Modern construction technologies involve the use of various types of foundations. Depending on the depth (distance from the base to the soil surface), they are deep (FGZ) and shallow (FMZ)
Modern construction technologies involve the use of various types of foundations. Depending on the depth of placement (the distance from the base to the soil surface), they are deep (FGZ) and shallow (FMZ).
FMZs have a burial depth that does not exceed four times their width. They can provide a solid foundation for a structure on fairly complex soils, including heaving ones. At the same time, they require significantly lower construction costs than FGZ.
No. 1. Types of foundation by type of prefabrication
Depending on whether factory elements are used during construction, or whether they are all formed directly on the site, foundations are divided into:
- monolithic . To make them, formwork is constructed into which concrete mortar is poured;
- prefabricated monolithic ones are obtained by filling ready-made component elements with concrete;
- prefabricated foundations are built from factory-produced reinforced concrete products.
Naturally, monolithic foundations are much stronger than prefabricated monolithic and, even more so, prefabricated foundations, but they require more time and effort for arrangement.
Materials
Types of shallow foundations, determined by the material of manufacture:
- reinforced concrete;
- concrete;
- rubble concrete;
- from stone materials (brick, rubble).
Rubble is a natural material, which is pieces of limestone or granite, which are quite durable. Rubble concrete is a type of concrete using rubble as a filler.
In modern construction, FMPs are most often made of concrete and reinforced concrete.
No. 2. Types of foundation by design
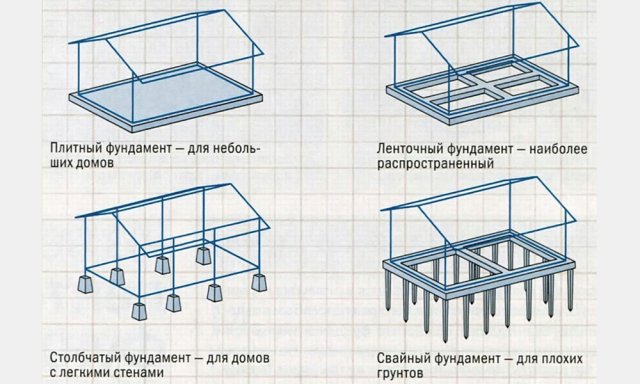
All foundations used in private construction can be divided into four groups:
- strip foundations - this is a continuous sheet of reinforced concrete (much less often made of brick), which is laid under all the load-bearing walls of the house and has the appearance of a closed contour or ribbon, which is where the name comes from. The most common type;
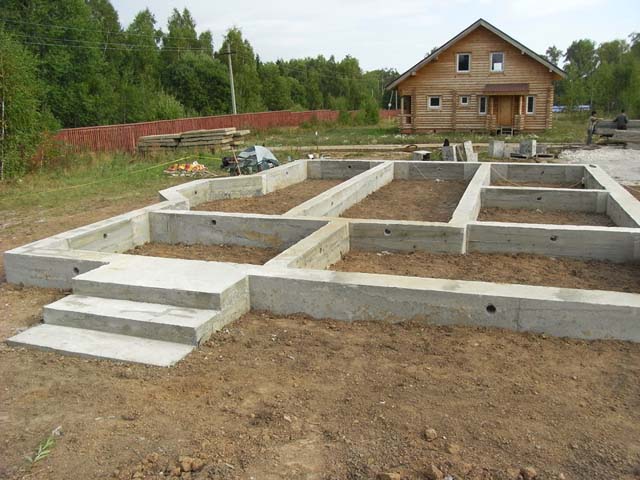

- slab foundations also called “floating”, they are a solid monolithic concrete slab, which allows the load to be distributed most evenly;

- columnar foundations, as the name suggests, are a system of pillars made of concrete, brick, stone, less often wood, and located at an even distance from each other in the locations of the load-bearing walls and corners of the future house. For reliability, the pillars are combined with a grillage (a frame that connects all the pillars), but they can do without it. This type of foundation is suitable for small, lightweight houses;

- pile foundations consist of supports that are screwed or driven into the ground (the supports of a columnar foundation are installed in holes) to a relatively great depth. Piles can be reinforced concrete or metal, and are used on loose and heaving soils.

