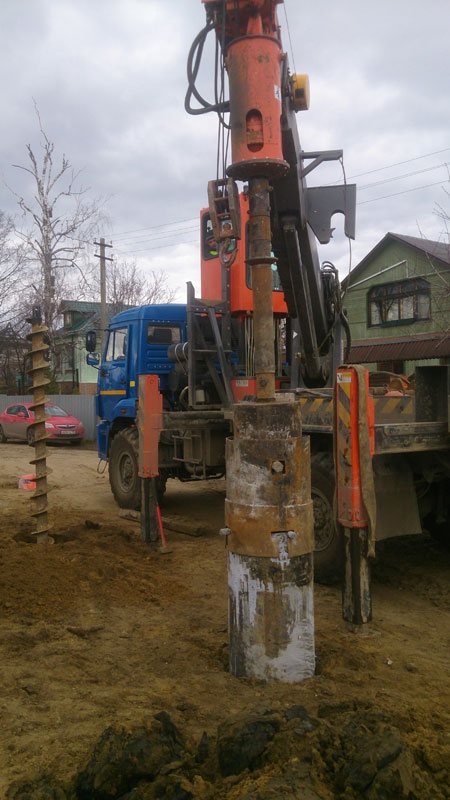
Construction of a secant pile
The main difference between a bored secant pile and a bored pile is a continuous installation with partial overlap and alternate reinforcement.
Fig. 1 : Construction of a secant pile
A secant pile is created by using a casing with a detachable shoe base. Its interior is filled with concrete mixture, after which the casing is removed.
Expert advice! Reinforcement of secant piles with a three-dimensional frame occurs one at a time. The pile is created directly in the well without the use of impact force. In some cases, vibration may be used.
The main advantage of secant piles is the ability to create them directly on the construction site. In appearance, ready-made secant piles look like a monolithic solid wall. Thus, high strength and complete protection from the penetration of groundwater is achieved.
Areas of use:
- Fixing underground structures;
- Strengthening buildings under construction with ground and underground floors;
- Protection of emergency buildings;
- Construction of metro lines;
- Construction of enclosing walls of river canals;
- Base for strip foundation;
- Densely built areas with weak loamy or clayey soil;
- Hydrogeological function, that is, protection of underground buildings from erosion by groundwater;
- Use in hydraulic facilities. Construction of secant pile foundations for dams for various purposes;
- Use in industrial facilities. Fencing of underground chemical, oil refining and metallurgical slag dumps to prevent the leakage of hazardous substances with groundwater.
The standard diameter of bored secant piles is sixty-two and seventy-five centimeters. When installed, the footage between the centers of each pile should reach ninety percent of the main diameter of the pile shaft.
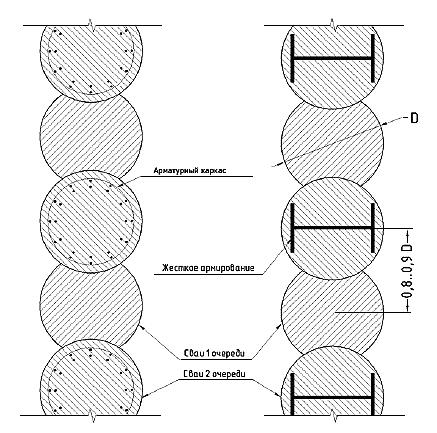
Rice. 2 : Bored secant piles (diagram)
When constructing massive structures, it is necessary to use reinforced concrete piles with a length of ten meters. Smaller pile pillars are intended for light and medium-sized buildings.
Expert advice! The depth of the drilled secant pile must be greater than the groundwater level in order to avoid undermining the structure being constructed from below. Also, before starting construction, it is necessary to conduct a chemical analysis of the water to determine its aggressiveness to the concrete mixture.
Areas of application
In industrial and civil construction, the installation of bored secant piles solves a number of problems related to strengthening the bearing capacity of the foundations of buildings and structures located in areas with dense buildings and in cramped conditions in close proximity to utility lines. They are used not only for fencing pits, but also in other elements with special construction conditions:
- Construction of support bases for strip foundations.
- Walls of underground parking lots and warehouses.
