The construction of a country house can often take several years due to lack of time, financial problems and other reasons. And the question arises about sheltering unfinished construction for the winter. After all, you can leave a finished foundation without first protecting it from the oncoming frosts, but you risk losing the integrity and quality of the work already done. What to do with what is already ready? Do I need to cover the foundation for the winter? If yes, how should this be done? Preserving the foundation for the winter is not a complicated procedure, but it has many nuances.
Preserving the foundation in winter: options
To ensure that the foundation of the future house, previously poured and completely ready for further work, does not crack over the winter, it can be preserved in one of several ways:
- cover with thick construction film, sprinkle soil on top and press down with stones;
- protect from excess dampness and water using drainage;
- make additional waterproofing on all sides of the base of the house;
- cover the base of the building with one of the types of greenhouses;
- insulate the outer sides of the foundation with polystyrene foam, and backfill with non-metallic material in a 20 cm layer with mandatory compaction of the soil.
Of course, each type of base requires its own conservation. But these methods can be combined and used for any ready-made base. After all, the main reasons for the destruction and deformation of the flooded foundation of a house are increased heaving, the proximity of groundwater and the lack of load on the foundation.
Having eliminated one or more causes of damage to the foundation during the winter season, you can safely leave the foundation of the house for the winter.
The snow covered him...
Properly executed foundation waterproofing is a necessary thing, but not sufficient. Insulation is also required, because waterproofing prevents the penetration of water, but cannot withstand the pressure of frozen soil. The North-Western region is characterized by frost heaving in clay and loamy soils due to seasonal freezing and thawing, heterogeneity of foundation soils under the base of the foundation and the presence of highly deformable peat soils. And regardless of the type of soil, the depth of its freezing is very important. The frozen soil swells and pushes the foundation upward, and around the entire perimeter with varying intensity. In this case, the weight of the foundation does not matter, since frozen soil has enormous strength. Therefore, by the way, basement walls that are not reinforced with ceilings can crack or even collapse under soil pressure, so if possible it is better to cover the basement.
Advice
It is faster and cheaper to make a floor from prefabricated slabs. You just have to order a crane to unload and install them. The installation of a monolithic floor is more labor-intensive; besides, the monolithic slab still needs to be “calculated” in order to select the reinforcement diameter and pitch.
R. M. Nikonorov, head of design management service MIRAX GROUP
Thermal insulation reduces the depth of freezing, and, as a result, reduces the thickness of the heaving layer. It makes no sense to use mineral wool boards or, for example, foam plastic as external insulation - they will quickly lose their thermal insulation properties. In conditions of a humid environment and various loads, extruded polystyrene foam has proven itself well. External insulation of the foundation using extruded polystyrene foam slabs allows you to remove heaving soils from the freezing zone and protect the waterproofing, extending its service life. The insulation boards are attached to bitumen-cement glue after the waterproofing has cured. In each specific case, the required thickness of the extruded polystyrene foam board is determined from a thermal engineering calculation.
What is conservation of construction for the winter?
So, individual housing construction projects, that is, private low-rise construction, are usually mothballed for the winter. Why does conservation not affect commercial construction sites (in particular, multi-storey buildings under construction), which, as we can all observe, continue to be built even in severe January frosts? Economic reasons play the dominant role here: the cost of a facility downtime for at least 1 calendar day reaches half a million US dollars (depending on the scale of construction), so technologists and engineers here do not skimp on materials:

Preservation of an unfinished house for the winter
- special components based on salts and polymers are added to the solutions to prevent water from freezing even at -40°C;
- the constructed structure is heated from the inside by special powerful heat guns.
We will tell you further how to do this correctly, so as not to expose the already erected structure to the danger of damage and destruction from frost, and also to avoid simply overpaying for the measures taken.
Consequences of lack of conservation of a construction site
To leave everything as it is and not carry out any work at all means to “kill” the construction site with your own hands, so it is simply necessary to carry out at least the minimum and easily accessible complex of protection for long-term construction. But it is worth considering that some events cannot be avoided, and some can be excluded to save money.