The choice of the type of foundation for a house depends on the number of floors and dimensions of the latter, the materials of the walls and ceilings, as well as the type of soil, the level of its freezing, the depth of groundwater, the presence of underground communications, and the need to equip the basement.
Made
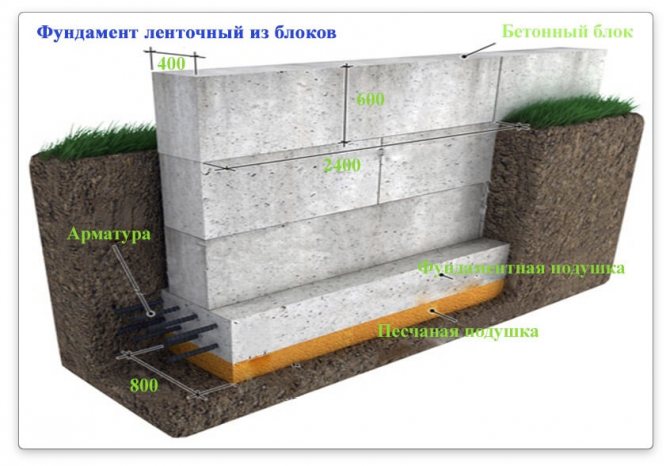
The essence of this type of strip foundation is the use of standard blocks. These reinforced concrete products are obviously durable, compact, and their use significantly speeds up this stage of construction. The downside is the need to use lifting mechanisms or equipment. In addition, blocks of standard length are not always able to perfectly fold into the required size, and this is the reason for the appearance of non-uniform inserts and the need for, albeit minor, additional correction work.
No. 3. Strip foundation for a private house
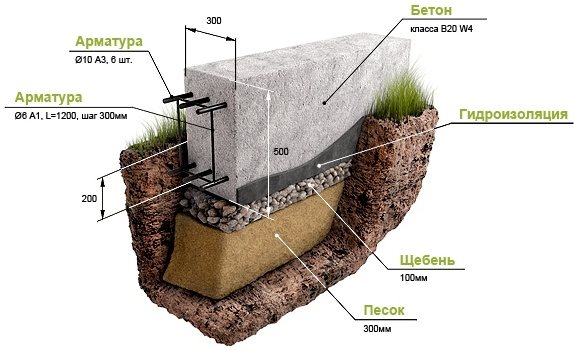
The most common type of foundation in the construction of a private house is considered to be a strip foundation. It is a strip or frame made of concrete, which is laid under load-bearing walls. A sand and gravel cushion is formed under the concrete, which allows for a more even distribution of the load on the soil and eliminates the need for more serious soil preparation before laying the foundation. The sand and gravel cushion acts as drainage and protects against the effects of groundwater. The foundation requires waterproofing and insulation work.

The main advantages of a strip foundation include:
- the ability to withstand decent loads, which is why it is used in the construction of both relatively light wooden houses and 2- and 3-story brick buildings;
- the ability to use such a foundation for arranging a basement;
- The shape of the strip foundation can be any (with the exception of prefabricated structures);
- minimum amount of excavation work.
Minuses:
- labor intensity of work;
- the need for specialized equipment (at a minimum, a concrete mixer, and for arranging a prefabricated structure - a crane).
Strip foundations come in two fundamentally different types:
- monolithic;
- made.
A monolithic strip foundation is formed by arranging formwork, installing reinforcement and pouring sand-concrete or rubble concrete mixture. It can be of any shape, and due to its integrity, excellent thermal and waterproofing qualities, as well as strength, are ensured.
A prefabricated strip foundation is created from ready-made factory reinforced concrete blocks, which greatly simplifies and speeds up installation. Individual parts are fastened with cement with reinforcement, the structure is inferior in strength to a monolithic one, and its main disadvantage is insufficient waterproofing at the junction of blocks, which in areas with high groundwater levels and in swampy areas can lead to premature resolution of such a foundation. Much less often, prefabricated foundations are built from brick , but their service life is shorter than that of concrete ones.

