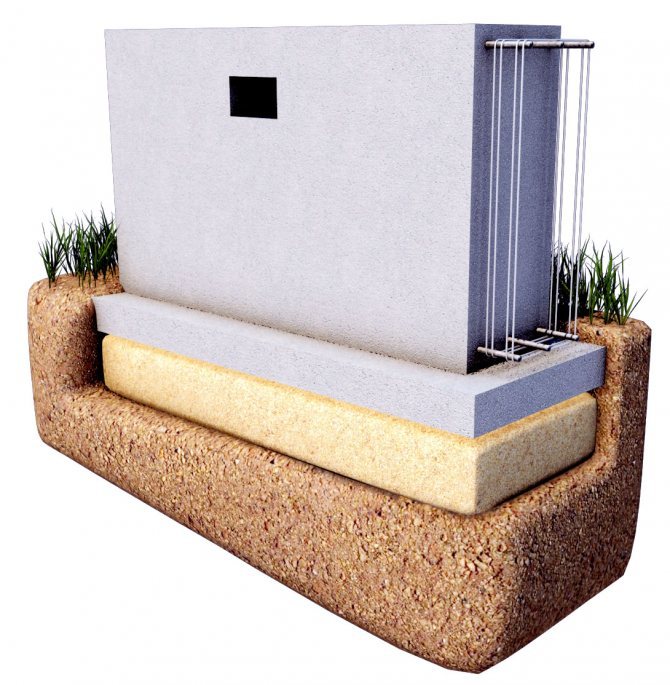
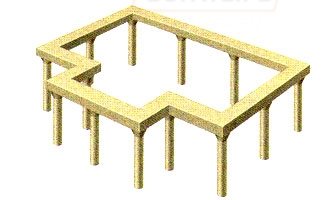
A columnar foundation is a system of pillars located at the corners of the structure, at the intersection of load-bearing walls and in other places where the load is concentrated. The gap between the pillars is on average two meters.
To ensure that the columnar foundation is a solid structure, a grillage is installed between its pillars. It serves to rigidly fix the foundation and to evenly distribute the load from the entire structure of the structure across all foundation pillars, increasing its stability and durability.
In terms of its reliability, such a foundation is not inferior to a strip or stone one, and in terms of saving money and materials spent on its construction, it significantly exceeds them. It is distinguished by the speed of construction and the absence of the need for thermal and waterproofing measures.
Depending on the design of the structure under construction and the materials used for the construction of a columnar foundation, the following types are distinguished:
- Tubular . It is installed using metal or asbestos pipes filled with concrete;
- Concrete and reinforced concrete. For their production, heavy concrete grades B15 - B25 are used. Reinforced concrete columnar foundation is considered the most durable - its service life is about 150 years;
- Brick . The material for its construction is burnt red brick;
- Stone . Flat stones or medium-sized rubble are used as the starting material.
Photo of columnar foundations
Different types of columnar foundations
Operating principle and requirements
A columnar foundation consists of several pillars united by a grillage (horizontal frame). A grillage is necessary for the joint operation of free-standing structures. To ensure stability and prevent overturning, the pillars are buried in the ground. The depth of installation depends on the load from the building and the characteristics of the soil.
Load-bearing capacity is ensured by support on the ground and surface friction. In the case of shallow foundations, little friction occurs. This type of construction is best suited for the construction of a wooden or frame house with a height of two or more floors. The construction of heavy stone houses on such foundations is impossible. The specific gravity of the building walls should not exceed 1000 kg per cubic meter.
Due to the low bearing capacity, it is required that the groundwater level be at least 50 cm deeper than the base of the foundation. If there is a layer of bulk soil on the site, they must be removed and replaced with medium-sized sand with layer-by-layer vibration compaction (maximum compaction layer 20 cm).
Information on the purpose of the calculator
An online calculator for a monolithic bored pile and columnar grillage foundation
is designed to calculate the dimensions, formwork, quantity and diameter of reinforcement and the volume of concrete required for the construction of this type of foundation. To determine the appropriate type, be sure to consult a specialist.
A pile or columnar foundation is a type of foundation in which the piles or pillars are located directly in the ground itself, at the required depth, and their tops are connected to each other by a monolithic reinforced concrete strip (grillage), located at a certain distance from the ground. The main difference between columnar and pile foundations is the different installation depth of the supports.