- Strengthening the walls and foundations of objects in disrepair or historical architectural monuments.
- Construction of underground tunnels for railway tracks, highways, subways, pedestrian crossings.
- Construction of filtration dams, dams and other hydraulic structures.
- Strengthening the coastline and crumbling slopes.
The construction of a protective structure “wall in the ground” is used not only in construction. In ecology, BSS supports function as a reliable barrier that protects the soil from the harmful effects of industrial waste from chemical production. This method is used to build the walls of sludge storage tanks at metallurgical plants, settling tanks at oil refineries and other underground structures for storing processed products of large industrial giants.
The same technology is used to protect soils from horizontal displacements, landslides and soil deformation from lateral forces.
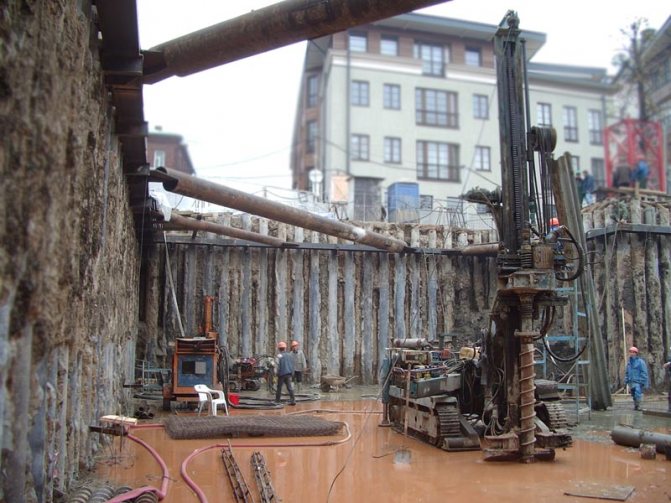

Strengthening pit walls in dense urban areas.
The difference between bored secant piles and bored piles
Bored secant piles are a variant of bored piles. The manufacturing technology is similar, the conditions of use are the same: both are used in areas where ground vibration cannot be allowed.
Bored piles: used for constructing foundations, located at standard distances from one another, all reinforced (see more about bored piles)
Brown secants: perform the function of a monolithic enclosing wall; they are installed in a continuous pattern, partially overlapping each other. Not every pile is equipped with a reinforcing frame, only one at a time.
If necessary, drilling is carried out using casing pipes: their function is to prevent the well from collapsing and deforming the soil.
Stages of work
The test drilling procedure performed by our specialists will save nerves and unnecessary expenses in the future. Soil assessment work includes several successive stages:
- Visit of a surveyor to study the future development site and soil type, as well as determine the construction coordinates with reference to the area.
- Creation of a project taking into account existing plantings, buildings, etc. on the site.
- Test screwing of several piles up to 12 meters deep in order to find a soil layer suitable in terms of density and thickness for effective installation of screw piles.
Based on the data obtained, a graph is drawn up with the coordinates of screwing in the piles. Thus, test drilling is a necessary stage at the very beginning of construction, which allows you to enjoy the comfort, safety and durability of the constructed house in the future.
Bored secant pile technology
In an earthen section, secant piles look like a solid wall. The parameters of their location and depth must be carefully calculated in the project.
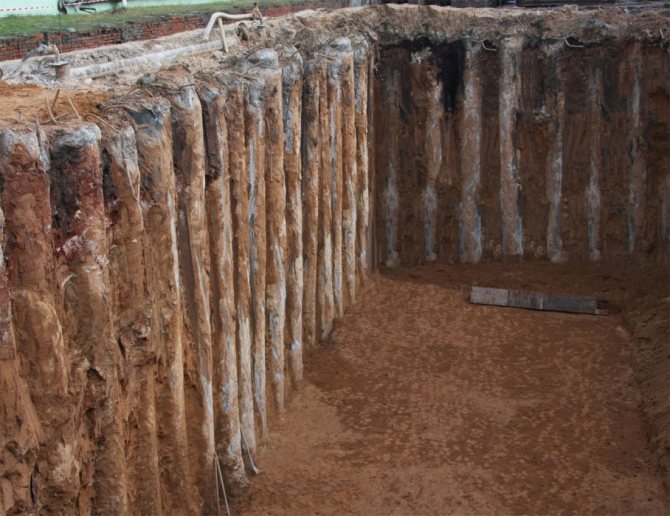

Rice. 3 : Bored secant piles (type of foundation)
The process of creating bored secant piles:
- Intelligence service . Conducting geological research to draw up a map indicating the direction and depth of groundwater. Taking samples of water droplets for chemical analysis to determine the degree of aggressiveness to the concrete mixture.
