Image of a metal column on an equipped foundation Despite the enormous popularity of frame strip or monolithic foundations, in some cases they cannot be used due to the characteristics of the soil, the loads per unit area of the structure, and the characteristics of the building itself. As a rule, column foundations are often built for industrial enterprises of heavy energy, mechanical engineering and for military needs.
Such frameless foundations can withstand enormous loads, but the calculation is always done for each column separately, because here a full collection of all permissible loads from the building itself, the soil and climatic conditions in the region of construction is carried out.
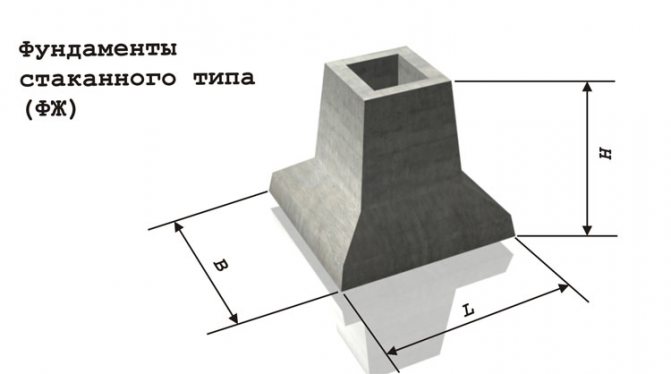
Foundations when connected to a column
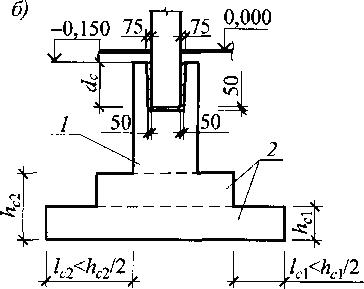
a - monolithic; b - national team; 1 — column support; 2 - slab part of the foundation
The connection between the foundation and the column is made monolithic for monolithic columns and glass type for prefabricated columns.
The gaps between the column and the walls of the glass are taken equal to 75 mm at the top and 50 mm at the bottom of the glass on each side of the column. These gaps are filled with concrete of class B 12.5 or higher.
The depth of the glass dp is taken to be 50 mm greater than the embedding depth of the column dc. The dc value must be no less than the larger column section size /c, and also no less than:
30d - in the 1st case of compression of the column in the section along the edge of the foundation; 20d - in the 2nd case of compression; here d is the diameter of the column reinforcement.
In the 1st case of compression, the limiting value dc = 30d can be reduced by multiplying it by the ratio of the column moment in the section along the edge of the foundation to the maximum strength moment of the column at a given value N, but take at least 20d.
The wall thickness at the top of an unreinforced glass is taken to be at least 0.75 times the depth of the glass and at least 200 mm.
The wall thickness of the reinforced glass is taken to be at least 150 mm.
To connect with a monolithic column, reinforcement with a cross-sectional area necessary to absorb the design forces of the column at the edge of the foundation is produced from the foundation (pillar). Within the foundation, this reinforcement is combined with clamps into a frame and launched into the column to a length not less than the length of the anchorage lаn.
The joints of outlets with column reinforcement can be overlapped without welding in accordance with the instructions of SP 52-101-2003.
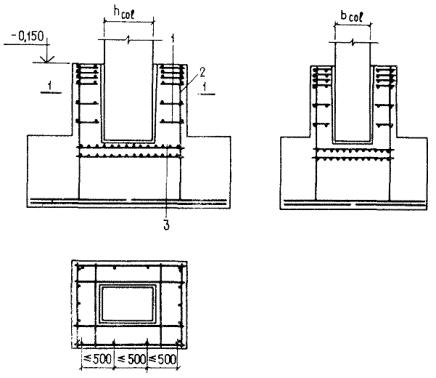
Foundations are reinforced with welded mesh only along the base. In this case, if the smaller side of the sole has dimensions b<3m,>3m, separate meshes with working reinforcement in one direction are used, laid in two planes. In this case, the working reinforcement of each grid is located below. The meshes in each plane are laid without overlap with a distance between the outer rods of no more than 200 mm (Fig. below).