The main conditions for choosing such a foundation are the presence of weak, vegetative and heaving soils, as well as a large freezing depth. In the latter case and with the possibility of driving piles in all weather conditions, this type is very relevant in areas with harsh climates. The main advantages also include the high speed of construction and the minimum amount of excavation work, since it is enough to drill the required number of holes, or drive ready-made piles using special equipment.
There are many different variations of this type of foundation, such as the geometric shape of piles, materials for their manufacture, mechanism of action on the ground, installation methods and types of grillage. In each individual case, it is necessary to choose your own option, taking into account the characteristics of the soil, design loads, climatic and other conditions. To do this, you need to contact specialists who can make all the necessary measurements and calculations. Attempts at saving and self-construction can lead to the destruction of the building.
Below is a complete list of calculations performed with a brief description of each item. You can also ask your question using the form on the right.
A columnar type foundation is a concrete or metal frame (grillage) supported by vertical pillars buried in the ground to a certain depth.
The material for constructing the pillars can be reinforced concrete, solid clay brick, blocks, metal pipes or rubble stone. A wider footing may be provided at the bottom of each support column to increase the support area. The cross-section of the vertical supports can be round or square.
Options for columnar bases.
The reliability of the foundation structure largely depends on the calculation of the columnar foundation and the correct location of the support pillars that must be installed:
- from all corners of the building;
- at the junction and intersection of walls;
- on straight sections of the grillage no further than two meters from each other.
The structure of the grillage frame should serve as a support for all load-bearing walls and partitions. If the building is long, additional transverse jumpers should be provided to ensure a more reliable connection between the longitudinal beams.
Pros and cons of the design
The main advantages include low cost, which is ensured by:
- reduction in the volume of excavation work during the construction of a frame building;
- reduction in the amount of required materials (compared to a strip foundation);
- a small amount of excavated soil does not require large equipment (dump trucks, excavators).
The disadvantages include the rather unpredictable behavior of pillars in case of violation of construction technology and errors at the design stage. Another disadvantage was the limited scope of application due to the low load-bearing capacity.
Preparation for calculation At the preliminary preparation stage, it is necessary to find out all the initial data for the calculation:
- dimensions of the building in plan;
- bearing capacity of the base (soil);
- load on the foundation from its own weight and overlying structures.
Reviews about columnar foundations
Cost-effective type of foundation. It cost me one and a half times cheaper than the tape one. Suitable for construction almost anywhere in central Russia. Reliable. Of the minuses, I would like to note the severity of the excavation work, especially the expansion device under the base of the pillar.
Alexander
I built such a foundation a long time ago, in 2008. It stands strong, does not crack or shrink, although the house has been screeded, plumbing and heating installed, and finishing done. The construction required four times less concrete than strip concrete.
Semyon
is very difficult to drill wells for pipes. The gap under the grillage caused inconvenience. Although, when we had a flood, the water simply flowed under the house and after three days the draft dried out all the soil. But for other owners, the flood caused a lot of problems.
Michael
Geological surveys
Many people, when constructing a frame house on their own, neglect to study the characteristics of the soil. It is important to study the geological conditions of the site. When designing a building, specialists carry out quite expensive geological surveys, which include drilling and studying the resulting material in the laboratory. The result of all work is the exact values of all characteristics necessary for the calculation.
In conditions of self-construction of a frame building, a visual examination can be performed. To do this, drill or dig a hole 50 cm below the expected base of the house foundation. It is important to determine the type of soil and make sure there are no water-saturated layers. The type of soil will be needed in further calculations.
Sometimes it is necessary to perform the test several times in different places. Even if the quality of the foundation in one well is good, a lens of unstable soil may be located in the soil. If it is small, you can try to bypass it, but if it is large enough, you will have to choose a different type of foundation.
Regulations
The main document describing the design and types of foundations on pile supports, as well as regulating their design and calculation, is considered to be SNiP 2.02.03-85 “Pile foundations”.
House on stilts
A more modern document, developed not so long ago, is SP 24.13330.2011. In the modern edition of SNiP, no significant changes have been added, although some replacements and clarifications were made after the advent of new technologies and materials. In case of doubts and significant disagreements, one should still rely on the joint venture, which provides specific examples.
The Rules outline the main requirements for the development of a specific type of foundation - pile.
The joint venture describes various types of supports, engineering and geological characteristics, discusses the nuances and particular examples of calculations for newly constructed buildings and reconstructed structures. The provisions of SP 24.13330.2011, as well as SNiP 2.02.03-85, do not apply to pile foundations constructed:
- for structures under dynamic loading;
- in permafrost;
- at a depth exceeding 35 m;
- for structures related to oil refining enterprises.
