Choosing a foundation for a country house or country house can be a serious problem for a novice builder. After all, the correct installation of the foundation of a house depends on a lot of factors - from the groundwater level to the type of soil. How not to make a mistake?
The foundation is a load-bearing structure that bears the main load from the structure. It distributes pressure evenly and prevents the building from sagging and sinking into the ground. There are several types of foundation. But which one should you choose?
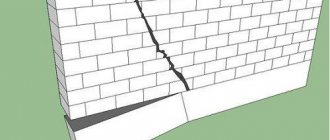
A strong foundation is needed even for small buildings
Before building the foundation...
Before starting any work on the construction of the foundation, it is necessary to at least carry out geological exploration and design and survey work on the site. They will help you take into account many important parameters. In particular:
- terrain ;
- presence and level of groundwater ;
- soil condition and soil type ;
- soil freezing depth;
- presence and location of underground communications on the site;
- seismic activity.
Strip concrete foundation is suitable for almost all types of terrain
At the design stage, other factors are determined:
- number of floors , presence of a basement , total area of the building;
- design features and total load of the building’s load-bearing structures;
- planned service life of the building (temporary or permanent structure);
- the material from which the building will be constructed.
Construction of the foundation taking into account the topography and groundwater
Let's consider which types of foundations are better suited for a particular topography, taking into account the depth of groundwater.
| Nature of the relief | Pile foundation | Strip foundation | Surface monolithic slab | Recessed monolithic slab with basement |
| Flat | + | + | + | Geological soil survey required |
| Smooth slope | + | + | Requires site leveling or terracing | Geological soil survey required |
| Rugged slope | + | Geological soil survey required | Geological soil survey required | Geological soil survey required |
| Level hills | + | + | Requires site leveling or terracing | Geological soil survey required |
| Rugged hills | + | Geological soil survey required | Geological soil survey required | Geological soil survey required |
| Groundwater | ||||
| Superficial | + | Requires drainage and dewatering (irrigation) | + | Construction is not recommended |
| Below the foundation level | + | + | + | Requires ring drainage around the perimeter of the foundation |
The depth of the foundation depends on the level of groundwater. To accurately determine the depth and “pattern” of water in the area, several wells are drilled, soil samples are taken and a chemical analysis of the water is done. For the construction of a light frame, wooden house, garage or barn, the groundwater level can be from 5 m and below . For a brick or stone permanent structure, groundwater should not lie above 7-10 m .
However, with a well-designed drainage system, these values can change downward.
Sand pillows
It is advisable to use the construction of a foundation on sand cushions to save building materials, to partially or completely replace unsuitable soils at the base, and to raise the floor above the level of shallow groundwater. To build them, sand is poured into pits in layers, which are carefully compacted and watered. In heaving-hazardous soils when freezing, it is not recommended to install such a foundation without drainage. Otherwise, the pillows may silt, which will lead to a loss of their original properties.
Foundation depending on soil type
First of all, do not forget that the foundation and soil will form a single system. Subsequently, three more factors will be added to them: air temperature , building weight and groundwater . Therefore, there will be three main questions when constructing a foundation:
- Will the soil-foundation bond withstand temperature changes in your region?
- Will the foundation withstand the load created by the building, and to what extent will it be transferred to the ground?
- what impact will groundwater have in the warm and cold seasons?
Prefabricated monolithic foundations are considered the most resource-intensive
The possibility of installing one or another foundation, depending on the characteristics of the soil, is presented in the table.
| Soil condition | Movable lightweight structure | Fixed heavy structure |
| Deep layer of hard soil | Foundation:
| Foundation:
|
| Deep layer of compacted soil | Foundation:
| Foundation:
|
| A layer of soft or loose soil on a solid base | Foundation:
| Foundation:
|
| A layer of soft or loose soil on a soft base | Foundation:
| Foundation:
|
| Alternating layers of hard and soft soil | Foundation:
| Foundation:
|
buried foundation ( profile ) means any foundation installed below the maximum freezing point of the soil. It is used in the construction of multi-story and long-term structures made of brick or wood lined with brick. Such foundations are designed for maximum service life and are slightly susceptible to soil fluctuations and temperature changes.
Recessed stone-brick foundation is a reliable solution for long-term structures
A shallow or shallow foundation is installed at a maximum depth of 50 cm. It is better suited for the construction of temporary structures, garages, bathhouses, wooden houses, frame or panel outbuildings.
Is it possible to use screenings to prepare concrete?
Screenings can be added to concrete as a fine filler instead of sand. Its task is to evenly distribute the load after the solution hardens and ensure the volume of the finished product. After all, the screening fills the gaps between the grains of crushed stone and improves the adhesion between different components.
The following advantages of screening in the use of concrete can be identified:
- Unlike sand, screenings contain more particles of different sizes: some are less than a millimeter in diameter, others can approach 10 mm (in the 0-10 fraction). Thanks to this, they better fill voids in the concrete mixture.
