The lifespan of a building is directly related to the start of its construction. Properly installed ventilation in the foundation of a house will prevent the destruction of floor and wall materials. The durability of residential and non-residential premises and the health of the people in them depend on this stage of work.
You will learn everything about the rules and regulations for constructing a ventilation system to protect the foundation of a house from the article we presented. We will tell you about the reasons why moisture removal from the foundation is mandatory. We will introduce you to proven methods, calculation schemes and installation stages.
Options for ventilation systems and schemes
The construction of a ventilation system is regulated by domestic SNiPs (Building Norms and Rules) and international construction standards.
Reasons for regular ventilation
Some consequences of a missing or improper foundation ventilation system:
- The appearance of condensation, a gradual increase to 100% humidity;
- Rotting of wooden beams, ceilings, rough materials of the floor structure;
- The accumulation of natural radon gas released from the soil, the inhalation of which leads to oncology;
- Reproduction of mold, fungi, and other microorganisms that cause allergic diseases and bronchial asthma.
To maintain the humidity regime, it is necessary to evaporate the accumulated moisture and remove it from under the floor of the house to the street. Neglecting building regulations can cause irreparable harm to the health of the residents of the house.
Organization of natural ventilation
The choice of ventilation option is determined by economic feasibility.
There are two main ways to arrange natural ventilation:
First method. Installation of special holes in the foundation, called vents or vents.
Openings located in opposite walls cause a draft, which removes moisture from the space limited by the foundation
Second method. Installation of supply and exhaust air ducts. They take moisture and harmful gases from the basement and discharge them outside through exhaust ventilation risers.

It is possible to install one exhaust pipe for small basements. Holes for fresh air circulation can be made in the floor.
The first method is cheaper to construct, but will require additional costs for heating the house during operation. The second method is effective only with an integrated approach to energy saving.
It requires large expenses for insulating the foundation, creating a waterproofing barrier, constructing a blind area, air ducts or pipes. Investments will not pay off without insulation work and high-quality insulation of the entire house from the inside.
Forced system device
Natural ventilation depends on the temperature and density of the air mass outdoors and indoors. It does not work when the air temperature outside and in the basement are equal. When humidity is high and the efficiency of the natural air exchange system is low, it is supplemented with electrical appliances and fans.
Forced ventilation is usually used:
- in basements with an area of 40 m2 or more or with isolated compartments;
- in the architectural design of a house without ventilation ducts and pipes above the roof;
- in rooms equipped with sources of odors and humidity in the basement - workshop, garage, sauna.
The power of supply and exhaust ventilation devices is calculated based on the volume of the basement.
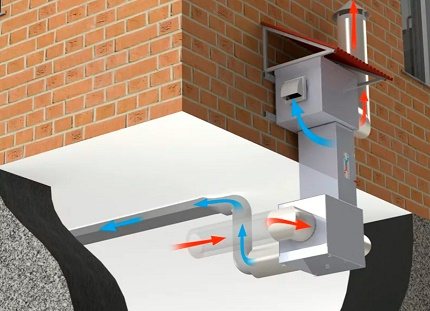
Supply fans intensively pump in fresh air from the street, and exhaust fans remove exhaust air outside. Typically, the supply and exhaust system is used either for exhaust or for supply
In mechanical ventilation systems, either a supply fan or an exhaust fan are activated. If the mechanism operates on the inflow, then the air it pumps spontaneously displaces the exhaust air mass from the basement. If the hood is in operation, then air is drawn into the rarefied space by itself, naturally.
When is it possible without ventilation?
There is no need to install vents or air ducts in any foundation without a subfloor. No basement - no problem.
But not always, but only when at least one of the following two conditions is met:
- A concrete slab is installed on the grillage of a columnar foundation, and the space inside is completely filled from the ground to the floor with a material that filters water well - sand, expanded clay, granulated foam glass. Excess moisture in them evaporates simply and quickly.
- A drainage system has been installed to remove water from the foundation. Excess water is collected by drains - perforated drainage pipes, and discharged into a collector well or waste pit outside the site.
- A durable waterproofing is installed, wrapping all base elements with a water-impervious layer of adhesive or welded material, as well as a complex of materials.
You can omit ventilation vents when using a crawl space or basement for storage. You just need an open passage to the living area of the house and ventilation windows with bars or opening transoms.