Conservation is a series of measures aimed at preserving an already erected structure from destruction when exposed to atmospheric factors, and it is not a bad idea to worry about the safety of the construction site for others. At the same time, conservation makes it possible to quickly put the object into construction in the spring without additional preparatory and restoration work.
Conservation itself implies drainage of water and protection from moisture of the construction site and stored materials purchased for future use. Without protective cover, building materials accumulate moisture, which, when frozen, destroys their structure. Moreover, even if at first glance, after defrosting, no damage is detected, it still exists: at a minimum, a decrease in the strength of the material due to microcracks, and at a maximum, subsequent rapid destruction (delamination).
Options for preserving the base with insulation
After the strip foundation structure has been poured, numerous puddles form.
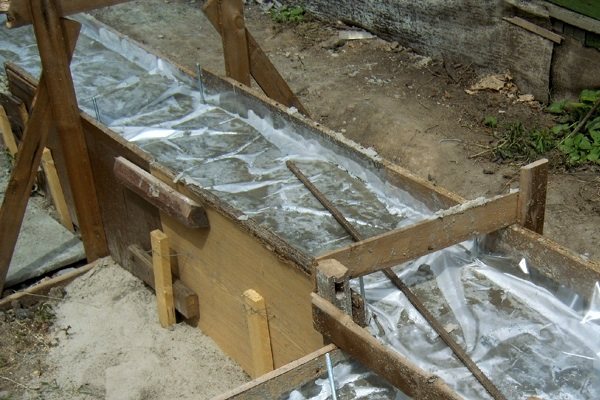

Moisture accumulates in them. Covering the entire perimeter with film is impossible in principle.
The horizontal position of the material will not allow it to withstand the snow cover.
Therefore, the film is stretched onto shields and placed on both sides of the tape.
Features of conservation of foundations for a long period
If you understand that the construction of the building will be suspended for more than a year, then with the onset of construction you will have to partially re-open the foundation and perform additional work. For this:
- remove plastic film from all surfaces so that the concrete and masonry dry well during the summer;
- extend and make drainage lines according to a permanent work pattern;
- arrange a permanent blind area around the perimeter of the entire building;
- install a lightning drain at least 10 meters high, mount a drain from it and a grounding circuit;
- ensure reliable waterproofing of all vertical and horizontal surfaces.
In order to reduce the lateral pressure of the soil during heaving and maintain the thermal insulation properties of the material, use insulation for walls with a thickness of at least 100 mm. All these measures will allow you to preserve the foundation for up to 5 years without continuing construction.
Methods for protecting foundation structures
Proper conservation of the foundation before winter will not only preserve its integrity, but will allow the concrete to gain maximum strength over these months. As a result, it will be possible to begin the construction of walls with the onset of a thaw and thereby complete construction faster.
How to preserve the foundation for the winter? In order to ensure reliable high-quality protection of the foundation, the list of work performed should include:
- insulation of the building perimeter;
- presence of vertical and horizontal hydraulic insulation;
- replacing heaving soils with compacted dry sand;
- installation of a hydraulic lock along the entire perimeter of the building.
If the groundwater level is high, drainage pipes should be installed to ensure efficient drainage of water.
Insulation of foundations for the winter period
Since the most difficult operation to preserve the foundation of a house in winter is insulating it on each side, it is worth considering such work in more detail.
Such work should be carried out immediately after the foundation itself has dried, when the formwork is removed. Then you can not only leave the base of the house unloaded in winter, but also get warmer floors later, when the building is built.
The insulation process will look like this:
- polymer-bitumen mastic is applied to the vertical surfaces of the tape (supports, slabs) as a waterproofing layer - this will prevent moisture from spoiling the finished base;
- The vertical sides of the base are covered with expanded polystyrene slabs, using adhesive compounds for this - this will insulate the foundation and additionally protect it from damage;
- additional finishing of the slabs attached to the base is carried out using plaster - this will extend the service life of the foundation for many years;
- backfilling is carried out with non-metallic material in a layer of at least 18 cm with dense compaction.
Of course, the cost of materials and funds for such a foundation will be much greater than when creating a simple foundation. But the heat savings in the house during its operation will cover these costs in the first year of residence. And the likelihood of damage to the foundation from heaving is reduced to a minimum.
