At the design stage of the construction of a residential building, in order to correctly determine the geometric dimensions of the foundation, it is mandatory to collect the loads acting on the building structure. The overall load-bearing capacity of the house or structure, its durability and strength depend on how accurately the calculation is performed. Based on the results of the calculated data, the area of the foundation, its configuration, and the depth of the lower mark are selected. There are regulatory construction documents (SNiP), which clearly describe the principle of drawing up the collection of loads and their maximum permissible values.
How the calculation is performed
What is included in such a calculation, and what needs to be taken into account? Let's look at some parameters.
- Different types of soil have different bearing capacity, so you can’t rely on the fact that your friend’s house has been standing on a shallow strip foundation for several years, and nothing.
- Taking into account the weight of building materials, the mass of the structure is calculated.
- What is the snow load on the roof in the region. The type and shape of the roof play a huge role in this calculation.
- Wind load. Any house, especially a tall one, experiences significant loads in windy weather, and if the wind constantly blows in the same direction, the foundation will be subject to additional load. This is especially noticeable in light houses, with a not very strong foundation.
- Weight of furniture, plumbing and finishing materials.
The obtained data and collected information serves to take into account the load-bearing characteristics, size and supporting area of the foundation being built. Neglecting these requirements leads to the situations described at the beginning of the article.
Type of loads
The foundation design is under the influence of permanent and temporary loads, the significance of which depends on many factors: the climatic region of the building, the types of foundation soils, building materials for the main structures of walls, roofs, and ceilings.
Constant loads
Constant types of loads include:
- Self-weight of building structures.
- Calculated indicators of soil pressure on the lateral surface of a strip foundation.
- Pressure from groundwater.
When performing calculations, forces from constant weight are considered the most severe type of load.
Live load
The building structure may be subject to periodic temporary loads, such as:
- Snow, the indicator of which depends on the thickness of the snow cover in each specific region.
- Wind, determined from a table of average wind rose indicators in a given area.
- Seismic (for areas with increased seismicity).
- From the weight of furniture in the premises and the movement of people.
Indicators of temporary loads can be found in DBN V.1.2-2 2006 “Loads and impacts” in section 6 according to table 6.2.
Load calculation for strip foundation
When calculating the load on a strip foundation, you need to determine the amount of concrete to be poured, for which you need to find out the total area, taking into account the installed formwork. The resulting figure (in m3) must be multiplied by the mass of 1 m3, which ranges from 2000–2500 kg. When calculating the foundation, it is better to play it safe, so we will take 2500 kg as a basis.
You will need to know the total weight of the house, the snow load on the roof and the wind pressure. These 4 indicators are added together and divided by the base area. It looks like this:
(foundation mass + house mass + snow + wind load) / base area = the required figure.
Since the calculation is approximate, you need to have a safety margin of about 25%.
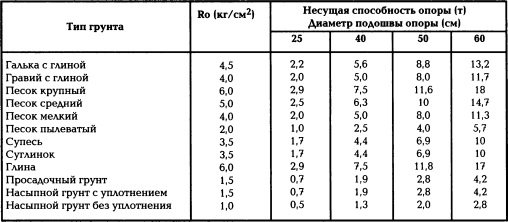
Determination of specific load per 1 sq.m. soil
Finally, we find the sum of all completed results, not forgetting to calculate the permissible load on the foundation. At the same time, it is worth considering that the pressure created by the walls with a roofing system on the support will be higher than their adjacent counterparts.
Watch the video on how to carry out a full calculation of the pressure on the foundation of a house.
The fixed indicator of soil resistance is calculated using the tables specified in SNiP 2.02.01-83 and describing the rules for the manufacture of foundations of buildings and structures.
- We find the sum of the masses created by all elements of the structure, including the base: 800 + 2399.04 + 7,000 + 4,200 + 2,000 = 16,399.04 = 16.5 t/sq.m.
- We determine the soil resistance index; for sandy loam with a porosity coefficient of 0.7 it is 17.5 t/sq.m.
From the calculations obtained, we can conclude that the pressure created by the building chosen for the example is located within the permissible limit.
Load calculation for a columnar foundation
In order to determine the load on a columnar foundation, you will have to multiply the cross-sectional area of the column by its height, as a result of which the volume of one support will become known. The obtained data is multiplied by a number indicating the density of the material from which the pillars are made (q). In this way, the load for one column is calculated, and to find out the calculated load of the entire foundation, we multiply the result by the number of supports.
