When considering Finnish technologies for constructing private houses, it is impossible to do without paying attention to the foundation structure. From a technical point of view, a frame structure can be installed on any foundation - from monolithic concrete to simple boulders. But still, when constructing frame buildings, two types of foundations are used, one of which is called an insulated Swedish slab, and the second is known as an insulated Finnish foundation. Structurally, the base is represented by a shallow, strip-type foundation with a monolithic insulated floor poured onto the ground. The system provides thermal insulation of the entire perimeter of the object, laid under the blind area.
Design features
The construction technology of the foundation, known by the abbreviation UFF, provides the following features:
- the presence of a shallow foundation strip laid from block material on a supporting concrete base, the width of which starts from 60 cm and the thickness from 20;
- screed with a reinforcing layer eight centimeters thick, poured over fifteen-centimeter polystyrene foam slabs;
- separation of the foundation strip and the floor with five-centimeter polystyrene foam, a layer of which rises from the sole to the edge of the base part;
- an insulating layer under the blind area, for which 12 cm thick PPS is used around the perimeter of the building.
The thickness of the insulating material depends on the climatic conditions of the area in which construction is taking place. Sometimes polystyrene foam material is replaced with ordinary foam plastic; you can buy polystyrene foam here: http://www.lbud.com.ua/teploizolyacionnye-materialy/penoplast-anserglob-eps30-lb140001-09.html .
Before concreting begins, polyethylene pipes are laid into the structure to create a “warm floor” system.
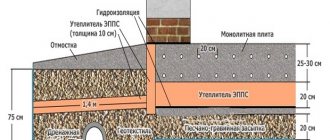
The main difference in the construction technology of an insulated Finnish foundation is the insulation of the floor, which is not connected to the foundation tape. This gives the structure additional stability when erecting it on weak and heaving soils. In addition, effective insulation of the entire perimeter of the house enhances the protection of the foundation from the negative effects of low temperature conditions.
Another important feature of the Finnish foundation option is the height of the basement, which requires the purchase and transportation of additional building materials. The size of the plinth is determined taking into account the structure of the soil and the thickness of the turf layer removed during construction work.
In what sequence is the Swedish stove installed?
Compliance with the construction algorithm of the Swedish slab affects the strength properties of the base and energy-saving characteristics. The general scope of work includes:

The soil under the insulated slab does not freeze, which minimizes the risk of frost heaving problems in foundation soils
- Construction of the pit.
- Installation of drainage pipes.
- Laying communications.
- Laying insulation.
- Reinforcement.
- Warm floor assembly.
- Concreting.
Let's consider the main features of the stages.
Marking the area
This stage of work involves transferring the foundation project to local conditions. Before marking begins, it is important to carry out geodetic surveys aimed at determining the nature of the soil and the depth of the aquifers.
During the marking process, the following are determined:
- foundation contours;
- ways to connect utilities.
After marking, it is important to protect the site from precipitation by installing a storm drain.
We carry out excavation work
Earthworks include the following work:

To ensure normal operation of the insulated Swedish slab (USP) and prevent frost heaving, it is necessary to provide a groundwater drainage system
- Clearing the construction site of construction debris and vegetation.
- Extraction of fertile soil layer to a depth of 0.4-0.5 m.
- Formation of a compacted sand cushion with a layer thickness of 30 cm.
- Extraction of soil around the perimeter of the pit for drainage lines.
- Filling clay at the bottom of the pits, moistening and compacting the clay layer.
After completing the excavation work, proceed to the next stage.
Setting up a drainage system
Sequencing:
- Lay down geotextiles.
- Pour in crushed stone.
- Compact the crushed stone.
- Lay drainage pipes.
- Fill in a layer of crushed stone.
After laying all layers, cover the bedding with geotextile fabric.
We lay utility lines
When performing work, observe the following sequence:

All necessary communications must be laid under the slab in advance.
- Install communications.
- Add a layer of sand.
- Compact the sand bedding.
After installation, it is important to check the correct connection of utility networks.
We select insulation and install it
When choosing a heat insulator, give preference to insulation with reduced thermal conductivity.
It is advisable to use extruded polystyrene foam, which has the following advantages:
- resistance to the development of microorganisms;
- environmental cleanliness;
- resistance to moisture.
Lay polystyrene foam in two layers with overlapping sheets of 40-50 cm. Use special fasteners for fixation.
We lay the reinforcing mesh and install the heated floor
When performing reinforcement, pay attention to the following points:
- use tying wire to connect the reinforcement;
- lay the reinforcing mesh in two tiers;
- ensure a distance to the heat insulator of 30-40 mm.
Install heating lines taking into account the layout. Use plastic supports for laying pipes.

Higher thermal power of underfloor heating is achieved by denser pipe laying
Recommendations for laying underfloor heating lines
When laying heating lines, pay attention to the following points:
- ensuring a distance of 100 mm between heating lines;
- making a distance from external walls of 150-200 mm;
- correct pipe laying according to the developed diagram.
After laying the lines, check the tightness of the system with compressed air.
We install the formwork
Installation of a Swedish slab requires the construction of formwork around the perimeter of the foundation. For formwork, plywood or board panels reinforced with supports are used. The inner surface of the formwork structure is lined with polystyrene sheets. They provide thermal insulation of the foundation from the end part.
We pour the concrete mass
When concreting, observe the following requirements:
- pour concrete in a 10-centimeter layer;
- fill at intervals of no more than an hour;
- use a vibrator or slab to compact the concrete.
Moisten the surface of the concrete during the hardening process, cover the base with polyethylene to protect it from moisture evaporation.
Advantages and disadvantages of using UVF
Let's look at the advantages of a foundation poured using Finnish slab technology:
- profitable and less expensive solution for areas with a sloping surface;
- the ability to equip a high basement;
- ease of adaptation to heavy objects by increasing the size of the heel and tape section, as well as the configuration of the tape itself;
- the option of using block material creates the opportunity to completely abandon the installation of Finnish formwork;
- the installation of such a foundation does not cause difficulties, the work is carried out by a small team of builders;
- since the load-bearing capacity is performed by the base and the heel located under it, in the future you will be able to easily repair communication lines, because the screed poured along them is “not connected” to the foundation tape;

- even after the construction of the house is completed, you can install a “warm floor” system and lay communications;
- the building materials and technological methods used can significantly reduce the total weight of the facility under construction;
- Finnish stoves perform well, maintain a comfortable microclimate, and save energy resources;
- the structure can be installed on any type of soil composition, even with shallow groundwater.
With all the advantages, it is fair to talk a little about the disadvantages. The main disadvantage is a lot of excavation work, which increases the cost of the structure. But this problem can be compensated for by the size of the base.
Precast concrete piles
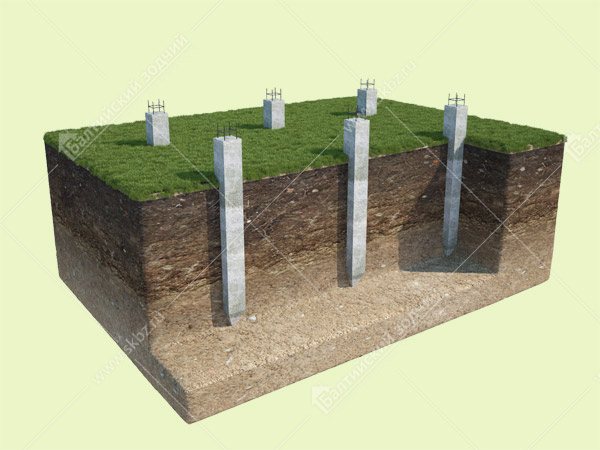

