Construction is a labor-intensive and scrupulous process. At the initial stage, the concrete composition should be selected. The list of components can be changed depending on the purposes and further operation. Strict compliance with technological requirements, recommended proportions and the use of high-quality materials will ensure easy operation of the solution and durability of the building.
Cement consumption per 1 cubic meter of concrete (M100, M200, M300, M400, M500).
In concrete, cement is the compound that binds all its components. The technical characteristics of the solution depend on its quantity and quality - strength, frost resistance, water resistance, corrosion resistance.

Cement consumption for concrete.
As part of the mixture, the price for it is the highest, so the issue of cement consumption per 1 cubic meter of concrete is acute - too much, the profitability of construction will decrease, cracks will appear after hardening, too little - the required technical and operational characteristics will not be achieved.
Cement consumption per 1 m3 of concrete (M100, M200, M300, M400, M500).
To calculate how much cement is needed per 1 cubic meter of concrete, you need to know what it will be used for. On average, 1 m3 of concrete will require from 240 to 320 kg of cement, depending on the brand of cement. Next, we will consider which brand of concrete should be chosen for what purposes and what cement consumption will be in the manufacture of each of them.
Calculation rules.
When performing calculations, it is necessary to take into account the mobility of the finished solution. If the volume of cement is less than required, it will not be able to hold the binder and filler. As a result, after drying, concrete may crack under the influence of the external environment.
However, it is also not worth significantly exceeding the recommended value. This can also cause cracking. That is why each cube of the finished mixture can contain only one kilogram of hardener less or more than that obtained as a result of the calculation.
Let's find out how much cement is needed per 1 m3 of M200 concrete.
As a rule, M200 concrete is used for floor screed and foundation construction. The reason is that this brand is characterized by high strength and frost resistance. In addition, the material combines perfectly with the reinforcement frame. If we consider concrete in terms of load perception, then M200 is considered a medium-strength material.
But to prepare a high-quality product, it is necessary not only to select all the components correctly, but also to combine them in the correct ratio. Let us give the required quantities of all ingredients for concrete M200.
How much cement and other components does it contain:
- Portland cement – 265 kg;
- sand – 860 kg;
- gravel or crushed stone – 1050 kg;
- water – 180 l;
- plasticizer – 4.8.
If you decide to prepare the solution with your own hands, then using this proportion is not convenient. It is best to use the parts ratio approach.
In this case, the required amount of ingredients will look like this:
- cement – 1 part;
- sand – 2.8 parts;
- crushed stone - 2.8 parts;
- 20% of the total mass of the mixture should be removed from the water.
We calculate how much cement is needed per 1 m3 of M300 concrete.
In order to get 1 cubic meter. of high-quality M300 concrete, you need to use 366 kilograms or 244 liters or 5.88 bags of M400 cement, and in the case of using M500 cement, respectively: 319 kilograms or 213 liters or 4.26 bags of M500 cement.
When performing calculations, it was taken into account that the density of cement is about 1500 kg/m3. This indicator corresponds to the average looseness of cement - typical for material supplied in 50 kg bags. Compliance with the specified proportions of the content and quality of cement in concrete during its preparation will allow us to obtain ready-mix concrete of the M300 grade, which meets all construction requirements.
Consumption of cement grades M400 and M500 per 1 cubic meter of concrete.
If in order to obtain the necessary technical characteristics it is necessary to know the proportions of sand and crushed stone, then in order to calculate the financial costs of construction it is necessary to calculate the cost of cement per 1 cubic meter of concrete. This data has been calculated and summarized in the appropriate tables:
| Concrete grade | Weight of cement, kg |
| 100 | 166 |
| 150 | 205 |
| 200 | 241 |
| 250 | 313 |
| 300 | 329 |
| 400 | 417 |
| 450 | 469 |
Similar reference data have been developed for M500; if necessary, this indicator is calculated using figures for the proportions of the components for preparing the mixture.
Drawing up proportions.
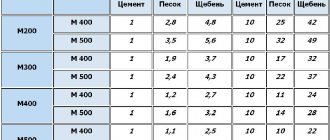
To calculate the amount of cement spent on a cube of concrete, you need to know the brand of the mixture; in addition, the brand of the binder used is also taken into account. The proportional ratio of the components is indicated in special tables. In construction, M400-M500 are more often used, and the proportion is calculated in mass parts.
| Concrete grade | Proportion by weight cement/sand/crushed stone |
| 100 | 1/4.6/7 |
| 150 | 1/3.5/5.7 |
| 200 | 1/2.8/4.8 |
| 250 | 1/2.1/3.9 |
| 300 | 1/1.9/3.7 |
| 400 | 1/1.2/2.7 |
| 450 | 1/1.1/2.5 |
| Concrete grade | Proportion by weight cement/sand/crushed stone |
| 100 | 1/5.8/8.1 |
| 150 | 1/4.5/6.6 |
| 200 | 1/3.5/5.6 |
| 250 | 1/2.6/4.5 |
| 300 | 1/2.4/4.3 |
| 400 | 1/1.6/3.2 |
| 450 | 1/1.4/2.9 |
This means that to prepare M300 concrete from M400 cement you will need to take 10 kg of cement, 19 kg of sand, 37 kg of crushed stone. The result will be 66 kg of finished material. The average density of the mixture is 2200 kg/m³, so the mass of the binder component consumed is 2200/66*10≈330 kg. Such calculations have already been compiled into special tables to facilitate the work of designers and builders.
Selecting the required class of concrete.
The required grade of concrete must be indicated in the design documentation for the construction site. If the construction is carried out independently, you should decide on the brand of the mixture, since this will decisively affect the strength and cost of the building or structure being constructed.
The purpose of the most common grades of concrete is given below:
- M100 - used for constructing concrete footings, installing parquets, and small architectural forms;
- M150 – used for constructing paths and sealing fence supports;
- M200 – for the construction of walls, porches;
- M250 – production of monolithic foundations, grillages, foundation slabs, light-loaded floor slabs, stairs, retaining walls;
- M300 – for any loaded structures: walls, ceilings, foundations;
- M350 – load-bearing walls, columns, floors, beams, monolithic foundations.
Additives for concrete mortar.
- Modifiers. Designed to increase the strength and frost resistance of concrete.
- Plasticizers. Increases the mobility and water resistance of the mixture.
