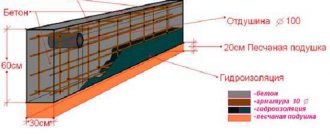
One of the main disadvantages of wooden building materials is their high susceptibility to rot and vulnerability to wood-boring beetles. Since these processes are a direct consequence of increased wood moisture, most often such damage occurs in the lower part of the walls, for which the lower crowns have not been properly waterproofed.
It should be noted that moisture insulation of the lower crowns means not only the physical and chemical treatment of building materials, but also a number of design solutions, during which a slight modernization of the foundation may be necessary.
This review examines what affects the durability of the base of a log house, and what technologies exist to prevent its destruction.
What destroys the lower crowns of log houses
Modern technology for building wooden houses involves installing a log house on a stone foundation.
In this case, the foundation of the house is exposed to several dangerous factors:
- capillary moisture coming from the foundation;
- humid atmosphere from the basement;
- lack of sunlight, since the lower part of the wall is often in the shadow area;
- drip moisture and temperature changes from the outside of the walls.
Damaged logs
In the latter case, the situation is aggravated by the fact that if the base configuration is incorrect, moisture flowing from the walls during rain accumulates in the lower logs and in the inter-crown seals.
A direct consequence of the factors listed above is the development of microbiological formations in the wood, affecting its structure and ultimately leading to a complete loss of strength in the lower crowns of the frame.
The greatest biological danger to logs is represented by fungal structures, the first signs of which are the so-called blue discoloration, sometimes penetrating into the very core of the log.
The nutrient medium for such fungi is lignin, cellulose and oxygen. But the main catalyst for their development is always high humidity.
The second factor in the biological damage to wood is wood-boring beetles, the appearance of which is almost always associated with fungal infection of wood.
Taking into account the above, the main methods for solving the problem of lower crowns are:
- saturation of wood with antiseptic compounds that impede the development of microbiological formations;
- reduction in the capacity of the external capillaries of the logs, necessary to stabilize the internal moisture content of the wood at an acceptable level.
As mentioned earlier, the solution to the listed problems is carried out not only through additional processing of wood, but also through the use of special design solutions, the most significant of which will be discussed below.
How to waterproof a log house from the foundation?
The foundation is the basis of the entire building, whatever its size, the foundation will be simply necessary. When building a house, you need to take care not only of building the foundation, but also of protecting it. It is imperative to lay waterproofing between the foundation and the log house in order to protect the house from water, which threatens it with the formation of mold, mildew, high levels of humidity, dampness, and so on.
Scheme of a columnar foundation.
Types of waterproofing
There are two types of foundation waterproofing:
- Anti-filtration.
- Anti-corrosion.
Waterproofing a wooden frame from a concrete screed.
The second is used in most cases, the first is not always used, only when the moisture is too “aggressive” (when substances that have a bad effect on the foundation are dissolved in the water). There are painting, pasting, impregnating, backfilling and plastering types of anti-corrosion insulation. The difference between these types lies in the materials used, and the use is made taking into account the assigned tasks.
Waterproofing is carried out in two planes at once - it is necessary to provide protection from the ground, both under the foundation and along its walls. These manipulations will prevent moisture from penetrating into the foundation. Horizontal waterproofing is carried out using a plaster composition, which is based on cement-polymer mastic, cement-sand mortar or emulsion paste. In addition, a layer of polyethylene can be laid between the soil and the base. Vertical insulation is carried out using impregnating, plastering and painting materials.
In the case of a block base, work will need to be done to seal holes in the blocks and level out roughness.
If you want the house to stand for a very long time, then using waterproofing between the log house and the foundation is simply necessary.
Return to contents
Foundation diagram with waterproofing for a log house.
Waterproofing between the log house and the foundation is necessary to prevent moisture from entering the basement; it helps prevent the foundation from absorbing moisture. Moisture is formed for several reasons, in particular runoff (melt snow, rain) and groundwater (underground).
If the base is not sealed, water may enter the basement, which can lead to the formation of mold, dampness, and in the worst case, possible destruction, which can lead to shrinkage of the house, cracks in the foundation and its eventual destruction.
Waterproofing laid between the foundation and walls and between the foundation and the ground will help ensure long service life and dryness in the basement.
Return to contents
Waterproofing work involves the use of certain materials suitable for providing insulation between the foundation and its adjacent objects. Waterproofing involves the use of roll material and bitumen mastic:
- Coating type of waterproofing (insulation with bitumen mastic).