If the calculation turns out that the foundation does not meet the requirements, then you can increase the cross-section of the pillars or increase the number of supports, reducing the distance between them.
Weight of building structures
When calculating loads, the weight of the following structures must be taken into account:
- foundation;
- walls;
- floors;
- flights of stairs;
- partitions;
- roof.
The weight of standard fillings of window and door openings can be ignored when designing a private house, since it will not exceed the weight of the walls and partitions.
When calculating, it is necessary to multiply the resulting value by the reliability factor ϒϝ.
| Structures of buildings: | reliability factor ϒϝ |
| 1. metal | 1,05 |
| 2. concrete (with an average density of more than 1600 kg/cubic m), reinforced concrete, stone, reinforced stone, wood | 1,10 |
| 3. concrete (with an average density of 1600 kg/cubic m or less), insulating, leveling, finishing layers (slabs, rolled materials, backfill, screeds, etc.) | 1,30 |
Foundation
Since in the future the magnitude of the load will be used to calculate the area of the foundation base, it is necessary to take into account its weight, since it also exerts pressure on the ground.
To determine the weight of the foundation, you simply need to multiply the volume of the structure by the volumetric weight of the material. Most often, the foundation is made of precast or monolithic reinforced concrete. The volumetric weight of the material of a strip or columnar foundation is 2000-2100 kg/cubic. m. For a solid (slab) foundation, this value will already be 2500 kg/cubic. m, since in such a structure there is much more steel reinforcement.
Walls
Walls are the structural elements of a building that enclose or divide it along its entire height, regardless of the number of floors. The floors and roof rest on load-bearing walls. The load produced by the walls depends on their thickness, height and volumetric weight of the material. To determine the weight of the walls, you need to calculate the volume of the material and multiply it by its volumetric weight (density). In addition to the main structural material, you also need to take into account the weight of the insulation, as well as facing materials.
| Name of building materials: | Volumetric weight, kg/cubic. m |
| 1. concrete | up to 2400 |
| 2. high-strength concrete | 2000-2800 |
| 3. concrete is porous | 350-1000 |
| 4. gas silicate block | 200-600 |
| 5. expanded clay concrete block, foam concrete | 500-1200 |
| 6. reinforced concrete | up to 2500 |
| 7. vinyl siding | 800-1550 |
| 8. natural stone | 800-2500 |
| 9. building brick | 1000-2200 |
| 10. foam | 10-25 |
| 11. extruded polystyrene | 15-30 |
| 12. tree | 420-1200 |
Floors
The weight of the floors can be determined by multiplying the volume of the material by the density. If the floors are made of reinforced concrete hollow slabs, then their weight will be 30% less than that of monolithic reinforced concrete. The weight of floors made using wooden beams can be determined by knowing the volume of lumber required and the density of the wood. When calculating the load created by the ceiling, it is necessary to take into account the weight of the floor coverings, as well as the weight of thermal insulation if the ceiling is insulated.
Flights of stairs
Staircases and flights of stairs rest on walls and ceilings. Their weight also needs to be taken into account. To simply determine what load the stairs produce, it is enough to multiply the area of the stairs and the height of the riser, and then take into account the slope of the flight, that is, divide the resulting value by cos α, where α is the angle of inclination. By multiplying the resulting value by the number of floors of the building, you can obtain the volume of staircase material. Next, everything is as usual, the volume is multiplied by the density of the material and the weight is obtained. If both the floors and the stairs are made of the same material, for example, reinforced concrete, then the weight of the stairs can not be taken into account separately. At the same time, when calculating the foundation, the area of the floors must be taken without deducting the area of the stairs.
Partitions
The weight of partitions is calculated similarly to the weight of walls.
The weight of the partitions must be taken into account as the load from building structures when designing each floor on which the partitions are installed.
Roof
To calculate the weight of the roof, you need to know the weight of the materials used in its manufacture, including insulation and vapor barrier. In individual construction, pitched roofs made on wooden rafters are usually used. Asbestos-cement sheets (slate), ceramic tiles, and profiled steel sheets are used as roofing.
| Name of building materials: | Volumetric weight, kg/cubic. m |
| 1. ceramic or cement roofing tiles | up to 2200 |
| 2. slate | up to 2800 |
| 3. profiled metal sheets (metal tiles) | 5-10 |
| 4. extruded polystyrene | 15-30 |
| 5. glass wool, mineral wool | 15-250 |
| 6. foam | 10-25 |
| 7. tree | 420-1200 |
Load calculation for a pile foundation
Calculation of the load on a pile foundation is performed as follows:
- The total mass of the future building is multiplied by the safety factor.