How to calculate a column foundation
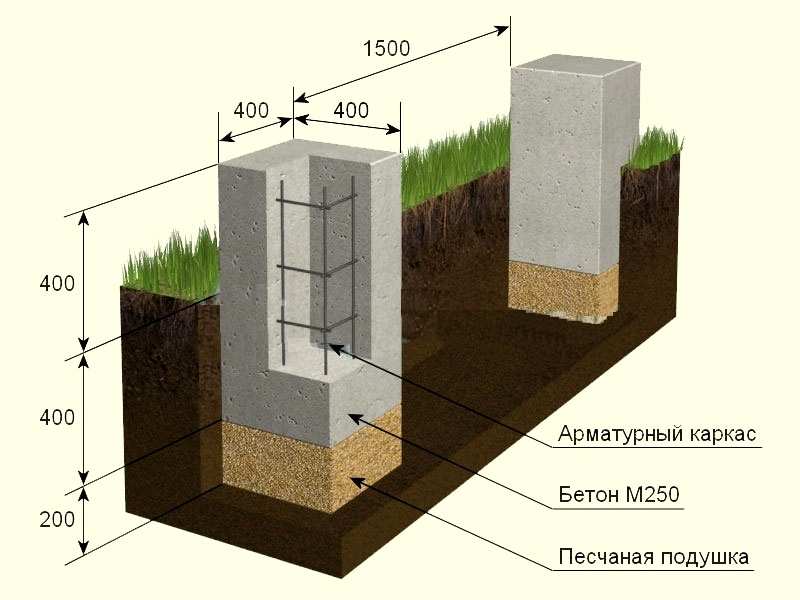
As a rule, the calculation of the foundation for a metal column implies whether the soil is able to withstand the design load of the foundation with which it will act on a square centimeter of area, and the collection of all data on future construction. In fact, you need to obtain complete information about the building, soils and groundwater, collect and systematize the data obtained and, based on it, transfer the finished project to the builders. To do this you need:
- receive from the architect a design of the future building, specifications of building materials and communications;
- calculate the total support area;
- collect all parameters, systematize them and obtain the actual design pressure of the building as a whole.
Reinforcement of the foundation base with meshes
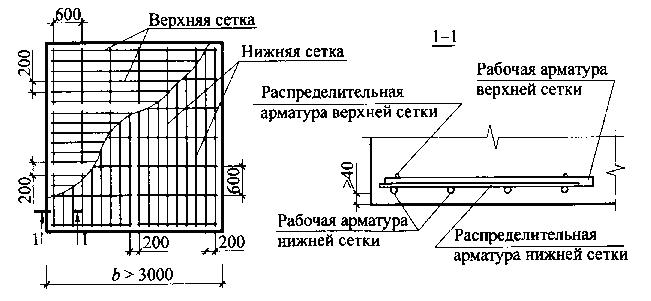
The minimum protective layer of concrete for this reinforcement is accepted: if there is a preparation of lean concrete under the foundation - 40 mm, if not - 70 mm.
If the normal cross-section of the column support as a concrete element is not provided with strength, the column support is reinforced with flat welded mesh with a reinforcement percentage of the entire longitudinal reinforcement of at least 0.2% (Fig. below).
Construction of a glass-type foundation
The glass-type foundation is a prefabricated structure made of factory-produced reinforced concrete blocks. Such blocks consist of two parts - a base base plate and a pyramidal shaped column (shoe) emerging from it with a cavity in the central part, in which the reinforced concrete column is fixed.
Important! Glass blocks, depending on the location of the column installation, can have a central and lateral load. The base plate in blocks intended for central loads has a square cross-section; for lateral loads, rectangular slabs with an aspect ratio of at least 0.6 are used.
The cross-section of the shoe depends on the size of the column installed in it. Standard products are produced for columns with a cross-section of 300 and 400 mm, their dimensions increase in increments of 100 mm. The minimum thickness of the bottom wall of the shoe is 20 centimeters.