- Pasted type of waterproofing (roll insulation).
Scheme of hydraulic protection of the foundation.
Protecting the foundation from moisture by using bitumen mastic is the most cost-effective option among all types of waterproofing. The properties of bitumen mastic guarantee the reliability and elasticity of the coating. Using mastic, you can seal the pores and cracks that exist in concrete by creating a durable and moisture-resistant film.
When choosing bitumen mastic for work, you need to opt for an option with high heat resistance, which will not be affected by temperature changes. It is important to know that many bitumen mastics lose their elasticity already at a temperature of -5°C; it is possible that the mastic will even begin to crack if the soil temperature drops below 15°C.
The temperature limit is very important; you need to take into account that the mastic is resistant to temperatures above 60°C, so that the mastic does not slide off when exposed to high heat. Thus, when purchasing mastic, pay special attention to its temperature and thermal stability in order to extend the life of the material used.
In cases where the area where the construction is taking place has a low groundwater level, a drainage system is provided on it and there is no likelihood of flooding, then this waterproofing option using bitumen mastic is just right and will be sufficient. But when a more reliable type of waterproofing between the foundation and the ground is required, it would be advisable to apply roll insulation directly on top of the mastic.
The roll waterproofing method involves the use of rolled material, such as glass insulation or roofing felt. This type of waterproofing is considered the most reliable; it provides the highest degree of protection for the foundation.
Roofing felt is a practical and profitable product; it is slightly inferior in quality to glass insulation, which is not only more expensive, but also more reliable than roofing felt, which provides a longer period of protection.
Return to contents
Diagram of the device of roll material for waterproofing.
Carrying out the waterproofing process with your own hands is not particularly difficult. It is important to take care of properly organized preparatory work before waterproofing. It is necessary to prepare the working space, for this it will be necessary to ensure a distance between the ground and the foundation of approximately m, which will ensure the ability to work without restrictions on movements and difficulties in accessibility of the foundation along its entire height, starting from the base.
To begin with, we inspect the foundation and if we find any irregularities or depressions, we carry out work to seal them. This applies to strip foundations. If the foundation is concrete, then you will need to seal the joints between the blocks. All work is carried out using cement.
When these works are completely completed, you can begin to use bitumen mastic on the outside of the foundation. It must be applied in two layers, lubricating all areas with gentle movements. Application is done using a wide brush with stiff bristles. It is important to pay attention to the application method: the first layer is applied with movements in a horizontal direction, and the second (after the first has completely dried) with vertical movements.
Waterproofing using rolled material is known and widespread in two different types - horizontal and vertical. Each of these types involves applying material along the outside in a certain direction. That is, vertical insulation is applied vertically, horizontal insulation is applied horizontally. Both types of gluing take place; it is impossible to say which is better and which is not. Each of them is selected for a specific foundation, focusing on the terrain and soil.
Horizontal waterproofing is more reliable, but vertical waterproofing is much easier to apply. Rolled waterproofing must be applied to an already applied layer of mastic. When using waterproofing, it is necessary to heat its lower part with a burner, gradually unroll the roll and apply it to the foundation. At the end of application, you need to warm up all the resulting joints and treat them with mastic to ensure reliable protection.
In cases where waterproofing is carried out in winter (which, of course, is best avoided), it is important to first clear the foundation of snow and frost. Next, the surface warms up and only after such preparation the waterproofing procedure begins.
Only after a correctly carried out procedure for waterproofing the foundation can you proceed to installing the log house on top of the foundation. Two layers of roofing material are laid between the log house and the foundation. And between the logs it is necessary to place wet moss (the so-called bear insulation).
It is important to carry out all work carefully and carefully so that the structure lasts a long time. If you do not have confidence in your abilities, then it is better to entrust this work to specialists.
Special design of the lower crown
Cause of the problem
If you imagine the volumetric structure of a log house, you can see that the classic lower crown, assembled “in a bowl,” cannot be placed on a single-level foundation without a gap. It should be remembered that the larger such cracks and gaps are, the higher the likelihood that they will become moisture accumulators and cause the logs to rot.
In this connection, sealing the lower crown begins not with treating the logs with mastic or impregnation, but with pairing its geometry with the geometry of the foundation.