Reinforced concrete piles are solid structures with a square cross-section with transverse reinforcement.
The scope of application of these products is low-rise construction.
Advantages of reinforced concrete piles:
— Long period of operation, subject to technology (up to 100 years)
— Strength, a pile pierced with threads of stressed or unstressed reinforcement, can withstand the weight of multi-story buildings constructed from heavy panels.
— Stability, the concrete pile is immersed in the ground to a sufficient depth, which allows it to rest on stronger layers of soil.
— Suitable for all types of soil, as well as on difficult terrain (for example, with a slope)
Difference from USP
Let's look at how the UFF foundation differs from the USHP (insulated Swedish plate).
Finnish technology is often used to eliminate various shortcomings that exist in the case of “Swedish” stoves. One such example is a low base.
Some believe that a low base has a negative impact on the object. There are certain concerns that it will be covered in snowdrifts during snowy winters.
The “Swedish” option is more expensive, requires close attention, the use of special equipment, technical means, and the involvement of competent specialists.
The volume of excavation work is increasing, and installing a foundation using the USP method will cost a decent amount to pay for the entire range of necessary measures.
USP is considered a whole complex aimed at building a foundation. It contains a complex drainage system and communication interchange; certain knowledge is required. In comparison, the Finnish method seems simpler and more accessible.
Construction technology
The process of constructing a Finnish foundation consists of certain stages:
- the building site is inspected, the necessary calculations are carried out, design and estimate documentation is developed;
- the outline of the future pit is marked;
- a trench is developed for the installation of a shallow foundation strip;
- drainage is arranged from crushed stone;
- a layer of waterproofing material is laid;
- the support pad of the foundation tape is reinforced;
- block material is being laid;

- from the inside, the foundation base is insulated with expanded polystyrene slabs;
- all internal parts of the pit are covered with fine gravel and sand;
- floor insulation material is laid and reinforcement is performed;
- the heating system is installed according to the “warm floor” principle;
- concrete solution is poured;
- the area for the blind area around the entire perimeter of the object is insulated;
- The blind area is poured, construction waste is removed.
The foundation is ready; in cross-section, the Finnish slabs resemble a kind of layer cake.
Site marking, soil development
The building plot is marked out in accordance with the design specifications.
It is necessary to take into account the existence of external communication systems, access roads, construction areas and other factors.
The diagonals of the contour are indicated by stretched cords, which leave a margin of up to fifty centimeters from the outer walls of the object.

The turf layer of soil is completely removed. A trench is dug along the load-bearing walls, the depth of which corresponds to the design. A reserve is provided for the installation of bulk drainage.
Drainage system, underlying base, installation of foundation tape
Fine-grained crushed stone is poured into the prepared trench, the layer of which should be about twenty centimeters. The pillow is compacted and covered with geotextile strips.
After this, a layer of sand is poured, and you can install the formwork of the Finnish foundation strip, using plywood for this.
The frame base is knitted from reinforcement, which is laid in the formwork and filled with concrete mortar.
While the concrete gains the necessary strength, you can take time to level out the excess soil. Concrete blocks are laid on the hardened concrete strip, taking into account the estimated height of the base part. If it is large, experts recommend laying a mesh for reinforcement every three block rows.
The outer and inner surfaces of the base are insulated from the negative effects of moisture. For this purpose, pasting materials are used for waterproofing, and the internal walls are coated with mastic compounds.
Fill up the underlying layer, lay insulation material
From the inside of the basement, polystyrene foam boards are placed vertically, the thickness of which must be at least ten centimeters, and fixed to the walls. The excavated bottom is covered with geotextile strips and filled with crushed stone, which serves as a drainage system.
The backfill layer is carefully compacted.
Three layers of rolled material are laid on the crushed stone, the strips are coated with mastic and glued together into a single sheet. A certain margin is provided to wrap the edges onto the vertical walls of the base.
Slabs of insulating material are laid across the entire area of the pit to create a layer of at least twenty centimeters.
Reinforcement installation, pipe laying, concreting
The reinforcing layer is made from ready-made or home-made meshes, the cell size of which does not exceed fifteen centimeters. The heating system pipes are laid on top and fixed.
The length of the pipeline in a single circuit should not exceed ninety meters if the line diameter is fourteen millimeters. For sixteen-millimeter pipes, the contour length increases to one hundred and twenty meters. Taking into account the total area of the object, you will get several such contours.
It is recommended to complete the concreting process in one go, without technological interruptions. In this case, you should order centralized delivery of concrete mixture produced in a factory. During concreting, the supplied solution is constantly compacted by submersible vibrators.