The production of glass-type foundations is regulated by the requirements of GOST No. 24476-80 “Precast reinforced concrete foundations”. This regulatory document puts forward the following requirements for glass bases:
- All elements of the prefabricated structure must be made of concrete grade M200, which corresponds to water resistance group B2 (moisture absorption of no more than 5% of its own volume);
- The sole and sub-column are subject to mandatory reinforcement. To strengthen the slab, reinforcing mesh of the 1.410-3 series is used, and hot-rolled reinforcement of class A2 and A3 is used to strengthen the column supports.
Important! In addition to the rod reinforcement, the sub-columns are also reinforced with a reinforcing mesh, from which a three-dimensional frame is formed, located along the four walls of the shoe to their entire height. When strengthening a glass foundation, the reinforced frame is recessed into the concrete at least 5 centimeters.
Reinforcement of a reinforced concrete column with a spatial frame assembled from meshes
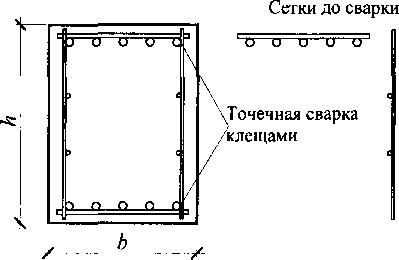
In reinforced concrete columns, where, according to calculations, compressed reinforcement is not required, and the amount of tensile reinforcement does not exceed 0.3%, it is allowed to install meshes only along the edges of the column, perpendicular to the plane of action of the larger of the two moments acting on the foundation. In this case, the thickness of the protective layer of concrete must be at least 50 mm and at least twice the diameter of the reinforcement.
If it is necessary to reinforce the walls of the glass in concrete columns, a spatial frame should be installed within the glass part with a depth below the bottom of the glass by at least 35 diameters of the longitudinal reinforcement. In this case, the area of all longitudinal reinforcement is taken to be no less than 0.04% of the area of the column outside the glass (Fig. below).
What types of columns are there?

Reinforced concrete. They are durable, produced in industrial conditions, therefore they comply with all quality standards, as well as the grade of concrete. Load-bearing reinforcement is already provided inside such columns, but columns of this type are heavy and powerful construction equipment must be used for their installation.
Metal. They are lighter than reinforced concrete, but completely different installation methods are used here. In addition, when making calculations, you need to clearly decide initially which type of column is best to use.
Glass-type foundation installation technology
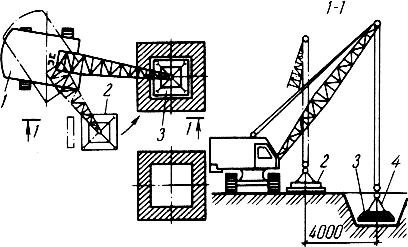
Glass foundation blocks are heavy - from 1.3 to 5.8 tons, which requires the use of crane equipment for their installation. In addition to the jib crane and its operator, two installers must be involved in laying the glass foundation.
According to current regulations, the installation time for one glass block weighing one and a half tons should be 27 minutes.
- Stage No. 1 - preparatory and excavation work
The area where the glass foundation will be installed is cleared of construction debris and surface vegetation. If the project provides for the installation of blocks at the bottom of the pit, the soil is excavated using an excavator.
When installing blocks in shallow depths, the pit is excavated to a depth equal to the height of the base plate of the glass block. The pit can be arranged for each block separately, or in the form of a continuous line that follows the contours of the walls of the building.

If it is necessary to create a compacting bedding, the length and width of the pit should be 30 centimeters greater than the similar dimensions of the base plate. After excavating the soil, the pit is cleaned, its bottom is leveled and compacted.
- Stage No. 2 - arrangement of compaction
The compacting bedding under the glass foundation is made of sand and fine crushed stone. The need for it arises in conditions of low-density soils, which are prone to shrinkage under the weight of the building and foundation structure.
Important! The compacting layer must protrude 30 centimeters beyond the base slab, otherwise the block will not be evenly supported on the preparation, which can lead to distortion of the reinforced concrete structure.
The thickness of the compaction varies depending on the weight of the glass block, but under any conditions the thickness of the layer of sand and crushed stone should be identical.
The first layer is crushed stone - it is evenly distributed and leveled at the bottom of the pit. Crushed stone is compacted using a manual compactor or jib crane attachment. A layer of sand is poured on top of the crushed stone, which is watered with water from a hose and compacted in the same way.