Conservation of the construction of brick and block (foam block, gas block, shell rock) house
First floor without ceiling
Builders do not recommend winterizing the construction of a house at this stage. It is advisable that the walls already have a ceiling laid.
It is very important that there is a reinforcing belt along the top of the walls. If winter occurs at the construction stage, when the reinforcing belt has not yet been laid, then without protective measures water gets inside the bricks (or blocks), which leads to their destruction and guarantees efflorescence on the brick in the spring
If the wall is multilayer (well) and insulation is laid between the two walls, then remaining uncovered the insulation will absorb moisture, and the water in it will freeze and expand, which will completely destroy the structure of the material, and thereby render it unusable.
Therefore, preserving the house at this stage is labor-intensive and does not guarantee complete safety of the walls from getting wet and possible cracking.
If conservation is still necessary at this stage, builders recommend:
- Cover the top of the wall with waterproofing film, then load the film with bricks, or bend it in two directions, then press it against the wall with boards and nail it.
The same is done at the window sill level. Waterproofing walls - Free-standing walls erected above the floors must be braced (with struts or struts) if their height exceeds 3.1;
5.6; and 6.5 m with a masonry thickness of 38, 51 and 64 cm, respectively. Spacers - Inside the house, the floors are covered with straw mats (to protect the soil from freezing and heaving) and waterproofing film, the film is pressed with soil or sand to the walls from the inside, raising it by 20-30 cm.
- If there is a financial opportunity, then it is worth installing temporary lathing floors.
Place a waterproofing film or roofing felt on top of the sheathing and press it with bricks. Temporary overlap - There is no need to close the walls from the outside.
- Cover door and window openings with boards, sheets of metal, roofing felt or plastic film.
Windows and doors covered with plywoodWindows covered with roofing felt
Windows boarded up
- Water is removed from the house by leveling the surface of the site or using a ditch system (described above).
Protection of the first floor with overlap
This stage is more favorable for preservation for the winter.
Necessary activities:
- Lay waterproofing (roofing felt, PE film) over the ceiling, overlap it, seal the joints with adhesive tape, and securely load bricks on top from the wind. The edges of the hanging film are pressed against the wall with slats and nailed.
- Close door and window openings with boards, metal sheets, roofing felt or PE film.
- At this stage, it is already worth making a blind area that will protect the foundation from water flowing from the ceiling.
- Water is drained from the house by leveling the surface of the site or by installing a system of grooves described above.
The house has been roofed, the rafters have been laid, but not yet covered with roofing material
Rafter part without roofing material
At this stage, the walls were erected, the ceiling above the first floor and the staircase were laid, the gables were built, and the rafter structure was laid.
Preservation at this stage:
- It is necessary to protect the interior from moisture; for this purpose, a temporary lightweight roof is constructed. The sheathing is placed on the rafters, and waterproofing (roofing material, roofing membrane or reinforced PE film) is laid on it. The waterproofing is secured with wooden slats.
- If at this stage the gables have not yet been built, then these places need to be covered, for example, with plywood or boards to protect the waterproofing from blowing and the interior space from water and snow.
- Cover the openings with shields.
- A blind area and grooves are installed to drain water away from the house.
Stages of preserving the foundation for the winter
According to the general opinion of construction specialists, interrupting construction at the foundation stage is even more profitable and useful, because During the period of inactivity, the foundation will gain greater hardness and give uniform natural shrinkage. Therefore, conservation of the foundation is useful, but abandoning it to the mercy of fate in the rain and frost is not acceptable.
Preservation of the foundation for the winter implies:
1. Providing thermal insulation
– optimal stage of foundation conservation, i.e. even a slightly damp base with reliable thermal insulation will not freeze until internal forces of self-destruction form. Moreover, having reliable thermal insulation, you can leave even a wet foundation for the winter, because the chemical processes of concrete hardening are accompanied by the release of heat, which does not allow the foundation to freeze even in severe frosts. But even good thermal insulation without reliable waterproofing becomes a useless operation.