Load collection
Loads on a building can be temporary or permanent. Permanent ones include the weight of all elements of the building, and temporary ones according to the joint venture “Loads and Impacts” are divided into two types: long-term and short-term. Long-term impacts include the weight of furniture and equipment, while short-term impacts include the weight of people and precipitation. In the general case, precipitation such as snow and wind are taken into account when calculating. For foundations, you only need to know the weight of the snow cover.
To collect the constant load from the entire building you need to calculate:
- wall weight;
- floor weight;
- roof weight;
- own weight of the foundation.
A lot of structures can be summarized in one small table.
Construction type
| Construction type | Weight |
| Frame walls 150 mm thick with insulation | 30-50 kg/m2 |
| Flooring on wooden beams insulated with material with a density of up to 200 kg/m3 | 100-150 kg/m2 |
| Self-weight of reinforced concrete foundation | 2500 kg/m3 |
| Roof with load-bearing structures | |
| Metal | 40-60 kg/m2 |
| Ceramic | 80-120 kg/m2 |
| From flexible tiles | 50-70 kg/m2 |
Important! It is important not to confuse the units of measurement in the table. For all structures, except foundations, the values are given per square meter (thickness has already been taken into account).
These values are standard; to obtain the calculated values, you will need to multiply them by a special load reliability factor. This coefficient is given in the SP “Loads and Impacts”. For a frame house, all values are presented in the table.
| Construction type | Load safety factor |
| Wooden | 1,1 |
| Reinforced concrete with a density of more than 1600 kg/m3 | 1,3 |
| Insulating layers, backfills, screeds manufactured in the factory | 1,2 |
| Insulating layers, backfills, screeds manufactured on the construction site | 1,3 |
According to regulatory documents for residential buildings, the standard payload (long-term temporary) is assumed to be 150 kg/m2. For this value the safety factor is 1.2. From here we get a calculated value of 180 kg/m2 floor area.
Next, we proceed to find the load from the snow cover. To do this, you will need the already familiar SP “Loads and Impacts,” in which Table 10.1 shows the values depending on the climatic region. The snow region is determined from the maps presented in the joint venture “Building Climatology”. The safety factor for snow load is assumed to be 1.4.
Important! When the roof slope is more than 60 degrees, the snow load is assumed to be zero, since with such a slope the snow will not linger on the roof.
Load-bearing capacity of a screw pile: calculation
The bearing capacity of screw piles is found by multiplying the area of support by the bearing force of the soil. Let's consider this calculation using the example of screw pile 133, immersed in clay soil:
- First we find the area of support. Using tabular data, we find out that the diameter of the screw is 30 cm, so the area of the sole is: 15x15x3.14 = 706.5 cm².
- Now we will use the table to determine the load-bearing capacity of the soil. For clay soils it is 6 kg/cm².
- Now we find the load-bearing capacity of the pile elements: 706.5x6 = 4.2 tons.
Conclusion: one pile element model 133, with a depth of immersion in clay soil of 2-2.5 m, can withstand a load of 4.2 tons.

Screw piles
How to take into account the reliability of a structure in calculations?
However, the calculation described in the middle of the article is approximate. It does not take into account the safety factor of parts. To do this, it is necessary to make a final calculation using the formula: N=F/Y, where N is the required load, F is its approximate value obtained by the calculation method described above, Y is the safety factor. The latter indicator depends on the correctness of the calculations and the number of pile elements. Its selection is carried out according to the following parameters:
- with the number of elements equal to 5-20 pieces, the coefficient is 1.75-1.4 (in this case, a low grillage on suspended supports should be used);
- coefficient 1.25 is used when testing on a reference pile element and is approximate;
- to conduct more accurate tests, a coefficient of 1.2 is used.
Example: in continuation of our calculation for the pile element of model 133, we will find the specified load-bearing capacity: 4.2/1.2 = 3.5 tons. This indicator will be used when conducting accurate geotechnical studies. If average tabular indicators are used, then the desired value is 4.2/1.75 = 2.4t.
