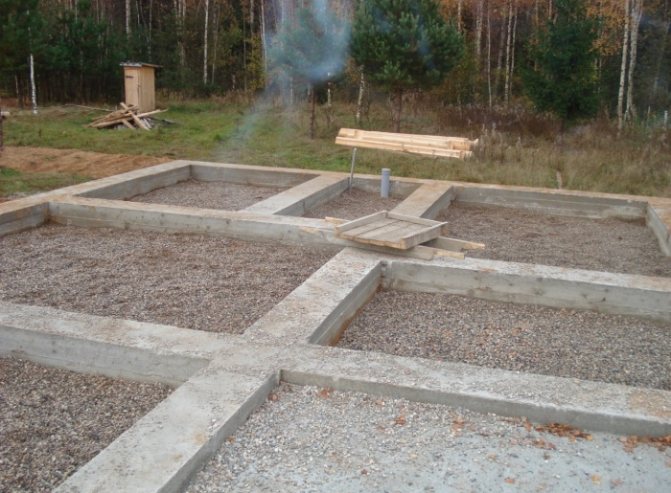
A strip foundation for a frame house is constructed on dry and heaving soils. Adhering to simple technology, many build it themselves.
Pouring a strip foundation requires the ability to work with concrete.
Types of strip foundations
Construction of a frame house
Strip foundations are divided into types according to their design:
- monolithic - this type is installed directly on the construction site;
- prefabricated - this foundation includes foundation pads and blocks manufactured at the factory and installed at the construction site;
Based on depth, strip foundations are divided into:
- shallow;
- buried.
For the construction of a frame building, a shallow monolithic one is more suitable. It has the form of a base that runs along the entire length of the load-bearing walls and is buried no more than half a meter. In winter and spring, this foundation, together with the soil, rises upward, and then returns to its original position. In this regard, there is no deformation of the main structural elements of the building.
Construction technology
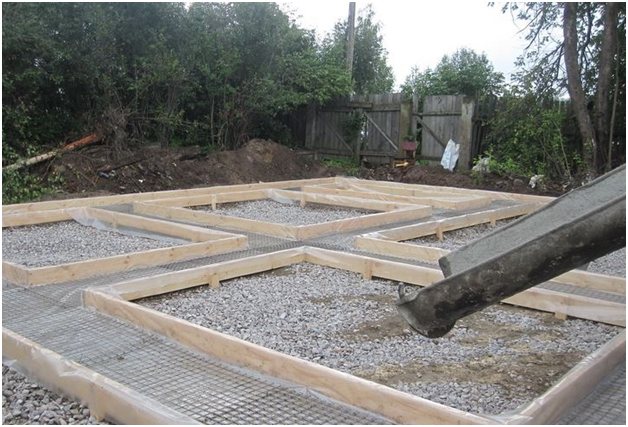
To build a strip foundation , it is necessary to mark out the building site, remove the soil, install formwork, and lay concrete after installing the reinforcement frame. In this case, technologies are used to reduce heaving forces harmful to reinforced concrete.
First, drains are laid (the level of the base of the tape), then the soil under it is replaced with crushed stone and sand. Then the blind area is insulated, allowing the geothermal heat of the subsoil to be retained under the building.
Waterproofing all concrete surfaces dramatically increases the service life of the cottage's load-bearing frame elements operating underground.
Full-scale axle offset
Since to install the foundation it is necessary to make trenches, transfer the drawing from the project to the building site, marking is necessary. The removal of the wall axes occurs as follows:
- object reference - the corner of the home should be 5 m from the center of the street, the driveway, the border of the site - 3 m, it is worth taking into account the location of the septic tank, water intake source, communication wells (3 - 10 m, respectively)
- cast-offs - used instead of pegs, consist of two vertical bars, pointed at the bottom, with a horizontal board between them (60 - 80 cm), mounted 1 - 1.5 m from the edge of the trenches
3 strings/cords are pulled along the cast-offs (the side edges of the tape + the axis of the wall), which can be removed during excavation work and installed back after completion. A frame house must have identical diagonals, so the axes are laid out at right angles to each other using the triangle method with a hypotenuse of 5 m, legs of 4 m, 3 m. SP standards allow an error of 1 cm.