Separately, it is worth highlighting the intermittent strip foundation , which is laid not in a continuous line, but in separate sections, but clearly under the load-bearing elements. This design allows you to save a lot of money when constructing lightweight buildings.
In cases where there is weak soil under the strip foundation , its base needs to be expanded, and this is done by forming ledges , resulting in a stepped structure: the main load will be placed on the wide part (sole). It is also possible to form a foundation in the shape of a trapezoid : the lower wide part will become the main support. If groundwater is located at shallow depths, it is recommended to use special grades of concrete and additionally protect it with bitumen mastic.
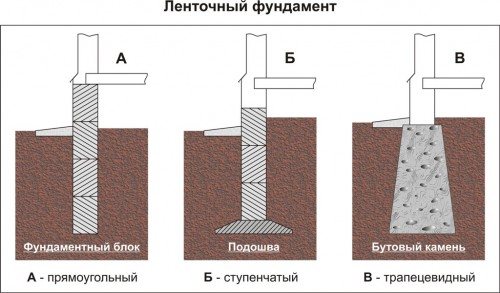
As is clear from the above, a strip foundation can be erected from the following materials:
- reinforced concrete structures provide the greatest strength and durability, are relatively cheap, but require a lot of time;
- Rubble concrete structures are distinguished by the presence of large particles of gravel, bricks, and boulders in the concrete solution. They are inexpensive and can withstand decent loads;
- brick foundation - actually ordinary brickwork, but buried in the ground. This type of foundation is used when it is not possible to build a monolithic concrete foundation; it can support the weight of houses up to five floors.
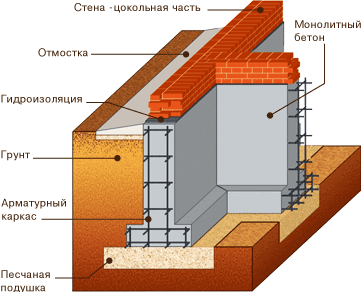
Based on their depth, foundations are divided into:
- shallow (depth 50-70 cm) - option for slightly heaving soils, i.e. those that are little susceptible to frost heaving;
- deep-seated ones are laid at a depth of 20-30 cm below the soil freezing level. Used for the construction of heavy structures and in places with difficult soil.
Before construction starts
Surely there is no construction that can be started without having a detailed plan for its implementation. It is in a competent project that the success of future construction in general and the construction of a strip foundation in particular is hidden.
Even at the design stage, corrections to the calculations can be made by:
- Type of soil under the future building;
- Its theoretical resistance to gravity;
- Practical loads;
- Depth of occurrence;
- Design sole width;
- Reinforcement calculation;
- The need for a drainage system;
Practice shows that not every builder can handle foundation calculations, which means it makes sense to immediately trust the professionals. To confirm the correctness of this conclusion, we can say that the quality, reliability and durability of the entire building depend on a correctly calculated foundation, just like the peace and positivity of its inhabitants (inhabitants).
No. 4. Slab foundation for a private house
Slab foundations are installed in areas with loose, heaving and moving soil. A monolithic concrete slab, located under the entire future building, prevents the negative effects of soil movements and allows you to evenly distribute the load of the house on the soil. Under the influence of swelling of the soil, this type of foundation is able to evenly rise and fall again (that’s why it is called floating ) - cracks do not appear in its structure and the load-bearing walls of the house.
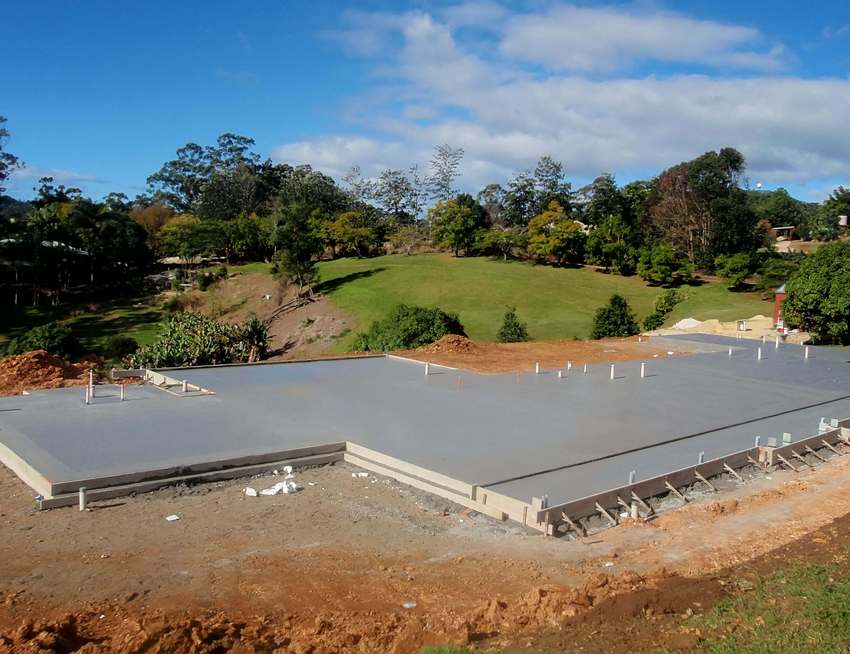