- Stage No. 3 - marking the reference axes
At the bottom of the pit, the installation site for the glass block is marked. The alignment axes are secured to the stripping boards using twine or wire with a diameter of 2 millimeters. At the intersection of the axes, a plumb line (weighing at least 0.5 kg) is installed and the central point of the base plate is transferred to the ground.
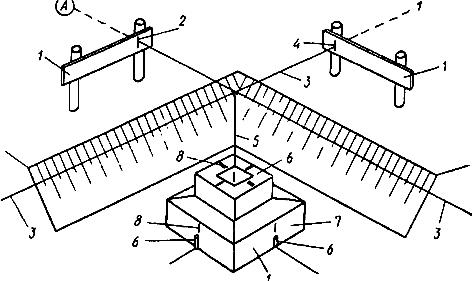
Using the dimensional template of the installed slab, the lateral contours of the block’s position are transferred to the ground, which are marked using reinforcement pegs and string stretched between them.
Expert advice! After marking the foundation, the horizontality of the poured layer is checked using a level and leveled to a perfectly level level.
- Stage No. 4 - installation of the block
Before installing the blocks, one of the builders checks the condition of the mounting hinges on the reinforced concrete structures; if they are bent, they are straightened with a hammer.
Next, on the edge of the glass, guidelines are applied using paint, indicating the design sides of the location of the block axes. One installer slings the block, hooking the jib crane cable hooks into the mounting loops. Slinging can be done with two or four hooks, depending on the dimensions of the reinforced concrete structure.
Figure 1.8 : Sequence of installation of a glass foundation
After checking the reliability of the hooks, the installer moves away from the glass to a safe distance and gives the command to the crane operator to lift the block. The lower wall of the raised product is cleared of adhering earth, after which the crane moves the glass to the place of installation.
At a height of 15-20 centimeters above the ground, two installers begin to manually adjust the installation of the block, turning and shifting it in the required direction.
At the command of the installers, the crane operator completely lowers the block to the ground , after which, using crowbars, the builders align its position relative to the marking axes. When the block occupies the required spatial position, the sling is dismantled and the installation of the next structure begins.
Advantages and disadvantages
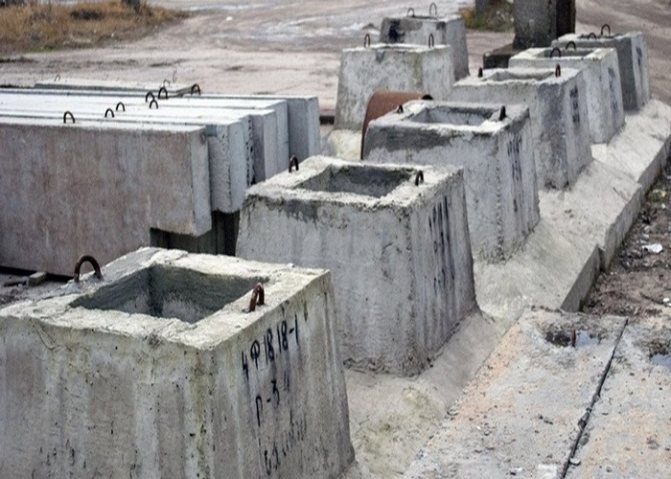

Glass-type bases have a high quality of finished factory elements, which is achieved through compliance with all regulatory requirements.
Glass-type bases have a number of advantages:
- High quality of finished factory elements, which is achieved through compliance with all regulatory requirements.
- Quick and easy installation of structures from ready-made elements.
- High technical and operational characteristics.
- Durability and reliability. Provided that the installation technology is followed, the service life of the structure is at least 100 years.
- Compared to the costs of installing a strip foundation, the costs of glass-type foundations are much lower.
Among the disadvantages it is worth mentioning the following:
- Installation of the structure is quite expensive due to the need to use large construction equipment.
- The massiveness and large weight of one product require the use of lifting construction equipment during installation.
- For the same reason, transporting elements is difficult.
Why does the foundation need to be reinforced?
Reinforcement allows you to increase the power and strength of the concrete base several times. Of course, a durable structure that will withstand gigantic loads and will be timeless can be obtained without the use of reinforcement.