2. Ensuring waterproofing is the most important point that cannot be avoided. Excessive accumulation of moisture in winter leads to accelerated destruction of the foundation. Water, even without freezing, successfully destroys fresh concrete structures due to the “washing out” of the binder component. A wet foundation acquires a porous soft structure that is unable to cope with external influences. Therefore, continuous waterproofing is an integral stage of conservation.
It is worth paying attention to the fact that “dry” foundations are completely waterproofed (horizontal and vertical), but “wet” foundations must be waterproofed without an upper horizontal preservative layer. It is necessary to leave an “open” area of the structure for the evaporation of excess moisture, which is protected from precipitation by leaky “capes” of waterproofing
3. Groundwater drainage
or measures to prevent flooding - a recommended measure especially in the stages of lack of thermal and waterproofing. But when performing reliable hydro- and thermal insulation, this is an unnecessary operation, because... It is more expedient to backfill the foundation. But in cases where there is a further need to carry out work on the foundation in the spring, this event becomes extremely necessary.
At a distance of a meter along the perimeter of the foundation, a compacted trench measuring 50*50 cm is made, and a blind area from the foundation must be made in its direction, along which water will flow into the ditch. But the volume of the “channel” will not be enough, so it is necessary to dig several improvised reservoirs to the side to accumulate water, or significantly expand and deepen the ditch itself.
It is also important to take care that there is no accumulation of water on the internal foundation area. Why are drainage systems also used? • If there are sewer channels in the foundation, then the layout is carried out so that they are used to drain wastewater outside into the trench
• If there are sewer channels in the foundation, then the layout is done in such a way that they are used to drain wastewater outside into the trench.
• If it is not possible to drain wastewater outside, a drainage hole is dug in the center of the foundation site.
It is worth noting that when constructing foundations with utility basements, it is imperative to organize external drainage, for which drainage systems are taken into account at the design stage.
Conservation of a construction site
For whatever reasons, the construction of the facility was suspended in the winter, it is necessary to carry out a set of necessary work to prepare for the conservation of the facility itself and the materials brought for construction.
Snow and frost can greatly damage the foundation
There are several reasons that can cause damage to prepared building materials and erected structures:
- Atmospheric precipitation - water from rainfall is absorbed into materials and accumulates in the cavities of building structures. With the onset of the first frosts, the water freezes and expands significantly, which can cause destruction of building structures and damage to materials.
- Low temperatures can cause deterioration in the properties of some building materials, which lose their properties and become very brittle. To prevent damage to material resources, it is very important to cover them correctly.
- Water and frost cause a phenomenon called soil heaving - frozen wet soil begins to push foundation structures to the surface of the earth. Shallow foundations suffer greatly from this phenomenon.
- Excessive snow load in winter can cause the collapse of building structures that are not designed to withstand a load of such force.
- The last reason in favor of conservation is not related to natural phenomena or the design features of the building. At a site unprepared for wintering, there is a danger of theft of materials that are not guarded by anyone during the winter period.
Preservation of building materials in winter
It is very important to preserve all materials that were brought to the site but not used for any reason so that they are not destroyed by the weather.
All lumber is stacked on pads. Storing lumber When storing them, try to leave about 5 mm of free space between them, which will give them the opportunity to ventilate. This will allow the wood to get rid of excess moisture reserves. All wood materials should be treated with antiseptics (except for those that you plan to use, for example, for formwork). They need to be covered on top with plastic film or roofing felt.
All under-roofing materials, materials for waterproofing cellars, roofing materials for covering roofs should be stored indoors, in a dry place, where you can also leave nails or other fasteners, glass and metal parts
It is important that rolled waterproofing materials (tar paper, roofing felt, PVC membrane) are stored in a vertical position, otherwise they will crack at the bends (usually closer to the middle of the roll). Storage of waterproofing
Paints, drying oils, etc. Solvent-based materials should be stored in tightly closed containers. Cement, lime, gypsum, alabaster are afraid of moisture, and it is better not to leave them on the site for the winter, but if there is no other choice, then they are stored indoors (sheds, for example, or cabins)
These materials can be placed in bags on the floor if the floor is dry. Any entry of moisture or excessive dampness into the room will lead to hardening and further unsuitability of these materials. Spoiled cement
Bricks that are to be used for laying stoves are best stored in a dry place. The rest of the unused bricks should be stacked, covered with film on top to protect the material from snow and water. The same goes for blocks. The sand is placed in a heap inside the formwork to protect it from spreading. The top of the sand should be securely covered with a strong film (for example, reinforced with polyethylene or roofing felt), and weighted with bricks from the wind. Waterproofing also helps protect the sand from moisture and prevent grass from growing in it in the spring.
