Caring for the foundation after pouring is an important stage in the construction of a monolith. The quality of the structure depends on how the work is done correctly. The main task is to maintain the required humidity and temperature; for this you will need to organize watering and protect the monolith from wind and sun. How often, how much and why you need to water the foundation after pouring is a question that we will discuss below.
Proper aging allows you to extend the service life of the base
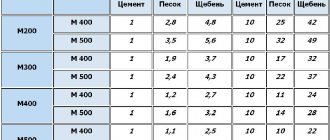
Concrete composition
Concrete is an artificial stone that is obtained after hardening. This happens when excess moisture comes out of the solution. This process is called maturation and lasts four weeks. During this time, stable connections between the components are formed.
Table of concrete proportions in kilograms per cubic meter
The mixture contains: cement, water, sand, gravel, and various additives. If necessary, they speed up or slow down the process of hydration - solidification. With the help of additives you can work in the cold season. Additives affect the elasticity of the solution and prevent shrinkage. But the main role is played by cement, sand, gravel, and water.
The condition of the concrete mixture depends on their quality.
Crushed stone
This is a natural material that is obtained by crushing rocks. Acts as a coarse filler.

Crushed gravel with fraction 5-20
It adds volume, prevents shrinkage, and creates the necessary strength. The strongest crushed stone is obtained from granite; cheap ones, made from slag, are also used. The amount of crushed stone in the concrete solution is at least 1/3 of the total volume. The crushed stone fraction comes in two types: 5–20 mm or 20–40 mm. The thicker the concrete slab, the larger the fraction needed.
Sand
Sand is a fine filler, the purpose of which is to add volume, ensure good cement adhesion, and, after drying, prevent it from cracking. The density of the material must be at least 1.5 kg/m3. fraction size 2–5 mm.

It is more expedient to sift this component from small impurities
River sand is used, which is well distributed in the solution due to its round shape. Sand is used clean, without clay and dust, the total amount of impurities should not exceed 5%.
Cement
Cement is a substance that binds components in concrete. Consists of clinker, gypsum additives, minerals. After cement gets into the water, solid formations are formed, with the help of which the sand and crushed stone are bonded. It is divided into several brands. The most used at home is the Portland cement brand.
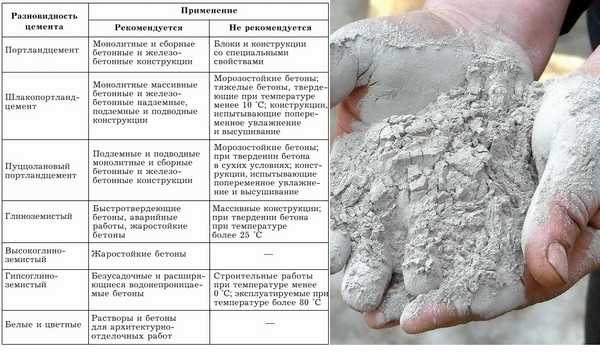
Types of cement and their applications
You need to purchase finely ground cement, it dissolves quickly in water and sticks together better.
Water
It is better to use fresh water without harmful impurities. Sea and standing are not suitable for mixing mortar, as they contain a lot of salts and impurities that prevent the cement from hardening. For the hydration reaction to take place, 5% of the total mass is water. But they add more so that the mixture is fluid; it is convenient to fill the foundation with such a solution.
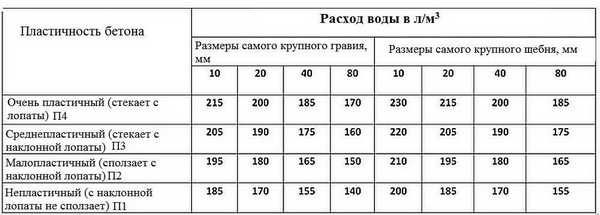
Table of the amount of water depending on the size of the crushed stone and the fluidity of the solution
Plasticizers and antifreeze additives
These are special mixtures that improve the properties of concrete. They allow you to work at sub-zero temperatures and can increase or decrease the rate of hardening. Modern additives affect not only the solution, but also the reinforcement used for the frame, making the mixture light, elastic or dense.
These additives allow you to fill the solution in the winter season
Plasticizers are used to accelerate strength gain. They reduce the amount of water in the mixture, which reduces cement consumption and makes it possible to obtain more durable concrete.
Antifreeze additives lower the freezing point of water and accelerate the hardening process of concrete. Using additives, you can reduce cement consumption and work at low temperatures.
In winter time