Drainage
Any foundation requires drainage, constructed using external underground sewerage technology:
- production of trenches - they run along the perimeter of the building at the depth of the base of the MZLF, have a cross-section of 50 x 50 cm, a general slope towards the underground tank, where the stacks will be collected by gravity (4 - 7 degrees)
- underlying layer - 10 cm of compacted crushed stone 5/20 mm over geotextile (the edges need to be extended onto the sides of the trench to cover the entire structure from above with the material)
- installation of wells - vertical pipes with a plugged bottom 30 - 80 cm in diameter in the corners of the cottage to clear clogged areas from the surface of the ground
- laying drains - pieces of perforated corrugated pipe (two-layer winding with dornite/geotextile), interrupted inside the wells
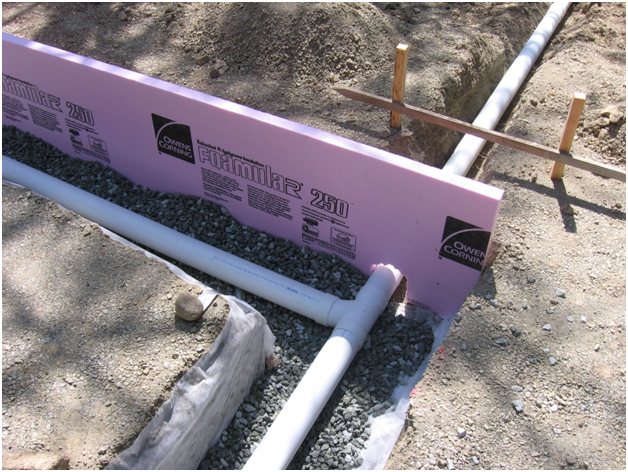

After that, all that remains is to fill the trenches on the sides and top (10 cm) with crushed stone so that the frame house receives reliable protection against swelling.
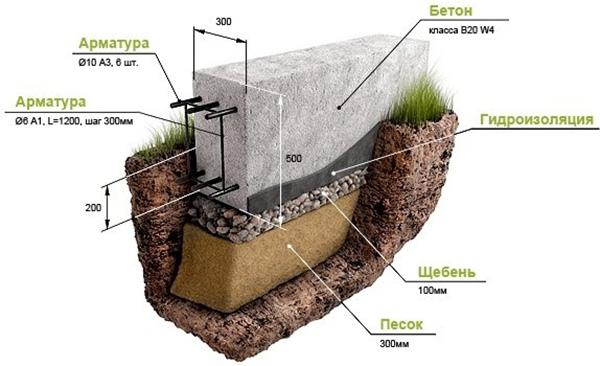
Bedding, footing
To prevent cracking of the foundation from swelling and leveling the bottom of the trench, 40–80 cm of non-metallic material, compacted in layers (every 10 cm using a vibrating plate), is required. There are several schemes for inert cushion (depending on the geological conditions of the building):
- crushed stone to the full depth - at high groundwater level
- sand 40 – 60 cm – with low groundwater level reduces the construction budget
- crushed stone + sand – equal thickness with low design soil resistance
- sand + crushed stone - with a possible seasonal rise in groundwater level

The following problems are solved by footing:
- no maintenance of cement laitance when pouring
- protection of waterproofing carpet from punctures by crushed stone
- reduction of the lower protective layer for reinforcement

The footing is a 5 - 7 cm screed made from a mixture of grade B7.5 (lean concrete). It is poured into formwork, the width exceeds the size of the tape by 20 - 40 cm for reliable support.
Plantar waterproofing
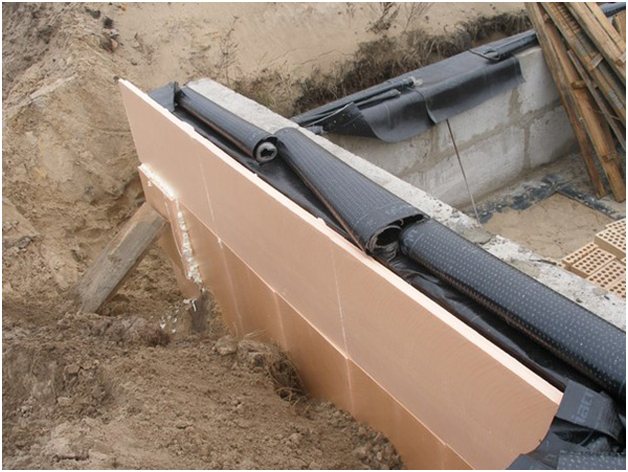
A membrane, 0.15 mm polyethylene film is laid on the screed, or roll waterproofing (TechnoNIKOL, Bikrost) is fused. It is necessary to protect reinforced concrete structures from soil moisture and pressure water.