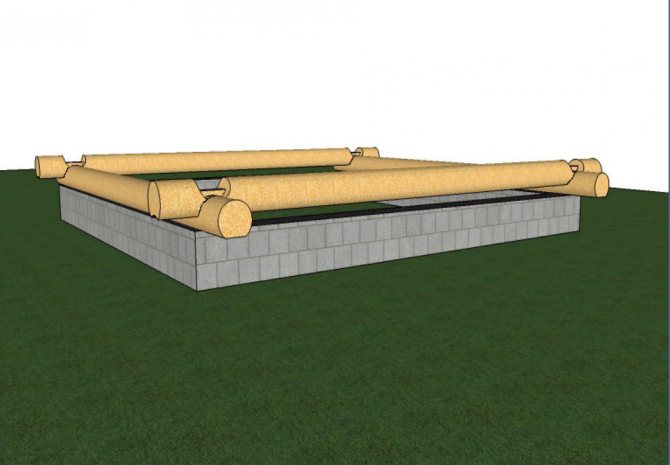
There are two options for solving this problem:
- production of a two-level foundation;
- sawing logs to create a dense contact zone along the entire perimeter of the crown.

Example of a multi-level foundation
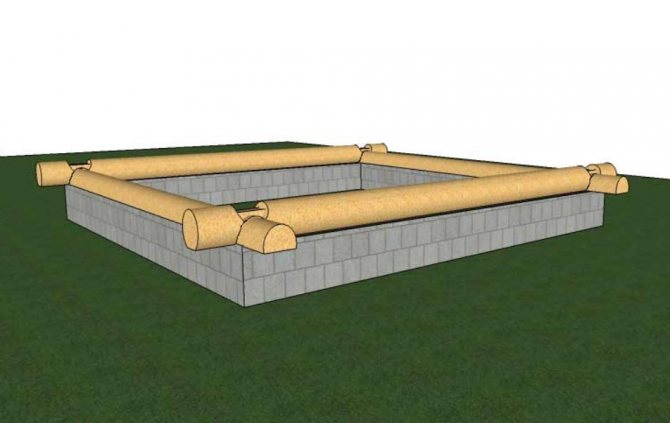
Second method, schematically
The first option is used for the construction of small buildings (baths, barns, etc.).
The second method is more commonly used, as it avoids the need for “shaped casting” in the corners of the foundation and allows the use of a solid interlining board made of durable wood.
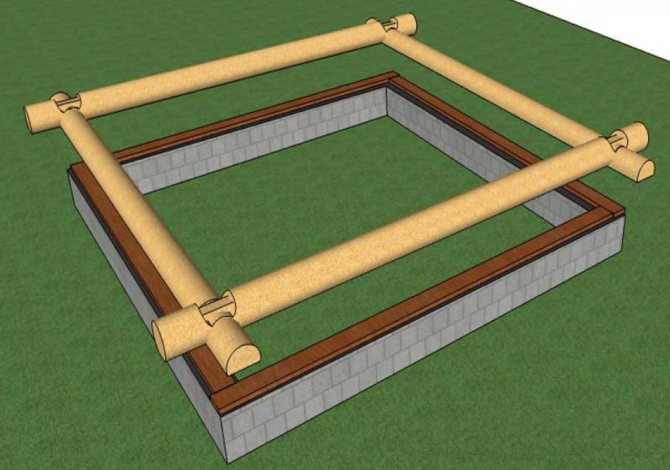
Laying board
We will separately consider such a solution as the above-mentioned spacer board, which is the simplest way to extend the service life of a log house by a good ten years, and also greatly facilitates the repair of the lower crown, if the need arises.
The essence of this solution is that a wide board made of the most stable type of wood (oak or larch) is laid between the foundation and the lower crown of the log house.
Please note that a wide board is always made from the central sectors of a log, the maximum stability of which is observed only in larch.
At the same time, it is important to take into account one feature of this technology: additional processing of the padding boards with any chemical compounds is not carried out. The sealant is laid using the same method as for inter-crown gaps.
Vertical and horizontal waterproofing
Vertical waterproofing is carried out in a place located between the base of the foundation and the level of rainwater ingress when splashing. It requires a particularly careful approach to the quality of the material used, or more precisely to its moisture resistance, which will guarantee that the floor in the bathhouse will not be damaged by water. The main task of this type of insulation is to provide reliable protection at the points where horizontal insulation is discharged and directly at the joints of the vertical insulation itself. Taking into account all the nuances, be it the thickness of the layer, the choice of soil, as well as the installation of various protections using polystyrene foam boards, asbestos cement sheets and other protective materials, should be carried out at the design stage and when backfilling the pit.