We recommend: Monolithic private house - a combination of traditions and new technologies
For this purpose, during winter concreting or autumn, the following measures are recommended:
- Thermos device . The process of hydration produces heat. If its leak is eliminated, no additional heating will be required. The thermos effect is achieved by equipping the formwork with special insulated panels, as well as by applying heat-insulating covers to the concrete.
- Electricity use . Artificial heating of a concrete structure is carried out by heating elements, steam generators or by exposure to a warm air flow.
- Combined method . It is based on covering the structure with a “tent” and using a heat gun. Another option is to introduce special additives into the solution that reduce the freezing point of moisture. At the same time, the concrete mass is covered with heat-insulating materials.
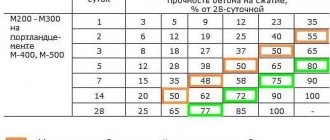
Concrete grade
Concrete is a common building material, without which it is difficult to imagine any construction. It is used for the construction of monolithic buildings, various foundations, and reinforced concrete structures.
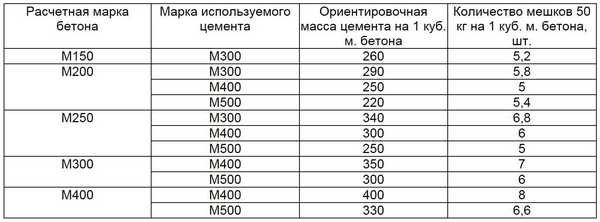
Conformity table of brands and classes
Depending on the task and location, the solution is mixed in different proportions, this determines the brand. It is divided according to three main characteristics:
- Grade is an indicator of the compressive strength of concrete, marked with the letter “M” and numbers. The number indicates what load the solution can withstand in kgf/cm2.
- It is also classified according to its water resistance. This indicator is marked with the letter “W”. The numbers show the pressure at which the solution does not allow water to pass through.
- It is also divided according to frost resistance. This indicator is designated by the letter “F”. The numbers show the number of freezing cycles after which the material does not lose quality.
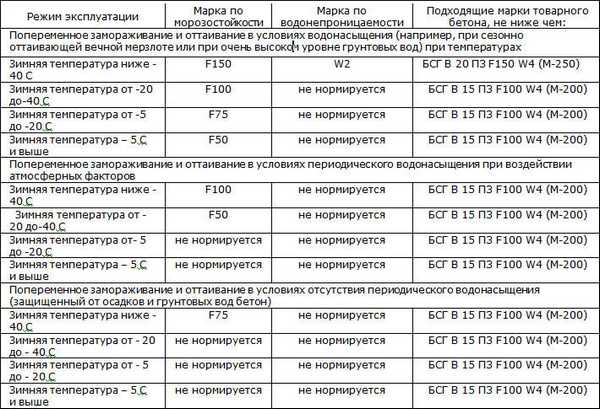
Table for choosing the composition for frost resistance and water resistance
For each type of product, the appropriate brand is used. For example, high-rise buildings, bridges, strip foundations, roads - buildings with varying degrees of compressive and tensile load.
Dust removal
At large industrial facilities, in public buildings, in garage complexes, in home workshops - everywhere they try to make the floor concrete. He is very practical. A properly executed screed does not absorb moisture. It has a solid base and a smooth, even surface. It is difficult to slip on it, and it is easy to care for. The only drawback is the formation of a large amount of dust. Over time, chips and traces of delamination appear on the front surface. And if the concrete floor is not properly cared for, even the most minor defects will become dangerous to human health.
Their appearance becomes possible for various reasons. And all of them are associated with intensive use of floors. Mechanical loads, chemical influences, non-compliance with laying technologies, incorrect concrete composition, low-quality components taken when mixing the solution - all this leads to the fact that even the strongest floor gradually begins to fail.