A frame house consists almost entirely of lumber, which absorbs any moisture. Therefore, reinforced concrete surfaces must be waterproofed later.
Formwork
Depending on the depth of the tape, formwork of different designs can be used:
- plank, plywood panels - at a depth of 40 - 70 cm
- L-shaped polystyrene modules - for non-buried strips, belts
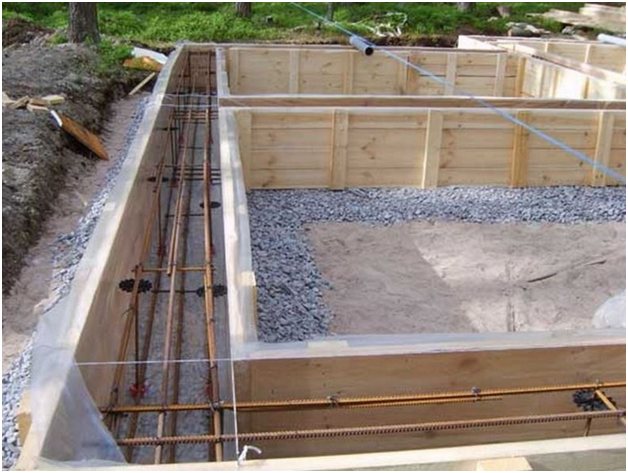

In order for the house to have a stable spatial geometry, heaving forces are eliminated by insulating the outer surface of the MZLF and blind areas. Thermal insulation can be placed in the formwork (pressed against the outer panel from the inside) or this material can be used to cover the side of the tape after stripping.
To maintain the geometry of the foundation, it is recommended to use a board with a thickness of 4 cm (guaranteed no deflection when laying concrete). The spacing of the jibs on the outside of the boards is 30–50 cm, the lintels in the upper part are similar.
Reinforcement cage
Concrete structures work exclusively under compression from the forces exerted on them by the house , snow/wind, and operational loads. Therefore, the foundation is reinforced with two belts of longitudinal rods, which absorb tensile forces during possible heaving of the soil. The main requirements are:
- minimum percentage of reinforcement – 0.1 – 0.3%
- selection of reinforcement section - by calculation depending on bending moments
- providing a protective layer – 2 – 7 cm
- rational schemes for tying connections - U-shaped clamps, rods bent at right angles
- overlap, connection of rods - at least 40 - 60 cm, spacing of joints of adjacent rows 60 - 80 cm
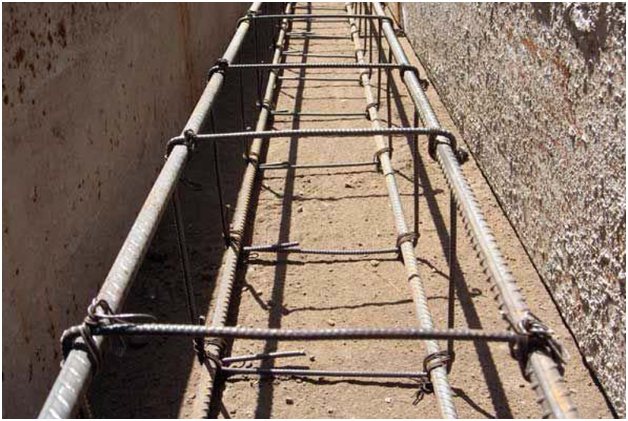

In individual construction, taking into account the minimum weight of “frameworks,” A400 reinforcement (longitudinal rods) with a periodic section of 8–16 mm is used. Clamps, transverse and vertical jumpers are made from smooth A240 reinforcement. They are bent exclusively in a cold way; heating is strictly prohibited. The reinforcement method looks like:
- production of frames - for straight sections, longitudinal rods (usually 2 upper + 2 lower) are tied with rectangular clamps (step 30 - 60 cm)
- laying - frames are placed on concrete or plastic spacers inside the tape
- couplings - straight frames are connected in corners, T-shaped junctions with U-shaped clamps or L-shaped anchors
Lateral protection of the frame is provided by plastic elements placed on longitudinal bars or clamps.