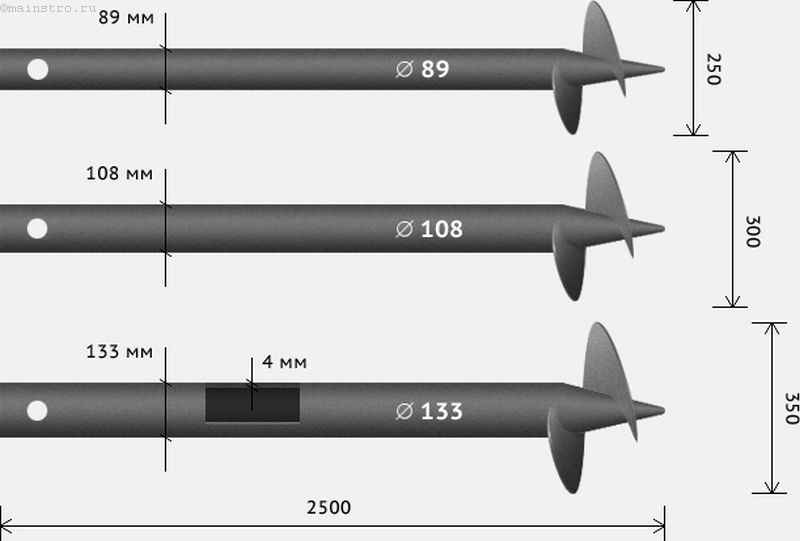
Screw piles: dimensions
We determine the maximum load-bearing capacity of one pile element
To find the maximum load-bearing capacity of one pile element, several data will be required at once. For clarity, let’s take the following indicators:
- The installation of piles will be carried out on sandy soils with a bearing capacity of 15 kg/cm².
- The support used is model 219 with a base diameter of 600 mm.
- Since we will use no more than five piles in the field, and the bearing capacity of the soil is precisely determined, we use a coefficient equal to 1.75.
The maximum load-bearing capacity is calculated as follows:
- We find the support area of the screw pile: 30x30x3.14=2826 cm².
- We calculate the approximate load-bearing capacity: 2826x15 = 42.4 tons.
- Now the exact load-bearing capacity of the screw piles is determined: 42.4x1.75 = 24.23 tons.
Conclusion: the bearing capacity of one element of screw piles with a support diameter of 300 mm is slightly more than 24 tons. That is, the permissible loads (weight of walls, ceilings, furniture, etc.) on supports at such a burial depth should not exceed 24 tons. As you can see, a correctly calculated load-bearing capacity of screw piles ensures that our foundation will withstand the weight of floors, walls, wind and snow loads.

Screw piles

Screw piles
Calculation procedure
First of all, determine the minimum base area for all pillars in total. The calculation is carried out according to the formula:
S = P/Rо,
where P is the total weight of the house structures, found at the preparation stage in kilograms;
Ro is the calculated resistance of the load-bearing soil layer (on which the foundation rests) in kilograms per square centimeter.
The value of the calculated resistance can be summarized in one table:
| Foundation soil type | Ro at a depth of 1.5 m or more, kg/cm2 | Ro at the earth's surface, kg/cm2 |
| Pebble with clay | 4,5 | 3 |
| Gravel with clay | 4,0 | 2,7 |
| Coarse sand | 6,0 | 4,0 |
| Medium sand | 5,0 | 3,33 |
| Fine sand | 4,0 | 2,7 |
| Dusty sand | 2,0 | 1,33 |
| Sandy loam or loam | 3,5 | 2,33 |
| Clay | 6,0 | 4,0 |
| Filled soil with compaction or subsidence | 1,5 | 1,0 |
| Filled soil without compaction | 1,0 | 0,67 |
Important! Building on fill soil is highly discouraged. When it is found in the geology of the site, it is most often completely replaced with coarse or medium sand.
Having calculated the value of the total area of the pillars for a frame house, find the required dimensions of the base for one foundation and their required number. The supports must be placed at the corners and junctions of the walls and distributed evenly around the perimeter.
Length of driven piles
There are reinforced concrete, concrete and wooden driven piles. Shape: round, square, T-shaped, I-beam, hollow.
Standard lengths range from three to 16 meters. Minimum for reinforced concrete pile:
- 3 meters for solid.
- 4 meters for hollow.
You can use more or less, they are made to order. At large immersion depths, composite piles are more often used, and the driving method is rarely used, usually combined.
The diameter of reinforced concrete piles is up to 80 centimeters, shells - up to a meter.
See additional information on reinforced concrete piles:
|
|
| Examples of pile foundation calculations in more detail | Cost of pile foundations - see |