Dust on the surface of concrete Source janiclean.com
Features of foundation care
The monolith is poured in the warm season, because at sub-zero temperatures the solidification process of the solution stops.
In summer, under the influence of weather conditions and internal processes, the temperature rises, so water quickly evaporates from the solution. The top layer of the monolith heats up more than the inner layer, causing it to harden faster.
As a result, gaps appear inside the foundation, which contributes to the formation of cracks. In winter, water gets into the cracks, freezes and breaks the monolith. To prevent this from happening, the base must be constantly wet.

Timely watering prevents the formation of expansion joints and tears
You need to carefully monitor the corners, since the sun's rays and wind hit them from both sides. The edges of the monolith dry quickly and then crumble, so they are watered and covered with film. To avoid causing mechanical damage to the corners, the formwork is dismantled a week after pouring. By this time, the concrete mixture will have gained sufficient strength.
It hardens best at temperatures from +18 to +22 °C and air humidity of 80%. If the temperature is above +25 °C, the monolith is covered with film or covered with sand. To prevent the film from being torn off by the wind, it is pressed down at the edges with a weight or stapled to the formwork. The film creates a greenhouse effect, does not allow moisture to quickly leave the solution, then the reaction continues and the concrete gains its design strength.

An example of covering a poured base with film
What activities are needed?
The formation of a concrete structure with maximum strength is a long-term physical and chemical process, which is based on the hydration reaction, i.e. formation of chemical compounds of cement with water . This process can take years, but the most active stage ends after 27-28 days.
For a full reaction, a certain humidity and temperature regime throughout the entire period of the main hardening. As the temperature decreases, the reaction slows down noticeably. The optimal mode is temperature within 17-24 degrees and humidity 75-85 percent .
Important!
The most active strengthening of concrete occurs in the period 10-12 days after pouring. At this stage, it is especially important to ensure normal levels of humidity and temperature.
The hardening of the concrete mass is accompanied by its shrinkage , and this phenomenon becomes more intense with increasing drying speed. Severe shrinkage leads to the formation of numerous cracks. This circumstance requires taking measures to prevent excessively rapid drying of the material after pouring.
It should also be taken into account that the hydration reaction proceeds with the release of heat , and its uneven distribution throughout the volume can also lead to cracking of concrete.
Only ensuring uniform, gradual hardening of the solution under optimal temperature and humidity conditions ensures the required quality of the material.
The purpose of caring for concrete after pouring is to create the required conditions .

Why water concrete?
After concreting, in the first day, the solution actively gains strength, and therefore requires increased attention. In the first week, it gains more than half of the declared strength, about 70%, if the necessary conditions are created. To maintain the desired temperature and humidity, the foundation is watered and then covered with film.
The total maturation time for concrete is 28 days. After this period, you can begin to load the base.
It is recommended to remove the formwork after a week, by which time the solution will set and the monolith will not break during formwork removal.

Disassembly of the formwork system, depending on the time of year, should be carried out no earlier than 7 days after pouring
How to water concrete
How many days to water the foundation after pouring is the main question faced during construction. Concrete requires special attention in the first days after pouring. The process of hydration - hardening - occurs in it. To protect the poured base from cracking and mechanical damage, you need to properly moisten it.

Watering should be done evenly, without sudden splashing.
During the first hours, the foundation should not be watered with a hose with strong pressure. The poured concrete has not yet set, and the jet will damage the surface of the monolith. Water must be sprayed through special nozzles or using a watering can.
When the temperature is above +25 °C, the concrete mixture hardens quickly and you need to start watering every 2 hours. In the first 24 hours after concreting, the base is watered every 3 hours day and night.
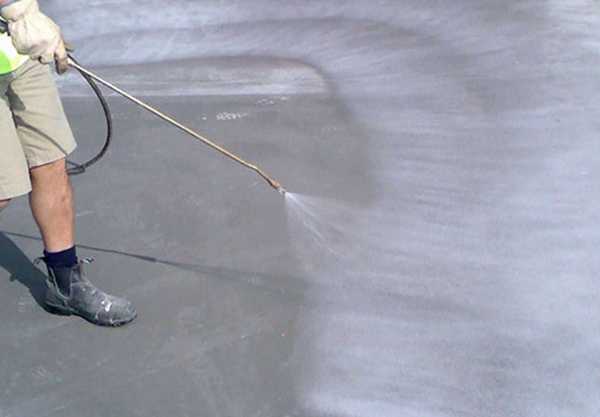