Containers, water barrels, and a concrete mixer available on the site should be turned upside down to prevent them from being torn apart by frozen water in winter, or brought indoors.
You can get acquainted with conservation from a regulatory point of view by using the document: TKP 45-1.03-165-2009 “Preservation of objects under construction.”
Preserving the structures of an unfinished house for the winter and preserving building materials constitute a small part of the cost of the entire house. If conservation is carried out correctly, there will be no problems when using the house in the future. By following the rules for preserving an unfinished house, you will be able to continue construction next season without fear of a pitfall on the part of materials and structures.
Preservation of the foundation for the winter
For safe wintering of the foundation, its construction must be completely completed. Here are the main steps:
- Make a double geotextile wrapping of perforated pipes in drainage wells.
- Before pouring, build drainage and bedding under the leveled area.
- Dig a well to drain drainage water. It must be deeper than the base of the foundation and located no closer than 4 meters from the construction site.
- Lay roofing felt or special foundation films in several layers under the foundation.
- Fuse a Bikrost-like material onto the walls and top edges. Carefully cover all cracks with mastic or plaster open surfaces with a moisture-resistant mixture.
- At a depth of 30-40 cm, lay hard foam plastic under the blind area. They also cover the outer surfaces.
- Sand or crushed stone should be poured into the space around the formwork and on top in a layer of 20 cm. It is advisable to compact it using a vibrating plate.
Since snow is a good natural insulator, you can install wooden slabs vertically - they will retain the snow. But if winters in your region are associated with thaws, the disadvantages of such work may outweigh its advantages.
Whether it is possible to leave the foundation for the winter also depends on the type of monolithic structure. The slab, if waterproofed and insulated, usually easily tolerates all uneven deformations of the soil. With tape everything is much more complicated. The area between the ribbons becomes the “pool”. The tape itself warps and twists due to swelling of the soil. Therefore, a number of additional actions need to be taken with the strip foundation:
- Disassemble the formwork around the tape. Swollen boards only contribute to waterlogging of the concrete.
- Cover and seal all surfaces with waterproofing.
- Insulate the blind area with polystyrene foam.
Due to the fact that there is no house yet, there is no heat source and peripheral thermal insulation is ineffective.

Without thermal insulation it is impossible to preserve the structure
Here are some more tips on how to protect your foundation from moisture and low temperatures in the winter:
- Place straw, spruce branches, branches or sawdust on top of the tape, and cover the top with film.
- Plow and harrow the ground. Loose soil is a good heat insulator and concentrates more water without letting it pass into the depths.
- Install snow-retaining boards from boards. This will have a positive effect if the snow does not melt during the winter.
- It will not be possible to protect the space between the tapes from water. Therefore, film-covered wooden slabs are installed with a slope on all sides of the tape.
A foundation without a building, left for the winter, can be compared with the foundation of unheated buildings. And for them, a 5 cm layer of polystyrene foam is used under the entire foundation, the blind area is insulated with the same material to a width of about a meter, and a layer of 10 cm is placed at the corners of the blind area.
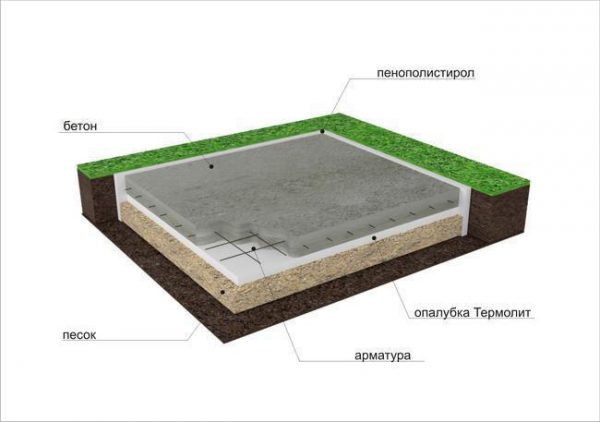
Insulation of a slab foundation
Of course, if the house is designed for further year-round living, it is not economically feasible to spend so much heat insulation on the foundation. Therefore, the main thing is to ensure high-quality thermal insulation and drainage of groundwater. The blind area is done after finishing the walls.
