The strength, stability and spatial rigidity of high-rise buildings are ensured by the joint work of horizontal (floors) and vertical (walls and frames) structures. Through the floors, vertical and horizontal loads acting on the building are transferred to vertical load-bearing structures, and from them to the ground. The intensity, direction and nature of load transfer depend on the geometry of the vertical elements and their location in plan.
In the design and construction of high-rise buildings, a variety of design solutions are used, made by designers depending on various factors:
- functional purpose;
- building height;
- natural and climatic conditions;
- integrated safety of high-rise buildings;
- urban planning situation;
- architectural and planning solutions;
- architectural and compositional requirements;
- engineering systems and equipment.
The first four factors are important; the rest largely depend on the specific construction conditions.
Depending on the adopted structural design of the building, vertical load-bearing structures can consist of either a system of posts and beams such as frames, or a system of diaphragm walls - solid or lattice, or both together (combined systems). Diaphragm walls can be made of linear elements or combined into three-dimensional structures - cores (trunks) of rigidity. Flat walls, in turn, can be continuous in plan, crossing the entire building, or have an arbitrary location.
Since horizontal loads, such as wind and seismic loads, are of critical importance in the design of high-rise buildings, vertical load-bearing structures must consist of sufficiently rigid structural elements to prevent unwanted deformations of the building. In order to increase rigidity in the longitudinal and transverse directions of the building, a system of horizontal connections is installed. Horizontal loads are transferred through the floors to vertical braced structures. The transfer of horizontal loads occurs through connections that absorb shear forces and are arranged between vertical load-bearing structures and floors.
The choice of vertical load-bearing structures, their combinations and connections is a choice of the building’s structural system, the rigidity of which is determined by calculation and depends on many factors. The most important factor in terms of ensuring the stability of a high-rise building is its ability to resist wind loads, which increase with the height of the building.
Based on their functions, the structural elements that make up a high-rise building are divided into two groups, depending on their purpose: load-bearing and enclosing. The load-bearing structures of the building consist of interconnected horizontal and vertical elements. Together they form a structural system, which is called the load-bearing frame of the building.
The criterion for choosing a structural system for a high-rise building is to satisfy the conditions of rigidity and stability, as well as the comfort of people on the upper floors, depending on the magnitude and nature of wind loads:
- horizontal movements of the building due to the action of the sum of the total standard vertical loads and the average component of the (static) wind load, taking into account the rotation of the foundation, should be no more than 1/500 of its height;
- acceleration of vibrations of the upper floors under the influence of the standard pulsation component of the wind load should not exceed 0.08 m/s2.
If these conditions are not met, it is necessary to increase the rigidity of the high-rise building, which is achieved either by replacing the structural system with a more rigid one, or by including additional vertical load-bearing structures, which include walls, frames, trunks (stiffening cores) and their combinations. To increase the rigidity of buildings, vertical load-bearing structures, in turn, can be additionally reinforced with connections, for which bracing systems are used, both in the form of individual flat or lattice diaphragms arranged in plan, and in the form of bracing belts - trusses, provided in one or more levels along the height of the building.
Horizontal load-bearing structures - the floors and coverings of a building - perceive the vertical and horizontal loads and impacts placed on them, transferring them floor-by-floor to the vertical load-bearing structures, the latter, in turn, transmit these loads and impacts through the foundations to the base. Horizontal load-bearing structures of high-rise buildings, as a rule, are of the same type and usually represent a reinforced concrete disk (prefabricated, monolithic or prefabricated-monolithic) or (more recently) steel-reinforced concrete; they absorb the vertical and horizontal loads and impacts falling on them, transferring them floor-by-floor to vertical load-bearing structures - columns, walls, pylons and through the foundation to the base (soil).
Vertical load-bearing structures are classified into four main structural systems of high-rise buildings - frame (frame), wall (frameless, diaphragm), barrel and shell:
frame - with a spatial frame frame, used mainly in the construction of multi-storey earthquake-resistant buildings. In turn, frame systems are divided into frame-frame, frame with rigidity diaphragms, frame-barrel;
- wall (frameless) - the most common in residential construction, it is used in buildings of various planning types with a height of one to 30 floors;
- the barrel system is used in buildings above 16 floors. It is most advisable to use a barrel system for multi-story buildings that are compact in plan, especially in earthquake-resistant construction, as well as in conditions of uneven base deformations (on subsiding soils, above mine workings, etc.);
- the shell (box-shaped) system is inherent in unique high-rise buildings for residential, administrative or multifunctional purposes;
- combined (mixed) systems combine individual features of two other systems, these include frame-wall, frame-barrel and box-barrel, etc.