It is permissible not to install ventilation vents if ventilation will be carried out through windows and doorways in an equipped, operational basement or basement
It is up to the homeowner to decide whether special vents or ducts are needed in the foundation of a home with an exposed subfloor. Refusal of products in the above cases is permitted by IRS-2006R408.3. In other foundation structures, a ventilation system is required.
Do I need to close the holes for the winter?
Many sources recommend closing the vents in the basement during cold weather to preserve heat in the house. Experts argue that such a decision is wrong and can harm the structure of the house and the health of its residents.
Covering the holes is not allowed under any temperature conditions. In such cases, the wood begins to deteriorate, and fungus and mold appear in its tissues.
If the floor becomes cold when the vents are open, the fault is not the ventilation, but a consequence of poorly executed thermal insulation of the subfloor. In the case when absolutely all technological operations are followed, the floor remains warm with open vents, even in quite severe cold.
Since highly radioactive radon systematically evaporates from the soil, albeit in small volumes , if access to air is blocked, in just a couple of months a concentration can accumulate that will be harmful to the health of others.
Specifics of ventilation with vents
Holes in the foundation to circulate fresh air provide simple and inexpensive ventilation. Vents remove condensation well, keeping the basement dry.
Parameter calculation steps
For effective ventilation, the number of openings and dimensions are carefully determined. Regulates the location, size, number of vents SNiP 01/31/2003.
During construction the following requirements must be met:
- The diameter of the circular section must be at least 25 cm.
- The minimum area of one hole without reinforcement is 0.05-0.85 m2;
- The sum of the cross-sectional area of all vents must be more than 1/400 of the base of the house;
- With increased radon content in the soil, the total area of the openings is increased to 1/100 of the basement area.
Most owners of private houses prefer to install ventilation holes with a minimum permissible cross-sectional diameter, increasing the number of vents if necessary.

The geometric shape of the vents can be any. The most commonly used are round, square, rectangular sections
Naturally, if the foundation or basement level is laid with brick or foam concrete blocks, then the square configuration of the ventilation vents is a priority.
But when pouring a foundation concrete “ribbon”, preference is given to a round section. It is also obtained when drilling structures for ventilation after construction.
Vent location options
The design of exhaust and supply openings has the following features:
- It is recommended to make the first blows from each corner no further than 0.9 m;
- The distance between the holes is set to no more than 3 m;
- The distance from ground level is from 3/4 to 2/3 of the height of the foundation;
- There must be at least 30 cm from the opening to the bottom of the base plane;
- Place the vents symmetrically on opposite sides;
- If the foundation is low, you will have to dig pits under the vents.
Openings are also made in basement partitions.
Hole installation process
The sinuses are filled while the foundation “ribbon” is being poured with concrete. Typically plastic pipes are used for installation. They need to be filled with sand to prevent deformation and breakage, which is removed after the concrete has dried.

PHOTO 5 If for some reason the builders did not make vents during the construction of the foundation, they need to form ventilation holes in the finished structure.
Step-by-step instructions for performing the work:
- Draw the future foundation by placing on paper the calculated number of vents indicating the dimensions;
- Prepare cut pieces of pipes with sand equal to the width of the foundation “ribbon”, compact the ends tightly with a rag;
- Place pieces of pipes, sleeves, in the formwork for pouring concrete, attaching each end of the future vent tightly to the walls of the formwork;
- Fill the formwork with the pipes with concrete, after hardening, clean the pipes and install protective grilles.
Do not limit the holes with wooden blocks when pouring the foundation. Their dismantling will require additional effort, loss of time, and damage the concrete walls.