Concreting
To ensure that the house has the maximum possible resource, concrete grades B15 - B25 are used, laid in layers (60 cm maximum) for subsequent compaction with deep vibrator attachments in one direction. If, at the stage of preparing the mixture, the penetrating composition Admix is introduced into it, the concrete will receive water-repellent properties by default. You won't have to waterproof it later. The mixture can be added to a mixer ordered by the developer at the construction site.
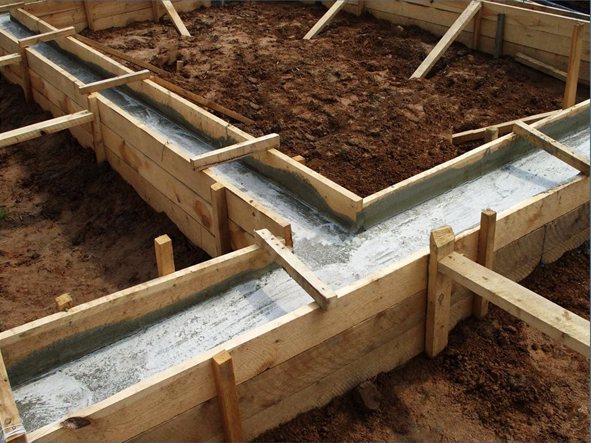

With sufficient compaction (5 - 10 seconds), the concrete almost instantly restores a flat surface when the vibrator attachment is removed. Cement laitance appears on the surface, the formation of bubbles stops, and the large filler is completely hidden inside the structure.
Waterproofing
To protect the foundation from getting wet, which leads to cracks opening in winter, all edges of the MZLF are waterproofed using the following technology:
- primer – produced by primers to increase the adhesion of the surface to waterproofing materials
- coating - epoxy, bitumen mastics in two layers to form a film with a 15-20 year lifespan
- pasting - hydroglass insulation, TechnoNIKOL, Bikrost, other rolled materials in two layers
- volumetric waterproofing - penetrating compounds are used, after entering into a chemical reaction with cement, the structure of concrete is changed to the entire depth

The first three methods are usually used in combination, but are still inferior to volumetric waterproofing, which has an unlimited resource.
Thermal insulation
In combination with measures already taken to prevent heaving, thermal insulation of the blind area and outer edges allows you to completely protect the frame house from heaving forces. The walls of the MZLF are covered with a 5 cm layer of extruded XPS polystyrene foam. PSB-S polystyrene sheets of similar thickness are laid under the blind area at a depth of 30–40 cm.

If the technologies specified in this manual are followed, the house is guaranteed to last three to four generations of owners. Advice from professionals will help you avoid mistakes, ensure comfortable operation, and a long period between repairs of the building.
Strip foundation calculations
Before making a foundation for a frame house, you need to make the necessary calculations. Foundation calculations depend on:
- types of soil at a construction site;
- presence of a basement in the house;
- determining the size of the house and the materials used, and ultimately all the loads on the house;
- availability of groundwater and depth of soil freezing.
Calculations of a strip foundation for a frame house
Soil characteristics are carried out in special laboratories. You can take soil samples from the construction site yourself and take them to the laboratory, or you can call geological engineers. It depends on your financial security. If you decide to conduct the research on your own, then you first need to dig a 1.5 m trench and examine the soil from it. You may have the following soil types:
- rocky;
- sandy;
- clayey
- rocky;
- gravel.
Gravel soil is best suited for foundations. It does not swell and does not retain moisture. And fine sandy soil is practically unsuitable for construction. Clay soil causes displacement.
When calculating the total load on a house, you can use this method: 1 linear meter of a house with a wall height of approximately 3 m weighs 1.7 tons. If the house has one floor, then multiply the perimeter by 1.7. And if the house has two or more floors, then the perimeter of the house is multiplied by the number of floors and by 1.7. It must be remembered that the fate of the entire house depends on the durability of the foundation.