The main structural systems are focused on the perception of all force effects by one type of load-bearing elements. So, for example, with rod structures, the interface between columns and crossbars must be rigid (frame) in both directions to ensure the perception of vertical and horizontal impacts.
Along with the main systems, combined structural systems are also widely used. In these systems, vertical load-bearing structures are assembled with different types of elements. These include systems: frame-diaphragm with connections in the form of walls - rigidity diaphragms, with an incomplete frame (load-bearing external walls and internal frame), frame-barrel, barrel-wall, barrel-shell, etc. (figure below).
Construction of a shallow strip foundation
The design of this type of strip foundation is different and depends on the variety. So, they distinguish:
- prefabricated foundation;
- monolithic foundation.
The prefabricated type of shallow strip foundation is a structure made of ready-made reinforced concrete block structures that are strengthened and connected to each other, which allows the foundation to be installed in any type of soil and in any natural and climatic conditions. For installation, it is enough to purchase ready-made blocks and install them during shrinkage in the place where the foundation is laid. A monolithic shallow strip foundation is manufactured directly at the construction site. Its main difference from a prefabricated one is that it is covered with reinforcing paint, which ensures the continuity of the entire structure, and, consequently, the strength and durability of the entire building.
The main components of a monolithic strip foundation are:
- upper plane - edge;
- the lower plane is the sole;
- base;
- up or “armrest”;
- “glass” or area for mounting poles;
- waterproofing;
- blind areas;
- slopes.
Applied structural systems of high-rise buildings
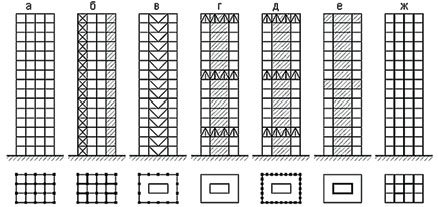
a – frameless (wall); b – frame; c – frame with stiffening diaphragms; g – barrel; d – frame-barrel; e – box-shaped (shell); g – box-barrel (shell-barrel)
High-rise buildings consist of various structural elements located both in the underground and above-ground parts of the high-rise building.
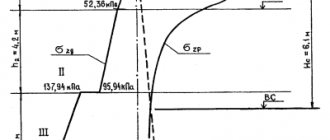
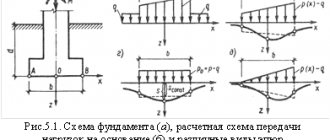
Underground structures. In the system “high-rise building - foundations - foundation”, the most loaded structures are the structures of the underground part, to which all vertical, wind (or seismic] loads acting on the building are transferred. The intermediate link in this system is the foundations, the choice of the type of which determines how reliable operation the rest of the supporting structures of the high-rise building, as well as the comfortable stay of people in them.
The foundation is the underground part of a building or structure that absorbs all loads, both permanent and temporary, arising in the above-ground parts, and transfers the pressure from these loads to the base.
One of the main factors influencing the choice of foundation type is the engineering and geological conditions of the construction site. The results of these surveys provide a preliminary assessment of the bearing capacity of the foundation, its possibility of settlement and their unevenness, and the general stability of the foundation. Unfavorable results may serve as grounds for abandoning the selected construction site due to safety requirements or due to the high cost of measures to reduce the intensity of the influence of these processes. In addition, the surveys make it possible to identify the possible impact of the construction of a high-rise building on the surrounding buildings.
The depth of the foundations is taken to ensure the rigidity of the underground part of the building, the embedding of the building into the foundation and the reduction of settlements and tilts of the structure.
Taking into account the above, the most effective foundation solutions for high-rise buildings may be the following options:
- slab foundations of increased rigidity, slab foundations of variable thickness, as well as box-type foundations with a developed underground part, on a natural or reinforced foundation;
- pile foundations, including in the form of deep supports with the lower ends embedded in bedrock soils - limestone;
- combined pile-slab (CPS) foundations (pictures below).