As for horizontal waterproofing, it is used to protect walls from capillary absorption of moisture and consists of several layers of bitumen roofing felt. Usually, two horizontal waterproofings, independent of each other, are made. The first is located under the basement floor, and the second is located at the support points of the walls on top of the foundation slabs. It is worth remembering the need for a reliable connection of horizontal and vertical insulation at their joints, as well as both horizontal insulation in the floor area.
Waterproofing between the foundation and the log house
The most important point affecting the durability of the lower crowns in houses made of timber or logs is the correct organization of waterproofing between the foundation and the log house.
The fact is that most of the now popular “stone” building materials have good capillary conductivity, and if additional waterproofing measures are not taken, the lower crown will always be wet.
In this case, moisture is cut off by laying sheets of roofing material or by covering the contact zone with liquid rubber.

Roofing felt waterproofing
Roofing felt is laid according to the standard method (on liquid bitumen), and an inter-crown sealant must be laid between the waterproofing and the crown.
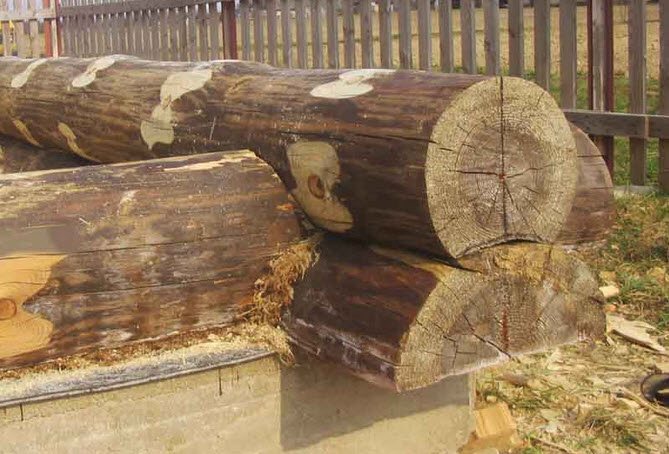

Correct first crown
Laying timber on the foundation
The first row of timber has been laid.
How to lay timber on the foundation when building a house, bathhouse or other building from it? There are various fastening options. An important point is the waterproofing of the base.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EXfJRUCvbUI
Protection from water is needed to prevent the lower crowns from rotting. If the differences in the foundation level exceed 1 cm, then the supporting surface must first be leveled.
Compliance with the technology of installation work allows you to obtain a high-quality result - a durable structure.
The lower crown of timber for a log house or frame-panel structure requires replacement most often, so the installation is carried out in such a way that repairs can be easily carried out.
Anchoring scheme
It happens that builders do not attach the first crown of timber to the base. Due to the significant weight of the structure, they believe that the erected structure will not move.
The studs are laid when the base is poured with concrete. At the same time, their height reserve is taken such that the first row of timber can be tightened using nuts without problems. To secure the lumber, holes are drilled in it for studs.
On screw piles with U-shaped or plate heads, the crowns located below can also be changed if they use up their resource.
Anchored, rigid fastening does not allow the structure to be repaired in the future.
Metal corners, staples, and nails (including wooden ones) are also used to secure laid beams to each other. These fasteners are used in conjunction with groove joining.
Base insulation
Before laying the first crown, the upper foundation surface is leveled even if there is a centimeter deviation of its level from the horizontal plane. Afterwards, waterproofing material must be laid.
Waterproofing the foundation under the lower beams of the building
The upper surface of the base must be without slope, drops, and perfectly leveled. They check this with a laser or water level, or a construction level. Leveling is often performed with cement-sand mortar.
It can also be used to close a gap if there is one between the lower crown and the foundation surface. Recently, construction foam has been mainly used for these purposes. After hardening, its excess is cut off with a knife.
At the end of the work, the sealed area is covered with a decorative strip or ebb.
As a moisture-proofing coating, roofing felt is often used simultaneously with glass insulation.

The materials are laid on the base so that they protrude beyond its edges by approximately 0.25 m. It is recommended to make a waterproofing coating of two layers.
Boards are placed between them. In the corners, roofing felt or other material used is overlapped.