- Mobility regulators. Allows you to extend the setting period and maintain mobility during transportation.
- Anti-frost additives. Ensure normal setting of the solution at low temperatures, down to minus 20 degrees.
- Setting accelerators. They increase the setting speed, ensuring the fastest possible strength gain in the first day.
When using additives, the consumption of materials per 1 m3 of concrete should be determined taking into account the manufacturer’s recommendations. Violation of the instructions for use can have the completely opposite effect.
How to calculate cement for leveling a floor
- The first step is to measure the slope of the floor. Most often it is measured in millimeters, but in some cases ties of 2–3 cm are necessary.
- Then you need to multiply the layer thickness by the floor area.
- Let's find out the consumption rate using the table.
- We multiply the consumption rate by the previously obtained volume.
Let's look at an example. Floor area - 20 m2, screed - 1.5 cm (converted to meters: 1.5/100 = 0.015 m). Therefore, 20*0.015=0.3 m3.
We take the norm of cement at the rate of 319 kg per 1 m3.
319*0.3=95.7 kg.
Cement is usually sold in bags of 25 kg and 50 kg. So we will need two 50 kg bags.
Table of average construction calculations
| Concrete grade | Amount of cement (l) | Quantity of cement (kg) |
| Concrete grade M-100 | 111 | 166 |
| Concrete grade M-150 | 137 | 205 |
| Concrete grade M-200 | 161 | 241 |
| Concrete grade M-250 | 200 | 300 |
| Concrete grade M-300 | 213 | 319 |
| Concrete grade M-400 | 278 | 417 |
| Concrete grade M-150 | 313 | 469 |
It is necessary to distinguish between the brand of concrete and cement - these are completely different things.
Cement marking is determined by two attributes: maximum load and the ratio of additives to the total volume of cement. The letters M or PC in the name indicate the maximum degree of load that the cement can withstand after drying. For example, the PC400 brand can withstand loads of up to 400 kg/m³.
The letter D in the marking indicates the amount of additives in the cement mixture. Thus, cement marked D20 contains 20% impurities. Additives affect the strength and ductility of the material, so their ratio must be taken into account during construction.
The most common cement grades used in construction are PC400 and PC500 with the percentage of additives D0 or D20.
Cement PC400 D20 is the most popular. It is used both for domestic tasks (plastering, floor screed), and in industrial and agricultural construction for the manufacture of reinforced concrete structures, beams and foundations. This brand has good water resistance and frost resistance.
It is important to remember that the resulting concrete is always of a lower grade than the cement used in its production. The grade of cement should be two to three times higher than the required grade of mortar.
Cement consumption per 1 cubic meter of concrete mixture
In concrete, cement is the compound that binds all its components. The technical characteristics of the solution depend on its quantity and quality - strength, frost resistance, water resistance, corrosion resistance. As part of the mixture, the price for it is the highest, so the issue of cement consumption per 1 cubic meter of concrete is acute - too much, the profitability of construction will decrease, cracks will appear after hardening, too little - the required technical and operational characteristics will not be achieved.
What does consumption depend on?
The main requirement for concrete is to achieve the required strength after hardening. Based on this, in accordance with construction standards describing the quality of components, their ratio and technical characteristics are selected. This is done taking into account the strength grade of the composition; the recommended ratio of ingredients is indicated in specialized reference books. To calculate how much cement will be contained in 1 m³ of concrete, the following factors are taken into account:
- brand, density, required setting time;
- plasticity of the solution and its mobility;
- type of sand, fraction, presence of impurities, the proportion of which does not exceed 15%, otherwise this filler is subjected to pre-treatment - sifting or washing;
- fraction, type and other technical characteristics of crushed stone - flakiness, density, contamination, if it exceeds the norm, the crushed stone is cleaned;
- the presence of additional components that improve characteristics - hardeners or plasticizers.
Drawing up proportions
To calculate the amount of cement spent on a cube of concrete, you need to know the brand of the mixture; in addition, the brand of the binder used is also taken into account. The proportional ratio of the components is indicated in special tables. In construction, M400-M500 are more often used, and the proportion is calculated in mass parts.
| Concrete grade | Proportion by mass C/P/Shch |
| 100 | 1/4.6/7 |
| 150 | 1/3.5/5.7 |
| 200 | 1/2.8/4.8 |
| 250 | 1/2.1/3.9 |
| 300 | 1/1.9/3.7 |
| 400 | 1/1.2/2.7 |
| 450 | 1/1.1/2.5 |
| Concrete grade | Proportion by mass C/P/Shch |
| 100 | 1/5.8/8.1 |
| 150 | 1/4.5/6.6 |
| 200 | 1/3.5/5.6 |
| 250 | 1/2.6/4.5 |
| 300 | 1/2.4/4.3 |
| 400 | 1/1.6/3.2 |
| 450 | 1/1.4/2.9 |
This means that to prepare M300 concrete from M400 cement you will need to take 10 kg of cement, 19 kg of sand, 37 kg of crushed stone. The result will be 66 kg of finished material. The average density of the mixture is 2200 kg/m³, so the mass of the binder component consumed is 2200/66*10≈330 kg. Such calculations have already been compiled into special tables to facilitate the work of designers and builders.
When calculating the amount of solution, take into account that the volume yield is less than the total volume of all components due to compaction during mixing. The most popular fraction of crushed stone is 20 mm, it provides the required strength and is affordable. The amount of added water required to prepare 1 cube of the mixture is determined during the manufacturing process, since it depends on the moisture content of the sand used and the technical parameters of the mixture.
Cement
Cement consumption depends on many parameters, including the size of the base and the purpose of the mixture.
The mass for construction work can be mixed on your own, without contacting specialized organizations. However, the calculation of cement (hardener) should be carried out very carefully in order to determine the amount of concrete with high accuracy.
A deviation in one direction or another can subsequently have a sad effect on the quality of the entire building as a whole. How much cement and how many cubes of concrete are needed is determined depending on many factors. This includes the size of the base, the purpose of the prepared mixture, and more. The volume of concrete is measured in cubic meters. It is imperative to know, down to the kilogram, how much cement is required for the foundation.
It is recommended to use Portland cements and quick-hardening compounds
In modern stores you can find many types of mixture brands. They differ in the principle of application in construction. The most common are Portland cement, Portland slag cement, pozzolanic cement and quick-hardening cement.
