Arrangement of communications in strip foundations It is rare to find a house that could exist without communications. They vary in functionality and characteristics, but they must be laid immediately before pouring the foundation. Already at the design stage of any building, pipe entry points for water supply, sewerage, and less often power wiring are initially provided. And this is an excellent option, because in such cases nothing prevents you from making a high-quality pipe entry, installing the necessary sleeves and insulating the entry through the walls of the future strip foundation.
There is also a situation, for example, when an old house was purchased and there is a need to modernize existing communications by laying new ones or strengthening old ones. In such cases, it is more difficult to enter, and in this case sometimes it is necessary to use construction equipment and special tools.
Given the height of the pipe entries, according to building regulations, the only networks that can be laid through the base are gas pipes or power cables. But sewerage, ventilation and water supply must be laid at a depth of 40 cm below the soil freezing line, and strip foundations are practically never found at such a depth. Therefore, for a private house, all communications are provided as low as possible to the zero level, and pipes are laid below the base of the foundation.
Requirements
The rules for installing life support systems (electricity, water supply, sewerage) in cottages built on a slab foundation are regulated by established standards under SP No. 31-110-2003, No. 31.13330 and No. 32.13330. At the same time, practicing engineers recommend paying special attention to the maintainability of communication lines.
According to the current rules in construction, holes in the hardened monolith are not punched for utility networks, but places for laying sleeves are organized at the stage of formwork construction.
The following factors must be taken into account during the process:

To lay the “warm floor” system and water supply lines, pipes with a diameter of 16 to 20 mm are used. For sewerage installations, polyvinyl chloride pipes with a standard diameter of 110 mm are used. If, according to the project, the house has a lot of plumbing fixtures, the sewer line is long, or there is no provision for a pit, then pipes with a diameter of 160 mm are used.- The minimum permissible sleeve size is 5 cm.
- When seasonal temperature changes occur, linear expansions occur in the soil, so when laying engineering systems, special compensators are used.
- Water supply lines are laid below the freezing level, otherwise heating cables are run in parallel or polystyrene shells are used.
- The electrics are placed in sleeves with a bending radius of 0.3 to 0.7 m. This position makes this communications unit repairable in case of damage. The power supply lines are routed to a panel, which is usually located next to the house.
- It is forbidden to introduce a gas pipe into the house through the thickness of the foundation; for this purpose, a hole is made in the outer wall and a sleeve is inserted into it for protection. All places where pipes are connected must be located in such a way that the contact point can be inspected at any time and repaired if necessary.
Under the base area of a monolithic foundation, in the body of which heating pipes (for example, USHP) pass, the soil cannot freeze, which will allow the developer to further save on heating the utility lines.
How to make a hole in the foundation for sewerage
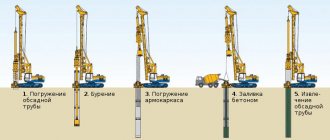
The foundation, especially the slab foundation, is an extremely rigid material. When it is pierced, cracks may occur. Experts are still arguing about what is the best thing to do: make a hole for the sewer pipe when laying the foundation, or leave it for later. We will consider the option when such a hole was not provided in the foundation. How to break through the foundation for a sewer yourself? This can be done using a jackhammer, or drill it using a hammer drill. An excellent alternative is the diamond drilling method.
The tools that will help you make a hole in the foundation are as follows:
- Hammer,
- Punch,
- Diamond drilling rig,
- Hammer drill.
When you break through the foundation, you may encounter obstacles in the form of stones or reinforcement. Stones can be crushed using a punch, and the reinforcement can be drilled with a drill. In the absence of a drill, the concrete is pierced with a punch, periodically hitting it with a hammer. This is a very labor-intensive and time-consuming process. Dust that will accumulate in the hole during operation must be removed by blowing.
An impact drill will help you make a hole in the foundation for the sewer. Drilling is carried out at minimum speed with breaks so that the drill can cool. However, you cannot drill a hole that is too deep with a drill. To do this you will need a drilling rig.
At what stage of construction is the laying carried out?
In the case of the construction of a slab foundation, the installation of utility networks in the building area must be carried out before the preparation of the underlying layer. Most builders are of the opinion that it is easier and more convenient to install engineering lines before the stage of laying the reinforcing frame, when the formwork is already ready.
If you lay water supply and sewer pipes before erecting the formwork, it is easy to miscalculate the outlets and risers, which may end up either inside the wall itself or too far beyond it. Therefore, experts recommend laying communication systems as the slab foundation has already acquired its shape due to the installation of the molding structure.