The first crown must be placed on top of the waterproofing. This is due to the fact that capillary moisture reaches the lumber from the soil through the monolithic base. The wood quickly rots and the building requires repairs.
Working with a chainsaw
The preliminary stage before laying the first crown of timber on the foundation is to prepare the material and tools.
Everything you need for the job is presented in the table below.
No.Tools and accessoriesMaterials
| 1 | large mallet, tape measure, square, marker | wooden beam |
| 2 | ladders or trestles | anchors, staples, nuts with washers, dowels, studs, nails, metal corners |
| 3 | levels of different systems (water, laser) | antiseptic compounds |
| 4 | wrenches, plane | polyurethane foam |
Wooden products must meet the following criteria:
- be free from knots and also free from jagged edges;
- the surface of the beam must be flat;
- For work you need to use lumber from the heartwood of trees, which does not give off a blue tint.
It is recommended to give preference to lumber with a large number of annual rings.
For a log house, the height of the strip base above the ground surface should be at least half a meter. Additional construction is often done with bricks.
The material for row 1 can be treated with waste oil, and the rest with antiseptic compounds.
The beams should be processed carefully so as not to miss any area. Otherwise, it will serve as a source of spread of the putrefactive process. The quality of the selected material is of paramount importance in ensuring the durability of the building.
The timber is laid on the foundation with or without securing it. If structural elements are joined to locks, then if dismantling is necessary, the entire dismantling process becomes much more complicated.
Fixing beams on piles
The joining of beams in the corners is carried out in the following basic ways:
- in half a tree with a tenon, when on one beam the upper half is cut off (the length of the width of the lumber being joined), and on the other - the lower half;
- into the paw, while the cut out connecting parts of the logs are connected without including their end parts.
The latter option has received the greatest practical distribution. The photo below shows, in addition to the main ones, rarely encountered methods of connecting beams without and with residue.
Protective ebb

Low tide
In some cases, it makes sense to mount additional flashings above the lower crown, minimizing the flow of moisture into the first inter-crown seams.
On the front facades of houses, such a solution is not always acceptable for aesthetic reasons, but on the rear walls, which are often shaded or stand adjacent to outbuildings, such protection will not be superfluous.
Please note that it is advisable to make such ebbs from the most protected material, since it will have to work in conditions of constant humidity.
Installation of basement drip sill
The gap formed at the place where the casing is laid on the waterproofing layer poses a serious danger to the entire structure; atmospheric moisture stagnates in this part. This drawback is eliminated by installing metal ebbs around the perimeter of the log house. On a strip of iron 20-25 mm wide, a bend is made at an angle of 120 degrees, the structure is fastened with self-tapping screws, and the area adjacent to the beam is treated with sealant. For the manufacture and installation of the drip sill, all the tools are available in the household.
Chemical treatment
A huge number of different impregnations and mastics make novice builders tempted to cover the first crowns of a log or timber house with a thick sealing layer that completely eliminates the circulation of moisture.
The expediency of such an action is very questionable, since complete sealing will lead to the opposite effect - the log will remain stably moist and, as a result, will turn into an excellent incubator for microbiological substances.
But what is really worth doing from the operations of chemical preparation of wood for long-term use is antiseptic treatment, which minimizes the risk of biological contamination of wood.
We recommend not experimenting with the so-called “folk methods of antiseptic treatment (vitriol, old machine oil, etc.)”, since in this case there is always a risk of getting a stable source of carcinogens, emitting them, by the way, not only into the external environment, but and in the underground

Fumigation of logs
In any hardware store today you can purchase inexpensive antiseptics that are certified in government laboratories and have a number of additional useful qualities (for example, almost all antiseptics can be used as a primer before painting).
Among the “ancient” methods of extending the life of the lower crowns of a log house, it is worth mentioning fumigation, which consists of burning logs in an open fire.
The essence of the technique is that when the outer layer of the log is fired, the capillary network of the wood becomes clogged, through which dangerous saturation with moisture occurs. But - what is important - in this case the effect of vapor permeability is preserved, which, by the way, is absent in many polymer sealants.
works on construction sites in Moscow and the Moscow region and provides services for the assembly, repair and restoration of log houses in wooden houses of any design, including restoration of the lower crowns. You can clarify the details of cooperation and order a work estimate via e-mail or by phone numbers published on the “Contacts” page.
Calculate the cost of painting and insulating your home right now