic base
It is equipped with concrete filling. Prefabricated includes large and small blocks.
For the tape base, the bottom and sides of the trench are carefully leveled. The difference in height to the foundation is a maximum of 2 cm.
The bottom of the trench is filled with sand, gravel, and compacted. With proper organization of excavation work, the walls will be smooth and no formwork will be required.
When the base is ready, reinforcement is installed underneath the cushion, the frame is filled with concrete, after 14 hours the formwork is placed under the concrete walls, and the mortar is poured.
If the base is prefabricated, the soil is prepared in the same way, but without compaction. The lower blocks are placed on a sand bed, the remaining rows are filled with mortar.
Pile base
When constructing a pile foundation on an embankment, it is possible to eliminate excavation work. During the process of screwing in piles, pits will not be required.
If the properties of the embankment are of average quality, it is not too prone to heaving, you do not need to replace part of the soil with a sand cushion. The piles are stored in the ground on stable layers and are mounted strictly vertically. The level is calculated and checked before screwing, after which it is almost impossible to correct a heavy pile.
After the installation of the piles is completed, their height is leveled - they are cut off at the top, and the headbands are welded for subsequent fastening of the floor. The installation is completed with a grillage and channel strapping.
PRODUCTION OF FORMWORK AND REINFORCED FRAMEWORK
Formwork is most often made of boards or OSB boards; the height of the formwork should be 5-7 cm above the level of the base being poured. From the outside, it is additionally reinforced with soil filling. This operation will prevent deformation of the vertical walls of the formwork and prevent concrete from pouring out. Upon completion of the installation of the formwork, pipes for utility lines are installed.

Formwork and frame reinforcement
Simultaneously with the installation of the formwork, the reinforcement cage is knitted. The lower level of reinforcement is installed at a height of up to 10 cm above the waterproofing surface. The connection of vertical and horizontal sections of reinforcement is done with wire or using a welded joint. Usually, with a base height of 50 cm, 2 reinforcement belts are installed - lower and upper. The top belt should be at least 5 cm before the top point of pouring concrete.
When installing the reinforcement cage, you must be careful and careful not to damage the waterproofing layer.
WHAT ARE FILLED SOILS?
When forming an embankment, the soil is backfilled and further compacted to the required height. The following materials are used to form the embankment: sand, clay, various fractions of crushed stone, loam, rock. With the gradual growth of the embankment, compaction is mandatory; layer by layer, the bulk soil is compacted to achieve greater density.

Materials for forming the embankment
Sand, clay, crushed stone or just earth have their own characteristics that must be taken into account when forming an embankment:
-sand is the most popular material for constructing a bulk layer; it does not require additional moisture, evenly fills all folds and voids, but at the same time requires additional compaction. Excellent water permeability. The sand embankment does not require additional time for natural shrinkage and is ready to begin construction almost immediately. The disadvantages include the fact that sand is easily washed away by water flow and has low load-bearing capacity.
-clay is a more viscous material that does not absorb moisture well; on the other hand, wet clay takes a very long time to dry. When forming an embankment, clay requires additional compaction; it holds its shape well and can withstand heavy loads; it is not washed away by water.
- crushed stone, gravel, screenings and other types of crushed rocks form a dense, rigid embankment with the best load-bearing capabilities.
- an embankment made of ordinary earth, as a rule, is not used in construction, but at the same time, this type of embankment is possible. The soil in this state has a disturbed structure and requires additional compaction using construction equipment.
When assessing the quality of the created embankment and its readiness for laying the foundation, it is necessary to evaluate its following characteristics:
- load-bearing capacity – a quality that characterizes the ability to withstand heavy loads without changing shape;
- density - how well the soil is compacted.
Construction
The creation of a slab base begins with the formation of a pit. Excavation work should be carried out with an excavator to reduce construction time. After leveling the bottom of the pit, the formation of formwork from panels of durable boards begins. Spacers are placed around the outside perimeter to protect the structure from collapsing under the concrete mortar.
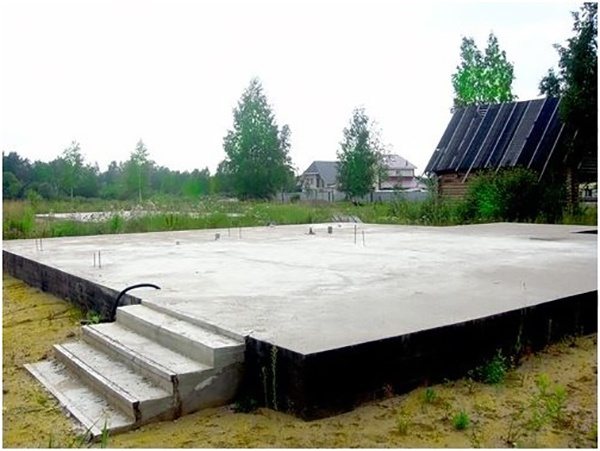

The slabs are good for use on bulk soils
Stages of work:
- Laying sand and crushed stone at the bottom of the pit. The sand is slightly wetted, the pillow is well compacted to obtain a thickness of at least 20 cm.
- Laying waterproofing over the entire area, taking into account the coverage of the side partitions of the formwork.
- Installation of reinforced mesh. The first belt goes down. The exact number of belts depends on the thickness of the slab. If required, make a second layer.
- Pouring concrete.
- Removing the formwork after the concrete has completely dried and gained strength.
For the strength of the structure, you need to choose a foundation, follow construction technology, and high-quality materials.
COMPACTION OF THE EMBARK, CONSTRUCTION OF A MONOLITHIC PLATE
When starting to construct the slab, it is necessary to take care of significant compaction of the embankment. This is due, as already mentioned, to the peculiarity of its structure. The natural structure, disturbed as a result of human influence, the heterogeneous composition and unevenness of inclusions of various rocks requires compaction and planning of a flat surface for the installation of a gravel base base.
A gravel cushion is formed on top of a 5-10 cm layer of sand. A layer of crushed stone or gravel 25-30 cm thick is laid on top of the sand and further compacted.
Next comes work directly related to the construction of a monolithic slab; the whole process fits into the following algorithm:
-laying a layer of waterproofing;
-installation of reinforcement cage;
-construction of formwork;
-laying of utilities;
-pouring the formwork with concrete and its subsequent compaction;
-technological work on curing concrete.
For waterproofing, polyethylene film or roofing felt is most often used. This coating is laid with a slight overlap of strips of 5-7 cm in 1-2 layers. The main task of waterproofing is to eliminate capillary wetting of the slab.
Preparatory work
A monolithic slab for the foundation of a house is expensive, but usually cannot be replaced by alternative methods without increasing the risk of the house collapsing in the future.
The slabs are actively used on unstable soils that are oversaturated with water.
Preparation for construction - accurate calculations, processing of the site, digging a pit.
Sand slab