- Wells . According to the design data, vertical tunnels are drilled at control points using casing pipes. Their depth and total area of location will depend on the design of the building and the level of groundwater passage.
- Well testing . Next, the bottom of the pipe is checked for leaks. If there is no groundwater, workers move on to the next stage.
- Concrete injection . The sealed casing pipe is filled with concrete mortar.
- Extract . Without waiting for the concrete mixture to harden, the pipe is unscrewed from the well. The lower shoe tip, under the pressure of a large mass of concrete, breaks off and remains inside. And the concrete solution fills the entire hollow space of the well.
- Standing . All wells filled with concrete, but not reinforced, must harden well. The result is concrete piles.
- Installation of the frame . Vibrating units are used to immerse the volumetric frame into the filled well. The frame can also be installed in the casing before concrete is poured directly. Drilling to install a reinforced pile is carried out by affecting adjacent piles.
- Rearrangement . Relocation of construction equipment units to the next control point.
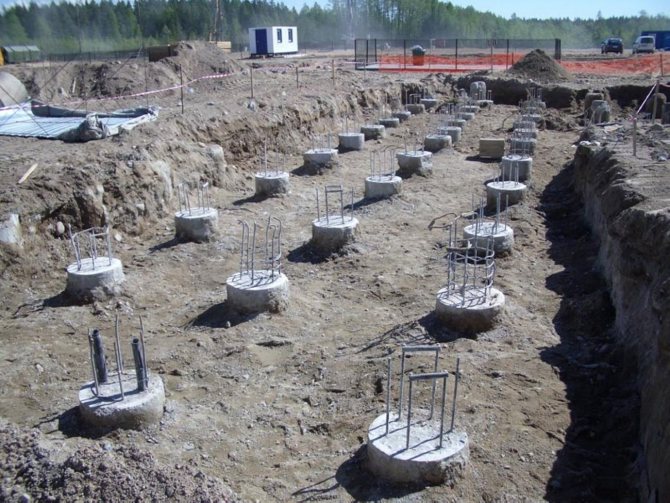
Upon completion of installation work for installing bored secant piles, they are connected along the upper level with a reinforced concrete belt. It gives additional strength and overall completeness to the appearance of the foundation.
Rice. 4 : Scheme of a foundation made of secant piles
When is it necessary to install bored piles in a casing pipe?
Depending on the soil, we use one of three methods for installing bored piles:
- dry. A well is drilled, reinforced, and filled with concrete. The technology is suitable for dense, slightly watered soils, when the walls of the well do not crumble and water does not penetrate inside;
- with clay solution. We flush the well with a thixotropic solution. It settles on the walls, forming a waterproof film. The method is used for fairly dense, moderately water-logged soils;
- with casing pipes. During the drilling process, we immerse a shell pipe into the well. Depending on the project, the pipe is either removed during the process of filling the rod with concrete, or remains in the well (in the case of particularly unstable soils, with strong underwater currents).
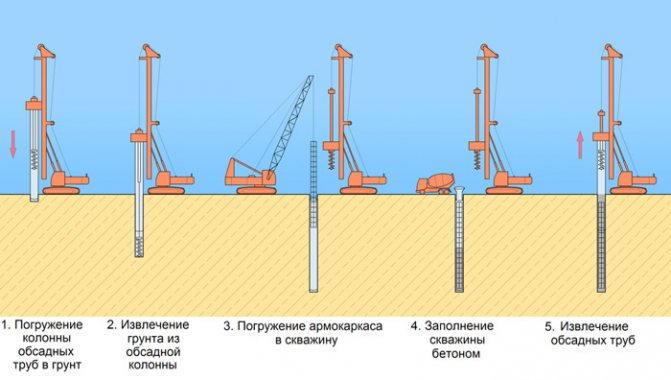
In fact, the casing is a removable or permanent formwork for a concrete core. The method is suitable for loose and water-logged soils. For dense dry ones, its use is usually unprofitable.