SNiP shallow strip foundation
The specifics of installing a strip foundation are regulated by building codes and regulations, the application of which is mandatory when carrying out work of this type. The dimensions of the trenches for installing the foundation depend on the type of soil and structural conditions, however, the depth should not exceed 70 cm, and a cushion made of sand or gravel must be installed under the base of the foundation. The width of the trench is determined based on the force of soil heaving, but it is mandatory that the trench sinuses are filled with soil or sand at the end of the work. When preparing a trench, it is necessary to measure the permissible load, and if the pressure for highly swelling soils exceeds the norm, the depth of the trench must be expanded or the base of the shallow strip foundation must be increased. However, subject to the proportion of the width and depth of the trench, strip foundations provide a stable and 2-3 times more economically profitable structure, and therefore, even with heaving soil, they can and should be used for the construction of low-rise buildings. When reinforcing, the reinforcement should extend outward 6-10 cm from the top edge of the concrete pour. It is necessary to connect the reinforcing rods with tying wire and weld only the letter C of the reinforcement. In addition to the above, individual SNiPs impose requirements for the distance between the reinforcement bars and the pitch of transverse reinforcement in the manufacture of a monolithic strip foundation. See also:
- Types of strip foundations
- Strip foundation for a house, price
How to insulate a shallow strip foundation
There are external and internal insulation of strip foundations. External insulation includes both the installation of heat-insulating concrete tape and soil waterproofing. Preparatory work deserves special attention. For example, to prevent foundation destruction or soil heaving, it is necessary to organize a drainage system. Sod allows you to hold the load on the foundation, in the form of snow or water. Planting, loosening and other works can be used as drainage. An equally effective method is thermal insulation , namely insulation of the outer part of the foundation with a special material, which allows concrete structures not to come into contact with the ground and not freeze. To do this, expanded polystyrene is mounted on special glue or dowels, then 2 m wide penoplex is laid, and in the corners the foundation is additionally reinforced with a layer of penoplex. Insulation of a shallow foundation from the outside is ensured by insulating the floor with penoplex.
Columnar types of foundations for a private house

Columnar types of foundations have become popular with an increase in the volume of construction using frame technology, the construction of panel houses and buildings made of timber (glued or sawn). The costs of arranging such structures will be several times less than when constructing strip foundations or slab foundations. For their installation, a necessary condition is the bottom frame of the base made of timber or beams.
Columns for foundations of this type are installed under wall structures around the perimeter of the house, as well as under internal partitions. The interval of their installation should be no more than 2.5 m (experts recommend from 1.5 to 2 m). The installation depth of the posts must exceed the soil freezing level. In this case, their upper part should be located at a certain distance above ground level. This design provides additional convenience when building houses on areas with uneven terrain (by changing the height of the posts, it is possible to ensure a horizontal arrangement of the framing).
The length of the posts is determined by the material used for their production.
It could be:
- concrete;
- a natural stone;
- brick;
- flagstone.
On average, their sizes vary from 38 to 50 cm. The cross-section of the columns for foundations of this type has the shape of a square or rectangle.
Depending on the method of arrangement, columnar foundations are divided into 2 types: monolithic and prefabricated.
Monolithic columnar foundation

To choose a certain type of columnar foundation, you need to take into account the characteristics of the soil at the construction site. If the groundwater is deep enough, experts recommend choosing monolithic foundations made of concrete with reinforcement. Just as when arranging strip structures, for columnar foundations it is necessary to have a reinforcing frame in the columns.
Stages of construction of a monolithic columnar foundation:
- Digging a hole (well).
- Arrangement of formwork.
- Knitting of the reinforcing frame.
- Pouring concrete mixture.
The space between the post and the edge of the pit should be over 0.1 m. It should be filled with sand or fine gravel. This will reduce the soil pressure on the foundation if it freezes. If there is a danger of horizontal soil movement on the site (in the presence of quicksand, etc.), it is better to use other types of foundations, since with monolithic columnar structures there is a danger of reducing the building’s resistance to overturning.

Calculation of a shallow foundation
Let's consider calculating the cost of a foundation using the example of building a house measuring 6*8 m. Option 1. Overall dimensions:
- tape section: 250x1000(h),
- sand cushion: 150 mm,
- cost per 1 linear meter – 4000 rubles.
Total: (8+8+6+6+6+6+2) x 4000 = 168,000 rubles. Option 2. Dimensions:
- tape section: 350x1000(h),
- sand cushion: 200 mm,
- cost per 1 linear meter – 4500 rubles.
