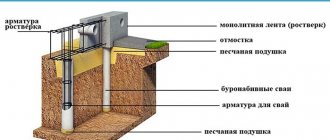
The foundation is the foundation of any building. The quality of the work on its installation determines how safe the structure will be, as well as how long the building will ultimately last. Foundation injection is a procedure that provides reliable protection from moisture and water. It is not so easy to do this, although numerous companies offer services of this kind.
Modern methods of strengthening the foundation
The most effective ways to restore the bearing capacity of foundation structures or strengthen the surrounding soil structure are currently:
- injection of cement-containing hardening solutions (microcementation),
- installation of drilled injection piles.
These innovative techniques are suitable for any type of foundation, including strip, slab or columnar, and can be used during the operation, construction and restoration of the facility.
The choice of the most suitable technology for strengthening the foundation in each individual case is made based on the following factors:
- design features of the object,
- operational mode of the facility,
- type and condition of underlying soil structures.
All these factors are determined during an expert technical inspection of the facility.
Strengthening by injection
Traditional methods for strengthening a strip foundation include deepening, widening, installing new supporting elements, and perimeter concreting. All these methods are complex, expensive, and require significant financial outlays.
If the foundation of the building has been damaged, but is still usable, REINFORCE offers to strengthen the foundation of the old house using injection. The method is also used if it is necessary to build several additional floors or fix “unstable” soil.
REINFORCE works in several stages:
- specialists clear the area;
- drill small radius holes in the concrete base to supply repair mortar;
- under a pressure of 0.4–1.1 MPa, the cement mixture is pumped into the damaged structure.
The solution, which is used to strengthen the foundations of buildings, evenly fills small and large cracks and freely passes into all gaps.
Method of injection with concrete mixtures
The use of injection technology is advisable in cases where:
- minor (local) cracks, voids and pores in the foundation structure,
- a slight increase in the massiveness of the object (relative to its original weight),
- normal wear and tear of the foundation during its service life,
- increasing the “fluidity” of the surrounding soil.
The essence of injection technology is to drill holes (holes) of small diameter in the foundation structure and fill them under high pressure with a cement-containing solution of a special composition using injectors. The distance between the holes is 50÷100cm, and their depth reaches half the thickness of the foundation (these parameters depend on the degree of damage).
As a result, all voids in the foundation are filled with this solution and the adjacent layers of soil are impregnated with it. After the solution has cured, the damaged parts of the foundation again form a solid structure, and the soil around it is monolithic, providing an increase in bearing capacity.
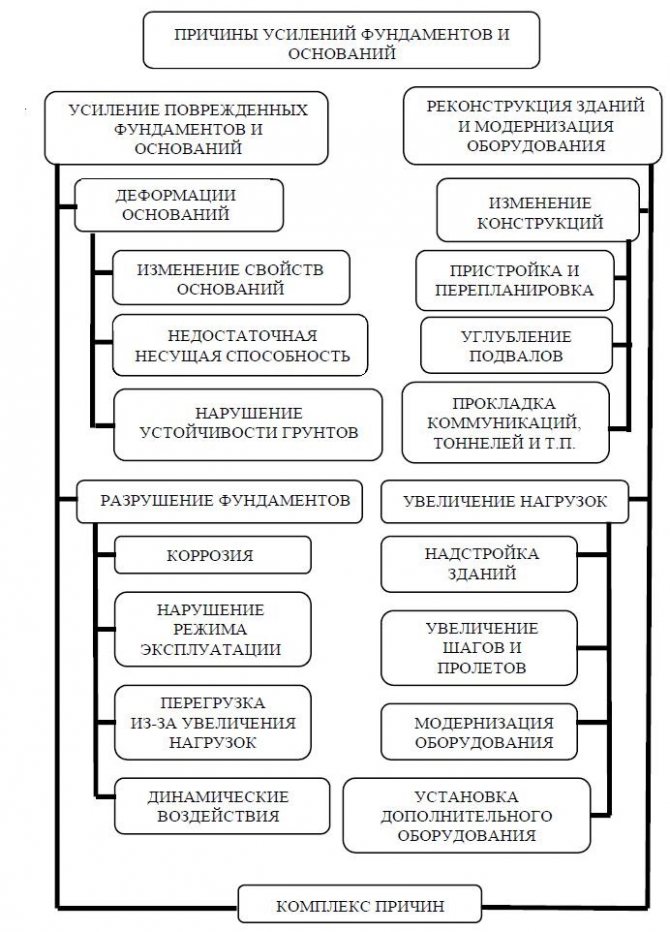
Why are foundations collapsing?
The reasons for the destruction of the foundation are different. It is important to understand why the problem arose in order to take measures to eliminate it. Here are some reasons leading to structural failure:
- Initially incorrect calculation of the foundation without sufficiently complete hydrogeological and geological studies of soils at the design stage.