All of them are made from the same ingredients, but differ from each other in the properties and qualities inherent in them. Each of these materials is not the same in price.
Most often during construction, the classic last option is used. It is the most affordable, has good consumer characteristics and is reliable and durable. Basically, Portland cement is sold without any kind of impurities, which makes it possible to independently improve its quality by adding the necessary mixtures.
Cement counting
How to calculate the amount of cement for the foundation? This depends on the brand of material used.
The marking indicates the consumption of the mixture per cubic meter of sand:
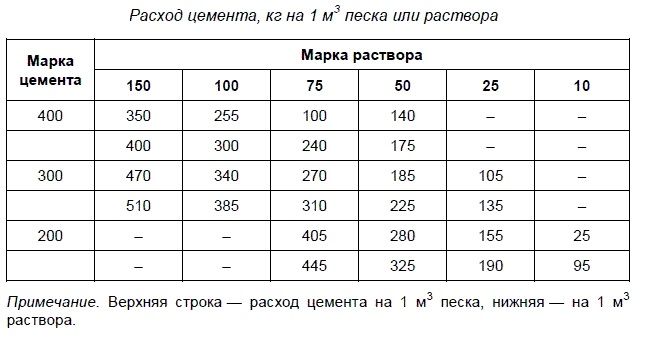
When calculating materials for the foundation of a house and answering the question “how much cement is needed for the foundation?” It is recommended to rely on verified data.
They will help determine the amount of each component for the solution, including water, so that the mixture turns out to be of high quality and meets all the necessary requirements.
How much cement is needed per cubic meter? In calculations, the following indicators of accuracy of consumption per 1 cubic meter are adhered to:
- hardener – 1 kg;
- sand –3 kg;
- gravel –5 kg.
The optimal ratio of cement, sand and crushed stone: 1:3:5
Based on this, if it is necessary to calculate the amount of concrete for the foundation, it is recommended to choose the optimal ratio of hardener, river sand and crushed stone 1:3:5. In this case, you need to familiarize yourself with the properties of each component.
You should also decide what brand of solution needs to be made. Calculating the amount of cement for the foundation involves properly mixing the ingredients so that the solution is of good quality without possible crumbling from exposure to external factors.
In addition, this will help determine the properties of the mixture such as strength, rigidity and mobility. The less gray mass in the mixture, the better the quality in terms of reliability and density.
Calculating the volume of concrete for a foundation can be illustrated with an example. To obtain an M150 grade solution, you should take 350 kg of M400 grade hardener per cubic meter of sand, and if you take M300 grade material, you will need 470 kg.
Preparation
When mixing the mortar, calculating the cement consumption is very important.
If its content is small, the solution will turn out flimsy.
After setting, it may happen that the mixture begins to crumble into small pieces and for a brick wall with a volume of 1 m3, 0.3 m3 of mortar is required, and, therefore, 100 kg of cement composition is required.
The calculation of concrete for a strip foundation is determined approximately the same way.
When purchasing a large amount of hardener, do not forget that it tends to lose its qualities over time, therefore, when purchasing a material, you should take care of its quick use.
The recommended formula for obtaining 1 cubic meter of solution when arranging the base is as follows:
0.8 m3 of crushed stone + 0.5 m3 of sand + 380 kg of cement.
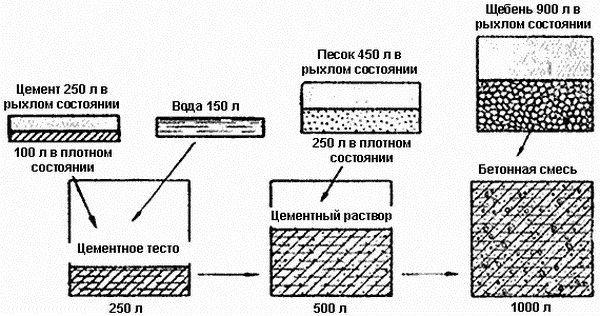
How to calculate the volume of water? It is determined by what consistency of the solution itself is needed. Most often, a 1:2 proportion of water relative to the dry mixture is taken. This allows you to calculate how many cubes of concrete are needed and calculate the cubic capacity as a whole. Watch this video for more details:
How much cement is needed for 1 cubic meter of concrete mixture?
If in order to obtain the necessary technical characteristics it is necessary to know the proportions of sand and crushed stone, then in order to calculate construction costs it is necessary to calculate the cost of cement per 1 cubic meter of concrete. This data has been calculated and tabulated.
| Concrete grade | Weight of cement, kg |
| 100 | 166 |
| 150 | 205 |
| 200 | 241 |
| 250 | 313 |
| 300 | 329 |
| 400 | 417 |
| 450 | 469 |
This will help determine the rate of consumption, as well as the quantity after calculating the entire volume of material required for construction. The quantity and cost of fillers are calculated using tables with their proportions for different brands. Similar reference data have been developed for M500; if necessary, this indicator is calculated using figures for the proportions of the components for preparing the mixture.
To deliver the required amount of water, it is taken into account that it depends on the moisture absorption of sand and other components, but on average it is recommended to store up to 200 liters per 1 m³ of concrete. The water must be clean, without salts and organic additives that can reduce the quality even if all proportions are fully observed.
Methods used for mixing concrete
In private construction, manual or mechanized methods of mixing concrete are used. Manual preparation makes sense for small volumes of work, but if you need to prepare more than 5 m3, then it is better to rent, or even buy, a mechanical concrete mixer with an electric drive. If the need for concrete is more than 50 m3, it can be recommended to buy ready-made factory-prepared concrete supplied in truck mixers.
Kneading by hand
For manual mixing, you will need a tub or trough with a low side. Initially, sand and cement are poured into this container and mixed until a gray homogeneous mass is obtained. After this, add water and make a regular cement-sand mortar. Next, they begin to gradually add crushed stone and, if necessary, water until a mixture ready for laying is obtained.
Using a concrete mixer
When mixing mechanically, approximately half of the required water is poured into a running mixer and half of the crushed stone is poured. This allows you to knock off the remaining cement mortar from the walls from the previous batch. After this, add all the necessary cement, mix for 2-3 minutes and add sand. Fill in the remaining crushed stone and add water to obtain the required consistency of the composition.