For example, during the construction of the famous Colosseum, the builders of that time had no idea about additional strengthening of concrete with reinforcement, but the building stood for thousands of years, despite its location in an earthquake-prone zone. What is the mystery of such strength? Archaeological research has shown that the depth of the monolithic concrete slab is 9 meters, thickness - 13 meters. That is, the Colosseum is “alive” only thanks to this colossus.
However, today it is not economically profitable to build such a foundation. The development of the metallurgical industry makes it possible to significantly reduce the cost of construction through the use of a simple and effective method - pouring a concrete mass onto a frame made of metal reinforcement or mesh. The result is a reliable reinforced concrete foundation, thanks to which your building will last, if not millennia, then definitely a couple of centuries.
After hardening, concrete becomes rigid and inelastic, so it can deform when uneven pressure is applied to the surface. The reinforcement laid inside takes on all vertical loads and distributes them evenly over the entire base area.
The use of reinforcement is associated with additional costs, so some people refuse to install it. If you also doubt the need for reinforced mesh, make design calculations, analyze the feasibility, consider a number of factors: the composition and characteristics of the soil, groundwater level, degree and depth of freezing.
If you are constructing a building from light materials (logs, beams, frame-panel structures), it is not necessary to reinforce the base. As for heavy building materials (brick, concrete block, foam block, gas block, cinder block), in this case it is risky to refuse to lay the reinforced mesh. Concrete without reinforcement does not work well in bending and tension, so the foundation will deform or shrink, which will lead to the formation of cracks in the walls and premature destruction.
Where is a glass-type foundation used?
The glass foundation is classified as a shallow foundation; during its construction there is no need to carry out a large amount of excavation work. Due to the fact that the entire structure is delivered from the factory in a form ready for installation, it is possible to install the foundation itself and erect the floors and walls of the building in the shortest possible time. After installing a glass foundation, there is no need to wait a pause in construction work, as is the case with monolithic foundations, which require a month of downtime for concrete to harden.
The above advantages are the key factors determining the demand for glass foundations in industrial construction . Such foundations are indispensable when arranging agricultural premises - pigsties, cattle stalls, chicken coops, storage facilities for crop products.

Glass foundations are also used in the construction of infrastructure industrial facilities - warehouses and hangars, garages, sewage stations.
In road construction, glass foundations are used in the construction of bridges, and they are also often used in the construction of basement condensation floors at nuclear power plants.
Important! In individual construction, glass foundations are used extremely rarely due to their high cost. Some types of frame houses can be built on it, but for private development the use of a pile foundation is preferable in all respects.
Installation of a monolithic grillage
To pour the concrete solution, it is necessary to install high-quality formwork
To pour the concrete solution, it is necessary to install high-quality formwork. Start with the lower retaining shields. To do this, it is necessary to cut boards equal to the pitch between the foundation columns. To secure them, it is recommended to drive retaining stakes into the ground. The formwork boards are laid on stakes flush with the top edge of the posts.
The side panels of the formwork are attached at the edges and securely fixed. The side strips of the formwork can be covered with roofing felt.
The next step is to reinforce the entire structure. Here, the standard use is an armored belt made of horizontal rods with a cross-section of 12-16 mm and longitudinal elements with a cross-section of 6-8 mm
It is important in the places of the pillars to tie the reinforcement with the rods protruding from the columns
Pouring the solution for the grillage should be done in one stage. Therefore, it is better to order a construction mixer or concrete mixer of the required volume. When pouring concrete, it is necessary to compact the solution every 30 cm. The total thickness (height) of the grillage, as a rule, does not exceed 60 cm.
After 7-10 days, subject to good dry weather, the concrete is considered completely hardened. Now you can remove the formwork and let the foundation settle. All surfaces of the grillage are also covered with waterproofing materials.
After the structure has completely dried, it is necessary to backfill the pit and compact the soil around the columns. The pit is backfilled flush with the mark of the above-ground part of the foundation columns. To decorate the support pillars and reduce the level of heat loss, you can use decorative cladding of the pillars with siding or lay natural stone.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=6hzHFmYjOjQ