If construction cannot be continued next season, the facility will still be re-opened in the spring so that the concrete dries completely during the warmer months. In the fall, the quality of waterproofing and the operation of the drainage system are checked. All violations are corrected and closed again for the winter.
It is estimated that a foundation that has stood for one season without being closed loses up to 20% of its strength. Thus, if it stands open for 5 years, it will become completely unsuitable for building a house.
How to close the vents in the foundation for the winter?
A few words about the foundation of a house already built in winter. High humidity is present in any structure located near the surface of the earth. A strip foundation that is well insulated and drained still accumulates excess moisture because it is not heated, but it maintains a positive temperature in winter. This causes wooden beams to rot and concrete to become damp.

To solve this problem, vents are made in the foundation strips. They are located above the snow level. Ventilation also saves from the accumulation of radon gas in the basement. Excess radon can lead to radioactive contamination of the entire home.
Many people try to protect the basement from freezing by covering the vents with various heat insulators. Should not be doing that. The drier the air in the underground, the better the basement retains heat. This means there will be a good microclimate on all floors.
Video on the topic
Ecology of consumption. Estate: If it was not possible to complete construction during the summer period and you do not intend to continue work in the winter, you will have to mothball the construction site until the next warm season. Preservation of a construction site has its own rules, depending on the stage of construction, let’s figure it out together.
If it was not possible to complete construction during the summer period and you do not intend to continue work in the winter, you will have to mothball the construction site until the next warm season. Preservation of a construction site has its own rules, depending on the stage of construction, let’s figure it out together.

First, let's imagine a case where the owner decided to do nothing and leave the unfinished construction as is until spring, without making any efforts. What does this mean:
- The walls of a stone house can crack, as can a concrete foundation.
- The ceilings are deformed and in the worst case, they will completely fall.
- The basement will be flooded.
Remember that an unfinished construction project is afraid of moisture, temperature changes, autumn and winter rains, and severe frosts. Conservation allows you to protect an unfinished building from all these external negative factors.

The process of conserving a construction site depends primarily on how far you have progressed during the warm period. There are four main options:
- Only the foundation has been built at the construction site.
- The walls and frame of the house were built.
- There is already a roof.
- There is façade and exterior finishing.
Experts believe that the easiest way to preserve the foundation for the winter is the foundation. In addition, it is even useful to leave the foundation for the winter without continuing construction - this will help it settle and in the future significantly reduce the risk of shrinkage, cracks in the walls and other unpleasant phenomena. However, the foundation cannot simply be left in the open air.

What should be done:
- Strip and slab foundations require heat and waterproofing. For example, roofing felt or polyethylene are used as insulating materials. Covering materials should be placed on top of the foundation and pressed on top to prevent it from being blown away by the wind. For waterproofing, you can also use bitumen mastic, which is applied to the foundation.
- If communication pipes have already been laid in the foundation, you should definitely close them with plugs, or, as a last resort, clog them with a rag.
- The reinforcement that sticks out from the foundation is coated with an epoxy solution, which will protect the metal from corrosion. As an option, the fittings are coated with anti-rust paint, but an epoxy solution is more reliable.
- The foundation is backfilled. Dry sand, sawdust, and expanded clay can serve as backfill.