- Violation of technology when preparing the mixture for forming a tape leads to concrete with reduced strength, frost resistance, and water resistance. This affects the load-bearing capacity of concrete and service life.
- Redevelopment of a house with critical deviations from the project, addition of a floor, attic.
- Changes in soil conditions and groundwater levels during operation. This happens for natural reasons, the movement of layers during seismic vibrations, changes in the condition and moisture of soils when the groundwater level rises during the construction of a loaded object in the immediate vicinity.
- Violation of waterproofing.
When and how it is advisable to use drilled injection piles
Bored injection piles are used in cases of significant violations of the technical and operational characteristics of foundations. Most often this occurs when:
- restoration of objects in disrepair,
- a significant increase in the massiveness of the object (for example, caused by large-scale reconstruction or an increase in the number of floors).
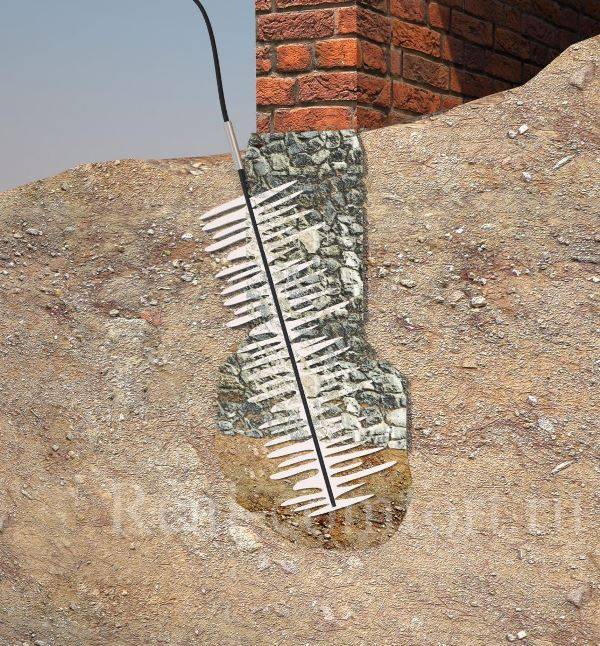

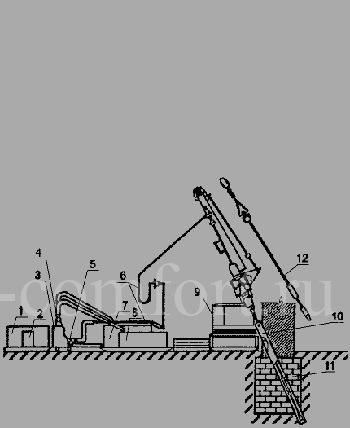
The production of drilled injection piles requires the formation of wells in the foundation. This operation is performed by core drilling machines. Then the internal space of the wells is cleared of contaminants with compressed air and filled with a cement-containing solution. Then a conductor pipe is inserted into the well.
After the solution has completely cured (takes up to 2 days), a new well is drilled in it, longer than the previous one, blown with compressed air and washed with drilling mud. A solid or sectional (welding of centering elements is required) reinforcing frame is placed inside this well and it is filled under high pressure with a concrete mixture.
This technology ensures the preservation of the soil structure and does not require excavation.
How injection is carried out - the main algorithm of actions
Injecting the foundation using technology is a mandatory condition that craftsmen must fulfill. For the most part, it is the quality of the work that influences the final result, rather than the features of the waterproofing material.
Initially, drilling is carried out using a powerful transformer. Strict marking of the building plan is required. After this, the main work is performed - directly pumping the chemical into the porous structure of the building using special equipment. However, this is not all that is required to ensure waterproofing of the structure.
After this, work is carried out to destroy mold fungi and salts that could get on the materials. Using mechanical devices or ordinary brushes, clean the surfaces of paint or plaster, if present. The seams, if they are damaged, are cleaned at least 2 centimeters deep (this is marked with a special meter). Dirt and dust are removed.
Next, the builders drill holes (from 25 to 32 centimeters). In this case, they are superimposed in a checkerboard pattern to each other. A chemical is poured into each hole.
When carrying out independent waterproofing, the question arises - when to start other work? The walls are left alone for 24 hours, or maybe more - depending on the structure and effectiveness of the composition. The following work is allowed to be carried out only after the composition has completely dried on the surface of the building.
Traditional methods of strengthening foundations and their disadvantages
In addition to the new techniques described, there are also traditional methods of strengthening foundation structures, the most common of which are:
- increasing the horizontal sectional area of the foundation (achieved by widening it),
- increasing foundation depth,
- installation of additional supports that redistribute loads,
- construction of a reinforced concrete belt around the perimeter of the foundation.
All of them differ from modern technologies in complexity, labor intensity and significant financial costs for implementation.
