When erecting structures, it is impossible not to pay due attention to such a nuance as the expansion joint in the foundations. The concept under study is a special connecting place that protects the equipped foundation from moisture entering the interior, ground vibrations and temperature changes. The relevance of the correct construction of the seam increases in most cases in seismically hazardous areas or during the construction of a strip-type foundation.
What is it and why is it necessary?
An expansion joint in a foundation slab is a specially placed gap or void, which is designed to absorb displacements caused by soil movement. This way it is possible to keep the foundation intact. In addition to soils, the construction of expansion joints provides protection against sudden temperature changes. This solution in design and construction is especially relevant for seismically active regions.
Types of expansion joints
The installation of expansion joints in foundations is most in demand when laying strip types of building foundations.
In modern construction, several types of expansion joints are used:
- Expansion joints.
- Sedimentary seams.
- Shrink seams.
- Seismic seams.
Application of shrinkage, temperature structures
Expansion joints must be used in regions where the climate affects the materials used in the construction of houses.
A special feature is the division of the building into separate sections, the size calculations of which are carried out during the design. At the preparation stage you need to consider:
- How deep does the soil freeze?
- Seismic activity of the region.
- Climatic conditions of the area.
The condition for installing deformation joints is a waterproofing layer.
Shrinkage joints are necessary to protect bulk concrete foundations. During its service life, concrete releases moisture into the ground, shrinking in size.
The process causes shrinkage, splits and cracks form. Thanks to the shrinkage structure, the deformation process stops. When the concrete pour is completely dry, the shrinkage joint must be sealed.
Basic rules for making suture joints
To calculate the number of products, you need to contact a specialist. For high-quality protection of a concrete foundation or building, you need to consider:
- A vertically located expansion joint must be placed along the entire height of the building.
- The architectural design of the building influences the calculations of additional structures to prevent deformation at the corners of the building. For example, it is necessary if there are extensions.
- The average width is 100-120 mm.
Deformation
- If the concrete base has a waterproofing layer, there is no need to install additional seams.
Expansion joints on a house: proper waterproofing
When choosing sealant and materials for waterproofing, you need to consider:
- Basement.
- Pressure of wet soil on foundation walls.
- Length, width of the expansion joint.
- Characteristics of existing deformation disorders, the likelihood of new ones.
- Load from the building.
After installing waterproofing materials, check the tightness of the connections. If waterproofing operations on expansion joints were carried out correctly, the building will last a long time, without any hint of damage.

Filling with sealant
Expansion joint in the foundation: types and their structure
A seismic expansion joint in foundations is created in an area that is subject to earthquakes of varying strengths. Thanks to the construction of expansion joints, it is possible to minimize the consequences of shocks to the earth's surface.
When constructing them, the foundation is conventionally divided into separate cubes with identical sides. The expansion joint of the foundation is made along the edges of these cubes. Once organized, the structure appears divided into compartments. To protect against the harmful effects of ambient temperature, the seams are covered with waterproofing materials.
A popular option in construction among expansion joints is the sedimentary type. This type is relevant for buildings with variable number of storeys. As the number of floors increases, the load on the foundation will increase and it will experience subsidence into the ground. Thanks to the presence of special seams, the structure will not crack and will maintain its integrity.
Such a seam represents a division of the foundation into several nodes. Each seam must be protected by a special design unit. Arranging a sedimentary joint will require additional funds and take significant time - but in the future you do not have to worry about the integrity of the walls.
The temperature seam in foundations is especially important in regions characterized by sharp changes in temperature both throughout the year and in the daily cycle. Sudden jumps lead to the destruction of the internal structure of building materials, which, in turn, leads to deformations and cracks in the walls. The presence of expansion joints allows you to avoid such problems.
When developing a building project, a special calculation is made of the squares into which the foundation should be divided to create expansion joints. When performing this work, all the characteristics of the region are taken into account - seismicity, soil freezing depth, temperature range throughout the year, characteristics of the future building and much more.
Expansion joints in strip foundations of fences make it possible to ensure the safety of the future fence and protect it from cracking and possible complete destruction.
A temperature-shrinkage joint in a monolithic foundation should be created if a large volume of concrete is used during the work. Especially if concrete is poured over the monolith frame.
After pouring, concrete gradually releases moisture and decreases in size. This causes displacement of the remaining parts of the structure and creates the risk of cracks and collapses. Therefore, the presence of expansion joints when laying a monolithic foundation is mandatory.