It is more advisable to apply moisture using a sprayer
Then, during the first week, the monolith is moistened every 4 hours during the day and once at night. The second and subsequent weeks until the foundation is fully matured, the foundation is watered twice a day.
During the hot period, when the temperature rises above +35 °C, the amount of humidification is increased. If you hear hissing during watering, this is the first sign that the concrete lacks moisture. At a temperature of +5 °C, the hardening process stops and there is no need to water the monolith.

It would also be useful to protect the composition from dirt and excess moisture.
How many days to water the foundation depends on weather conditions, brand, and additives used to prepare concrete. The main indicator of normal watering is a moist foundation throughout the entire ripening period. At temperatures from +18 to +22 °C, the solution gains the required qualities in 28 days.
Proper watering of the foundation ensures:
- minimal shrinkage of the mixture;
- regulation of the evaporation process;
- preservation of concrete inside without microcracks.

As an alternative to sprayers, you can use a regular hose with an adjustable nozzle for watering.
If the monolith is watered incorrectly, microcracks form in it, frost resistance decreases, and uneven shrinkage occurs. All this will lead to a deterioration in the quality of concrete, and then to its destruction. For irrigation, use water that does not contain harmful impurities Na, Mg, Ca. The water must be acidic with a value no higher than pH 7 and not contain salts. The use of such water is unacceptable, as it harms the hydration process.
Features of care in the summer
Caring for the foundation means creating conditions under which the process of maturation of the concrete mass occurs within the prescribed time frame. This is necessary so that it does not crack, and by the end of construction it gains the necessary strength.
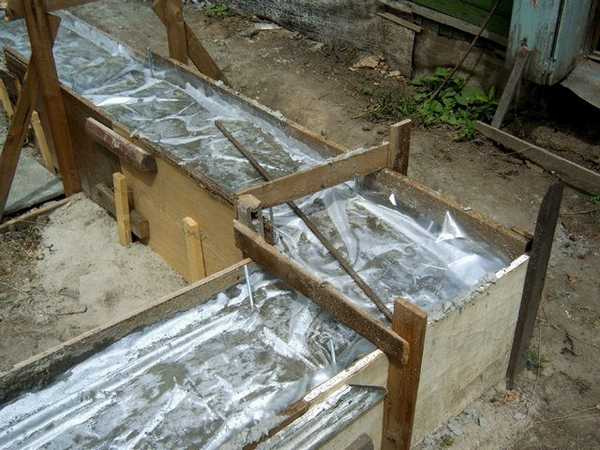