The finished concrete must be unloaded completely into a pallet placed under the concrete mixer. It is not permissible to scoop the mixture with a shovel from the mixer.
Recommendations
Problems often arise when making solutions. Cement of a lower grade is brought to the site than is required for the manufacture of a composition of a certain strength class. To achieve the desired effect, its amount increases by 15%. 10% more fine-grained sand is added and this will not affect the quality.
Most often, cement is offered in 50 kg paper bags. This is a convenient container that allows you to quickly calculate its volume to complete the planned work. To do this, calculate how many bags of cement are contained in 1 cube of concrete. To obtain this volume, M300 will require 329/50 = 6.58 bags or 6 bags and 29 kg. This value is multiplied by the volume of solution that is poured. If you need to make a 40 m³ monolith from M300, then you will need 40·6.58=263.2≈264 bags or 13.2 tons. In this case, the quality of the mixture will correspond to the declared parameters, subject to the manufacturing technology.
A correctly calculated amount of cement per cubic meter of mixture will allow you to achieve the desired technical and operational characteristics. We must not forget about the quality of fillers and water. They must comply with the declared parameters and not contain foreign inclusions or impurities. This will help to pre-calculate the financial component and optimize construction costs. When purchasing, it is better to opt for quality brands 400 or 500, since you will need fewer of them at a similar price.
Why do you need a cement calculator for different brands?
Building materials are usually divided into different classes, with which quality is inextricably linked, and, as a result, cost, and therefore popularity. Cement is no exception, and there are 6 main grades, from M100 to M500. However, it is not used by itself, but in relation to fillers and water it turns into a monolith that competes with natural stone, that is, concrete. To calculate the mixture of the latter, you need a cement calculator that takes into account its proportional relationship to other components. But simply mixing cement with sand and water does not mean getting a solution with the desired properties.
Concrete is also divided into several classes. Its digital value indicates the load that a cast cube with a twenty-centimeter side can withstand, and is expressed in kilograms per square centimeter (kg/cm2). Well, the numbers in the cement grade mean how strong the concrete will be. For example, dry binder material M300 is no longer available, but if it were available, it would make an M100 mixture. Since we are interested in a solution suitable for pouring the foundation of a house, cement classes from M100 to M250 are immediately eliminated. The first will produce a composition with a value significantly lower than 75 kg/cm2, and the latter will produce a composition not exceeding this value.
It is optimal to use the M400 grade; from such a dry material, with the addition of the required amount of sand and gravel, concrete will be produced in a wide range of classes, from M150 to M400. M500 cement can also achieve the latter indicator, but it also has great possibilities, for example, with the proper proportions, you can get M500 mortar, and this is already a very powerful foundation for any building. There are also brands on sale such as M600 and M800, but they are much more expensive than any previously named, and the first is considered military, used for the construction of bunkers. The second is considered especially durable and is used where the load on the structure is colossal, for example, this grade cannot be avoided when constructing pylons for bridges many kilometers long or when constructing particularly tall skyscrapers.
How much cement do you need to take per 1 cubic meter (1m3) of concrete to make a foundation?
It is necessary to calculate the cement consumption for the foundation before starting work, which will make it possible to approximately determine the required volume of building materials and draw up an estimate. Cement in concrete mortar acts as a binder, therefore, the characteristics and properties of concrete, and, accordingly, the strength, reliability, and durability of the foundation will directly depend on its quality and correctly calculated volume.
The question of how much cement is needed per 1 cubic meter of concrete for the foundation is also important because it is the most expensive and least stored component in the mixture. Thus, purchasing a larger volume of cement will lead to unnecessary financial costs, and after six months the cement will be unsuitable for any work.
At the same time, an insufficient volume of cement will make it impossible to fill the base in one go, and the need to purchase additional material, wasting time and money on transportation.
If the recipe and proportions are not followed, the concrete solution will be of poor quality, with operational and technical characteristics that do not meet the standard. To accurately calculate how much cement needs to be poured into a concrete mixture, you need to decide in advance on the brand of binder and concrete itself (these parameters are influenced by the scope of application of the mixture and the design features of the building).
On average, a cube of concrete contains 240-320 kilograms of cement. The exact figure depends on the brand of the driest mixture and the finished concrete solution.

Composition of concrete solution
Concrete is used in the construction of buildings as a foundation, for the construction of pillars or supports as a resistant stone structure, and also for strengthening houses and buildings. Based on the final result and purpose, the composition of the concrete may vary slightly. However, builders have developed universal components that are inherent in all brands of mortar, and rules for the preparation of strong material.
Ready-mix concrete (store-bought) is a rolling stock of four standard components mixed in specified proportions: cement, crushed stone (gravel), sand and water.
Cement as a base

Cement plays a major role in the preparation of concrete. The material has a binding property, hardens quickly and ultimately turns into a durable stone. Externally, cement resembles a powder with small particles of mineral origin. The grains combine with water and dissolve in it during cooking. The main factors when choosing a cement base are quality and shelf life. A cheap composition with impurities of unknown origin can reduce the strength of the building. As a result, the foundation will sag and cracks will appear. A similar result is observed when using stitched material mixed into 1 cube of concrete.
Filler
When selecting the composition of concrete and immediately before preparation, you should decide on the type of filler. Builders recommend using crushed stone or its equivalent - gravel. If it is necessary to create a final material that is lighter in weight, it is permissible to add expanded clay. A certain amount of filler will ensure the absence of cracks and additional strength of the concrete structure. When preparing the composition with your own hands, you should select particles of crushed stone or gravel from 5 to 20 mm in diameter. Components that are too small or large will result in an incorrect consistency of the resulting concrete.
How much sand is needed?
Fine sand acts as a compactor during the preparation of the solution. Once in the concrete, it fills the free space between the particles of gravel or crushed stone. Due to its fine structure, sand mixes well and guarantees strength when laying bricks or slabs. When selecting the composition of concrete, they prefer grain sizes of up to 3-5 mm. When independently selecting and mixing, sand from a river or quarry deposit is recommended.
What kind of water is suitable?

The liquid acts as a solvent for cement and sand in the preparation of the solution. The constituent components of concrete are mixed with water and create the finished product. The main requirement for water is purity. Additional components in the form of small particles or dirt can spoil concrete and reduce its properties. The amount of water in a cube of concrete is affected by the moisture content of the sand and the ultimate purpose of using the solution.