Construction of the foundation
Advantages and disadvantages
This type of foundation has many advantages:
- lack of requirements for highly qualified performers;
- The slab foundation is stable because it presses evenly on the ground. In addition, it has an extremely low specific gravity;
- this type of foundation can be erected even in places with high groundwater levels (due to the absence of large depths).
But there are also disadvantages:
- excavation work is still in demand because: it is necessary to remove the soil layer to the freezing depth;
- it is necessary to level the site for the base;
Ready slab foundation
Strip foundation device
There are the following stages of construction of a strip foundation:
- Foundation marking
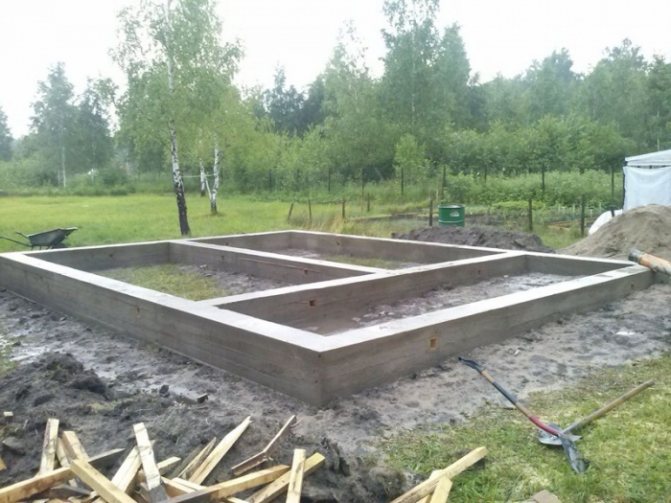
When all the materials and tools are prepared, it is necessary to mark the building in relation to the walls and facades. You need to clearly know where the foundation will stand. You also need to calculate the dimensions of the strip foundation for a frame house. After the calculations, the foundation is marked. For marking, use pegs and a rope stretched between them. Stretch the next row of ropes 10 cm more than the width of the walls. It is also necessary to make the corners straight. To do this, use a laser meter, or simply measure and compare the diagonals.
After this, according to the markings, they dig a trench half a meter deep. Sand preparation is laid at the bottom of the trench and filled with water.
- Construction of a strip foundation.
The next stage is the installation of formwork:
- Foundation waterproofing. First, waterproofing is laid on the sides of the trench surface. This may be a layer of roofing felt. But the disadvantage of roofing felt is that after a couple of years it will begin to peel off from the surface and the waterproofing will have to be repeated. Keeping pace with new technologies, Penetron can be used as a waterproofing material, which is added directly to the concrete mixture. It will make the foundation an impenetrable structure.
- Formwork installation.
Edged boards 5 cm thick are laid vertically on top of the waterproofing. It is recommended to knock down boards from the inside, and nails are directed from the outside. There should be no gaps between the boards. Most often, boards made from coniferous trees are used for formwork. Boards made of aspen and alder are allowed. They should not be damp and no more than 150 cm wide. The boards should be 30 cm above ground level. Reinforcement of a strip foundation for a frame house - Reinforcement of strip foundation. Reinforcement with a diameter of 10 to 16 mm is placed in the middle of the formwork, pre-cleaning it of rust and dirt. Before installing reinforcement, it is necessary to carefully inspect the formwork and eliminate all defects. The reinforcement is tied with wire or welded. Welding has the disadvantages that with this method of connecting reinforcement, the flexibility of the reinforcement decreases. You can knit the wire with pliers or use an automatic gun. About 5 cm of the top should be left without reinforcement, so that subsequently all the reinforcement is covered with concrete mixture.
- Concreting. After this, the formwork is filled with concrete. Concrete is made from M500 cement, sand in a ratio of 1:3, gravel and water. Sometimes plasticizers are also added. They provide strength to the foundation. The consistency of the concrete mixture should be neither liquid nor dry. It looks like thick sour cream.
You can either buy the concrete mixture ready-made or make it yourself in a concrete mixer. First, bulk materials are poured in, and then water is added. The concrete mixture is poured into the formwork to the specified level and leveled. The foundation is poured in several passes, since the amount of mixture is very large. The gaps between approaches should be no more than a day. You need to monitor how the concrete mixture behaves.
A vibrator is used to compact concrete. It removes remaining bubbles from the inside so that pores do not form in the concrete. The vibrator reduces the adhesion of the concrete and the concrete mixture is well compacted. When the foundation dries, it is covered with waterproof material. This prevents cracks from forming.