Total: (8+8+6+6+6+6+2) x 4500 = 189,000 rubles.
Do-it-yourself shallow strip foundation
A shallow strip foundation, in comparison with slab foundations and deep foundations, is characterized by ease of arrangement. Its creation requires an order of magnitude less financial costs and time. To build a shallow strip foundation with your own hands, you will need the following materials:
- Sand and crushed stone - for the compaction pad;
- Planed boards, timber, slats, nails or screws - to create formwork;
- Waterproofing material: glassine, geotextile, PVC membrane - for covering the walls of the formwork;
- Reinforcing bars, knitting wire and “fungi” stands - to create a reinforced frame;
- Ready-made concrete or, if prepared by hand, M300 cement, sand and crushed stone - for pouring the tape;
- Rags, oilcloth - for covering concrete while it is maturing.
Also make sure you have the required construction tools:
- Bayonet and shovel shovels, buckets and a wheelbarrow for transporting earth - will be needed when digging a trench;
- Hacksaw, hammer, screwdriver - for working with formwork boards;
- Grinder and metal circles - for cutting reinforcing bars;
- Construction stapler - for installing waterproofing on formwork;
- Concrete mixer;
- A variety of small tools - tape measure, level, hook for tying reinforcement, wire.
Building a shallow strip foundation with your own hands - if you know the technology for performing the work, the process is not complicated, but labor-intensive, so get ready for the fact that it will take quite a bit of time to lay out the foundation for the house (about 2 weeks) and roll up your sleeves and get to work.
Other types of foundations for a private house

Foundations in the form of solid or composite concrete platforms are used much less frequently compared to strip foundations. At the same time, there are situations when only this type of foundation can be used. If the site for the construction of a building contains predominantly unstable, sandy-clayey, heaving soils, or groundwater is at a depth of less than 1 meter, and also if the soil is deeply frozen, the most reliable solution is to install a reinforced concrete slab. On this basis, you can build a structure with any number of floors.
Slab foundation types are ideal for building houses using frame technology. This design is less complex, but its arrangement is a more expensive and time-consuming process than in the case of pile and strip structures.
Foundations of this type are called “floating” because they are built without being buried and interact only with the soil surface. Such structures are not affected by temperature changes and soil movements, so the building will be more stable.
Slab foundations used in construction are divided into two types of structures: monolithic and prefabricated. Foundations consisting of several slabs (prefabricated structures) are used in the construction of large buildings with a complex perimeter shape. For the construction of a cottage, a monolithic foundation slab made of reinforced concrete is quite suitable.
Advantages of slab foundations:
- Simple manufacturing technology.
- Foundations of this type can be used for construction in areas with heaving, mobile and subsiding soils.
- There is no need to carry out work to penetrate into the ground.
- Provide the possibility of construction at high groundwater levels.
Flaws:
- A large amount of concrete and reinforcement is required.
- For such foundations it is necessary to equip a basement.
- Slab foundations can be used exclusively on horizontal sections or in the presence of a slope not exceeding 1 meter over the entire length/width of the building.
Stages of creating a shallow strip foundation
The arrangement of a shallow strip foundation begins with the preparation of the work site - all vegetation and construction debris must be removed from the territory. Then the soil is leveled - you need to smooth out all the slopes and irregularities so that the place on which the foundation will be built has a flat surface.
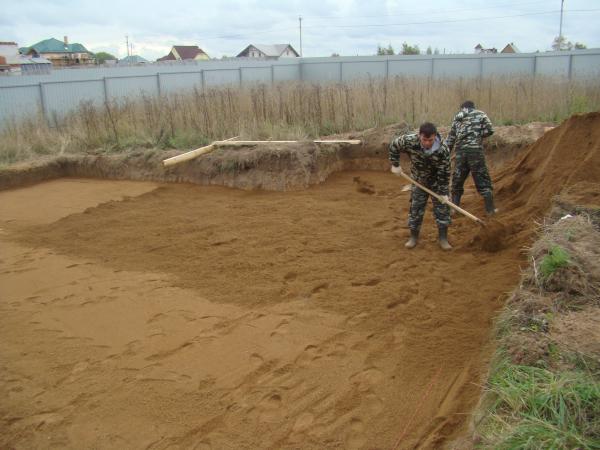

Rice. : Leveling the area for the foundation
Direct foundation work is carried out in the following sequence:
- Marking
First of all, it is necessary to carry out the design marking of the foundation on the territory allocated for construction. You need to mark both the inner and outer contour of the tape. To do this you will need scraps of reinforcing bars, twine, a square and a plumb line. To begin with, the marking guide point is determined - this can be any outer corner of the foundation strip. A reinforcing peg is driven into the guide point, the distance to the second corner of the wall is measured, and the second peg is mounted. Then string is stretched between the reinforcement and as a result you get the first marked wall of the building. Using a square and a plumb line, the extreme point of the wall is determined, perpendicular to the one already marked. We measure its duration, drive in a peg and check the correctness of the right angle.