Installation of internal sewerage
So, before starting the installation of the sewer system, it is necessary to determine where the collection will be located and where the pipe will go outside. Next, a hole is made in the foundation for the pipeline. Pipes located inside the house are installed so that wastewater is directed to the outlet. All pipes are connected to a common riser (pipe with a diameter of 100 mm). The lower edge of the riser goes into the underground. There is a pipeline connected to a pipe that is located in the foundation and has access to the street. The place where the riser and horizontal pipeline connect must be equipped with an inspection well.
Laying principles for slab foundations
When designing a slab foundation at the moment of determining the diagram of engineering systems, designers use the following principles as a basis:

Communication networks are laid before the screed is concreted.- It is not recommended to lay pipes under the slab without a protective sleeve. The sleeves must be slightly larger than the diameter of the pipes and at the same time made of high-strength material in order to prevent mechanical damage when pouring concrete mortar.
- To prevent the risk of sewer pipes freezing, they are laid below the soil freezing level. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the fact that the drains flow in the direction from the house, therefore they initially have a higher temperature than in the water supply lines. This allows builders to reduce the thickness of the shell for insulation.
- If water lines are laid above the freezing point, which is typical for most sites in all Russian regions, then the developer needs to consider measures for their insulation.
Self-puncture is performed using the following technology
- Along the expected puncture line, the pointed end is driven into the working pit with a sledgehammer into steel reinforcement. It serves as a guide for the pipe and warns of difficult obstacles in its path. The length of the reinforcement rod should not exceed two meters, otherwise the material may be deformed under the blows of a sledgehammer. As it enters the ground, the next section is welded and hammered in again. Work continues until the end appears on the other side of the road;
- On both sides of the road under which communications need to be laid, two pits (pits) are dug symmetrically. The depth of the pits should be slightly greater than the depth of the pipe. The pipe will be driven horizontally through the first pit until it appears on the other side. The dimensions of the working and receiving pit are selected taking into account the above and must provide for the possibility of a person being freely in it;
- Using the same technology, a puncture is made with a pipe placed on the fittings. To prevent the ends from breaking, a nozzle with jagged, sharpened edges is installed in front, and a glass-shaped nozzle is installed at the back. Under the blows of a sledgehammer on the bottom of the glass, the pipe begins to go into the ground. As it moves, the earth becomes compacted in the pipe and movement stops. A jet from the water pump removes it quite easily. Further actions are consistent until the nozzle appears in another pit.
There are various variations of this method:
- Using a bailer made from a large hydraulic cylinder;
- Using a mini horizontal drilling unit or various auxiliary means for driving in reinforcement, for example, a drill;
- Puncture at the pump base.
Having scoured the Internet, we found a thousand and one more ways of “author’s” laying communications underground. We have never doubted the unique abilities of folk craftsmen, but we still recommend that you use one of the methods we propose, since these methods are the most reliable and have a technical basis. It's better not to take risks.
Since the issue of self-piercing is mostly of interest to private property owners who want to either modernize their site or connect communications to it, it is worth remembering that even if the land is on your property, you cannot just take it and drill under it. This is especially true for work that is planned to go beyond private territory. We also note that punctures over 10 meters in length are performed using special equipment and using the HDD method.
Where and how can communication networks be established?
Communications with a slab foundation, including sewerage, water supply and cables, can be laid in two ways:
- Through the foundation - into the slab itself through formwork for basement floors with a large depth.
- Directly to the bottom of the pit under the foundation itself, if it is shallow. Here communications are located below the freezing level or are insulated with foamed polyethylene.
According to established rules, cables, pipelines and sewer networks must be routed along separate routes.
Trenches are dug under communications, strengthening the walls with compacted sand or medium-fraction crushed stone. Entry holes for utility lines must be at least 0.2 mm wider than the diameter of the pipes themselves. The tightness of the structure at high groundwater levels is ensured through the use of an oil seal. In dry soils, special elastic materials are used for this purpose.
As a rule, sewer networks lead to the base at a depth of at least 0.7 m from the ground surface to avoid mechanical damage from human traffic or during soil cultivation. To ensure gravity flow, the sleeve is placed at a slope of 4 to 7 degrees.
Cases for the electrical network, as a rule, match the shape of the prepared well. A cable with a metal cable is pulled through the sleeve, to which a rope is tied, so that, if necessary, it is easy to pull a new cable or hose through the case.