In modern construction, specialists often resort to combining several seams into one, thus creating universal seams that can withstand various loads and difficulties. For example, shrinkage and expansion joints provide the best efficiency and are quite simple to install. A universal expansion joint makes it possible to ensure the strength of buildings of various heights. When laying such a seam, the type of foundation does not matter.
Types of foundation expansion joints
The function of compensation structures is to divide the slab and strip base into separate blocks. The load is reduced significantly. During soil and temperature fluctuations, adjacent areas will not be deformed.
Types of compensation structures:
- Sedimentary. Protects strip and slab foundations from destruction. Recommended for soils prone to heaving and instability. Distributes the load evenly over the surface. Shrinkage occurs under normal conditions.
- Shrinkable. It is used to prevent the risk of cracking of the concrete structure during drying.
- Seismic. Recommended for use in areas where there is frequent movement of earth layers.
- Temperature. Protects the concrete base from deformation during temperature and seasonal fluctuations in the soil.
Compensation incisions must be placed at a distance from each other. Indicators can be found in building regulations. How frequently sutures can be placed depends on:
- Base material.
- Soil type.
- Dimensions, weight of the structure.
Standard indicators specified in building regulations can be used without additional calculations. For accurate calculations, you need to use formulas.
Compensation structures are recommended for slab, strip, and prefabricated foundations.
Sedimentary structures
Reasons for base shrinkage:
- Due to uneven distribution of load on the foundation.
- An area where the soil consists of layers of different composition was chosen for the construction site.
The load is distributed unevenly if the structure consists of several tiers, where each has its own number of storeys.
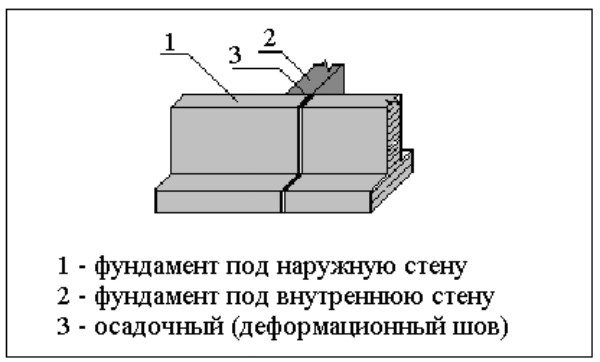
Sedimentary
It is rare to find construction sites that have uniform soil content. Refers to structures that occupy a large area. The solution is the installation of a sedimentary structure. It will prevent the appearance of cracks and save the building from vertical displacements. The design of the expansion joint is designed in such a way that when soil layers move, the problem area is under the movement, without dragging stable blocks along with it. Building distortions are excluded.
Shrinkable
It is used on monolithic slab bases, during the installation of which a lot of concrete was poured and reinforcing mesh was installed. After complete drying, any concrete mixture is freed from moisture. The base shrinks. Cracks and fractures appear, which affects the quality and bearing capacity of the concrete base.
The shrinkage joint eliminates the appearance of cracks and fractures due to shrinkage of a large concrete structure. The step at which the seam should be placed is determined after calculations, taking into account the characteristics of the underground and above-ground parts of the house.
Shrinkable
Features of temperature and seismic seams
In regions where temperatures differ significantly between winter and summer, cracks often form on concrete foundations.
- On frosty days, the heating season begins and deformations of the structure occur. When the room is heated from the inside, it is cooled from the outside.
- In summer, the outside of the building is heated, and the inside of the room is cooled by air conditioning.
Installation of a temperature compensation structure solves the problem with temperature changes. Used only for above-ground structures, plinths.
If the foundation is completely recessed into the ground, if the calculations are carried out correctly, the air temperature does not have a significant effect. The exception is areas with deep soil freezing. Temperature loads are significantly higher on the upper part than on the underground part.
Seismic
Seismic joints are required in areas where the layers of the earth are in constant motion. To avoid damage, the base is divided into separate sections, reducing the load during movement.
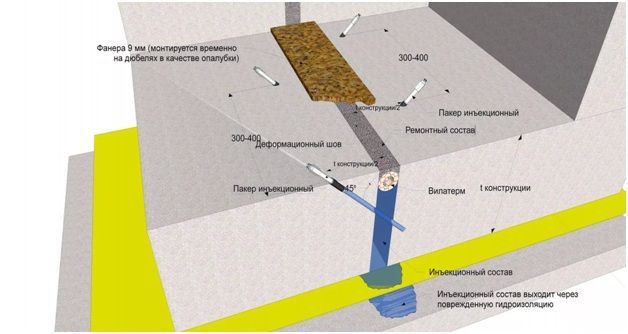
How to fill and insulate expansion joints
For the foundation of a building, the method by which the seam will be laid plays an important role. When arranging expansion joints, a number of features of the work should be taken into account:
- The gap in the seam should be equal to the height of the entire foundation. Otherwise, the meaning of performing this set of works is lost.