Thus, the functions of casing pipes are as follows:
- protection of the wellbore from soil shedding due to poor cohesion and pressure from adjacent soil;
- protecting the well walls from erosion by groundwater;
- protection of walls from destruction by metal elements during the reinforcement process.
Oleg Nikiforov, Khimki, 10.20.2017 14:47
Good day. There will be a house made of aerated concrete in Khimki. 1st floor + attic. Foundation on bored piles + grillage. The soil is solid sand. Is it possible to use your special equipment to drill such piles?
Chief Engineer PSK “Foundations and Foundations” 8,
We install bored piles in any region, including the Moscow region. Our equipment allows you to install piles in any soil. Call us, we'll talk in more detail.
Double Rotary Technology
The Double Rotary method involves the use of two rotational elements, one of which, the upper auger, is hollow inside. The mobile drilling rig drills a well while simultaneously rotating the casing pipe counterclockwise using the lower holder. It follows that the casing pipe rings the well before groundwater enters it. The concrete mixture hardens under the best conditions and the resulting concrete is of high quality. Consequently, secant piles form an absolutely waterproof wall against groundwater.
Expert advice! Using Double Rotary technology, the pile is immersed to a depth of up to twenty-two meters with a diameter of one hundred and two centimeters. The overall inclination of the well walls is practically absent. Also, on soft soils, when concrete is supplied under pressure, the final density of the pile column increases.
Advantages of Double Rotary technology:
- Application on different soils;
- High productivity, consisting of installing twenty-four piles per shift;
- The accuracy of the location of secant piles is checked by an on-board computer;
- Supply of concrete mass under pressure, which guarantees high-quality filling of the tunnel.
SNiP for bored piles in casing pipes
When constructing bored wells with casing, we are guided by the general SNiP standards for pile foundations and earthworks:
- 03.85 – regulates the construction of pile foundations;
- 01.87 – foundations and earthworks;
- 01.84 – structures made of concrete and reinforced concrete.
Steel casing pipes for bored piles - GOST 632-80. Standard casing diameters for bored piles:
- external from 62 to 167 cm;
- internal 54-158.
The weight of a casing pipe section for bored piles 1 meter long is respectively from 440 to 1740 kilograms, for a six-meter one - from 2220 to 8100. The thickness of the pipe wall with a smaller diameter is 40 millimeters, with larger ones - 50.
The turnover of casing pipes when installing bored piles, taking into account losses, depends on the depth of the well:
- up to 100 meters – 10 revolutions;
- up to 200 – 7;
- more than 200 – 5.
Calculation of the bearing capacity of a wall made of secant piles
The bearing capacity depends on the geological features of the work site.
There are two formulas.
- If the ends of the piles rest on rocky soil:
N = (or<) Yc/4YkYg x Rc.n. x A (Id/Df + a)
Yc – coefficient. working conditions of the pile, accepted 1
Yk – coefficient reliability of the foundation (accepted 1.4)
Yg – coefficient reliability of the soil under the pile (1.4)
Rc.n. – ultimate uniaxial compressive strength of soil in a water-saturated state
A – pile support area
Id – depth of embedment in the ground (for less than half a meter it is taken equal to 0)
Df – diameter of the pile embedded in the ground
a – when Id is less than half a meter, 1.5 is accepted, in other cases 0
- If the ends of the piles rest on compressible soil (non-rock):
N = (or<) Yc/Yk x (Ycr RA + U ∑ Ycf FiHi)
Ycr – coefficient soil work for sandy and clayey soils under the pile – 1
R – calculated soil resistance, taken from the table (for example, with an average clay soil of 0.3 and a pile depth of 5 m it will be equal to 650 kPa)
U – perimeter of the pile section
Ycf – coefficient. soil performance on the sides of the pile, depends on the drilling and concreting methods, taken from the table (for clays, regardless of water content - 0.6, for other rocks in dry conditions - 0.7, under water - 0.6)
Fi – calculated soil resistance on the sides of the pile (for clay 0.3 at a 5-meter well depth – 40)
Hi – soil thickness on the sides of the pile
The remaining values are the same as in the formula for rock support.