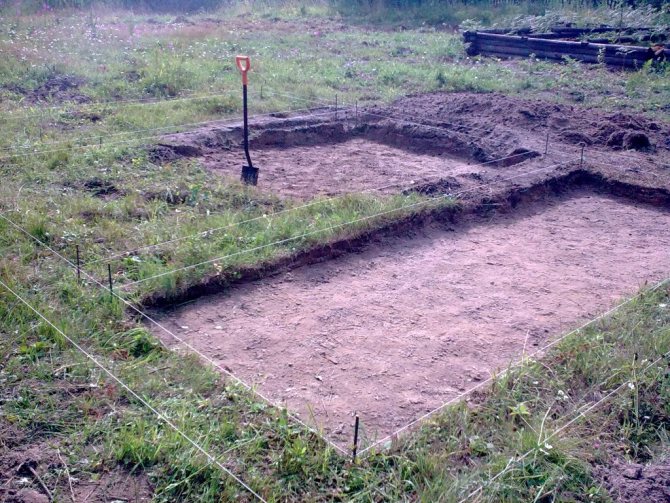

Rice. : Marking a shallow strip foundation
Similarly, we mark the remaining walls of the house and create a second marking contour along the inner perimeter of the foundation strip.
- Digging a trench
Upon completion of the marking, digging of a trench for the foundation begins.
The depth of the trench should be 20 centimeters deeper than the design depth of the foundation; additional deepening is necessary for the subsequent arrangement of the compacting cushion. Important : when digging, carefully monitor the verticality of the trench walls, since even the slightest deviation from the vertical will not allow you to install the formwork under the concrete perfectly level, as a result of which you will not get a uniform thickness of the base.
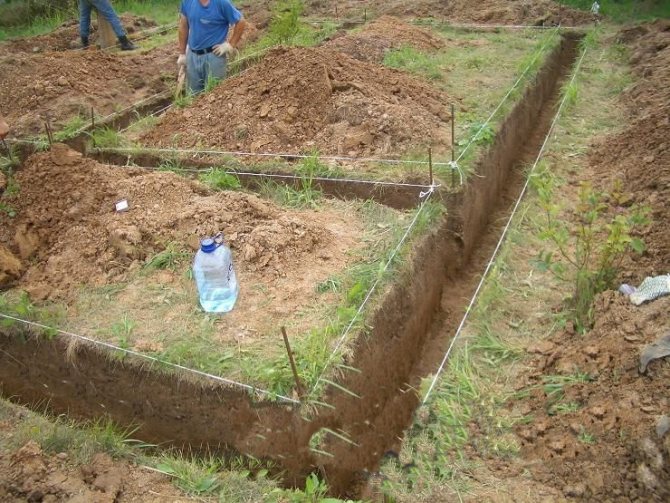

Rice. : Digging a trench for the foundation
If work is carried out in conditions of high flowability of soil and the walls of the trench are constantly collapsing, it is necessary to install supports from boards or sheets of plywood.
- Compaction bedding
Backfill under the foundation is necessary in order to reduce the buoyant effect of soil heaving forces on the concrete strip; it also prevents shrinkage of the foundation as a result of decompaction of the load-bearing soil layer. The bedding consists of two layers of equal thickness: the first is sand, which is poured with water from a hose and carefully compacted with a hand tamper, the second layer is crushed stone or gravel of medium fractions.