What does consumption depend on?
The consumption of cement per 1 cubic meter of foundation mortar must be calculated individually in each case.
It all depends on the required strength, frost resistance, and plasticity of the mixture, which is influenced by the intended purpose of the structure/building. Proportions are determined based on the required class of concrete, the required level of water resistance, mobility, and resistance to various influences.

Counting the amount of cement
To calculate the required volume of cement for a concrete mortar, you must first understand the characteristics of the mixture itself. Concrete is a modern universal building material that is prepared from cement, sand, crushed stone and water. GOST specifies the proportions and requirements for the solution, preparation formulas and volumes.
The volume of cement in the solution directly affects the properties of the mixture both during the work process and during the operation of the structure/building. Taking into account the cost of cement, its quantity also affects the cost of concrete, and, therefore, all construction and repair work.
When preparing concrete at home with your own hands, you usually take a universal solution suitable for many jobs, which is prepared according to the following proportions: part cement, 2 parts sand, 4 parts crushed stone, 0.5 parts water. If we translate everything into mass, it turns out like this: 330 kilograms of cement, 600 kilograms of sand, 1250 kilograms of coarse crushed stone, 180 liters of water.
Preparation of concrete mixture
It is possible to make a cube of solution correctly provided that the quantity and order of laying the components is strictly observed. Preparation at home involves using a small amount of the materials that make up concrete. In hardware stores you can find a mixture of dry ingredients that are manually mixed with water. As a result, you can knead the solution without using equipment. Builders use a specific cooking algorithm:
Adhering to the algorithm of actions and proportions when mixing substances will help to obtain high-quality concrete.
- On a clean surface, wiped free of moisture, pour the sand mixture and gravel (crushed stone) that make up the solution. For further preparation, make a slide with a depression.
- Place the required amount of cement into the created recess. This stage involves gently stirring the mixture.
- Pour the required volume of water into the hole of dry ingredients and mix thoroughly.
Manual preparation is used when it is necessary to carry out small work. In the case of a large construction site, preference is given to a concrete mixer. The advantage of the machine is its mixing speed and relatively long-term storage of the finished product. Before using the equipment, you should thoroughly wipe it and ensure a continuous supply of electricity.
Approximate tabular data
To determine the amount of cement per 1 m3 of concrete for the foundation, you can use special tables. There the brand of cement is taken into account and the required volumes and weights of the components are accurately indicated.
Features of the right choice
The grade of material is selected in accordance with the required properties and parameters. If, when calculating how much cement is needed per 1 cubic meter of concrete for the foundation, the master made mistakes, then the proportions of other components are violated, as a result of which the concrete may become unsuitable for construction. Such a foundation will not last long and can quickly become covered with cracks and chips, unable to withstand the load-bearing load.
What to consider when choosing cement:
- Compressive strength (class)
- Presence/absence of impurities
- Fineness and quality of grinding
- Curing speed
- Resistance to temperature changes, frost and heat
- Water resistance

If you look at the marking of cement, then everything is simple: previously, manufacturers indicated numbers from 100 and higher (M100, M200, M350, M500, etc.), which demonstrated the strength of the material in kg/cm3. But since 2003, the rules have changed and now they look at the strength class, designated by the letter B. Thus, in private construction, B32.5 cement (aka M300) is most often used, appreciating the most optimal price-quality ratio.
Should I use M500 for foundations?
Many novice craftsmen mistakenly believe that the higher the grade of cement, the better. But it is not always the case. For example, if you choose M500 grade cement for concrete for the foundation, it turns out that about 400 kilograms (8 bags) of cement will be used per cubic meter of mixture. And this is not good, because one cubic meter of solution should not contain more than 350 kilograms of cement.
It turns out that using M500 cement to fill the foundation is simply impractical and even dangerous. This material is intended for other tasks, but for the foundation it is better to choose cement grades M300/M400.
Every master should be able to calculate how much cement is needed per 1 cubic meter of concrete mortar. Thanks to the correct calculations and adherence to the technology for preparing the mixture, it will be possible to create a high-quality, strong and durable foundation or any other structure.
Component Requirements
The quality of concrete, its technical and operational characteristics depend on the ratio of the components. In addition, we should not forget about the economic component, which is determined, first of all, by the amount of cement consumed.
Therefore, correctly selected composition of the concrete mixture and determining how much cement is needed per 1 cubic meter of concrete not only ensures the quality of construction, but also makes the costs of its production economically justified.
Cement
Modern industry produces several different types of cement, produced using different technologies. For concrete, in most cases, four grades of Portland cement are used, from M300 to M600. The grade of cement means the amount of load that the prototype can withstand.
In private construction, the most common type of Portland cement is M400.
The industrial construction of buildings and structures, as well as the operation of reinforced concrete factories, are based on the use of M500 cement. The lowest grade is used for the preparation of concrete structures. not subject to loads. For example, for wall partitions and void fillings.
Sand
To prepare concrete, sea, river or washed sifted sand is used. This filler does not contain dust, debris, clay particles and other additives that can deteriorate the quality of the final material.
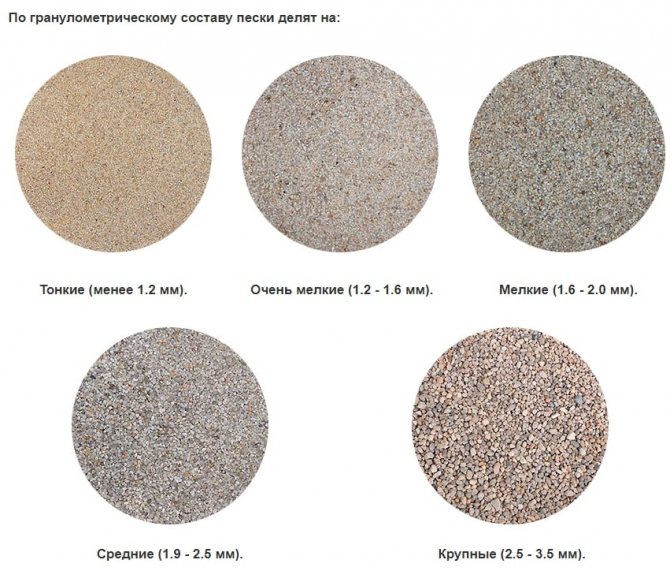
Based on the size of the constituent particles, sand is divided into:
- thin less than 1.2 mm;
- very fine 1.2-1.6 mm;
- small 1.6-2.0 mm;
- average 2.0-2.5 mm;
- large 2.5-3.0 mm.