Necessity of casing pipes
The construction of bored concrete piles using casing pipes, which can then be removed or left as a shell, makes it possible to form a strong support for a building in a crumbling or excessively moistened well.
The steel pipe has a high density so that it can easily enter the ground without deformation, and keep the internal space from falling into the soil.
If a long span is required to obtain the pile body, then the individual elements are manufactured and assembled in sections convenient for transportation, storage and lifting on the drilling rig.
The connection of individual sections is structurally implemented in 3 ways:
- welding;
- thread;
- special fastenings (clamps).
Threaded connections are used where bending deformation is possible - to increase the strength of long connections of pipes of relatively small diameters, as shown in this photo:

Prepared casing
In addition to the threads, each connection is reinforced by a welding machine with overhead stiffeners to prevent unwinding when lowering or removing the casing after pouring the solution.
Fixing clamps are used on inventory products that require repeated use by a construction organization. They fit tightly around the joint and have helical locking bolts running through both links.
The advantages of installing bored piles with casing are as follows:
- maximum use of load-bearing capacity;
- high-quality and fast execution of operations for filling the well space with concreting solution;
- the ability to perform work in mobile and water-saturated soils;
- constant monitoring of work performance in accordance with design requirements and actual geological and technical conditions;
- removal of large stones from the trunk during drilling;
- absence of exposure to vibration and shear (horizontal) vibrations of the soil;
- safety of each stage.
Additionally, this technology eliminates the possibility of so-called “necks” (a narrowed section of the concrete mass) appearing anywhere in the well when installing a reinforcing frame, controls the achievement of bearing rocks, and covers horizons containing dangerous soils (for example, quicksand). And yet, bored supports in casing pipes are allowed for use in almost all climatic zones.
Characteristics of bored piles
To build a foundation from bored piles, which are subsequently connected with a grillage, casing pipes of various lengths, Ø and designs are used. In loose soils, they must be of sufficient length to fix the position of the support for the house being built on them.
The parameters of piles of standardized construction projects are given in the table:
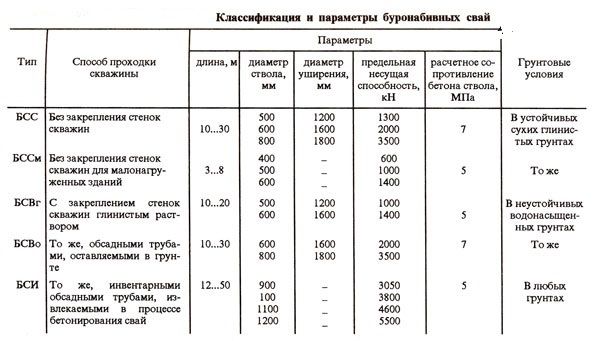
The pitch of the piles (when subsequently tied with a tape grillage) must be at least 3 Ø of the support. In this case, the selected distance can be 5 Ø, if the cross-sectional strength of the grillage allows.
Casing pipes vary in shape, Ø, wall thickness, ovality, non-straightness, corresponding to the following tolerances according to the standard:
- for pipes Ø 33.5 mm – Ø89 mm, deviations are no more than 0.3 mm;
- Ø108 mm – Ø146 mm – up to 0.5 mm;
- pipes of larger cross-section may have an error of more than 0.7 mm.
Casing pipes for forming a bored pile from asbestos cement are usually thick-walled, but this material is the most fragile compared to products of this type from other raw materials. The popularity of asbestos cement is explained by the low cost and prevalence of this product, but for an inexperienced worker, problems may arise when drilling to a sufficiently great depth. In the process of stage-by-stage installation of casing sections, the crucial point is the fastening of the elements and the operation of the drill inside the channel.