We arrange a warm blind area
Crushed stone and sand are placed in the base and covered with rolled material. Insulation is laid on top, reinforced, and concrete mixture is poured. The width of the blind area of a Finnish foundation must be at least one meter; permanent formwork can be installed.
The concrete is laid at an inclined angle directed away from the walls of the house.
What is Finnish foundation
A not too expensive universal foundation that would be suitable for any soil, heavy and not very heavy walls - a builder’s dream. One of these foundations is Finnish (a conventional name adopted among our builders). In short, it is a shallowly buried strip with ground floors and an insulated blind area. Let's talk in more detail about how such a foundation is built, and why it is considered one of the best solutions for low-rise construction.
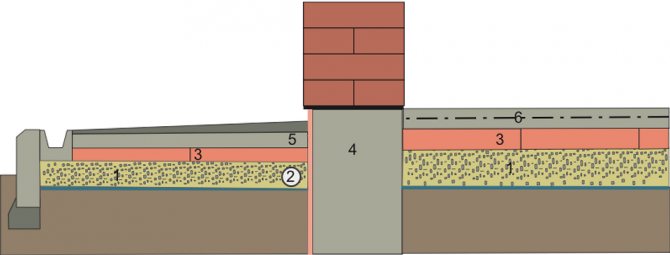
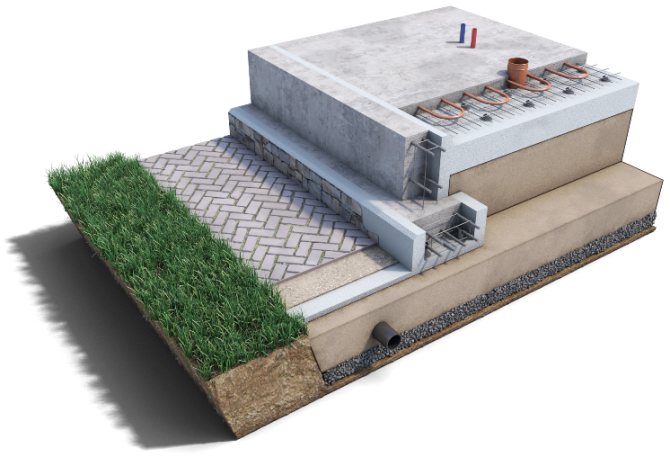
1—layer of sand gravel over geotextile; 2 - wall drainage; 3—EPS boards; 4 - reinforced concrete strip; 5 - blind area with a slope-forming layer; 6 - reinforced concrete slab (screed).
Insulated Finnish foundation
Based on their name, it is clear that this type of foundation comes from Finland and it is somehow insulated for some reason. Indeed, the Finns are the founders of this solution; it is cold in their country and they initially designed such foundations to suit their climate.
In Finland, where there is no oil and gas, but only trees and stones, there are strict standards for quality and heat conservation. The foundations are made quite strong and are effectively insulated. Maximum savings on traditionally expensive coolants (gas, diesel fuel, electricity) are beneficial both for each individual family in particular and for the entire country as a whole. Everything is simple, clear and reasonable.
The characteristic visual distinctive features of an insulated Finnish foundation (or UFF for short) are a stone load-bearing tape, not made of concrete like ours, but of rectangular gray blocks, pipes of all kinds of communications protruding from the concrete screed and terrace posts, made of the same as the tape, gray blocks, only now square.
Such blocks are not accidental; they are expanded clay concrete, a high-quality material with an unusual shape of blocks made specifically for such a foundation strip. Why expanded clay concrete? Expanded clay concrete block (CBB) is much warmer than the concrete we are used to, because... Expanded clay itself (fired clay) is a porous material in its structure; it has many air chambers that perfectly retain heat, this is a big plus.
In addition, such air chambers located between the expanded clay particles allow water, when freezing in the off-season, to expand freely without the risk of concrete destruction, this is another big plus.
The wall foundation block is rectangular, has two grooves for laying reinforcement in them, the terrace block is an octagon with a hole inside, again for laying and pouring reinforcement. This solution is clear and very easy to use.
The pipes sticking out of the screed are nothing more than water, sewerage and heat. The entire engineering cycle has already been completed in such a foundation, this is a huge plus, because There is no need in the future to invite various kinds of specialists to install communications in the house, pay money for it and waste time on it. The boiler is simply connected to such a stove and the required floor covering is laid. Fast, reliable and convenient.
What is good about an insulated Finnish foundation? Such a foundation is insulated (more on this later), it is slab, does not spring or sag when walking, is not limited in the height of the basement, all the necessary communications are already located in it, the heating system of the house is equipped with heated floors and additional heating radiators, it is protected outside from water and freezing, at the same time it is very durable, extremely reliable and, in fact, is a turnkey, high-precision engineering solution with unique heat-saving characteristics.