For concrete, all types of fractions can be used, but the best particle size will be in the range of 1.2-2.5 mm. When preparing a concrete mixture, it is necessary to take into account the moisture content of the sand, which can reach 10% of the volume, and make adjustments when adding water to the mixture.

Crushed stone and gravel
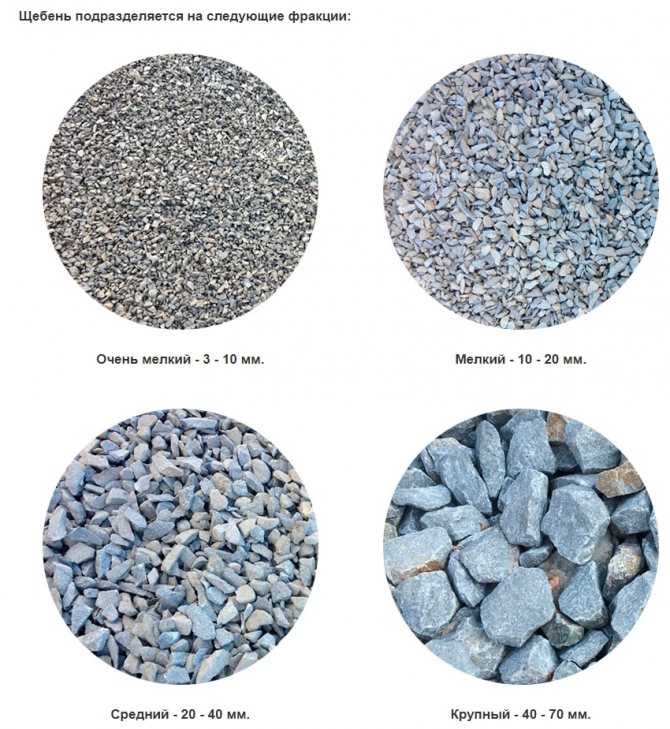
Used as a second filler, crushed rocks also have a gradation in size and are divided into:
- very small 3-10 mm;
- small 10-20 mm;
- average 20-40 mm;
- large 40-70 mm.
The first two fractions are called gravel, and the larger stone is called crushed stone. Sea or river pebbles, which have a smooth surface, cannot replace artificially crushed particles, as they will not provide proper adhesion of the components.
When choosing a coarse filler, it is necessary to take into account that the size of the largest particles should not exceed 1/3 of the future concrete layer.
An important technical characteristic of crushed stone and gravel is their voidness, which determines the volume of free space between individual particles.
The higher the void ratio, the more cement and sand will be required to prepare a high-quality concrete mixture. Depending on this, stone fillers are divided into porous up to 2000 kg/m3 and dense over 2000 kg/m3.

How much cement is needed for 1 cubic meter of mortar?

To determine how much sand and cement is needed per 1 cubic meter of mortar, it is important to know its purpose. To prepare masonry, plaster, foundation and other types of mixtures, different ratios of dry materials are used. The consumption of sand and cement per 1 m3 of mortar varies for each type of work, and often other dry or liquid compositions are added to the composition, increasing moisture resistance, strength, changing the rate of hardening of the mixture, etc.
What determines cement consumption for different solutions?
The preparation of cement mortar, the proportions of which may differ, requires strict adherence to technology and the correct determination of the ratio of components. To use different grades of concrete, different amounts of cement and sand are used. Remembering the proportions of cement and sand is not enough for high-quality construction; it is better to understand the principle.
Main factors influencing consumption:
- the amount of fillers in the mixture. The greater the proportion of crushed stone and sand, the higher the cement consumption per 1 m3 of solution. Cement is the binder of the components, which is responsible for holding all the fillers together. The ratio of bulk mixtures determines the amount of cement;
- brand of cement. As the grade increases, the strength of the final structure increases. It is worth remembering that the grade of the final mixture is significantly lower than dry cement, since sand is added to the composition, and gravel or slag can also be added;
- brand of solution. The cement-sand mortar is also divided by grade. For all types of work, GOST has recommended brands. After determining the desired brand of construction mixture, you can choose the right brand of cement. For example, to obtain an M100 mixture from M500 cement, you will need to mix 1 part Portland cement, 5.8 parts sand and 8.1 parts crushed stone. If the final goal is M450 solution, a proportion of M500 cement (C:P:SH) will be required: 1:1.4:2.9;
If your foundation is rubble concrete
In this case, the rubble stone poured into the trench is filled only with sand-cement mortar, because due to the use of gravel or crushed stone, voids will inevitably form in the foundation, which will significantly reduce the strength of the structure.
Such calculations will require a different table:
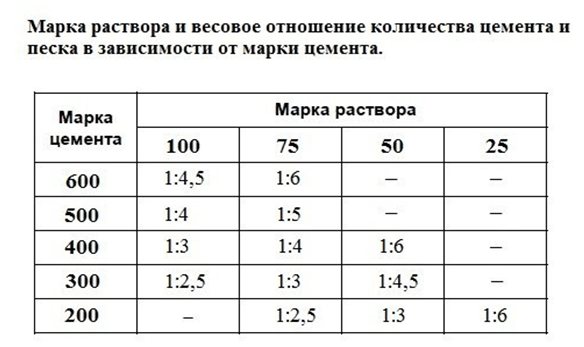
This calculation is also simple. For example, a rubble foundation requires 3 m3 of sand-cement mortar grade 100. M400 cement was selected. Reference data show that 300 kg of it is needed per 1 m3 of mixture. Therefore, according to the table, it turns out that the ratio should be 1:3, then it is easy to find the required amount of sand - it is 900 kg. Since we need 3 cubes, we multiply the figure by 3, we get 2700 kg.
A solution for rubble stones involves thoroughly mixing cement with sand and gradually adding water until the required plasticity is achieved. If there are additives in the solution, they should first be dissolved in water. They are introduced exclusively into the dry mixture.
