In private construction, a strip foundation is most often used, that is, trenches are dug. These are pit works, they are designed according to the rules of SNiP 3.02.01 - and everything is strict here. The stability and reliability of the future building half depends on them. Let's figure out how to prepare a foundation pit for construction.
Digging a foundation pit
Stages of excavation works
There are four stages of excavation work:
- Field work: research and adjustment of the site.
- Digging a pit.
- Cleaning the bottom with a bulldozer.
- Compacting, moistening or draining soils.
Before starting work, take the perimeter of the pit to the site according to the general plan and check the dimensions along the axes and diagonals with a deviation of no more than 2 cm. It is better to dig a pit in the summer so that heavy equipment can move around the site and pass without ruining the road. The weather should be dry, because after rain the soil often becomes more mobile, the bottom may silt, and the slope may collapse.
Soil consolidation
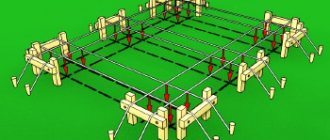
With vertical walls of pits, it is often necessary to temporarily fasten them, securing the soil and preventing it from collapsing. Justifies the need and determines the method of such fastening (PPR) - a work plan. Temporary supports must be strong and reliable, withstand additional loads from working construction machines without compromising the strength, and be easy to install and disassemble.
The designs of such fastenings can be very diverse. Most common in construction practice are fastenings in the form of systems with struts, sheet piling fencing of pits, anchor systems, etc.
Supports in the form of struts are used in large-width pits only when it is impossible to use another method of fastening. inside If the pit is shallow, the struts are installed in one row; in deep pits the number of rows can exceed two. It is clear that the struts interfere with the work inside the pit.
The enclosing elements themselves in shallow (up to 3 m) pits in cohesive (non-flowing) and low-moisture soils are boards (bricks) made of “fifty” boards nailed to the beams at intervals (gaps) equal to their width. With greater depth of pits, and also, regardless of their depth, with loose or highly moist soils, the enclosing elements are made solid.
In narrow pits, as well as when strut supports make it impossible to carry out work, anchor fastening systems are common. They include piles (supports), rods, racks and enclosing elements. Piles (supports) are driven at a distance from the edges of the pit, greater than the possible width of the collapse layer of its walls (the so-called “collapse prism”).
Rods (steel or wood) connecting the piles to the enclosing elements are laid in trenches - there they do not interfere with movement along the edges of the pit.
The cantilever structure for fastening the walls is installed in narrow pits. Its main part is walls made of wooden (for excavation depths up to 3 m) or metal sheet piles (up to 6 m) with the lower parts pinched in the ground. In deep pits (up to 10 m), the walls are made of driven or bored piles, arranged in one or two rows.
In narrow (up to 15 m) pits, spacer fastenings are used, consisting of spacers, racks and enclosing elements (sheets or tongue and groove sections). There may be from one to several rows of spacers along the height of the pit wall. The traditional material for spacers is wooden logs, and the fencing elements are inventory panels.
They can be replaced by an enclosing wall made of wooden sheet piling, buried 0.5-0.7 m into the ground at pit depths of more than 3.5 m. The presence of horizontal struts inside the pit is just as inconvenient as struts.
reusable fastenings from sliding spacer frames, consisting of tubular struts and telescopic spacers, are becoming widespread, characterized by ease of installation/disassembly . Holes are drilled in the height racks.
The spacer is an inner pipe with holes inserted into the outer one (also with holes), as well as a rotary coupling and two supporting parts adjacent to the fence panels. The inner pipe is pulled out from the outer pipe to the width of the pit (trench) and secured with a bolt passing through both spacer pipes.
Adjusting the length of the spacer to the exact width of the pit is done by turning the coupling, which has a screw thread.
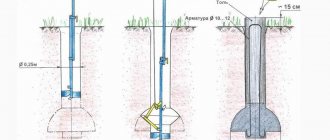
We determine the dimensions of the pit for the strip foundation
How are the dimensions of the pit determined:
- The boundaries of the foundation should extend beyond the load-bearing walls by 40 cm.