During the construction of a foundation or plinth made of bricks with rectangular cross-section holes for ventilation, the roof is reinforced. The upper part of the masonry is strengthened using a reinforcement cage. Metal rods are laid above the hole in a horizontal plane
Square holes in brickwork are obtained by laying elements staggered and using cut bricks.
Methods for protecting openings
All through vents should be closed with special plugs or valves that allow air to pass through. They protect the base from the penetration of birds, cats, rats, mice and other small animals.
Different types are used based on personal preference:
- Plastic products have a modern aesthetic design, a variety of shapes, including in the form of bends at right angles. They are often installed on small openings.
- Strong, reliable fastenings ensure durability of metal doors. Grids made of reinforcement, stainless steel mesh welded to the corners, are usually used on wide openings.
- For individual orders, beautiful and strong gratings can be made in workshops. They will become not only protective elements, but also decorative decorations of the facade.
Blinds and grilles made of polymers are used mainly in the arrangement of ventilation openings of small cross-section.

Devices that regulate the width of the opening, called dampers, will help regulate air exchange. Install them on indoor air ducts
If the ventilation hole in the foundation or plinth is blocked by a stationary grille, you can partially or completely open/close the opening using a damper mounted in the air duct.
Air ducts for the exhaust device
This form of supply and exhaust ventilation is suitable for all types of foundations. The floor on a monolithic, columnar, pile foundation will be as dry and warm as possible.
Preparing for system construction
For the installation of exhaust ducts, pipes or ducts are usually used. They can be plastic, metal, brick, wood. Each type of material has its pros and cons.
Selection of material for assembly
Main design differences:
- Metal ones have a long service life, get dirty slowly, but are expensive and difficult to install;
- PVC pipes are easy to assemble, thanks to the presence of a variety of fasteners, and are affordable;
- Wooden boxes are the most inexpensive option, they are environmentally friendly, but less durable.
What material to choose and how to make reliable ventilation in the foundation is decided by each owner based on his financial capabilities. In large cottages, exhaust pipes are often made of brick. They are connected to a common air duct system and provide good ventilation throughout the house.
Rules for calculating sizes
Precise parameters of the ventilation system guarantee the required air circulation.
- The length of the exhaust pipes is equal to the height of the house plus 1.5 m;
- The cross-section of the air duct must be at least 26 cm2 per meter of basement area;
- The total cross-sectional area of the exhaust pipes should be 15% larger than that of the supply pipes.
After all measurements and calculations have been completed, preparations for installation can begin. Check the serviceability of tools and devices, stock up on materials.
Stages of channel installation
Before starting all work, you should draw up a diagram of the location of the elements of the ventilation system.
Installation of air ducts is carried out in the following sequence:
- The supply channel is mounted through a hole in the base or in another place, its lower end is located at a distance of 0.5 m from the floor.
- The pipe joints in the foundation openings are hermetically sealed;
- Exhaust structures are mounted under the ceiling, connected into a common channel with the outer part of the pipe;
Adjustable dampers on the exhaust and supply air ducts will help prevent the basement from freezing in winter.
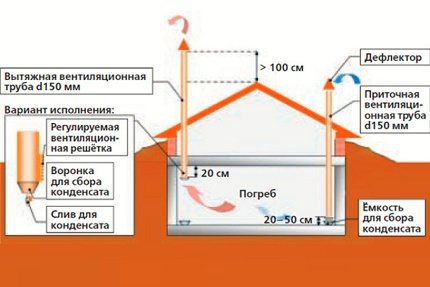
Above the roof, the exhaust riser is mounted vertically, protected from moisture on top by a deflector - a metal or plastic “umbrella”, the diameter of which is slightly larger than the diameter of the pipe
The height of ventilation risers rising above the roof is usually assumed to be equal to the height of the chimney pipes. In order to ensure stable draft in the hood, the top of the pipe should be 0.5 - 1.0 m higher than the ridge.
Determining the location for construction
A house built in a well-ventilated area may have a ventilation system with a minimum number of vents. It is enough to make only two openings in the foundation. For a building located in a low area, the number of vents is increased to the maximum.
The location of the holes should be planned taking into account the wind rose. For example, if calculations showed the need to equip 6 vents, then 2 of them should be located on the leeward side, 2 on the opposite windward side and 1 on the remaining sides of the foundation.