Principles of cementation technology
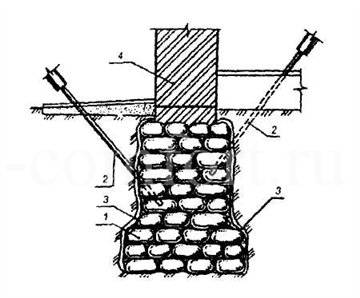
The sand for the solution used to cement the foundation must be fine, medium-fraction or bentonite. This will depend on the composition of the foundation building materials. Cementation (injection) is done in this way: first, a well is brought (drilled) at an angle under the area with destruction (if it is necessary to strengthen the soil), or a well is drilled directly into the foundation, and then concrete is pumped into it under pressure. The difficulty of implementing this method in individual construction is that it is difficult to create high pressure in pipes at home - this requires a special pump. Injection can be simplified by expanding the well and using an inexpensive centrifugal pump. With the correctly calculated number of cement “injections”, the foundation will again become a strong monolithic structure.
Cementation scheme
More information about cementation methods:
- Liquid cement-sand mortar can be injected into an inclined well drilled in the body of the base, which ends at a depth not exceeding the depth of the base by 0.3 meters. That is, it is necessary that the hole does not reach the sole 30 cm,
- The second method is that the well must pass through the foundation, with a depth of 0.5 meters below the base. Thus, all the voids under the sole will be filled with mortar, which will increase the load-bearing capacity of the foundation and increase the total area of the sole.
The cost of strengthening foundations: what it depends on
When calculating the cost of strengthening the foundation of a construction project, one should take into account the extent of damage, the required volume of building materials and the need to use special equipment. For example, injection technology costs on average 4,000 rubles per 1 linear meter of foundation, and to form drilled injection piles it is necessary to spend from 5,000 rubles per linear meter of foundation, since in this case the volume of necessary work increases, and it is necessary to purchase fittings and a conductor pipe. In addition, the speed of injection is higher than the formation of drilled injection piles.
Types of solutions for waterproofing
Depending on whether injection of the base or walls is required, a solution with optimal technical characteristics is selected.
The most common ways to ensure a building is insulated from moisture are by treating it with liquid rubber or liquid glass. Rubber is elastic, light and flexible. You don't need any construction skills to use it. An even layer is created with minimal training. Rubber is environmentally friendly, so there is no need to worry about the health of residents in the building.
Liquid glass, which contains potassium and sodium silicate, provides multifaceted protection. It will protect against the effects of low temperatures, salt rays, changes associated with wind and corrosion. It is also easy to use, but you need to correctly observe the volume of water and composition.
Processing doesn't work forever. Typically the validity period is no more than five years. It is necessary to repeat the procedure, if possible using an identical solution.
Injection waterproofing and its advantages
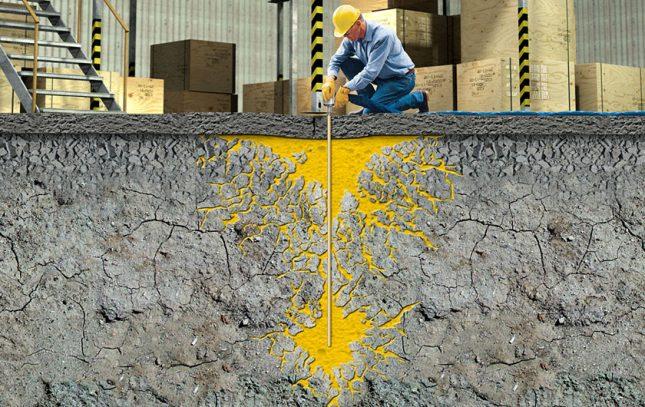

This technologically advanced and affordable method of getting rid of the destructive effects of moisture consists of pumping injection compounds into a layer of concrete under high pressure. These substances form a membrane that clogs all the pores and voids of the foundation. In addition to microcement, injection waterproofing involves such compounds as acrylate and polyurethane polymer gels.
Acrylates or acrylic acid-based gels are similar in density to water. They harden almost instantly, creating a strong adhesion to concrete. The setting time can be changed with special additives.
Polyurethane polymer gels are inexpensive and highly effective. The reaction of the gel with water leads to an increase in the volume of the substance by twenty times. The composition fills any voids, even microcracks, and there is no room left for moisture.
Work using this technology requires special equipment, but is inexpensive. In addition, waterproofing by injection creates a very durable and seamless membrane coating. It can protect even when pressure leaks occur. It is completely harmless to drinking water. The procedure for injection waterproofing foundations is quick and provides protection from moisture for a long time.
Strengthening structures with reinforced concrete frames
Compared to previous technology, this method is simpler and more economical. Its essence is to supplement the existing foundation with a reinforced concrete frame on one or both sides. To do this, soil is removed in the required areas of the existing foundation, then transverse holes are made for laying metal reinforcement. The rods are fixed using a cement-sand mixture or special glue. Then a reinforcing mesh (12-20 mm thick) is welded to the supporting elements. Next, the formwork is installed and the frame is concreted; the mixture is laid to a minimum thickness of 150 mm.