- Slope so that the soil does not crumble. The slope angle of the pit depends on the type of soil; at a depth of 3 meters it is: 45° for sand; 56° for sandy loam; 63° for loams and loess; 76° for clay. The angle of repose is especially important if the rock is wet. On sandy soils, the walls must also be additionally secured with shields.
- The depth of the trench depends on the type of building : for sheds, houses without a basement, frame houses and timber - 50-100 cm, for two-story mansions - 150 cm to the depth of soil freezing.
- The bottom should be 30-40 cm below the freezing level and at least 50 cm above the groundwater level.
- The weaker the soil, the wider the trench. The minimum width according to SNiP is the thickness of the walls with formwork plus the thickness of insulation plus 20 cm on each side.
Soil removal in Moscow
The volume of soil removed when digging pits exceeds that which will be used for backfilling. After all, a significant part of the volume of the pit will be occupied by the foundation. Therefore, excess soil is loaded onto dump trucks immediately after extraction by excavators and removed.
According to the law, the construction company itself or its specialized contractor, who usually performs a complex of excavation work, must load and remove soil from the construction site, as well as dispose of it in the future.
Soil disposal means recycling and burying it, or reusing it. Therefore, the cost of excavation development also includes the costs of removing and disposing of surplus earth from the construction site.
There are a number of vehicles from the fleet of construction equipment, the purpose of which is precisely the loading and removal of soil outside the construction site. Each excavation pit being developed is equipped with similar special equipment individually, depending on its characteristics.
A subtype of excavator called a backhoe loader has earned high praise from builders when loading soil. It is intended primarily not for digging holes (cuts), but for loading soil into dump truck bodies. The championship among such specialized construction machines is held by the JCB 4CX backhoe loader, manufactured in the UK and equipped with two buckets: front and auxiliary rear.
The machine is maneuverable, so-called. with a “crab” motion, offset by the digging axis, it is capable of turning around its axis by turning the wheels.
The soil is delivered to a special landfill for disposal by dump trucks of the Mercedes-Benz Axor, Volvo, Scania, TATRA, MAN, ZIL, KAMAZ, etc. brands. Moreover, in this series, the advantage of imported vehicles over domestic ones not so obvious. As an example of successful competition with foreign dump trucks, one can cite a representative of the modernized series of Russian KamAZ trucks - model 45144.
This dump truck has a load capacity of 14 tons with a platform volume of 18.8 m3. Its purpose is precisely the transportation of bulk cargo. Another KAMAZ 65201 can transport up to 20 tons of soil, and a Russian-assembled Hyundai HD370 dump truck produced by the Kommash plant (Mtsensk) takes on board up to 27 tons of cargo.
Regarding the price of soil removal (RUB/1m3), it should be noted that it depends on a number of factors:
- Volume of soil removed;
- Urgency of order;
- Distance of the special disposal site from the construction site;
- Methods by which soil is developed and transported.
The contractor (or developer) must have permits and a license that allows him to remove (and dispose of) the soil. Dump truck drivers must have the following documents on hand:
- A warrant for the removal of soil (in Moscow it is issued by OATI - the Association of Administrative and Technical Inspections).
- Project for moving earth masses.
- Agreement with a special landfill for soil disposal.
How much does the volume of soil increase when it is extracted?
An estimate of the expected volume of extracted soil is given by the so-called. “loosening coefficient”, the value of which is determined by the soil category. For the 1st and 2nd categories, characterized by densities of 600-1900 kg/m3 (sands, peats, plant soils, light loams, loess soils, gravel), the loosening coefficient lies within the range of 1.08-1.3.
For the 3rd and 4th categories, with densities of 1750-2000 kg/m3 (clays, heavy loams, gravel, soil with roots, heavy clays, clays with crushed stone), the loosening coefficient range is 1.24-1.32. The 5th and higher categories of soils (hardened loess, chalk and shale rocks, tuffs, limestones, sandstones, granites, basalts...) have the highest coefficient: 1.3-1.5.