In areas exposed to the wind and sun, it is advisable to “wrap” it with film.
Therefore, the following rules are observed:
- Avoid direct sunlight and wind exposure of freshly poured concrete. Rapid hardening negatively affects quality. To do this, the foundation is covered with plastic film or tarpaulin.
- When the temperature is above +20 °C, it is necessary to water the formwork walls before concreting. If the formwork is removed before the final maturation period, the sides of the monolith also need to be watered and wrapped.
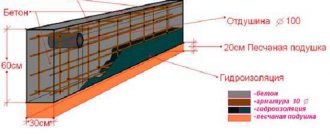
- Concrete must be protected not only from above, but also from below from groundwater. To do this, they make waterproofing at the bottom of the foundation and a drainage system. Protection is needed for two weeks until the solution acquires the desired properties.
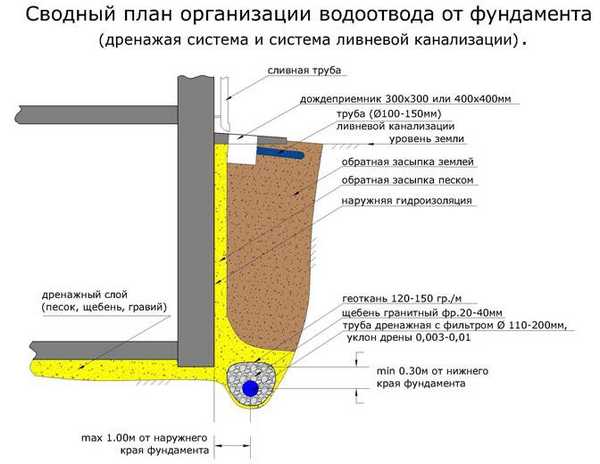
Wall drainage diagram
Features of care in the winter season
The main difficulty of concreting at sub-zero temperatures is that water freezes. When the temperature in the solution drops below −5 °C, the solidification reaction stops. To prevent this from happening, the poured base is heated.
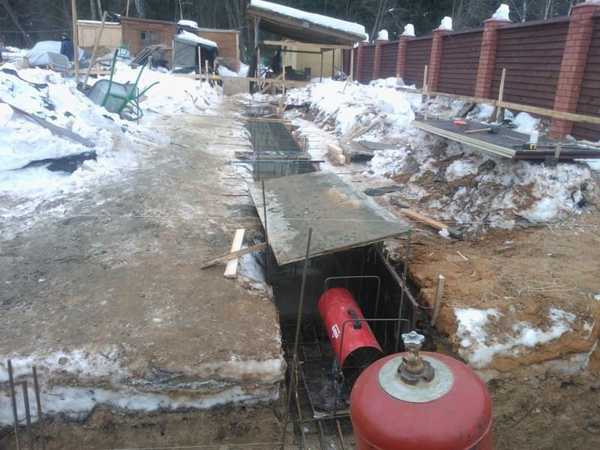

Heating the base using a gas cylinder
This is done in the following ways:
- Electric heating.
- Heating with a heat gun.
- Wrapping with mats that retain heat.
- With the help of antifreeze additives.
During winter concreting, the foundation can be heated with electricity. Electrodes are inserted into the raw mixture and connected into one circuit. After which it is connected to 220 V or 380 V. Due to the discharges that occur inside, the concrete heats up.

A less labor-intensive way is to add plasticizers
If possible, use a heat gun for heating. To do this, the foundation is covered with polyethylene or tarpaulin and a flow of warm air is directed inside. Heat guns are divided into three types: electric, gas and diesel, operating in autonomous mode.
To prevent the foundation from freezing, it is covered with warm mineral wool mats. Straw and rags are also used for insulation. The main task is to maintain a positive temperature so that the hydration process does not stop.

Laying out old rag luggage on a flooded surface
In winter, when it is not possible to heat concrete with electrodes or a heat gun, the solution is mixed with antifreeze additives. The mixtures allow you to work at negative temperatures, speed up or slow down the hydration process, depending on the task.
Concrete is not afraid of frost, but of temperature changes when freezing and thawing occur. This happens in early spring or late autumn. The lower the temperature, the slower the rate of strength development.
Additives, insulation, heating - all this prevents the water from freezing, which avoids freezing and thawing cycles. Objectives: eliminate cooling, prevent water from evaporating quickly. At temperatures above +5 °C, it takes three to four days for concrete to gain 50% strength. Heat conservation is an important task when concreting in winter.

Electric mats keep you warm
Formworks
Modern designs provide sufficient protection from drying out; the remaining open surfaces should be covered immediately after pouring in dry weather.
To prevent wooden formwork from absorbing moisture and ensure high-quality hardening of concrete, its inner surface is first coated with a special oil composition. It will not be superfluous to systematically spray the outside, especially in hot weather.
Small structures require increased protection from drying out compared to concrete masses, this is due to the developed plane in combination with the available volume. Edges and corners begin to dry out faster than other areas.