It will take about two days for the concrete mixture to harden. But the foundation gains strength within a few weeks. If you decide to build a bathhouse in parallel with the house, then after pouring the foundation for the house, you should begin constructing a strip foundation for the frame bathhouse.
Design selection and sizing
All types of strip foundations are built for lightweight frame buildings. The differences between them are in the installation method, materials and depth of installation.
The structure can be monolithic or prefabricated. In the latter case, concrete blocks are used, which are fastened together with cement mortar and reinforcement. The monolith is a continuous ribbon of rubble and crushed stone.
Foundations also differ in depth, which depends on the type of soil. Shallow ones are built on slightly heaving and dry soils. If the heaving is strong, buried ones are arranged. A minimum of equipment will allow you to make a strip foundation of any type. Each of them requires drainage work, insulation, waterproofing, and the installation of a sand cushion. These measures increase the service life of the foundation.
On slopes, the structure is subject to large shear forces, so installing belts there is not recommended. On fine sandy soils and embankments, the base is expanded with a concrete slab.
Tape depth
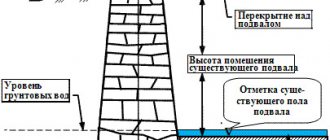
The depth of the strip foundation depends on the region where the structure is being built, as well as the total weight of the structure.
The weight of frame buildings is small, so the foundation for them is laid at a depth of 0.4 to 0.7 m. If construction is carried out in the northern region, where the soil freezes heavily, a different approach is required. The formula is used: the depth of the foundation base is 30 cm greater than the seasonal freezing of the soil.
Shallow foundations are built for lightweight structures. Recessed foundations are stronger and less susceptible to soil heaving. They are used mainly if they plan to build a basement under the house. Then the concrete base serves as its walls.
Laying a foundation deeper than 2.5 m is not recommended. If the bearing layers are lower, instead of building a strip foundation, another foundation option is used - installing supports from pillars.
Width, height of structure
Frame buildings are secured to strapping laid on top of the foundation. It is made of a reinforced concrete beam or wooden beam with a standard width of 15 cm. For the strength of the structure, the width of the concrete base itself should be 30-40 cm. If you plan to line the frame with brick, increase it to 50 cm.
The height of the tape should exceed the width by 2-4 times, which under standard conditions is 0.6-1.2 m.
Features of clay soil
Before creating a shallow foundation on clay soil, you need to remember its characteristics. The main rule to follow when building on clay areas is to be careful.
This type of soil is divided into several types:
- Loam. In such soil the percentage of clay is 10.
- Sandy loam. Such soils are a mixture of clay and sand.
- Clay. This type of soil has maximum clay content.
Before you start work, you should remember that the soil has the following features:
- softness;
- ability to change shape;
- change when wet.

Taking into account the characteristics of clay, experienced builders create formwork already in the process of creating a trench, since the walls of the recess can collapse. Before starting to create a foundation, you should determine the type of clay. It is divided into red and blue. The first type of soil contains a larger amount of sand. Such soil easily allows moisture to pass through and is more susceptible to change.
Blue clay has higher strength. That is why it is less susceptible to destruction. To accurately determine the type of soil on the site, you should seek help from specialists.
How to prepare the site
Preparation involves performing the following work:
- Removing vegetation on the site. Before creating a foundation in the area next to the future building, it is necessary to remove trees, grass and stumps. It is also important to remove all debris from the site.
- Moving the fertile layer of soil to the edge of the site. It is best to remove the fertile layer.
- Preparation of access roads for heavy equipment.
Only after such work is carried out is marking created on the site using pegs and a cord.
Materials for creating a foundation
The strip base for the frame structure is created using the following tools and materials:
- quarry sand;
- reinforcing bars;
- wire, which is necessary for tying the reinforcement cage;
- crushed stone;
- cement;
- waterproofing material;
- boards for creating formwork;
- saw;
- construction vibrator;
- shovel.
Before starting to build the base, it is important to determine the amount of materials needed to create the tape. To do this, it is enough to find out how much sand, concrete and reinforcement are used to create one meter of foundation. Based on this data, you can accurately determine the required amount of materials. It is worth remembering that materials must be prepared with a small margin.