This is what finished bored piles look like
A bored pile foundation ready for tying is shown in this photo:
In individual cases, the calculation must be performed by a professional based on engineering and geological surveys of a specific area. Calculation features and requirements that must be observed when designing a foundation using bored piles are given in SNiP 2.02.03-85.
Work technology
The technology used for constructing bored piles consists of several successive stages, which are not very difficult if the equipment is available.
The differences in the design of the resulting supports are as follows:
- After the concrete has been poured, the steel pipe casing is removed from the well.
- The casing remains in the ground and serves as a housing for the cement slurry. The only drawback of this technology is the lack of control over the possible seepage of groundwater into the cavity and, as a result, an increased risk of erosion of part of the concrete that has not gained strength. To protect against such effects of subsoil water, special additives - stabilizers are added to the cement mixture.
- The pile is made with or without widening at the bottom (heel). The shaft is expanded with a special drill (Kelly rod) or the casing is raised by 0.5 m during the initial supply of concrete, which is poured wider than the internal Ø of the casing.
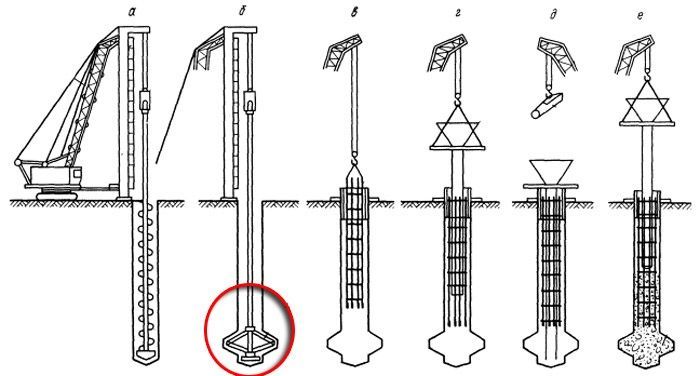
Bored piles with wider support have a greater load-bearing capacity compared to cylindrical structures and high stability in soft soils. But, if it is still not possible to support the base of the pillar - the pile will be hanging (distributing the load by friction of the side surface), then it is better to make even columns of maximum length, therefore, in a particular situation, they first calculate that it is better to use short piles with a widened base or long cylindrical pillars.
Various methods are used to immerse a casing column into drilled soil:
- impact, in which, simultaneously with drilling, pressure is applied to the outer part with hydraulic jacks, sequentially driving the growing sections into the well;
- rotational (the first section is inserted into the finished cavity, and then drilling continues through it and the section is immersed simultaneously with the extraction of soil).
The choice of the impact method depends on the permeability qualities of the site’s soils, and instead of jacks, vibrators can be used to immerse and remove casing for piles.
Equipment is installed at the site marked for drilling. A well is drilled to a given depth and section. The pile casing pipe is immersed at the desired level (it is indicated in the project). Then perform the following operations:
- remove soil from the pipe;
- a reinforcing frame is lowered into the cleaned lumen;
- supply concrete through a hose or trays in sufficient quantities (filling);
- sections of casing are sequentially removed from the filled well.
The sequence of operations when drilling with a 530 mm casing pipe to a depth of 7 m near the foundation of a residential building is shown in this video:
Preparation
The installation process of each element is carried out quickly and continuously. The following materials, tools and equipment are prepared directly at the construction site before the start of work:
- concrete mixer;
- dosing hopper;
- vibrator for driving and pulling out piles;
- composite vibration core;
- expander for the heel of the pile;
- frame welded from reinforcing bars;
- casing;
- clay solution;
- boards for making gutters;
- a set of quick release clamps;
- bottom valve;
- head conductor.
The use of automated equipment significantly speeds up all stages of construction and saves labor resources.

Non-removable drilled screw pipes
If, according to the design, the piled pipe cannot be removed, then it can be made in a special version that makes it easier to screw in and makes it difficult for groundwater to penetrate the cement mortar, shown in this photo.
In the event that the casing pipes are not removed after completion of the work, a mandatory note about this is put in the construction technical documentation for the building.