- The horizontal distance between the laid seams is determined depending on the building material. Wooden structures can have 60 meters between seams, and brick structures no more than 15.
- When analyzing soils, it is necessary to establish the degree of frost heaving of the soil at subzero temperatures. As the degree of heaving increases, the distance between the seams decreases.
- The expansion joint in the foundation should be 10 cm wide - this allows it to be insulated and waterproofed.
- At the junction with extensions, a seam is always provided, regardless of the distance to the nearest gap.
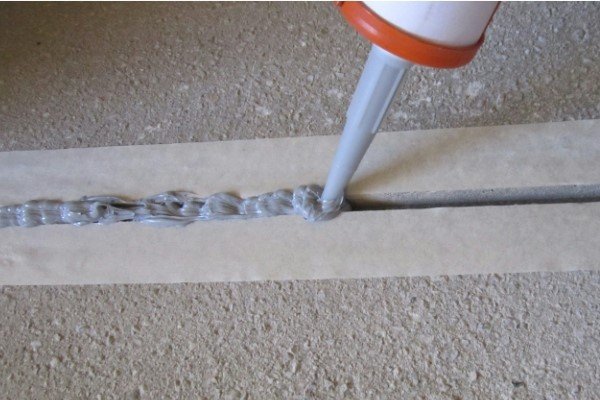
- After all the work on insulating the seam has been completed, it must be sealed with a special compound.
The specified rules for laying gaps are universal and mandatory for all types of expansion joints. At the same time, the development of the project for each foundation has its own characteristics and adjustments. In addition to creating a seam, it is important to properly ensure its insulation and sealing - this will extend its service life and reduce the risk of deformation.
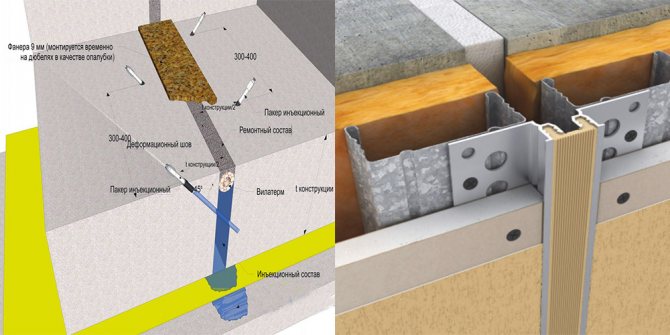
Construction of expansion joints
Various materials are used to seal expansion joints:
- Sealants made of bitumen with polymer compounds.
- Butyl rubber sealants. The cheapest option.
- Silicone based sealants.
- Polyurethane types of sealants.
In today's construction, the latter option of sealants is the most popular. They are expensive, but provide maximum strength when exposed to negative environmental factors and building pressure.
Chemical production uses only special polymer materials to create first-class sealants. The use of these means allows you to provide reliable protection to the foundation. If you do not pay enough attention to the structure, it can quickly undergo destruction, even collapse.
Before directly sealing the gap, it is necessary to perform a set of actions to prepare the surface. Without this, it is impossible to create a high-quality and durable coating. Polyurethane sealants guarantee high elasticity and provide a high level of adhesion to the surface. This type of sealant has high thermal resistance and can withstand temperature fluctuations from minus 100 degrees to +100.
Features of formation
Before installing the device, you should contact a surveyor to calculate the optimal number and placement of seams for the structure being built. Having established the desired values, we begin to implement the plans.
During execution, it is important to consider the following features:
- the size of the expansion joint must correspond to the size of the edge of the structural element;
- the optimal distance between nodes is 15 cm for brickwork, 60 cm for wooden structures, 90 cm for prefabricated monolithic and monolithic structures;
- soil heaving (as the degree of heaving increases, the distance between the joints decreases proportionally);
- design parameters of the structure;
- width (set depending on the type of unit and dimensions of the structure);
- seams are made both on the foundation (strip or slab) and on the structure itself;
- the need for additional protection of the units (for the tape - a layer of waterproofing, and for the slab - tarred tow).
We recommend watching how the seam is constructed in the finished base.