What is a footing and why is it needed?
The concrete footing performs several useful functions at once:
- Creates waterproofing of the foundation, increases its durability. Protects against groundwater and prevents moisture from passing further. Liquid cement mortar will not leak through this layer of concrete, and the base will not crack when drying due to the uniform distribution of moisture over the surface.
- Reduces the cost of cement-sand mortar. For the footing, an inexpensive concrete mixture is used - BZ.5-B7.5, which reduces the overall cost of the project.
- Provides a flat surface for the rough concrete base. On a straight site it is easier to make markings, set up reinforcement, attach beacons, prefabricated formwork, thanks to this the quality and speed of work increases.
- Eliminates shrinkage of the building.
- Increases the strength of the structure - foundation + reinforced concrete.
Regulatory documents - SNiP and Code of Rules
Forming a pillow is a responsible process, therefore the technology, materials, preparatory work and layer thickness are regulated by SNiP and the Code of Rules. The construction of structures in civil or industrial construction is subject to state and industry standards. Concrete preparation is carried out on the basis of the norms and provisions in the following documents:
- SNiP 52-01 of 2003 on reinforced concrete and concrete structures.
- SP 50-101, approved in 2004, on design requirements for the construction of foundations and footings.
- SP 52-101 (2003) on non-reinforced structures.
- SNiP 2.02.01 of 1983 on the foundations of construction projects.
- SP 63.13330.2012 - combined requirements for construction projects.
The standards establish the procedure for carrying out design and construction work.
The standards take into account factors such as:
- type of soil on the site;
- number of storeys, material, specifics of the building;
- environmental friendliness;
- ongoing efforts;
- level of seismic activity in the region.
Crushed stone pillow
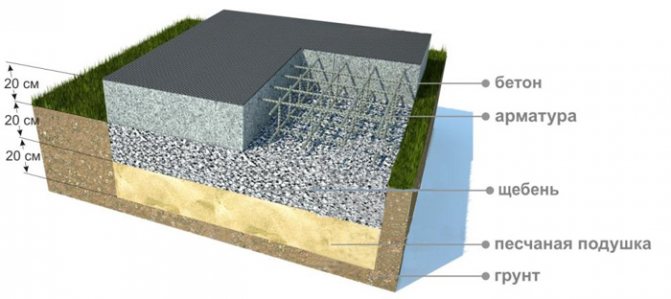
The construction project must necessarily contain data on the method of concrete preparation, the materials used for this and the thickness of the layers. On stable soils and groundwater below the freezing point, the thickness of the crushed stone layer is usually 200 mm. In this case, crushed stone is poured into the bottom of the trench when installing a strip foundation or over the entire building area when installing slab structures and is well compacted. The quality of compaction of the layer ensures the stability of the foundation structure and the absence of subsidence in the future.
At the same time, it is important to choose the right crushed stone; its strength should not be lower than M1200.
After excavating the soil to the required depth, the bottom of the trench or pit is compacted and covered with a membrane fabric such as geotextile. This prevents the germination of weeds and reduces the likelihood of moisture penetration into building structures. When constructing slab-type foundations, a layer of crushed stone is covered with rolled waterproofing, on top of which heat-insulating slabs are laid.

Compacting gravel with a vibrating machine
Crushed stone preparation for the foundation is not only a good support cushion, but also an effective drainage layer that drains water coming from the surface into the ground. The presence of a profile geotextile membrane allows the movement of moisture in only one direction.
What are the types of foundation preparation?
There are 3 types of base:
- sand and crushed stone;
- concrete;
- membrane
Sand and crushed stone