Types and brands of mixtures
The introduction of the concept of “cement grade” helps to calculate the cement consumption per cube of mortar if the input parameters are known. To prepare a mortar with the same construction characteristics from different brands of cement mixture, different proportions of fillers will be required. Cement is produced in production, starting from grade M100, but due to the low structural strength, the material is practically not used.
The most popular cements are M400 and M500, but some other types have also become widespread. The choice of mixture depends on the scope of application of the material.
The main areas of use of cement grade:
- M300 cement is used in installation construction, as well as during the manufacture of monolithic structures;
- M400 cement is successfully used in monolithic construction and during the preparation of reinforced concrete;
- M500 cement is actively used in the construction of buildings or slabs that must be resistant to moisture or located in water. The scope of application of this concrete mixture is quite wide: the creation of sidewalks, the construction of asbestos-cement structures, the formation of large concrete masses and all kinds of foundations;

M400 and M500 cements are the most popular
- M600 cement is used to create prefabricated structures and foundations that are subject to high loads;
- M700 is a suitable grade of cement for the construction of highly loaded and stressed structures.
Material consumption rates per cubic meter of different solutions
Today there are 4 main areas of use of concrete: foundation, masonry, screed and plaster. In each case, special requirements are imposed on the building mixture, which makes the choice of cement and its consumption different. The greatest consumption of cement per cube of concrete occurs when it is necessary to make masonry or plaster. The consumption of materials per 1 m3 of foundation mortar is slightly lower due to the use of a large filler fraction: slag, crushed stone or gravel.
GOST has records of cement consumption rates per 1m3 of mortar, taking into account the purpose of the mortar. Designation of concrete per cubic meter. meters is a generally accepted system of measurement.
Consumption standards per 1 m3 using M500 cement:
- on M100 – 170 kg;
- on M150 – 200 kg;
- on M200 – 240 kg;
- on M250 - 300 kg;
- on M300 – 350 kg;
- on M400 – 400 kg;
- on M500 – 450 kg.
Consumption rates for cement and sand per cube of foundation mortar
Calculating cement for a foundation calculator is the easiest way to understand how much material is required and the number of necessary components. Concrete calculations can be done with high accuracy and manually.
To determine how much cement is needed per 1 m3 of solution, we recommend following simple instructions:
How many kg of cement in 1 m3 of solution:
- in M50 when using M400 – 380 kg;
- in M100 when preparing concrete from M300 cement – 214 kg;
- in M200 with cement M400 – 286 kg;
- in M300 at M500 – 382 kg.
The data is presented if the cube contains 2-4 parts of sand and 3 parts of crushed stone.
Consumption rates of cement and sand per cube of masonry mortar
To prepare cement mortar for wall construction, a proportion of 1 to 4 is most often used. Thus, the cement consumption per cubic meter will be 0.25 m3 or 325 kg, and the sand consumption per 1 m3 of mortar will be 0.75 m3 or 1200 kg.

Cement consumption rates for masonry
Table 1: Mortar consumption for walls of different thicknesses
| Thickness in bricks | Consumption, m3 |
| 0,5 | 0,189 |
| 1 | 0,221 |
| 1,5 | 0,234 |
| 2 | 0,24 |
| 2,5 | 0,245 |
To calculate how many bags of cement are needed, just multiply 325 kg by the consumption per cubic meter, for example, walls of one brick - 0.221. You will get 72 kg of cement for laying 1 m3 of wall, provided that the composition does not contain other components (lime, clay, etc.).
Consumption rates of cement and sand per cube of screed mortar
Cement consumption per 1 cubic meter of solution is calculated according to similar rules as in previous mixtures. The recommended mixing ratio is 1 to 3. Difficulties in calculations often appear at the stage of determining the volume of the solution, so let’s look at an illustrative example. It is necessary to fill a surface of 3x4 m or 12 m2. The layer thickness will be 30 mm.

Cement consumption rates for screed
Calculation of cement for screed from the example:
- We calculate the required volume of solution: 12 m2 * 0.03 m = 0.36 m3.
- We determine the brand of cement, M200 solution is often used, and we use it as an example. We will cook from M500, and according to the standards, the consumption will be 410 kg.
- We calculate the required number of bags of cement: 410 kg * 0.36 m3 = 148 kg - this is 6 small or 3 standard bags of 50 kg each.
- We determine the cost of sand. To do this, we multiply the specific gravity of 1 m3 of sand by the required amount of the finished mixture: 1600 kg/m3 * 0.36 m3 = 576 kg, and since the share of sand in the total solution is 75%, we also multiply by 0.75 - 432 kg of sand. Sand consumption per 1 cubic meter of solution is approximately 1200 kg/m3.
Consumption rates of cement and sand per cube of plaster mortar
Cement consumption per 1 m2 of plaster greatly depends on the quality of the wall covering, the required layer thickness and the number of large holes. Again, for clarity, we will give an example of a calculation, remembering that a mixture of 1 to 4 is usually used. Input parameters: it is necessary to cover 60 m2 of walls with plaster 2.5 cm thick.
Calculations of cement and sand consumption per 1 m3:
- Amount of materials in cubes. For 1 m2 you will need 1 * 0.025 = 0.025 m3 of solution, where a fifth is cement and the rest is sand. Using elementary mathematics, we determine that 0.02 m3 of sand and 0.005 m3 of cement will be required.
- For the entire area of the wall you will need: 0.02 * 60 = 1.2 m3 of sand and 0.005 * 60 = 0.3 m3 of cement.
- The specific density of cement is on average 1400 kg/m3 (fresh 1100-1200 kg/m3, and compacted 1500-1600 kg/m3). We determine the cement consumption: 0.3 * 1400 = 350 kg.
- Required weight of sand: 1.2 * 1600 = 1920 kg, we remind you that 1600 kg/m3 is the specific gravity of sand.
All calculations are simple; it is only important to choose the right brand of the initial mixture and the desired brand of output solution. Everything else can be easily calculated in a few mathematical steps.
How much sand, crushed stone, cement is in 1m3 of concrete?
In construction, concrete grades are used that are designed to create products that perform specific functions in building frames. The parameters of concrete structures and their compliance with the tasks assigned to them depend on compliance with the volume and weight ratio of the components in concrete. Errors in establishing the proportions that make up a concrete batch lead to problems.