If the basement space is completely immersed in the ground, then it must be equipped with a mechanical ventilation system. In this case, it is constructively connected to the general network that provides air exchange at home
Supply and exhaust ventilation, which provides fresh air to the rooms being used in the basement, is usually connected to the general ventilation network. This way, one recuperator can process the entire building. In addition, exhaust ventilation risers can be located in one shaft.
Weighted assessment of the issue
Natural air exchange using vents in the foundation can be made from scrap materials and construction waste. All other options will require costs.
Will affect the cost of ventilation:
- The area of the basement and the height of the entire building when installing air ducts;
- Availability of equipment for forced ventilation. All simple fans and switches can be purchased for 3-5 thousand rubles;
- Additional devices. The cost of complex recuperators, split systems, hygrometers, sensors with turnkey installation starts from 20 thousand rubles, often exceeding the amount of 100 thousand.
For the well-being of residents and the strength of the house, it is worth choosing an effective foundation ventilation scheme. It can be completely free or very expensive, the main thing is that the air in the basement is renewed and the walls are dry.
The constructed ventilation system requires periodic measures to effectively maintain the microclimate in the basement.
How to make vents in a finished foundation
If only the foundation is laid, a basement wall with holes is installed on it - for example. In the case when the walls have already been erected (or not yet, but it is impossible to extend the tape for some reason), the vents are cut out in the existing base. To do this efficiently and not damage the base, it is better to invite professionals.

To keep the underground dry, foundation ventilation is necessary. It can be done in two ways - using ventilation holes in the base of the building (vents or vents) or by placing an exhaust pipe on the roof and making several holes for air flow from different sides of the foundation.
Subtleties of proper operation
It should be remembered that the movement of dry air eliminates condensation. High-quality ventilation is possible with proper operation of the ventilation system.
It is necessary to constantly monitor the weather conditions and carry out simple measures:
- Close the air dampers during long rains and melting snow in the spring.
- Regularly treat the inner surface of the foundation with lime or special antifungal impregnations;
- To combat excess moisture, you can use boxes with sawdust, sand, and salt, periodically replacing the filler with dry ones.
The basement should be ventilated in the dry summer heat, and in winter leave small gaps in closed sinuses for draft.

In winter, it is imperative to clear the snow from the walls around the entire perimeter of the house so that when the spring melts, water does not flood the foundation.
Even if the foundation of the house is protected by an effective wall drainage system, regular snow removal is required. During frosty periods and heavy rainfall, ventilation vents should not be covered with snowdrifts.
Signs of poor ventilation
Ventilation does not always ensure a high level of preservation of a comfortable microclimate inside the foundation. Sometimes in winter, cold air causes condensation to form when it comes into contact with a heated floor, causing frost to form on the walls.
The causes of dangerous processes can be:
- Incorrectly calculated number of vents and foundation air ducts;
- Close location of underground groundwater, swampy area;
- A large amount of moisture comes in during the rainy season and snow melts.
An imbalance in the relationship between temperature and humidity indicates insufficient ventilation. To establish equilibrium, additional measures are required to drain the basement and adjust the ventilation system.

The result of poor ventilation is black mold on the foundation and walls. If the structure is not dried, the entire house will be destroyed.
It is not for nothing that the foundation is called the foundation of a house. Its destruction due to fungus will inevitably lead to the unsuitability of the building. Walls damaged by mold can still be saved by partially replacing building materials; these methods are not applicable to the foundation.
Are vents needed in a strip foundation?
Recessed and shallow belts, with a low concrete grillage, do not have a ventilated space between the structure and the ground.
Waterproofing in these cases does not protect one hundred percent from moisture: there is still groundwater, from which the underground space is not protected.
What are the dangers of high humidity?
- even if the waterproofing is carried out according to the rules (there is a layer between the facade and the base), water vapor penetrates the house through the floor;
- supporting structures and finishing materials are destroyed;
- mold and mildew develop;
- There is stale air in the basement.

Saturation of concrete with moisture leads to its destruction. There is stale air in the basement. Mold and mildew develop
The vents save the building from an accident: the lower crowns, which bear the main load, rot from the water.
In what cases is a foundation without vents acceptable?
- if it is a foundation with a raised grillage without backfill (etc.);

House on TISE foundation. The original TISE technology assumes that the space under the house will remain open and ventilated. If the turf is only slightly damaged during the laying process, a lawn will quickly grow under the house.
- if artificial ventilation is installed in the operated basement;

- in some cases, experts assume the absence of vents if the basement is filled with moisture-absorbing material (expanded clay, sand) or if there is a high-quality sealed vapor barrier of the soil.