Technology, advantages, disadvantages, differences from USP
Frame houses have now become very popular, and one of the main questions facing the developer is - on what foundation to build a frame house? Among the various types of foundations suitable for building a frame house, most of which we have already covered on our website in the Foundation section, there is one more worthy of attention, this is the UFF - insulated Finnish foundation. Which, by the way, is very popular in Scandinavian countries, in particular in Finland, in contrast to USP, which is not popular in Sweden.
This type of foundation is similar to the more famous and widespread foundation in our country - USHP - insulated Swedish slab. But, despite the functional similarity, they also have differences. Let's look at the main differences between these foundations and the features of UFF.
So how does UFF differ from USHP: • UFF has a higher base, usually it is at least 40-50 cm • UFF insulation is done in rooms, and not over the entire area of the house, as in USHP • UFF has wider possibilities for installation on an area with height difference • cost of UVF is 10-15% higher
The higher price of UFF is mainly due to the height of the base, the high consumption of bulk building materials and the high labor costs during construction.
Advantages of UFF: • high base • warm floor, separately in each room
Disadvantages of UFF: • high price, like any slab foundation, but even higher than the price of USF • technologically advanced, difficult to repair • large investments at the first stage • cannot be done in stages, immediately after gaining strength with concrete it is necessary to build a house, because it cannot be left for the winter without a house covering it from above • a warm floor cannot be used for rare warm-ups in winter, it must work all season
Advantages of the Finnish foundation
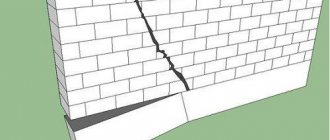
An ordinary shallow tape is subject to the forces of frost heaving. Theoretically, it should rise evenly in winter, and after the soil thaws, it should also fall evenly. Here are just small differences in the load (for example, if one part of the building is lower and, accordingly, lighter than the other), as well as quicksand often lead to the fact that the tape settles into the ground with a distortion or becomes deformed (if the reinforced frame cannot withstand). As a result, the building tilts or cracks appear in the masonry above the openings. In the Finnish version, the insulated blind area prevents the ground from freezing and the foundation does not “float”, so distortions are excluded.
With a conventional strip foundation, as a rule, a beam ceiling of the first floor is erected. Even with good underground ventilation, it deteriorates quite quickly. The service life of the structure usually does not exceed 30 years. In the Finnish version, concrete floors are laid on the ground - they are almost eternal.
The concrete base of the floor simplifies the installation of a water-heated floor . This system, combined with a massive slab with significant thermal inertia, ensures maximum living comfort in winter, and in summer such floors keep cool and allow you to save on air conditioning.
Field of application of UVF
Studying the technical characteristics of an insulated foundation made of Finnish slabs, we can confidently say that such a structure can be used in areas with different climatic conditions, is suitable for any soil composition, and can withstand loads of up to three tons per linear meter of strip foundation.
Each of the given characteristics corresponds to the majority of frame-type structures under construction, the height of which reaches two floors.

By increasing the supporting base of the foundation strip, it is possible to add the mass of the building structure at the rate of four to five tons. But in this case, it is necessary to perform a mandatory verification calculation using the strip foundation method.