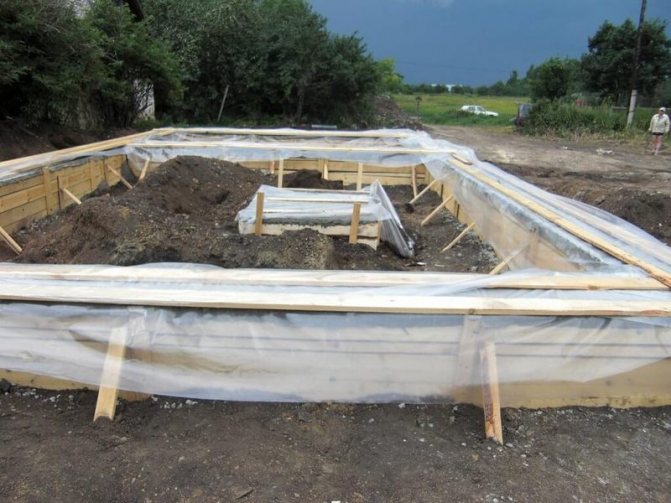

Important! The depth of foundation insulation must correspond to the level of soil freezing.
Pile and columnar foundations do not need hydro- and thermal insulation in the winter!
It is also necessary to ensure that water is drained away from the foundation, because in the spring the snow will begin to melt, and you do not need excess moisture. For this purpose, in the lowland, about five meters from the foundation, you can dig a small pit. In addition, drainage ditches are dug along the perimeter of the structure, which should lead to the drainage basin.
Foam boards or extruded polystyrene foam are used as foundation insulation.
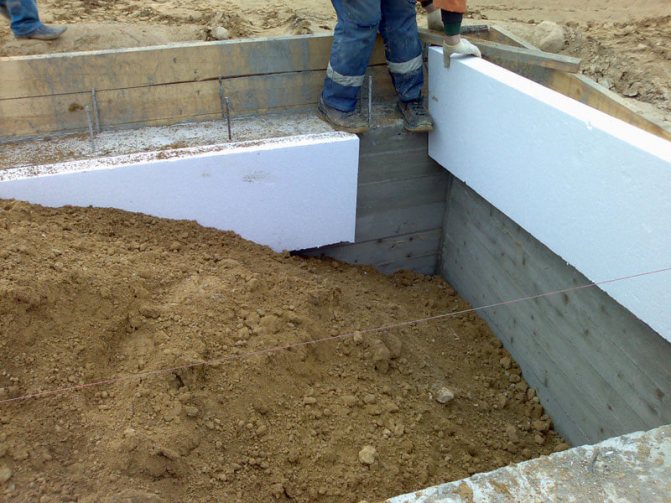

If an unfinished house already has a basement, special attention should be paid to its conservation. The best option is to cover the basement. Experts call prefabricated slabs the most affordable and fastest way. The basement covered from above will already be protected from precipitation. If you have managed to arrange the ceiling, all that remains before the start of winter is to lay waterproofing on it, for example, reinforced film or roofing felt, and press it with something against the wind.
You will have to carefully close the opening under the stairs to the basement. For this, boards, panels or shields are usually used. If the ceiling of the basement could not be equipped before the cold weather, the entire structure will also have to be covered with boards or other materials that can last through the winter, and waterproofing must be provided on top. The main thing is that this flooring is reliable and does not collapse under the weight of snow and the weight of a person who may accidentally wander onto the construction site.
Frost protection used for long-term preservation
If construction is expected to be frozen for a long period, the facility should be re-opened upon the onset of spring.
Here is another addition to the article in the video:
As a result of this, excess moisture will evaporate and the foundation elements will dry out.
The structure is prepared for the next onset of winter as follows:
- Drainage sewerage is being laid;
- Engineering systems are being fastened;
- The grounding loop is extended;
- A waterproofing coating is laid on all concrete surfaces;
- Horizontal and vertical insulation is installed;
- Backfilling is carried out using non-metallic material.
Share this article with your friends on social media. networks!
How to protect the foundation from groundwater?
Protecting the foundation from groundwater and precipitation is the most important stage of the work. To do this, you should make gutters (ditches) to drain water
You should also pay special attention to the drainage of rainwater (and that formed as a result of melting snow). To create channels and gutters for water drainage, low areas should be identified near the foundation (within a radius of no more than 4 m) along its entire perimeter
At such points, holes are dug to a depth greater than that of the foundation, and about 2.5 m wide. Such holes will collect water from the foundation. From the perimeter of the foundation to these holes, ditches are dug with a depth equal to that of the foundation depth. To prevent ditches from crumbling or becoming clogged, gutters can be laid at their bottom and the walls can be reinforced (for example, with wooden formwork). The number of outlet ditches must be such that there are at least 3-4 outlets from each wall. At the same time, in winter, it is necessary to monitor the ditches so that they do not freeze and clog the water outlet. An important point is the location of the vents. Vents should be approximately 0.5 m above the bottom of the outlet grooves.