In cases where the base (the foundation itself or the grillage) is located in the ground or is in contact with it, it is recommended to vent the foundation at the stage of pouring it. After building a house, it is problematic to establish high-quality ventilation of the foundation.
Ways to correct the situation
If increased humidity appears under the floor and fungus begins to multiply, this means that the ventilation is not coping with its task. The problem has several solutions.
Option 1. Refinement and modernization of the design
It is necessary to inspect, make calculations and plan measures to optimize the existing system or install a new one.
To increase basement ventilation you can:
- Increase the diameter of existing vents and drill new ones. It is better to use the services of a construction company that has equipment for diamond drilling.
- Install additional air ducts from the basement to the roof of the house. Increased draft will ensure effective reduction of humidity.
- Install a forced ventilation device with an automatic timer. It is convenient to set up a differentiated thermometer that turns on the fan at the moment when the temperature in the basement begins to exceed the outside temperature.
The appearance of condensation in small quantities can be removed using a regular household fan. Or periodically connect a heat source, for example, a heater.
Option #2. Reduce moisture penetration
The cause of high humidity is usually a high groundwater level. If the ventilation is done as competently as possible, then it is necessary to make or strengthen waterproofing protection. Suitable materials are polyethylene film with a thickness of 150 microns, roofing felt or its new versions - rolled weld-on materials.

Foundation waterproofing is carried out using bitumen-containing materials. Pasted or surface-surfaced roll options such as TechnoNIKOL brand products, bitumen and bitumen-polymer mastics
The process of laying polyethylene on the foundation of a small dacha or utility block:
- Place it on the foundation walls at a distance of at least 30 cm from the ground surface, secure it with planks;
- Lay the film so that one sheet overlaps the other by 15-20 cm;
- Carefully seal the joints with double-sided tape on each side of the canvas;
Spread sand in a layer of at least 3 cm or make a small screed to protect the film.
A good effect will be obtained with an insulated base with a blind area and the presence of a ventilation pipe. If there is no insulation, then condensation will collect on the film. In this case, you can make a slope in one direction so that the accumulated moisture flows beyond the foundation.
Option #2. Exchange or purchase of new home
In multi-storey buildings, residents of the first floors sometimes experience unpleasant situations related to the operation of the basement ventilation system. Management companies must solve such problems. But they are sometimes in no hurry to do this, even in the presence of litigation.

The specific culprit of the accident is determined by the cause of the flood. This could be due to improper construction, breakdown of communications, seasonal rise in groundwater levels, floods, etc.
Desperate people are even trying to exchange such apartments or live longer in the country. Sometimes they start building a private residential building on their own and fall into the same trap. Therefore, it is very important at the initial stage of laying the foundation to think through and correctly implement the ventilation system.
When building a private house, basement ventilation can be arranged either with your own hands or with the involvement of professional builders.
Calculation
Schematic display of location and size. The optimal number of ventilation windows should be one per 2-3 meters. It is worth considering where the wooden house is located; if it is located on a hill, then two vents will be enough, for a house in the lowlands from four. It is advisable for homeowners who are building a house to know the local wind rose diagram (a diagram of the wind regime in a certain place based on long-term observations) so that the ratio of air flows on each side is not a problem. Let's look at an example of how to make the calculation.
Let's say the dimensions of the foundation are 5 by 6 meters. The planned dimensions of the vents, which have a rectangular cross-section of 20 by 25 cm. It is necessary to calculate the minimum permissible number of windows and correctly position them along the walls.
The required area of the vents is determined by the formula:
S = F/400 = 30/400 = 0.075 m2,
where: F – basement area.
The required number of vents is determined as follows:
N = S/P = 0.075/0.05 = 1.5 ≈ 2 pcs.
where: P = 0.2x0.25 = 0.5 – area of one vent.
It turns out that you need 4 holes to avoid unventilated “bags”. They can be placed on the short or long side of the house. But the best ventilation will be if the vents are located on the short sides. The height above the ground is not lower than 30 cm from the ground.