- Small particles (with a diameter less than 0.16 mm) are capable of reacting with cement. As a result, insoluble calcium hydrosilicates are formed, which increase the strength of concrete.
- The edges of the screening grains are not rounded, which ensures their good adhesion to cement.
- Based on screenings, it is possible to make heavier concrete, since the weight of a unit volume of material is greater than that of sand.
- If you partially replace crushed stone with screenings, you will get concrete of higher density and strength. At the same time, you can save on cement without increasing its amount in concrete.
From the information above we can conclude that screening is well suited for concrete. In many respects it is even superior to sand. In addition, in the Sverdlovsk region its cost is lower than sand. This is due to the fact that there are practically no sand quarries in our region. Therefore, sand costs almost twice as much as screenings. For this reason, even concrete plants in the vicinity of Yekaterinburg are working on screenings.
Foundation material
The foundation is made of durable materials, although sometimes even wood or sand . Here are brief characteristics of each type of foundation.
| Foundation material | Characteristic |
| Brick foundation | Can only be laid on dry soils. On wet soils, it is permissible to lay baked clay bricks . It is not recommended to build this type of foundation at elevated groundwater levels. Suitable for constructing permanent and multi-storey structures made of almost all materials |
| Rubble foundation | The basis of the rubble foundation is large cobblestone or flagstone . The foundation is strengthened using cement mortar. Rubble foundations remain stable on heaving soils and are suitable for deep foundations. Can withstand buildings of almost any number of floors and sizes |
| Rubble concrete foundation | For its construction, concrete blocks or mixtures are used, which are laid in layers. The walls can be located at different heights and can be given any configuration. Buildings of any complexity, number of floors and layout can be erected on a rubble concrete basis |
| Reinforced concrete foundation | The strongest and most durable type of foundation. Does not “float” even on heaving soil. There are monolithic and prefabricated types. Buildings based on it are built “to last forever” |
| Sandy foundation | An ideal option for the construction of temporary buildings, one-story houses and buildings with low traffic. It is good to lay it on non-flowing soils and a flat surface |
| Wooden foundation | Rarely used in the middle zone. Mainly for the construction of small buildings: bathhouses, gazebos, canopies, summer kitchens, greenhouses. Withstands minor deformation and is easy to install. Disadvantages - short service life and low strength |
Screening proportions for concrete
The strength of concrete largely depends on the ratio of its components. The classic solution includes cement, crushed stone and sand. Screenings can completely replace both sand and crushed stone. Fine-grained varieties of concrete are often made from screenings and cement only.
The table shows the ratios of components for different grades of concrete with partial replacement of crushed stone and sand with screenings. The mass of cement (grade M400) is taken as a unit:
| Concrete grade | Weight of cement for the production of 1 m3 of concrete (kg) | Mass fraction of crushed stone | Mass fraction of sand | Mass fraction of dropouts |
| M100 | 214 | 6 | 3,6 | 2 |
| M150 | 135 | 4,6 | 2,6 | 2 |
| M200 | 286 | 3,9 | 1,7 | 2 |
| M250 | 332 | 2,8 | 1,3 | 2 |
| M300 | 382 | 2,5 | 1 | 2 |
| M350 | 428 | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2 |
In order to find out the required weight of each component to prepare 1 cube of concrete, you need to multiply the mass fraction by the weight of the cement. Let's explain with a specific example.
Let's assume that you need to prepare a concrete solution M150.
Here is the amount of materials you need to take for this:
- Cement – 135 kg
- Crushed stone – 135×4.6=621 kg (where 135 is the weight of cement, and 4.6 is the mass fraction of crushed stone)
- Sand – 135×2.6=351 kg
- Elimination – 135×2=270 kg
Water should be added to the resulting mass (20% by weight of dry ingredients).
Thus, we have a mixture weighing 1377 kg. You need to add 275.4 liters of water to it (1377x20:100).
The following table shows the indicators for complete replacement of sand and crushed stone with screenings:
| Concrete grade | Weight of cement for the production of 1m3 of concrete | Mass fraction of dropouts |
| M100 | 214 | 10,6 |
| M150 | 135 | 8,2 |
| M200 | 286 | 6,6 |
| M250 | 332 | 5,2 |
| M300 | 382 | 4,5 |
| M350 | 428 | 3,8 |
To find out the amount of screenings (in kg), you need to multiply the weight of cement by its mass fraction given in the table.
For example, to prepare a cube of M200 concrete you will need 286 kg of cement and 1887.6 kg of screenings (286 × 6.6).
You also need to add 15-20% water from the total amount of dry ingredients to the mixture.
So, when making a cube of M200 concrete, you use 2173.6 kg of dry mixture (286 + 1887.6). Therefore, you will need 434.72 liters of water (2173.6x20:100).