Reinforcement
After the casing pipes are completely lowered to the calculated depth, a reinforcing frame is installed in them. If the concrete element is of a significant length, it is not laid along the full length of the pile, but only in its upper part. At the same time, the thickness of the protective layer of concrete on all sides is maintained to be less than 7 cm (distance to the inner surface of the casing elements). The frame consists of at least 6 longitudinal rods Ø 18 mm class A3. The structure must be additionally reinforced with metal rings, the thickness of which should be up to 9 mm, width - from 6 to 9 cm.
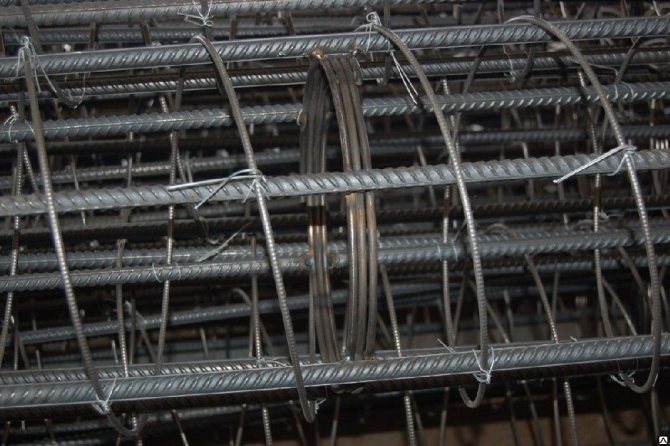

Symmetrical frame Ø smaller than pipe
The frames prepared for installation look like in this photo.
The upper part of the frame is left above the concrete level to ensure connection with the grillage of the base of the house.
The grillage can be installed after the poured concrete has reached the specified strength (about 80%). This will require at least 25 - 30 days. The grillage connection of free-standing supports serves to evenly distribute the load on the foundation.
Advantages of secant technology
The production of secant piles has more advantages in comparison with other types and technologies for creating pile supports.
- Accuracy . The technology of bored secant piles allows installation in dense urban environments using a minimum of construction requirements.
- Silence . The work carried out does not create noise or vibration background.
- Safety . There is no need to worry about violating the integrity of nearby foundation supports.
- Compactness . Production of bored secant piles directly on the construction site.
- No overspending . Minimum excess of the specified amount of concrete mixture.
- Economical . There are no costs for disposal of construction waste.
- Any soil . Application on various types of soil, ranging from loose sandy soils.
Advantages of bored secant piles and limitations in the device
The main advantage of secant piles over other pile foundations and sheet piling is the combination of practically unlimited load-bearing capacity with perfect construction safety. Drilling secant piles does not require piling equipment - impact, vibration, the operation of which leads to soil movement and, as a consequence, to a risk for nearby structures.
The only completely safe technology for creating other pile foundations is screwing. But screw foundations are not designed for very heavy buildings - multi-story city buildings, industrial facilities.
When constructing fencing, the main competing technology is sheet piling walls.

The only gentle method of driving sheet piles is pressing, but this is only effective on soft ground. When diving using the vibration method, we use leader drilling to reduce dangerous vibrations. But it does not eliminate dynamic loads completely (the well is not drilled to full depth), although it reduces it to a minimum.
It is important!
The advantage of secant piles over strip, columnar and slab foundations is the same as that of other piles: this is invariably the optimal option in terms of stability for any soil. In addition, the amount of reinforced concrete required for piles is much less than for monolithic foundations, and there is obviously less excavation work.
According to the same criterion, a pile wall is more profitable than the main competing technology for strengthening banks and slopes - concreting.
The disadvantages of secant piles include:
- a large amount of concrete;
- long installation times, since you need to wait for the concrete to mature;
- it is possible that there are chemically active components in the soil that exclude/complicate the installation of concrete structures.
These disadvantages are characteristic of any concrete structures. The alternative is only ready-made piles or sheet pilings, the disadvantages and limitations of which we have already discussed.
Since we have been building any foundations and fences for more than 10 years, in each specific case we approach the selection of the optimal design taking into account all the features of the object:
- soil characteristics;
- dimensions and purpose of the future structure;
- building density around the site.
- financial factor.
We will choose the most profitable option for you together with you.