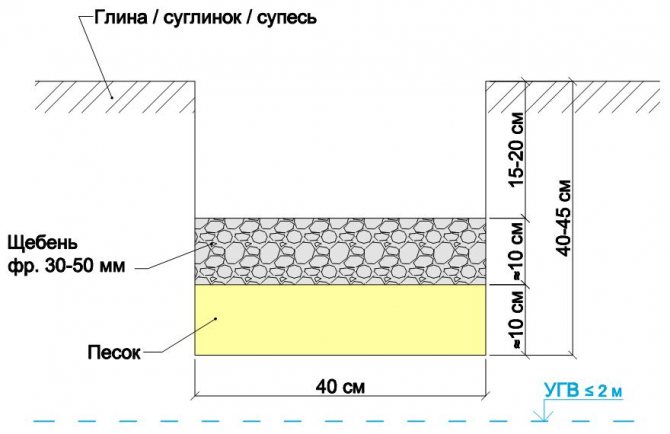
Rice. : Scheme of compacting bedding under the foundation
The thickness of the compacting bedding in normal soil conditions is 20 centimeters (10 - sand, 10 - crushed stone), however, when building on problematic soils, it can be increased to 30-40 cm.
- Formwork installation
Formwork for pouring concrete is made from planed boards 2-3 centimeters thick or moisture-resistant plywood. The formwork is installed on top of the dug trench to a height equal to the required height of the strip foundation base.
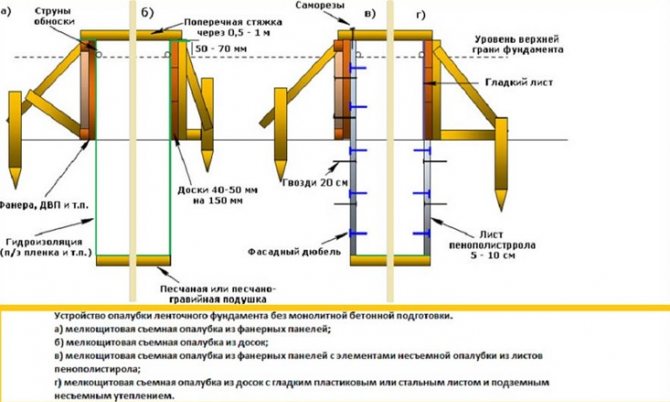
Rice. : Formwork diagram for a shallow strip foundation
The boards are fastened together using wooden blocks and supported with side struts for stability.
Important : when creating the formwork panel, make sure that the nails do not protrude from the boards, because if the protruding nails get into the concrete, dismantling the formwork in the future will be very problematic.
After installation, the internal walls of the formwork and the trench space are covered with waterproofing material, which will prevent the concrete from losing moisture during hardening.
- Installation of reinforced frame
To reinforce a shallow strip foundation, a frame is created consisting of two vertical reinforcing bars on the upper and lower contours and horizontal jumpers connecting them. To create the frame, corrugated reinforcement with a diameter of 10-12 centimeters is used, which is connected into a single structure using knitting wire.

Rice. : Reinforced frame of a shallow strip foundation
The frame must be monolithic along the entire length of the base, special attention must be paid to the joints of the reinforcement in the corners of the foundation strip. After creation, the frame is laid in the formwork, it must be raised above the bottom of the trench by 5 centimeters (special mushroom stands are used) and at a similar distance from the walls of the formwork.
- Pouring concrete
If it is not possible to pour concrete at once, it is necessary to ensure that the work is carried out in such a way that each new layer of concrete is poured before the previous one hardens. The pouring is carried out to the level of the required height of the foundation strip (the appropriate markings must be made on the formwork first), after which the concrete is compacted using a vibration compactor or, if it is not available, it is bayoneted with reinforcement to remove air voids.

Rice. : Pouring the foundation with concrete
After this, the formwork is covered with a damp rag and a vapor-proof material (oilcloth) and the time required for the concrete to completely harden is waited (28-30 days).
Important : if the maturation of concrete occurs during the hot season, the foundation must be regularly moistened by watering the concrete with water from a hose with a sprayer.
Contact us and we will do the work
- We are here
- Piling works, more details
Our company carries out foundation work in the Moscow region - contact us, we will help!
Useful materials
Column and strip foundation
A columnar-tape type foundation is installed in conditions of peat, swampy and sandy soils that are excessively saturated with moisture.
Recessed strip foundation
The buried strip foundation fully complies with the traditional principle of builders: “In order for the foundation to be of high quality and reliable, it should be laid to the freezing depth.”