The cheapest, but least durable option. Suitable for wooden houses. Sand will protect the building from the harmful effects of moisture, since thanks to its layer the foundation is at the same level as groundwater. Therefore, such footings are chosen for areas with difficult soil. A cushion of sand, crushed stone or gravel is made 20-60 cm thick. Geotextiles will have to be spread along the bottom of the pit if the groundwater level is high.
Sand is used with grains measuring 2-2.5 mm; crushed gravel sand is best. There should be no organic residues in it, otherwise the pillow will quickly silt up. The backfill is carried out in layers; every 50 mm it is necessary to compact it with a vibrating plate or tamper. The sand is first spilled with water. A more reliable base is obtained from a concrete slab, so it is better to install it for a residential building.
Concrete pad
This type will require large financial investments, but they are justified. For strip and slab foundations, concrete preparation is the best choice. When installing them, a heavy reinforcing frame is used, which requires a solid base. There are two ways to make a concrete pad. The first is to fill the crushed stone layer with liquid bitumen, and the second is to make it from low grade concrete. If there is no groundwater in the area, a 10-centimeter layer will be sufficient.
Before laying, sand or crushed stone is poured into the bottom of the pit, and the concrete pad on top is waterproofed with bitumen, waterproof films or roll materials. If the footing is not reinforced, its optimal thickness is 15-20 cm. Reinforcement will increase the strength of the structure; in this case, the thickness of the footing can be reduced by 6 cm.
Preparation with geomembrane
The material appeared on the market recently. The innovation lies in the studded profile, which serves both for waterproofing and for strengthening the soil. Manufacturers promise that with geomembranes there will be fewer shrinkage cracks due to the redistribution of forces when transferring load to the base. The fiber is laid on a sand-crushed stone layer, having previously laid out geotextiles. The membrane seams are welded. The geomembrane is durable and withstands temperature changes well.
Varieties
Sand pillow
The construction of a foundation on such material optimally distributes the impact of the soil. This version of the concrete footing is constructed in mid-spring or autumn, when the soil stops seasonal movement. When using this type of preparation, the bottom of the load-bearing base rises above the level of soil water, so the concrete structure avoids the destructive influence of ground moisture. This type of foundation cushion is used on soils with high humidity. The thickness of the layer is set within 15 cm.
To make a sand substrate you need a material with the following characteristics:
- Fraction 2-2.5 mm. The most suitable sand is low density, capable of good moisture permeability.
- Clay particles, limestone, salt deposits. Minor presence is allowed.
- Organic particles. They contribute to the formation of silt, which impedes the water-carrying capacity of the concrete base.
The construction of the substrate is carried out according to the following algorithm:
To lay the pillow you need to dig a pit.
- The soil under the pit is removed.
- The bottom of the trench is filled with prepared sand.
- The material is leveled over the pit, the uniformity of the backfill is controlled by the level.
- The pillow is being compacted.
Step-by-step instructions for performing concrete preparation

Preparatory work includes the following steps:
- Calculation part. First, engineering and geological surveys are carried out. Before constructing the foundation and the concrete under it, the depth of groundwater is determined, as well as the level of pressure that the soil will bear on the site of the future building. Based on this data, a construction plan is developed and the type of foundation is selected. The proximity to slopes and the occurrence of large compressive loads during the operation of the building are also taken into account.
- Preparing the construction site for laying the cushion. They move on to it after constructing the pit for the foundation. The fertile layer of dug soil is moved so that it can later be used.
The detailed guide discusses the option of preparing from lean concrete. The material received this name due to its low cement content. Its fragility makes it unsuitable for full-scale construction, but it is perfect for a pillow. Two classes of concrete mixtures are used depending on durability - B7.5 or B15. It is better to choose the first option, since the second contains expanded clay, which complicates the use of the material. To obtain a cubic meter of solution for preparation from B7.5 you need: 160 kg of cement, 2.2 tons of sand, 75 liters of water. The components are thoroughly mixed, then poured onto the area.
Detailed algorithm of actions for installing a preparation made of lean concrete:
- In accordance with the design data, the construction site is marked.
- Trenches are dug to the calculated depth. For foundations using a monolithic slab, a pit is dug.
- The area under the foundation is leveled and approximately 10 cm covered with crushed stone.
- Crushed stone is compacted with a vibrating plate.
- Formwork of the required height is installed. The value of the parameter depends on the thickness of the concrete layer. For optimal placement of reinforcement, the formwork should not be lower than 15 cm and higher than 30 cm.
- The pillow is reinforced with reinforcement using rods with a cross-section of 8 mm or more. A mesh will also work.
- Concrete solution is being prepared.
- The formwork is filled with the mixture to the top edge. The concrete is compacted.
- Reinforcement rods are inserted into the solution, which should protrude 20-30 centimeters above the concrete surface.
The pillow preparation is complete. Before building the foundation, you should wait until the concrete hardens.
When the base is ready, additional processing may be required - drilling holes and leveling. Such work is performed with diamond tools.
Features of the footing
Under the foundation slab

To remove excess moisture, a 10-centimeter layer of crushed stone or sand is poured, which is compacted with a vibrating plate. Formwork is mounted on top, and a mixture of lean concrete is poured into it. To reduce the pressure on the ground, it is recommended to leave a margin of 10-30 cm relative to the area of the foundation. This place is necessary for thermal insulation and finishing work. Concrete is poured to the upper edge of the formwork; reinforcing rods are installed for better adhesion to the foundation slab. The concrete layer is left to dry for 7-21 days. If tie rods were not installed, it is recommended to put two layers of waterproofing on top, and thermal insulation between them. Afterwards, the formwork is installed to fill the slab.
For strip base
The footing is done differently than under the slab. The area is marked, leaving allowances of 10 cm on each side. Trenches are dug and covered with a ten-centimeter layer of rubble. After compaction, it is covered with bitumen mastic. The formwork is installed, reinforcement is made inside it, and then the footing is poured. If the buried strip base consists of ready-made blocks, it is recommended to use compacted crushed stone impregnated with bitumen in the cushion. For resistance to damage, you can put waterproofing on top, and pour a second layer on top. For a shallow or shallow foundation, you can get by with crushed stone without bitumen or sand.
For FBS blocks
You can make two types of pillow: monolithic and prefabricated with the marking FL (strip foundation). First, the size and percentage of reinforcement of the cushion is calculated for the optimal selection of concrete grade and reinforcement. Next, prepare a base of crushed stone or sand and gravel. The layer must be compacted. The foundation cushion of FBS blocks is made 300 mm high and a multiple of 10 cm wide. The class of reinforcement is determined after calculating the load; rods with a thickness of at least 12 mm are taken. Reinforcement is done along the lower edge, retreating 70 mm from the base, the second row of mesh is made at a distance of 30-40 mm from the top of the pillow. The formwork here is the same as for a strip foundation. When laying reinforcement, you can use clamps. The final stage is pouring concrete and mandatory compaction of the layer, since the strength of reinforced concrete directly depends on the number of air bubbles in the mixture. After completion of the work, the structure is dried until completely hardened.
Which is better - membrane or concrete?
Experts have different opinions. On the one hand, profile geomembrane is a modern and economical material. It will simplify the preparation for the foundation and reduce the cost of the project.
What is the material: it is a rolled polymer, widely used in construction. It is used for drainage, waterproofing, and also in preparing the base for the foundation. The membrane is laid out on a leveled sand-crushed stone layer, and reinforcement is placed on top of it.
You can start pouring the slab immediately after preparing the reinforced frame, which significantly speeds up the construction process. A cushion of lean concrete takes several days to harden. Other advantages of the membrane: when laying the concrete mixture, it prevents the loss of cement laitance and additionally protects the foundation slab from groundwater.
Despite all the obvious advantages of geomembrane, the material has disadvantages. Experts on specialized forums note that the membrane is good for laying floors, but it is better to choose a concrete base for foundations. The fact is that the soil under the base of the foundation slab cannot be perfectly leveled; therefore, the size of the protective layer of concrete is not maintained. If you make a footing with a top part for a level, in the worst case there will be an overconsumption of inexpensive, lean concrete. In the case of a membrane, you can end up with a base that does not match the design.
What type of foundation will you choose?
Membrane
Footing
Stages of preparatory activities.
The preparatory stage, according to the rules, involves the following steps:
- the calculation part, which determines the thickness and dimensions of the foundation base, its ability to withstand deformations;
- arrangement of the work area;
- formation of the site.

According to SNiP 52-01, crushed stone is used as the main material for concrete preparation for the foundation.