If the opportunity to introduce communications at the stages of preparing the slab foundation was missed, it is possible to connect them after the construction of the house by attaching an insulated box to the wall or punching holes in a concrete monolith.
Since a slab foundation can serve as a floor in a house, the pouring process is often combined with the installation of its heating systems. The “active heated floor” system is a spiral, winding plastic or metal pipeline embedded in concrete through which heated water will move.
Thus, the surface of the foundation serves directly as a subfloor and the developer only has to think about the issue of finishing.
The active heated floor pipes are laid out along the laid reinforcement mesh in accordance with the working drawings . Nylon clamps are used for fastening to the reinforcing mesh. After installing all the underfloor heating pipes, it is necessary to install a manifold and connect the pipes to it. The installation of collectors is carried out in a place strictly defined by working drawings.
To properly introduce gas into the house, make a hole in the lower part of one of the outer walls, but not in the thickness of the foundation. Gas pipes are installed using a protective sleeve and seal, and only a single piece of pipe can be located inside the sleeve.
Cost of work
The price per meter of puncture of the soil layer under an obstacle for laying a water pipe depends not so much on the volume of work, the type of soil, but on the length and diameter of the channel being punched. Thus, laying 1 meter of water pipe using horizontal directional drilling will cost the customer on average 1300 -1600 rubles. When installing water supply pipes under roads, buildings and other obstacles using horizontal drilling, hydraulic or vibration puncture, the cost of 1 meter will be slightly lower - from 1000 to 1200 rubles.
Problems and their solutions

Most builders are of the opinion that it is not advisable to lay utility networks into the body of the foundation without access to them during operation.
At a minimum, pipes and cables may become unusable due to natural wear and tear.
At the same time, there is always a risk that problems will arise at a certain time with communications in the form of damage to the seal , disconnected contacts or clogged pipes. Therefore, there is an open question about the maintainability of communications laid in the slab foundation.
It is possible to install a repairable system if you initially place pipes and cables in special cases and take them out into a special pit - an inspection well, equipped in a technical room. If desired, the caisson can be closed with a decorative lid and used only as needed.
The pit is a separate underground room with concrete walls and bottom. As a rule, a structure measuring 0.7x0.7x0.7 m is made. First, a pit is made, and then a foundation slab is erected.
As a rule, the pit should be located outside the perimeter of the blind area . Thus, in the event of an accident in the pipeline, the wastewater will not accumulate under the foundation, but will flow directly into the pit. If desired, the owner can replace or repair communication networks at any time.
Installation of a pit entails a complication of the design of the foundation slab and an increase in construction costs. But as practice shows, the cost of replacing pipes is not commensurate with the risk of building a new foundation or house if, due to a domestic accident with communication systems, the entire power structure loses strength.
Advantages of the method
The popularity and demand for this method of laying water pipes is explained by the following advantages:
- Efficiency of work - compared to digging an open trench, puncturing takes 3-4 times less time.
- Low labor intensity - puncturing does not require significant physical effort and a large number of workers, as is the case with the trench method of laying pipes.
- All-season use - piercing the soil for water supply can be done at any time of the year using various installations.
- Environmentally friendly - this method of laying a pipeline avoids disturbance of the soil structure, damage to tree roots, destruction of natural landscapes, artificial lawns and plantings.
- Low risk of damage to nearby communications (sewerage, communication lines, gas pipelines) - when a puncture occurs, the likelihood of damaging nearby communications is much less than when excavating soil with an excavator or trencher.
- Low cost - even when hiring specialists with special equipment, digging a sewer using the puncture method costs 30-40% less than traditional trenching.
Repair options
If damaged underfloor heating pipes can be replaced by opening the floor covering and the top layer of concrete, then repairing communications under the insulation layer is accompanied by significant labor, time and material costs. In this case, violation of the compacted layer of the sand cushion will certainly lead to a deterioration in the stability of the base, which cannot be compensated for in any way after the emergency situation has been eliminated.
The maintainability of communication systems under a slab foundation, as previously stated, is ensured by placing sleeves under the lines:
- water supply,
- electricity supply,
- sewerage.
As a rule, all cases are discharged into a pit to which the owner of the structure has access. Damaged lines can be pulled out through the sleeves, as well as new and restored networks can be pulled through. You can also get to the pipes by digging from the side of the house.
In the latter case, the bearing capacity of the soil is impaired, so most practicing engineers recommend laying maintainable communication networks in a slab foundation. At the same time, the choice of optimal angles of inclination of trenches for sleeves and the layout of communication lines should be entrusted to professionals.