Next we will tell you what other fillers can be used in concrete mortar instead of screenings.
Determining the depth of soil freezing
First you need to find out the average depth of soil freezing in your region. In recent years, the weather has become capricious, with severe frosts alternating with prolonged thaws and an almost complete absence of snow. However, general rules exist for all climate zones.
When building a foundation, you must have a blueprint for your future home.
For unheated rooms, the freezing depth is taken with a margin of 10% relative to the average. It is measured from the ground level, and in rooms with a basement - from the estimated floor level of the basement. For heated premises, the freezing depth should be reduced by 20-30%.
A foundation built below the freezing depth does not guarantee protection against soil swelling as a result of severe frosts.
To eliminate deformation, builders often resort to tricks. For example, they reduce the area of the lateral surface of the base, give it a trapezoidal shape, cover it not with earth, but with non-heaving soil, etc.
Examples of foundations for specific structures
Here is a summary table of foundations and the areas on which they are located.
| Foundation type | Soil characteristics | Building height and permissible load | Device, material consumption, labor costs |
| Monolithic or prefabricated monolithic slab | All types of weak-bearing and highly compressible soils (heaving, sandy) | Any, with significant loads, reinforced reinforcement is required | The most complex and expensive, requires a lot of materials and labor |
| Tape | Most species, except very heaving and swampy ones | The design and permissible load are selected based on calculations | Used for all types of buildings, except high-rise ones. Suitable for creating warm basements |
| Columnar | Relatively stable soils | Best suited for frame structures | Allows you to significantly reduce construction costs |
| Pile | Weak surface soils on a more reliable foundation (piles are driven to reliable soil) | Often used for the construction of high-rise buildings, in low-rise construction it is used to save money | Requires a grillage; special equipment is used to drive piles to great depths |
Now we give examples of specific foundations and structures that can be built on their basis:
| Foundation type | Structures that can be built |
| Monolithic slab | Houses made of reinforced concrete, buildings made of brick, buildings made of stone, houses made of wood with several floors |
| Strip foundation | Wooden houses, block buildings, brick and stone buildings of small and medium weight, aerated concrete structures, extensions, bathhouses, garages, gazebos, fences. |
| Columnar foundation | Small houses made of lightweight materials, lightweight frame-type buildings, fences and fences, utility rooms, small bathhouses |
| Pile foundation | Small buildings with a total weight of up to 2.5 tons |
The next stages: reinforcement of the reinforcement frame and pouring of concrete.
Reinforcement is performed in two belts. Bottom belt - 4 longitudinal reinforcements at a distance of 3–5 cm from the edge on each side and 5 cm from the bottom edge of the foundation. The upper reinforcement belt is similar to the lower one. Vertically, every 70–90 cm, the reinforcing frame is tied with vertical reinforcement. The foundation is poured with concrete based on a grade of at least 250. After pouring the foundation, it is advisable to let it settle for at least two weeks. Then you can begin assembling the panel-frame house. To drain water from the foundation, a blind area is made around the entire perimeter of the house.
Reinforced concrete structures will become the reliable foundation required by prefabricated country houses, cottages and high-rise buildings.
Their main advantages:
- ability to repel moisture;
- resistance to soil freezing and resistance to temperature fluctuations;
- increased density, which plays an important role for the foundation;
- resistance to any chemical elements that may enter the soil.
Advantages and disadvantages of each framework (conclusions)
In addition to the characteristics of the foundation, the characteristics of the site should be taken into account. It is to this that you will first have to adapt. Let's summarize the information about each type of foundation.
Slab base
Advantages:
- long service life;
- Suitable for laying on most soils;
- foundation installation work takes little time;
- the base is one of the most durable due to the uniform distribution of the load.
Flaws:
- not suitable for temporary buildings;
- It is problematic to fill such a foundation alone;
- the most expensive type of foundation.
Tape base
Advantages:
- a house is built on it from almost any material (brick, blocks, wood, etc.) and a strip base of any configuration;
- you can build it yourself;
- material consumption is minimal;
- option is suitable for most soil types;
- you can change the width and depth of the foundation.
Flaws:
- If the building is too massive, the foundation may not be able to support it;
- it is impossible to construct a strip base in places with a significant difference in height;
- the strength of the structure decreases due to severe frosts and heat.
Device principle
First you need to dig a trench under the external and load-bearing walls of the future house. The trench is made 40–60 cm wide and 70–80 cm deep. 30-40 cm of sand is poured into the bottom of the trench. To compact the sand, it is compacted and spilled with water. If the landscape of the site has a significant slope, then the lowest point of the foundation should be at least 20 cm from the ground surface. Then the formwork is set to a width of 40 cm and a height of 50 cm. It is better to make the formwork from OSB or thick laminated plywood, but ordinary boards can also be used.