- The supporting area of 1 square section of the pile is determined by multiplying the dimensions of the two sides. When using round piles, the supporting area of one of them is calculated by the formula: R2 × 3.14. The data obtained is then multiplied by the number of piles used in the foundation.
- Now you need to find out the load per 1 cm2 of soil, for which the mass of the building is divided by the supporting area of the foundation, and make sure that the standard permissible load on the soil is normal.
One of the features of a pile foundation is the correct choice of the section and length of the piles, for which you need to know the characteristics of the soil. For example, in some areas, a 3 m long pile may not reach a solid foundation, and supports must be purchased only after preliminary geological exploration.
If necessary, the soil can be compacted by driving additional piles not provided for in the project, but this will lead to additional, unplanned costs.
Calculation of forces transmitted from the roof

The load from the roof is redistributed to the load-bearing foundation through the structures on which the roof rests. For a hipped roof there are four of them, and a gable roof transmits pressure along two load-bearing elements.
To determine the pressure of the roof on the load-bearing foundation, the ratio of its projection area to the area of the base to which the load from the roof is transferred is required, multiplied by the specific gravity of the roofing materials.
The specific gravity of various types of roofing, as well as the characteristics of other materials, can be found in reference or regulatory documentation. The differences in the weight of the roofing material used from analogues are not as significant as the differences in the weight of the material used for the construction of floors. The weight of one cubic meter of roofing material ranges from 30 to 80 kg, depending on what is used: roofing felt or ceramic tiles.
Soil analysis
When designing a foundation, you can independently perform a geodetic analysis of the soil, having learned:
- Soil type.
- Groundwater level.
It is also necessary to find out the level of soil freezing, which maps with such data can help with.
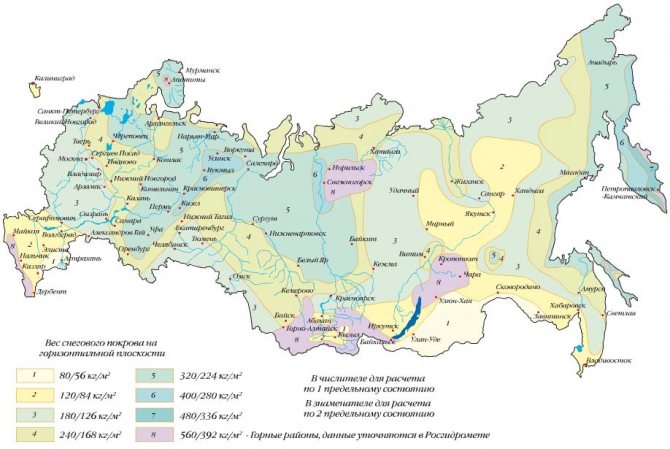
Rice . Level of soil freezing in Russia
Using a hand drill, several wells are made around the perimeter of the site and in the center, up to 2.5 m deep, as a result of which you can see what type of soil it is, and the next day you can see whether water has appeared in it and what its level is.

Rice . Soil layers in the Moscow region
As for the type of soil, additional information will help you understand this difficult issue:
- If the soil crumbles when you remove the drill, it is sandy soil.
- You can roll the extracted soil into a cylinder, but at the same time it is all covered with cracks - this is sandy loam.
- It turns out to roll a cylinder, but when you try to bend it, it breaks - it’s light loam.
- The rolled cylinder at the bend is covered with numerous cracks - this is heavy loam, which contains a lot of clay.
- The cylinder rolls easily, does not break or crack when bending - this is clay soil.
Using the data obtained, you can determine what type of foundation is best to make in this area and whether it is necessary to make a drainage system for it.
Information on the purpose of the calculator.
The online calculator for a monolithic strip foundation
is designed to calculate the dimensions, formwork, quantity and diameter of reinforcement and the volume of concrete required for the construction of this type of foundation. To determine the appropriate type of foundation, be sure to contact a specialist.
All calculations are performed in accordance with SNiP 52-01-2003 “Concrete and reinforced concrete structures”, SNiP 3.03.01-87 and GOST R 52086-2003
A strip foundation is a monolithic closed reinforced concrete strip running under each load-bearing wall of a building, thereby distributing the load along the entire length of the strip. Prevents subsidence and changes in the shape of the building due to the action of soil heaving forces. The main loads are concentrated at the corners. It is the most popular type among other foundations in the construction of private houses, as it has the best ratio of cost and necessary characteristics.