Component Requirements
It is important to understand what values of concrete properties and what grade of concrete are required. Therefore, the components of the concrete composition must meet certain requirements to obtain an artificial stone that has the specified quality parameters. When selecting, you should consider:
- for cements - setting time interval, volume (weight), activity;
- for sand - purity, humidity, size and shape of fractions, volume (weight), voidness;
- for crushed stone - size and shape of grain fractions (concentration of lamellar and needle-shaped forms), weight (volume), strength, moisture absorption, cleanliness;
- for water - purity, volume.
These parameters form the final brand indicators of concrete characteristics, as well as equally important intermediate indicators of properties - workability and density of the solution. Inattention to the initial quality of crushed stone, cement, water and sand leads to a shortage of brand values. The quality of the structure may suffer because of this.
The most important parameters are the freshness of the cement and brand characteristics (for example, strength, frost resistance, etc.). The higher the numerical value of the brand, the higher the characteristics.
For the filler, the large irregularity of grain shapes and surface roughness (limestone, crushed granite) are important. If gravel grinding with round grains is used, the strength is reduced. The filler should be removed from dust and dirt by washing. This requirement also applies to sand. It, as a sedimentary rock, should consist only of grains up to 0.3 cm in size and should not contain clay impurities.
To clean, the sand mixture should be washed with water. Sand is prepared by sequential sifting through meshes with cells of 0.25, 0.12 cm and 0.315 mm. The last fractions that pass the sieve become fillers. It is also important whether dry or wet sand is used. The moisture in it distorts the actual proportional relationship with other components.
The correct water-cement ratio ensures the required duration and intensity of the solution hydration reactions. The optimal amount of water is 40% of the weight of dry cement. Increasing its volume delaminates the mixture, contributing to a lack of strength; insufficient volume stops hardening. The solution should be thick, but not hard, workable, but not leaking through the seams of the formwork.
Brands of concrete and ratio of sand, cement and crushed stone
The proportions of the components of the mixture determine the grades of concrete, and they, having expressed characteristics, are used to create specific structural elements (walls, foundations, flights of stairs, partitions or paths in the garden) of buildings. Concrete has a developed classification of grades, for example, according to:
- compressive strength (“M”);
- water resistance (“W”);
- mobility (“P”);
- frost resistance (“F”), etc.
Various additives that increase heat resistance, ductility, frost resistance, hydrophobicity, etc. also help to modify (significantly enhance) the characteristics of concrete.
Thus, the weight ratio of the components determines the parameters of concrete. The established practice of using various compositions has revealed the exact weight ratios of the parts of the solution, which ultimately determine the properties of concrete. The grade determines the amount of cement in the mixture relative to sand and crushed stone. Therefore, in some cases, you should refrain from using PGS, since due to ignorance of the exact ratio of sand and gravel in it, it is impossible to predict in advance the quality of the future concrete product (for example, a foundation).
It is necessary to predict the quality of concrete based on the exact ratios of cement and fillers. An example is concrete grades from M100 to M450, prepared on the basis of M400 and M500 cements. Table 1 shows their proportions in parts. For example, the ratio 1.0: 4.1: 6.1 means that 4.1 kg of sand and 6.1 kg of crushed stone are taken for cement weighing 1 kg.
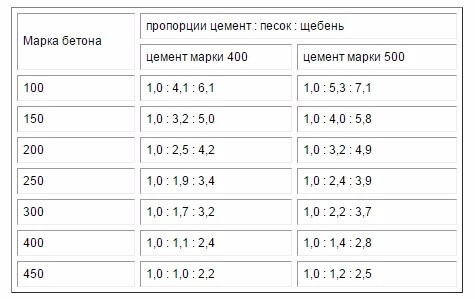
Table 1.
Thus, lightweight concrete M100 is laid in sidewalks, paths, screeds inside buildings, and non-load-bearing, weather-proof structures are created from it. Lightweight concrete M150 is already allowed for the formation of lightweight foundations (garages, sheds). Retaining structures, staircases, and platform bases are cast from grade M200. Concrete M250 is even stronger, therefore it has proven itself in private construction, including when casting reinforced floor slabs.
The most used brand is M300 when pouring grillage piles and strip foundations of brick buildings up to 3 floors high, blind areas. M400 concrete is used to form foundation slabs of high-rise buildings, columns, beams, piles, monolithic pools, etc.
Calculations and indicators of components per cube of concrete
During production, it may be necessary to use units of volume of components, for example, when several cubes of components are delivered to the site for mixing concrete. Also, for example, crushed stone and sand can be supplied not in tons, but in cubes. The mass of cement M400 (M500) per cubic meter is from 1600 to 2500 kg, sand - 1500 kg, and crushed stone (fraction up to 4 mm) - 1410 kg. You need to know that adding sand to the mixture does not increase its volume beyond 1 m3. The fine structure of cement fills the voids between grains of sand, so the weight of the mixture increases, but the volume does not.
Therefore, one m3 can “absorb” up to 400 kg of sand without consequences. To find out how many components should be in 1 m3, you need to make a calculation. One cubic meter of any concrete mixture has a certain density. The calculation involves dividing the density of the concrete mixture of the declared brand by the sum of the parts of the components (Table 1) that are included in its composition. The answer is the weight of one part of the composition. Next, you need to multiply the result obtained by the numerical value of the parts indicated in the proportions for cement, sand, and crushed stone.
As a result of the calculation, it will become known how much of these materials is used to fill one cubic meter of concrete of the selected brand. The following approximate densities of grades of substance are accepted (in 1 cube):
- M400 and above - 2500 kg;
- M250, M300 - 2200 kg;
- M200 - 1800 kg;
- M100, M150 - 1600 kg.
Material consumption per cubic meter of installation is shown below in Table 2.
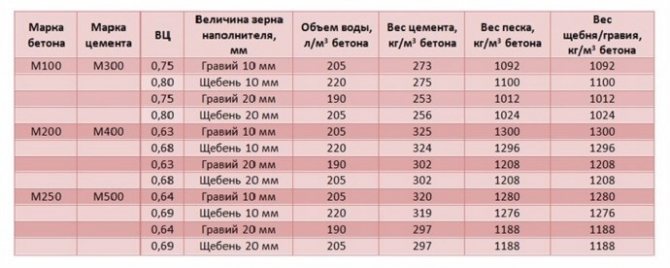
Table 2.
What kind of concrete is needed when laying paths?