Digging a pit
How to dig a pit:
- The top layer of turf is removed over the building area at a distance of at least 1.5 meters from the outer perimeter.
- Digging begins. Step back from the foundation line with formwork and waterproofing at least 20 cm. In fact, builders recommend stepping back 50 cm. If the depth is more than 1.25 m, then reinforce the walls with shields with spacers.
You can dig either manually or using machinery. Trenches for shallow foundations are often dug manually, without expensive equipment. It is also not allowed to work with equipment if there is an intersection with hidden pipes or cables - such areas are also developed manually.
You can place the excavated soil no closer than 50 cm from the edge of the pit; if the soil is sandy, then no closer than 2 meters.
Removing the fertile layer
It is not as simple a procedure as it may seem to a layman. It is very eloquent that since 1996 this type of excavation work has become necessary according to the law. Today, any construction process begins with it.
All work related to the removal of fertile and/or vegetative soil layers is subject to documentation in the construction work plan. In order to determine how thick the fertile soil layer is, specialized geological studies of the site are carried out.
After this, the above-mentioned plan is made, which is subsequently taken into reality using geodetic markings and surveying.
In order for the removed soil layer to have a given thickness, it is necessary to use special construction equipment operated by qualified machine operators. There should be no mistakes in removing soil, because every centimeter counts. Any mistakes at this stage lead to significant fines from state environmental services.
Usually the top layer of vegetation is cut off by bulldozers. Its development is carried out first along the edges of the pit with the transition to side penetrations. The removed topsoil layer is removed and stored until subsequent placement on infertile lands, compensating (partly) for this deficiency. Backhoe loaders and dump trucks are involved in this work.
Compacting the pit
The dug pit is prepared for the foundation. Please note: as a rule, the pit is not dug to the design level, but a layer of untouched soil is left approximately the thickness of an excavator’s tooth. It is processed manually so as not to disturb the density of the soil under the future structure.
A cushion and waterproofing are placed in the trenches under the strip foundation, and commercial cement is poured.
If wet soil appears, it means groundwater is close. This is either incorrect calculations, or a seasonal rise in water on loams and sandy loams. On such soils, it is necessary to maintain a distance from the groundwater level to the base of the foundation of up to 1 meter.
We will bring sand to fill the sand bed and level the site for building a house, and we will rent out an excavator. We work in Moscow and Moscow Region, call!
Soil development and excavation
In the past, this stage was a long and labor-intensive task prior to any construction. The main reason for this was the laboriousness of manual soil development, which for many centuries was the only way to do it.
Modern construction technologies suggest the possibility of doing it in three ways:
- Mechanical.
- Soil erosion (hydromechanical).
- Blasting works.
The latter method is widely used in mountainous areas, characterized by an abundance of stones in the ground and low population density, which creates the necessary preconditions for the safe conduct of explosions. The second method is cost-effective if there is a natural reservoir near the construction site.
The most popular among builders and the most widely used method is the mechanical method, i.e. development using construction equipment.
For manual excavation of soils, it was very difficult to quickly and efficiently remove them from pits, including due to the above-mentioned increase in the volume of soil loosened by excavators. Throwing it out of the pits required the use of a huge army of diggers.
However, the manual method also had advantages - cleaning the soil in the process of gradual, slow excavation. This effect is still used today, which is why you can sometimes find diggers on construction sites. The mechanical method of soil development involves the participation of specialized construction equipment. This includes well-known excavators and bulldozers.
The power of these construction machines allows the work to be completed in a short time. However, before they begin, a preliminary study of the soil should be carried out to determine its bearing capacity to comply with the loads from special equipment.
When work is carried out in winter, the frozen soil is first excavated using hydraulic hammers, which are attachments to special equipment. The costs of this stage are quickly recouped by the subsequent ease and speed of soil development using construction machines.