The final process is to provide the foundation with a load (this is especially true for shallow foundations). This is done to ensure that the foundation is “settled”. To do this, it is enough to place all the building materials on a covered foundation.
Dig - not build...
If for some reason the construction of the foundation stopped at the excavation stage, then, alas, it is best to simply fill up the foundation pit or trench. The fact is that downtime always negatively affects the condition of the soil foundation. When preparing a pit, the natural structure of the soil is disrupted, plus, as a result of freezing and thawing of precipitation, by spring it is significantly deformed. This will require additional strengthening, which means investment.
Foundation conservation work
The process of preparing a poured foundation for the upcoming winter period depends on its type and design.
It is important to follow the sequence of steps and procedures, since even minor deviations from mandatory technologies can lead to devastating consequences
Strip foundation
This type of foundation is one of the most susceptible to destructive effects from swelling soils, as well as high humidity and low temperatures. Therefore, preservation of the strip foundation for the winter is necessary, and in order to protect the foundation for the winter, several types of work should be performed, the main of which are:
- mandatory removal of formwork, since wood attracts moisture and then transfers it to concrete;
- waterproofing of the entire structure, for which different materials can be used: plaster, coating, primer, roofing felt, etc.;
- construction of a drainage system, and it is recommended to do it while working on the foundation (but it can be done immediately before conservation);
- insulation using polystyrene foam, polystyrene or other suitable materials, followed by covering with reinforced film.
In any case, it is necessary that before preserving the strip foundation for the winter, it must gain strength for at least a month at positive air temperatures.
Monolithic slab
This type of foundation, left without load, is most susceptible to deformation, erosion and displacement in winter. Its vulnerability is due to the fact that due to its relatively small thickness, the entire structure is actually located in the zone of soil freezing.
The presence of a sand-gravel cushion and a waterproofing layer protects against soil water and swelling, but in any case it is impossible to leave the slab foundation unpreserved for the winter. It is necessary that before the onset of cold weather, concrete gains strength for at least 30 days at positive air temperatures.
Before leaving the base for the winter, it is necessary to protect not only its surface, but also the surrounding area from moisture. You can use film, waste slag, expanded clay, etc. You must first provide insulation - polystyrene foam, polystyrene, dry sawdust or sand are suitable for this.
Screw pile foundation
This type of base is least susceptible to moisture, low temperatures and swelling frozen soils. Pile structures can be erected both in summer and winter. They are used on weak, crumbling, swampy, etc. soils, as well as in areas with high groundwater levels.
Special preservation of the pile foundation for the winter is not required; the preparation technology may only include tying from rolled metal. You should also first check that the internal space of the installed piles is filled with concrete, and that it is desirable to have a cap on top.
Columnar foundation
Structures of this type are used primarily for the construction of relatively light buildings, for example, frame, wooden, panel houses. The peculiarity of such bases is that they have little contact with open air and soil.
They are practically not subject to destruction due to lifting forces from frozen soils. The only exceptions may be some types of shallow structures: in this case, uneven lifting of individual pillars is possible.
To prevent such damage, it is recommended to create a grillage. This will be the conservation process - but it should be borne in mind that this work must be completed before the onset of cold weather.
When protection is not needed
The most vulnerable types of foundation are strip and monolith. If the piles and pillars are installed, but the grillage is not filled, the base is not in danger.
You can abandon the idea if at least a month has passed since the pouring of the monolithic slab - the concrete has already gained the required strength and will last through the winter.

Base ready for wintering
When the vertical and horizontal type of waterproofing is completely completed, no additional protection is required. There is no need to do anything if the sinuses are back powdered and compacted.
When a clay hydraulic lock is installed along the perimeter of the planned blind area, the need for conservation also disappears.
Reasons for preserving the base:











