Concrete grade for the foundation slab
Monolithic foundation slabs are included in the class of non-buried foundations. Concrete is poured into a pit, along the perimeter of which formwork is placed, with a reinforcement cage installed, on a compacted sand and crushed stone cushion. The height of the slab is from 0.2 m. A base of this type can be used on various soils. This is an excellent option on unstable soils. In order for the constructed foundation to last as long as possible, to be strong and reliable, it is necessary to select the appropriate grade of concrete for the slab foundation. There are a number of factors to consider when making your choice. Material and labor costs will depend on its correctness.
Concreting of reinforced concrete floors
Concrete for flooring must be prepared correctly and used in accordance with established rules and regulations. A ceiling is a structure that is designed to divide the entire structure into floors. The level of stability and strength of the building, as well as the sound and heat insulation of the room depend on the flooring.
For reinforced concrete structures, use concrete prepared according to the following recipe: part M400 cement, 4 parts crushed stone of a fraction of 20 millimeters, 2 parts clean sand, water in the required volume to achieve a working consistency.
First, formwork with a frame is made, concrete is carefully poured into it, and carefully compacted with an in-depth vibrator. The best effect can be achieved when the radius of vibration exceeds the radius of the vibrator at least 5 times.
Concrete for a monolithic floor is poured in one go, the whole process starts from the corner and ends in the opposite corner. Typically the thickness of the slab is from 8 to 12 centimeters. The formwork is dismantled after 2-3 weeks, when the concrete gains 80% strength. To prevent it from drying quickly, cover the area with any damp means - burlap, sawdust, film, and during the first 7 days of hardening, sprinkle water over the surface.
The floor slab is considered ready for further work after 28 days, when the concrete has fully gained strength according to grade. Typically, solid slabs are heavy and working with them is difficult because of this. Therefore, today in construction, round hollow slabs are actively used (the voids in them are filled with polyethylene pipes with a cross-section of up to 7 centimeters), which have a reduced weight and better sound and heat insulation properties.
In individual construction, ready-made floor slabs can be used, which are manufactured in a factory and quickly and easily mounted on load-bearing walls. But where it is not possible to install such slabs, monolithic floors are made.
Features of a slab foundation
The foundation slab is used mainly in areas with problematic, unstable soils, in places where groundwater is close to the surface. Also, such a base is used when there is a risk of landslides or on bulk soils.
Pouring the slab
The technology for creating a monolithic slab is implemented in several stages:
- conduct a geodetic survey of the construction site;
- dig a pit of the required depth;
- lay out the formwork;
- the bottom of the excavation is covered with a sand-crushed stone cushion, the thickness of which varies from 0.1 to 0.3 m;
- knit reinforcement in two rows;
- fill the form with concrete.
A slab-type foundation is also called “floating” because it can withstand quite significant ground movements without affecting the construction. Also, such a foundation allows the construction of multi-story, heavy buildings.
The large consumption of building materials, and therefore money, for the implementation of the project in practice is considered the main disadvantage of a monolithic foundation. Construction work is also accompanied by greater labor costs compared to the creation of other types of foundations.
Choosing the highest grade of concrete will provide a high-quality result in terms of reliability, strength and durability, but financial costs will increase significantly. In most cases, this will not be justified from the point of view of the existing loads, therefore, in each specific case, the choice of concrete grade should be approached taking into account the factors acting on the foundation being constructed.
Advantages and feasibility of use
Pouring the slab directly at the site of construction of the future house allows you to save on delivery and assembly of the structure, however, the use of integral technology is due to the order of special equipment (concrete mixer truck) and the construction of a drainage gutter.
By performing minimal preparatory activities and following the construction instructions, the entire installation procedure can be completed in a matter of days with your own hands.
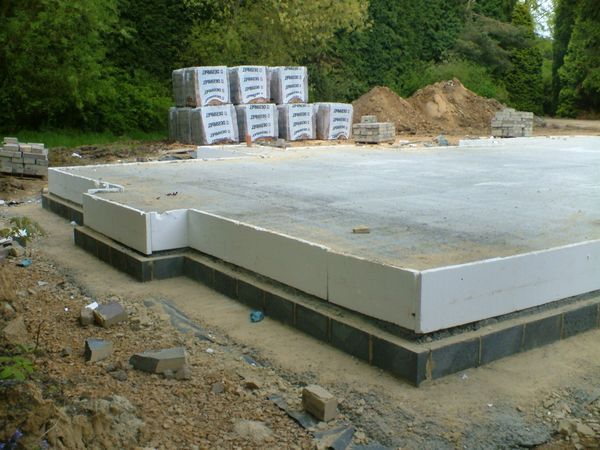

Slab foundation is most suitable for unstable and heaving soils
The advantages of the stove include:
- moderate ease of construction;
- practicality and reliability of the functioning of the base;
- resistance to seasonal ground fluctuations;
- the possibility of manufacturing a basement floor that is insulated and protected from moisture;
- significant period of operation.
The only disadvantage of a slab foundation for a house is its high cost. However, the high cost of the material is more than compensated by the guarantee of reliability and safety against harmful environmental factors.
Classification of concrete
The main components of concrete are cement, water, filler and various additives. The first serves as a binder, with the help of which other constituent elements are connected.
Scheme of concrete varieties
The following materials can be used as fillers:
Fillers are designed to reduce internal stress in concrete as it gains strength (hardening).
The final strength of the monolith depends on the presence of water in the required proportion in the solution. Excessive amount of liquid leads to mechanical weakening of the created structure.
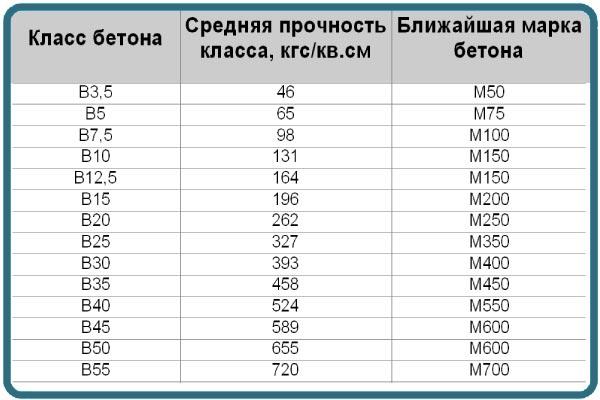
Concrete is classified according to the criteria given in the table below.
It is recommended to use compounds with an increased degree of frost resistance to avoid the appearance of cracks after several years due to temperature changes. The range of parameter values is from F25 to F1000. Frost resistance is an important parameter on very wet soils, where there is constant contact of the supporting structure with the soil.
The value of the water resistance coefficient ranges from 2 to 20. When constructing the foundation, choose W2 - W12, focusing on the groundwater level.
The final quality of the pour is determined by many factors. One of the main ones is the correct ratio of incoming components. High quality material should be used.
Areas of use of different grades of material
Concrete grades
The grade of concrete determines the construction area in which it can be used. It shows how a foundation that has gained full strength will resist operating loads. The brand is the main characteristic when choosing a building material; its strength is shown in kgf/cm2. At the same time, water resistance and mobility are reduced.
Among the existing grades of concrete (from M50 to M1000), M100-M450 have gained practical distribution.
The table below shows the grades of material and their characteristics.
Due to its high cost, the M500 is not popular. The most widely used concrete grade among private developers is M350. It is the best option in terms of the price of the material and its quality.
Factors determining the choice of concrete for a monolithic slab
When building lightweight structures on a slab, such as a garage, gazebo, barn, small frame or wooden house, the foundation material can be selected with an approximate consideration of the existing loads. Concrete grades M200 and M250 are suitable. Very rarely a slab foundation is made for light structures. Often they make do with pile or columnar types of foundation.
Monolithic slab foundation on sandy soil
To choose which concrete is best suited for creating a reinforced monolithic slab in a particular case when constructing heavier buildings, it is necessary to analyze a number of factors:
- geological conditions at the construction site: soil type, its structure, groundwater level;
- climatic features of the region: temperature regime and degree of air humidity;
- the weight of the building being erected and associated loads from snow, furniture, residents, household appliances and equipment.
All the factors considered must be taken into account in order to correctly determine the appropriate brand of concrete. Independent construction of the foundation (the entire structure) requires certain knowledge and practical skills in performing the work.
If the necessary experience is not available, then it is better to use the services of specialists who will not only competently construct the object, but also select the material suitable for specific conditions.
Ready mix in bags
Concrete grades for creating a monolithic slab
In hard, rocky and sandy types of soil, the entire load from the structure is distributed evenly. To build lightweight buildings on them, you can use concrete grade M150 or M200. Heavier buildings will require the use of M300 or M350.
Clay soil is characterized by a high degree of heaving; its volume increases greatly when it freezes unevenly in different directions. In this case, only the M350 - M450 varieties are suitable.
On any soil, the heavier the building being erected, the higher should be the grade of concrete used to build the foundation for it.
In most cases, to pour a monolithic slab foundation, you can use concrete with the following performance characteristics:
- from F200 degree of frost resistance;
- mobility P-3;
- waterproof coefficient value, starting from W8;
- brand M300;
- class B22.5.
Concrete mix
A slab foundation requires the use of appropriate building materials, including special insulation. You need to know what exactly the concrete composition should be for a foundation of this type. For concreting the slab, you should take concrete with a general strength class of B22.5, and its water resistance should be W8 or even more. The next important factor is frost resistance, and it should be equal to F200.
The concrete foundation used must have mobility P-3, this will be sufficient. If the groundwater is high, sulfate-resistant special mixtures would be appropriate, but this requires not only the quality of the concrete, but the reinforcement used, the class of which depends on its fastening in the reinforced frame. Special waterproofing materials required for monolithic foundations must also be used.
To pour the mixture, you should clearly and correctly know what kind of concrete is needed for the foundation and how to calculate the amount of mortar for pouring. Not only is the high-quality functional preparation of the concrete mixture important, its compaction after pouring is also very important, which should go over the entire area at once. The pouring of this foundation must be carried out immediately over the entire surface, and this is a very important requirement.
In addition to knowing and understanding what kind of concrete is needed for the foundation of a house, you should also take into account aspects of the binding of the reinforcement used. The installation of a common reinforcement belt should be started immediately after the formwork is manufactured.
The armored belt consists of a mesh with cells 20×20 cm on average, where reinforcement No. 14 is used. It is necessary to maintain a gap between the reinforcing meshes; it is enough to make a distance of 10 cm. Fixation between these meshes is achieved thanks to a vertical support called a fungus.
Calculation of the required volume of material for pouring the foundation
To determine the amount of concrete required for constructing a slab, you need to know its volume. It is found by multiplying the height by the width and length or by the area of the base.
The table below, according to GOST 7473-94, shows the correspondence of the class of concrete to its brand and the consumption of cement (M400) with a certain frost resistance, water resistance, mobility per 1 cubic meter of solution along with crushed stone, sand and water.
Knowing the volume of the slab, using the table you can determine the required amount of sand, crushed stone and cement to fill the foundation with the required strength. You can easily prepare the working mixture in the indicated proportions yourself.
The technology for constructing a slab foundation is presented in the video below.
Recommendations for choosing crushed stone, sand and concrete grade for constructing the foundation are given in the video below.
The correct choice of concrete grade used for the construction of a slab foundation will determine the service life, reliability and strength of the entire structure. The choice of material is determined by the geology of the site and the mass of the future building. Products with the required parameters can be purchased in the form of ready-made mixtures or prepared independently.
Mixture composition
The composition of any concrete solution includes the following components: cement, crushed stone or gravel, sand, water. The mixture is prepared in a concrete mixer, which ensures a higher quality of mixing and, accordingly, the final solution than with the manual method.
The main component of a concrete mixture is cement, the consumption of which depends on the brand of the finished mixture. Sand is chosen from river sand or any sand (but pre-cleaned from clay, which can make the sand greasy and unsuitable for work). Crushed stone is chosen in fractions of 10-20 millimeters; it must be clean, without screenings and debris. Add clean water, without any impurities, so that the solution does not separate.
Choosing a brand of concrete for the foundation

Building a house is a responsible, labor-intensive and costly process. Therefore, careful planning at all stages of building a house, including the process of selecting the necessary materials, is extremely important. When choosing the type of foundation, it is necessary to take into account the size and weight of the structure, as well as the type of soil.
The choice of type and quality of foundation construction will determine how strong, durable and reliable the structure will be. The strength of the foundation is ensured not only by the chosen type of foundation, but also by the quality of the materials used to fill it. Therefore, before starting construction work, it is necessary to find out what kind of concrete is needed for the foundation, its grades and classes.

Compound
Foundation concrete is made from many components, which can be divided into groups:
- Mineral component. These are mineral elements, in particular sand, gravel and crushed stone. The stone skeleton is responsible for the load-bearing capacity, and the resistance of the foundation to loads will depend on its quality. The share of this group in the solution ranges from 70 to 80%.
- Active group. This group includes a cementitious gel-like adhesive that binds mineral elements together. This group affects the strength of the base and the degree of shrinkage.
If you correctly select the composition of concrete for the foundation, it will provide the necessary level of strength of the underground structure and will also withstand seasonal soil movements.
Stamps
There are various grades of concrete for foundations. Their choice depends on the type of foundation, the weight of the future structure and other indicators. Therefore, it is extremely important to know which grade of foundation concrete is suitable for different foundations and types of structures.
- M 100. This composition can be used in the initial stages of construction. Sand concrete of this brand is used for making footings and constructing foundations for light garage structures, wooden dachas, fences, chicken coops, sheds and other dacha buildings.
- M 150 . This brand of sand concrete is recommended for preparatory work, as well as for the construction of a lightweight strip foundation. Can be used for one-story structures built from aerated concrete or cinder block.
- M 200. A frequently used brand of concrete for the foundation of a private house. It can be used when high-strength concrete is needed, as well as for the production of reinforced concrete structures.
- M 250 . This composition has a high cement content, so it can be used to create fairly strong structures.
- M 300 . Allows you to build the foundation of a house up to five floors high. This brand has a high strength rating, so it can be used for monolithic floors.
- M 350. Can be used in the construction of critical structures, for example, for the construction of curbs, roads and other structures that must withstand significant loads.
- M 400. Used for the construction of buildings up to 20 floors high. Therefore, it has high strength and resistance to mechanical damage.
- M 450. Used for the construction of high-strength load-bearing floor slabs. Recommended for various structures that must withstand very heavy loads.
- M 500. This brand is rarely used due to its high cost. It is advisable to use it only for the construction of cash vaults or other special facilities. However, it is this material that is recommended to be used if extreme strength and reliability of the structure is required.
If you already have a ready-made construction project, it will indicate what grade of concrete is needed for construction, so you won’t have to choose the optimal material yourself . The house design indicates all the characteristics of the mixture, so you just need to purchase the material specified in the documents.
Class
Concrete marking includes not only the brand, but also the class of the material. The concrete class is designated by the letter B , and shows information about the degree of compression, water resistance and other characteristics. Concreting the foundation should be carried out only using material of the required class. When choosing it, you should consider the following characteristics:
- Mobility. It is designated by the letter P. This characteristic of the material indicates its homogeneity and flow rate. In this case, even a slight increase in water in the mixture can reduce its strength, which will lead to significant problems with the foundation in the future.
- Waterproof. It is designated by the letter W. The indicator ranges from 2 to 12. The value of this indicator should be taken into account if there is groundwater on the site.
- Frost resistance. It is designated by the letter F. This indicator characterizes the number of frosts and defrosts that the material can withstand. Particular attention should be paid to this indicator in the northern regions.
Therefore, in addition to the brand of the base mixture, it is also necessary to take into account its class. Before choosing a material, you should take into account the load on the foundation, the climate of the region, as well as geodetic features and the degree of soil heaving.
Installation of a slab for the foundation
To obtain a reliable, durable foundation for a house, it is important to choose the right material. Particular attention is paid to concrete. The following requirements for it should be highlighted:
- water resistance must correspond to at least category W8;
- In terms of strength, concrete with a grade of at least M300 is selected;
- frost resistance must correspond to F200;
- The mobility of the solution during manual pouring is sufficient P3.
To reinforce the slab, you can use any steel reinforcement with a periodic profile with a diameter of at least 12 mm. Often preference is given to A500C rods, which have the necessary strength and are designed for welded joints.
At the preparation stage, you should also prepare the necessary tools - a shovel, a crowbar, a grinder for cutting reinforcement, a knife and scissors for cutting rolled materials, a hacksaw for metal, a hacksaw and a hammer for making formwork, pliers, a hammer drill.
When preparing and pouring the solution, you will need a vibrator, a construction mixer, a trowel or trowel, a grater, and a rule. Quality control and measurements are provided by a building level, tape measure, metal ruler, square.
Earthworks and formwork
To build a slab foundation, it is necessary to carefully prepare the construction site. First of all, the fertile layer of soil is removed and the site is leveled using a level. If necessary, additional soil is brought in, which is backfilled on the site and compacted. It is advisable to use a vibrating platform for this.
The next step is digging a pit (“trough”). The size of the pit exceeds the dimensions of the slab by 20-30 cm for installing the formwork. Its depth is chosen to be 30-40 cm greater than the height of the buried part of the foundation. The bottom of the “trough” is carefully leveled horizontally and compacted.
drainage outlets on it . Next, the bottom is covered over the entire area with geotextiles. This layer will keep the cushion from migrating into the ground, while freely allowing moisture to pass through.

An important stage of preparatory work is filling the pillow. To do this, pour a layer of sand, and then a layer of crushed stone or gravel. The total thickness of the pillow is on average 30 cm.
If construction is carried out on highly heaving soils, then the thickness increases to 40-45 cm. Every 8-10 cm of backfill, compaction is performed (recommended with a vibrating plate). Communication pipes and drainage pipes are laid inside the cushion.
The preparatory stage ends with the installation of formwork. It is installed along the entire perimeter of the future foundation slab and strictly determines its dimensions. Installation begins with installing beams at the corners with a height equal to the height of the foundation.
We recommend: Calculation of a foundation on piles for a private house. How to choose screw piles for a house?
A cord is stretched between the beams, following which intermediate beams are driven in increments of 1.5-2 m. Plank walls are nailed to the vertical beams. Boards 15-20 cm wide and 2.5-3 cm thick are used, which are tightly fitted to each other.
From the outside, the formwork is strengthened with jibs (supports). Particular attention is paid to the strength of the corners. When installing the formwork, you should remember that the surface of the slab is formed along the upper edge of the board, which means that the horizontalness of the foundation depends on the evenness of the installation.
We recommend reading: How to properly prepare a plot of land for construction?
How to properly prepare concrete?
The reliability of a slab foundation increases significantly in the presence of such an element as concrete preparation (concrete footing). Taking into account the large area of the main pour, the footing performs the following functions: preventing concrete from leaking, uniformly distributing the solution, mitigating the effects of sudden swelling of the soil, and simplifying the correct installation of the reinforcement system.
Concrete preparation parameters are determined by SNiP 52-01-2003 . Among the main provisions, the following norms should be noted:
- use of lean concrete based on a mixture of grade M50;
- layer thickness is 5-10 cm;
- exposure after pouring for 28 days for the material to gain strength.
Lean concrete for footings contains only 6-7% cement. The mixture contains a minimal amount of ingredients, which speeds up the hydration process, and therefore the hardening of the mass. The solution is poured into the formwork over the entire surface and carefully leveled using the rule. The evenness of the surface is controlled by the building level.
Laying waterproofing
Waterproofing a slab foundation is considered a mandatory structural element. It must reliably protect the concrete slab from soil moisture and flood waters. The waterproofing layer should protect the slab both from below and from the sides. Protection can be provided using rolled, coating and sprayed materials that are waterproof.
The most commonly used are roofing felt and thick polyethylene film . Bitumen coating is used as additional insulation . The rolled material is laid on top of the concrete preparation with overlapping strips. The overlap length is at least 15 cm.
To provide lateral protection, the material is lifted onto the formwork walls (from the inside). The modern construction industry offers improved polymer materials that effectively act as waterproofing.

Insulation
Thermal insulation in a slab foundation is an optional, but desirable element . Its installation is especially important during construction in cold regions. The insulation can be laid on top of the waterproofing or on top of the foundation slab when making a floor screed. It should not be forgotten that thermal protection is significantly deteriorated in the absence of end insulation.
The following materials are used as thermal insulation for a monolithic foundation.
Styrofoam
It is technologically advanced, easy to install, does not rot, and is highly water resistant. Among the disadvantages are toxicity when heated above 50 degrees, fragility and flammability.
The material is available in the form of slabs of various thicknesses. It is widely used as insulation for foundation slabs, incl. due to low cost.
Extruded polystyrene foam
In appearance it resembles polystyrene foam, but differs in the manufacturing method. It has good thermal insulation properties and increased strength. Available in rolls and slabs.
Criterias of choice
When choosing the optimal grade of concrete for pouring the foundation, the following factors must be taken into account:
Base type
When deciding which brand of concrete to choose, you should consider whether the house will have a basement, as well as the degree of soil freezing. When choosing a foundation, the depth of groundwater is also of great importance. Therefore, one should take into account such a material indicator as water resistance. The M 350 brand of concrete for the foundation of a house has a much higher water resistance than sand concrete M 200. However, you can save on the material if you use a mixture of the M 200 brand. However, it is additionally recommended to use additives that increase the water resistance.
Load accounting
To determine what brand of material is needed, you should calculate the load that the base will constantly experience. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the maximum indicators. The weight of walls, ceilings, roof with construction system, furniture and household appliances, as well as the weight of people are taken into account.
For light structures, you can use a strip foundation made from material grade M 150 or M 200. For the foundation of a structure made of timber, logs, gas blocks or ceramic blocks, it is better to use concrete of at least grade M 250. The base of brick and other heavy structures is best made from grade M material 350.
Climate and geology
The choice of cement grade is also influenced by soil characteristics. One of the important factors is soil heaving. It is typical for clay and loamy soils. When clay soil freezes, it increases in size, causing the load on the foundation to be uneven. In this case, it is recommended to fill the foundation with material grade M 300 or higher.
If the soil has a low heaving rate, then you can use a foundation made of M 200 concrete. This applies to sandy and rocky soil. This type of soil has a homogeneous structure, so the load will be distributed evenly.
Consumables and necessary tools
When choosing concrete, you should be guided by the characteristics of the climatic zone and the characteristics of the soil. In practice, experts correctly recommend focusing on the following factors:
- water resistance of concrete – not lower than W6;
- marking of the concrete mortar and its strength class - not lower than M-250 (B20);
- mobility – optimal indicator P3;
- resistance to frost - depending on the climate zone (for the middle zone - not lower than F 150).

Tools and accessories required for the work:
- excavator - for digging a pit;
- concrete mixer - to maintain the solution in working condition and its subsequent unloading;
- wooden scraps of boards or building rules;
- hammer and nails;
- hydraulic level (building level);
- shovels and bayonet shovels;
- wire and hook for tying the reinforcement cage;
- formwork slabs.
Principles for calculating foundation thickness
A monolithic slab is considered the most expensive type of foundation, although it is the least labor-intensive. A foundation slab for a house made of aerated concrete can be installed in the shortest possible time. All operations are mechanized: excavation work is carried out using specialized equipment - graders, bulldozers. Concrete is poured using an automatic mixer. However, the construction of the thinnest foundation will require about 25 cubic meters of concrete, and this is a huge mass - 50–55 tons.
It is advisable to install such a foundation in two cases: when you, together with a group of other summer residents, are developing a new site, and when the house is being built on specific soil: then there is simply no alternative to a monolithic slab.
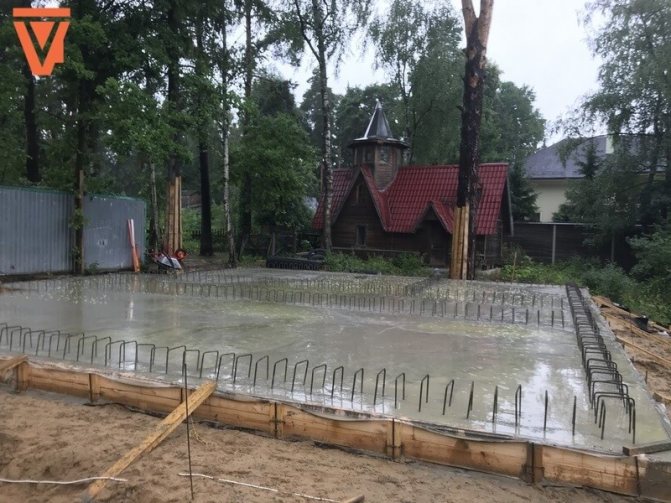

Conditions for slab foundation
The slab foundation differs from all others in its amazing versatility. A monolithic concrete slab, despite its massiveness, remains stable on the most problematic soils.
Slabs, as foundation foundations, are indispensable in permafrost conditions, on swampy non-reclaimed lands, on peat bogs, and on mobile loess soils.
The monolithic concrete pad has a large area, so it does not sag on any soil. Moreover: if such a foundation is built on heaving soil, then it will absorb all the loads:
- when the soil freezes, when the ice crumbs increase in volume, the slab will rise along with the house;
- when the ground thaws, the slab will take its previous position - also together with the house.
Thanks to this property, a foundation made of monolithic slabs is called “floating”.
Construction of a monolithic foundation slab
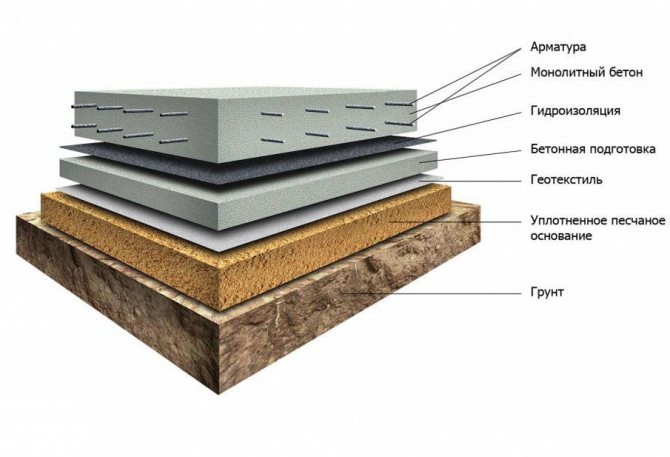
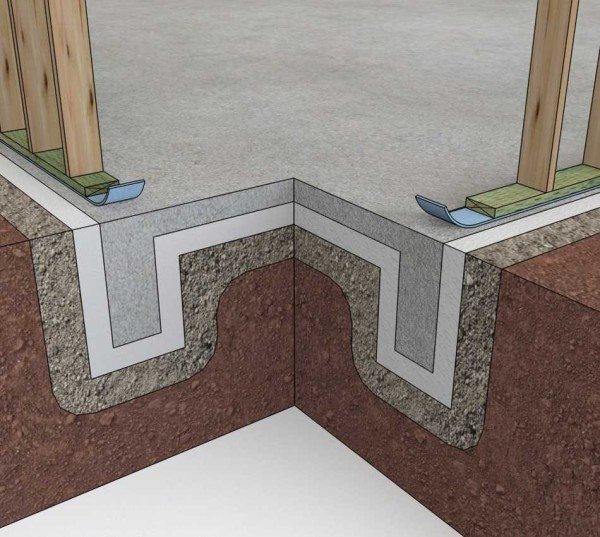
The classic design of a monolithic foundation consists of the following elements:
- sand substrate 100–300 mm thick - a layer of sand that acts as a shock-absorbing lining;
- gravel or crushed stone layer 200 mm high - a mass that distributes the load;
- footing - a thin layer, no more than 20-50 mm, - a rough base for a concrete mass;
- insulation – 100 mm padding made of polystyrene plates; can also act as waterproofing;
- waterproofing layer - polymer or roofing material flooring;
- monolithic slab reinforced with a three-dimensional two-level steel mesh: its thickness can reach 600 mm.
Scope and types
A monolithic slab for a house belongs to floating, non-buried foundations; it can also be shallow. It got its name due to the fact that a reinforced concrete base is poured under the entire area of the house, forming a large slab.
A prerequisite is the presence of a sand and gravel cushion, which redistributes the load from the house to the ground and serves as a damper during frost heaving. Often such a foundation is the only possible solution. For example, on unstable, loose soils or on clays with a large freezing depth.
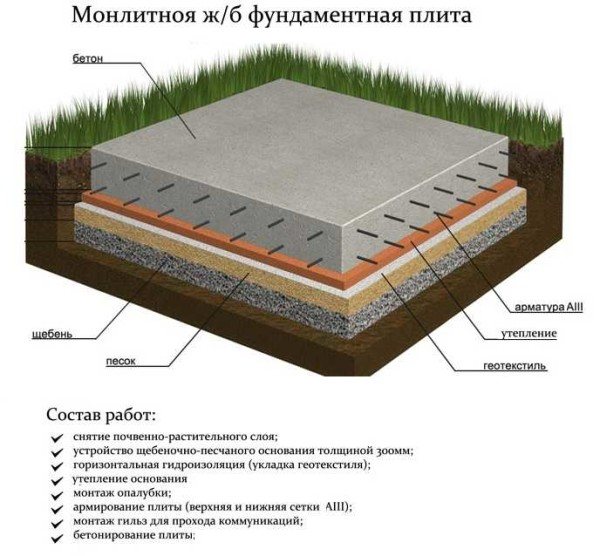
Classic insulated foundation slab for a house
The construction of a monolithic slab foundation is simple and reliable, but its production requires a large amount of reinforcement and large volumes of high-grade concrete (not lower than B30), because the entire area occupied by the building is reinforced and concreted, and with a margin for greater stability. That’s why such a foundation is considered expensive. In principle, this is true, but it must be considered. In some cases, its cost is lower than deep strip laying - due to less excavation work and less concrete.
The depth of the monolithic slab is determined depending on the weight of the house and the type of soil. With shallow depth on heaving soils in winter, the house along with the base can rise and fall. If the reinforcement and slab thickness are correctly calculated, this does not affect the integrity of the building. The plate compensates for all changes due to elastic force. In the spring, after the soil has melted, the house “sits” into place.
There are four types of slab foundations:
- Classical. A reinforced concrete slab is placed on a sand and gravel bed with or without insulation. The thickness of the concrete layer is 20-50 cm, depending on the soil and the mass of the building. The thickness of the layers of the cushion depends on the depth of the fertile layer - it must be completely removed. The resulting pit can be filled 2/3 with sand and gravel.
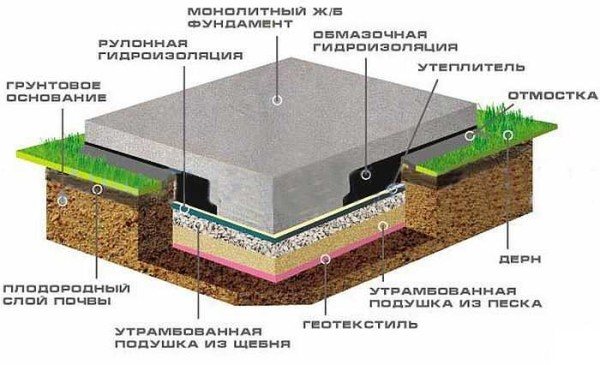
The classic version of the foundation is a monolithic slab without insulation
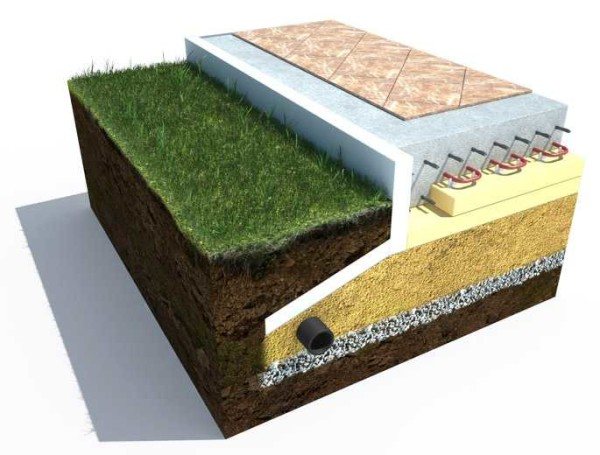
USHP - insulated Swedish stove with built-in heated floor

This is what a Russian slab foundation looks like in cross-section
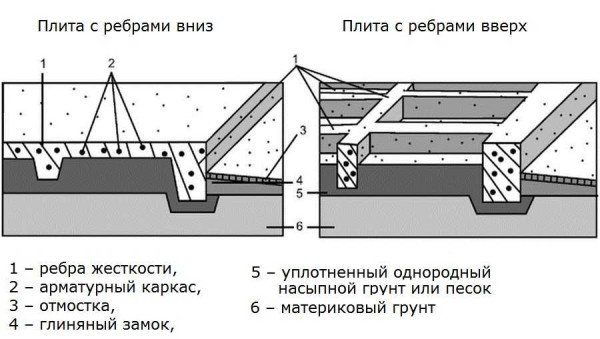
The structure of the foundation slab with ribs down and up
What brand of concrete is needed for a slab foundation?
What kind of concrete is needed for a slab foundation is a question asked by most owners of suburban areas who are planning to build a house. Usually the foreman helps in selecting the brand of concrete when calculating the estimate, but how can you be sure of his competence and be confident in the quality of the constructed foundation?
In this article we will tell you how to choose the right brand of concrete for the construction of any type of foundation.
Determining the grade of concrete for the foundation based on the load.
First, you need to understand what material the building will be built from, since this parameter directly affects its mass and therefore the load of the foundation. During frame construction, the load is usually small and sometimes even M200 grade concrete is sufficient. If you are building a wooden house from logs or timber, then you need to choose a mixture not lower than M250. Walls made of foam concrete are similar in weight to wood, so you can choose M250. When using gas silicate blocks, stronger concrete is needed - M300. And if you decide to build a more solid structure from sand-lime brick or precast reinforced concrete, then the foundation must be strong and consist of concrete grade M350 or higher.
What kind of concrete is needed for a slab foundation depending on the soil?
The grade of concrete may vary depending on the condition of the soil. The most suitable soil for construction is sand or rocky soil - here the grade of the mixture can be left at the minimum calculated level relative to the wall material. When building on clay or loamy soils that are prone to movement, the grade of the concrete mixture should be increased by one level.
For example: you are building a country house made of foam concrete, calculations have shown that it is optimal to use M250 grade concrete, but the construction will take place on an area with clay soil - in this case, it is necessary to increase the strength of the slab foundation and choose the M300 class.
Which concrete to use for the foundation based on its type.
The type of foundation is one of the important factors for determining the grade of concrete. The main point when choosing is the presence of a basement that requires the proper level of waterproofing. Each brand of concrete has its own water resistance index, for example, for M250 it is two times less than for M350. And in order for the foundation to be reliable in every sense, it is necessary to take this factor into account.
Final provisions when determining the grade of concrete for the foundation.
Perhaps the most important factor, both when choosing a brand and during construction, is the right choice of contractor. An experienced master will professionally help you with your choice, explain why it was made in favor of a particular mixture, accept the concrete, control its quality and you will receive a reliable foundation without unnecessary overpayments for a high-class mixture. Our team specializes in the construction of foundations in St. Petersburg and the region. Strip, slab, foundation with a plinth - any type of foundation will be performed at the highest level.
How to calculate concrete proportions for floors
Calculation of the proportion of components for the implementation of floors is carried out individually in each individual case. Only strict adherence to technology and high-quality mixing guarantee that the concrete corresponds to the chosen brand.
What affects the content of concrete
The quality of installation and the material itself is influenced by a huge number of factors.
Reducing it in the composition of the solution will make it less durable, increasing it will make it more durable (but also expensive). Strength also depends on the selected fraction of crushed stone and the volume of water in the solution.
The optimal size of crushed stone is 5-20 millimeters. It is best to take pure quartz sand, which does not contain impurities that could reduce the quality of concrete. Water is taken in a volume sufficient to obtain the material of the desired consistency. Much when determining the volumes of components depends on what characteristics the concrete should have - frost resistance, elasticity, strength. Often special additives are added to the composition, which give the material the desired properties.
Choosing the type of concrete for the solution
The grade of concrete for monolithic floors and other structural elements is selected in accordance with the requirements and operating conditions.
- Grade M100/strength class B7.5 – proportion 1 part cement, 5.8 parts sand, 8.1 parts crushed stone: used during the preparatory stage in the construction of a monolithic foundation and road surface.
- M150/B12.5 – 1:4.5:6.6: for pouring a monolithic foundation, making the floor of small buildings, garden paths and roads.
- M200/B15 – 1:3.5:5.6: for floor slabs, pile and strip supports, stairs, roads, wall retaining structures.
- M250/B20 – 1:2.6:4.5: for blind areas, platforms, paths, stairs, fences, retaining walls, floors of multi-storey buildings.
- M300/B22.5 – 1:2.4:4.3: all tasks for M250, for all types of foundations, floors in any buildings.
- M350/B25 – 1:2:4: construction of foundations for various buildings, roads, columns, structures with increased loads.
- M400/B30 – 1:1.6:3.2: for the construction of hydraulic structures, bridges, high-strength buildings. In individual construction, such concrete is usually not used.
- M450/B35 – 1:1.4:2.9: similar to the previous brand, but has higher water resistance, suitable for the construction of dams, dams, subways, etc.

Calculation of concrete mixture proportions using an example
To make it clearer, you can perform concrete calculations using the example of a specific task. Having done this once, in the future it will be possible to prepare concrete of any grade for floor slabs or other structures with various characteristics.
Typically, concrete of the M350 grade is used in construction, which is optimal in terms of characteristics and cost.
The basis of the ratio is the mass of cement. So, to obtain a mortar for floor slabs, 50 kilograms of sand and about 100 kilograms of crushed stone are taken for 25 kilograms of cement. The ratio is 25:50:100, also known as 1:2:4. The water content is determined in accordance with the desired indicator of the plasticity of the mixture, adjusting during the mixing process. Various plasticizers and additives can be added to the composition to enhance certain properties.
For floor slabs, as a rule, a solution is taken with the following proportion: 1: 3: 6 and 0.5-1 volume of water (the exact volume depends on the mobility of the mixture).