There are several types of strip foundations, such as monolithic and prefabricated, shallow and deep buried. The choice depends on the characteristics of the soil, the expected load and other parameters that must be considered in each case individually. Suitable for almost all types of buildings and can be used when constructing basements and basements.
The design of the foundation must be carried out especially carefully, since if it is deformed, this will affect the entire structure, and correcting errors is a very complex and expensive procedure.
When filling out the data, pay attention to the additional information with the sign.
Additional Information .
The following is a complete list of calculations performed with a brief description of each item. You can also ask your question using the form on the right.
Determination of soil bearing capacity
Below is a table that can help you understand the bearing capacity of the soil. Knowing what type of soil you extracted during test drilling will help you find it in the table and get more information.
| Soil type | Load bearing capacity |
| Sandy loam | From 2 to 3 kgf/cm2 |
| Crushed soil with silty-sandy filler | 6 kgf/cm2 |
| Dense clay | From 4 to 3 kgf/cm2 |
| Crushed soil with clay aggregate | From 4 to 4.5 kgf/cm2 |
| Medium density clay | From 3 to 5 kgf/cm2 |
| Gravel soil with sandy aggregate | 5 kgf/cm2 |
| Moisture-saturated clay | From 1 to 2 kgf/cm2 |
| Gravel soil with clay aggregate | From 3.6 to 6 kgf/cm2 |
| Plastic clay | From 2 to 3 kgf/cm2 |
| Coarse sand | Medium-density - 5, high-density - 6 kgf/cm2 |
| Loam | From 1.9 to 3 kgf/cm2 |
| Medium sand | Medium-density - 4, high-density - 5 kgf/cm2 |
| Sand, sandy loam, clay, loam, ash | From 1.5 to 1.9 kgf/cm2 |
| Fine sand | Medium-density - 3, high-density - kgf/cm2 |
| Dry silty soil | Medium-density - 2.5, high-density - 3 kgf/cm2 |
| Water-saturated sand | Medium-density - 2, high-density - 3 kgf/cm2 |
| Wet, silty soil | Medium-density - 1.5, high-density 2 kgf/cm2 |
| Water-saturated silty soil | Medium-density - 1, high-density - 1.5 kgf/cm2 |
Table 1 : Design resistance of different types of soils
Foundation settlement
Another strictly standardized value when calculating a strip foundation is its settlement. It is determined by the elementary summation method, for which data from the geotechnical survey report will again be needed.

Formula for determining the average settlement value according to the scheme of a linearly deformable layer (Appendix G SP 22.13330.2011).
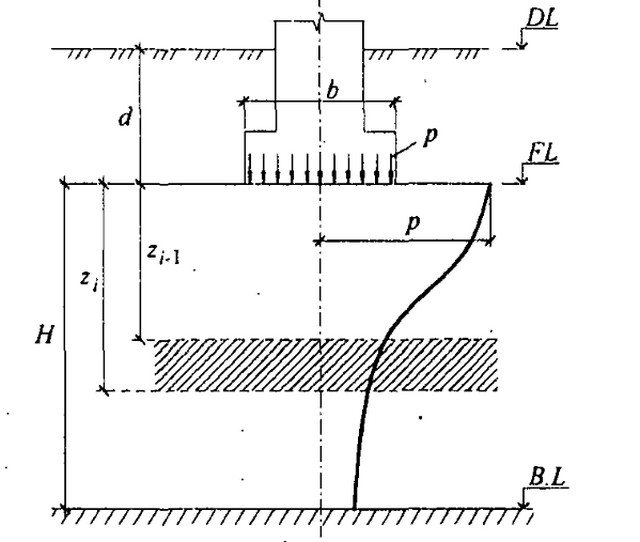
Scheme of application of the linearly deformable layer technique.
Based on the experience of construction and design, it is known that for engineering-geological conditions characterized by the absence of soils with a deformation modulus of less than 10 MPa, weak underlying layers, macroporous IGE, a number of specific soils, that is, under relatively favorable conditions, calculation of settlement does not lead to the need to increase the width of the base foundation after calculating the bearing capacity. The margin for the calculated draft in relation to the maximum permissible is usually obtained several times. For more complex geological conditions, the calculation and design of foundations should be carried out by a qualified specialist after carrying out engineering surveys.