The slab foundation is made of several layers:
- geotextiles;
- sand and gravel cushion;
- insulation layer:
- concrete with reinforcing reinforcement frame.
The thickness of the main concrete layer ranges from 30 to 100 cm, only monolithic structures , so the concrete is prepared and poured into the formwork on site. In rare cases, ready-made concrete prefabricated slabs , but this method is only allowed when constructing small, lightweight buildings, since the strength of such a foundation is not very high.
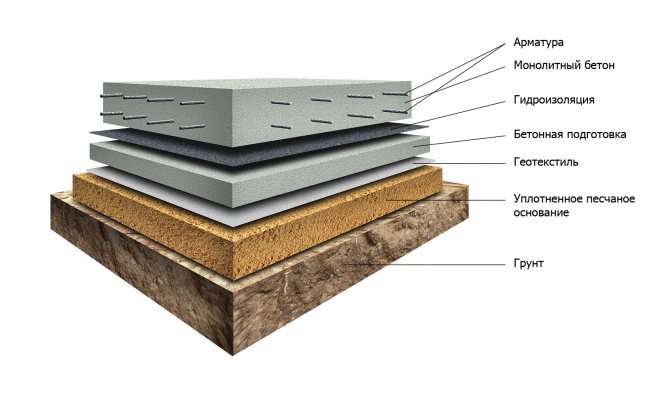
A sand and gravel layer is used to level the base; sometimes it is replaced with low-strength concrete. It is imperative to use waterproofing material when organizing such a foundation. If it is necessary to build a large house, then it is recommended to make expansion joints - the foundation is simply cut and divided into several smaller parts. This helps prevent cracks from occurring.
Advantages of a slab foundation:
- uniform distribution of load-bearing structures on the foundation;
- sufficient strength, ability to withstand vertical and horizontal deformations;
- for areas with weak types of soil, this is actually the only option to organize a strong foundation;
- the floor does not require additional floor slabs, and with high-quality insulation, such a foundation can even be used as a subfloor.

Minuses:
- inability to arrange a basement;
- high cost, this is the most expensive of all types of foundation for a house, so its use is justified only in areas with loose soil;
- the need for flat terrain, otherwise the site must be properly planned.
No. 5. Columnar foundation for a private house
For light wooden and frame houses, a columnar foundation is ideal, which is characterized by relative ease of arrangement and low costs . Such a foundation is a privilege for areas with normal soil, but provided the foundation is laid at a depth below the groundwater table, it can also be used on heaving soils.

A columnar foundation consists of pillars equidistant from each other, sunk into the ground. The pillars can be :
- concrete with reinforcement;
- brick;
- wooden;
- stone;
- rubble concrete.
The most durable are concrete and rubble concrete, they can withstand heavy loads, brick pillars are inferior to them, and wooden pillars can only be used as a foundation for small wooden buildings (barn, bathhouse, etc.). To increase strength and reduce mobility, the pillars can be connected on top with reinforced concrete strapping beams.

It is recommended to install a sand layer about 50 cm thick under a columnar foundation - it will prevent heaving. The pillars are installed at a distance of 2-3 m from each other along the contour of the house, in the corners of the building and in the locations of load-bearing partitions. A columnar foundation can be:
- monolithic _ All supports are created on site, reinforced concrete or rubble concrete and wooden formwork are used;
- made. For its construction, factory-produced concrete supports are used. They are installed on special “glass cushions” about 0.15 m thick.
The number and depth of pillars are calculated taking into account the type of soil and structure. If the building is small and light, then it is even permissible to use a shallow foundation (this is about half the standard depth) and a non-buried foundation (40-50 cm).
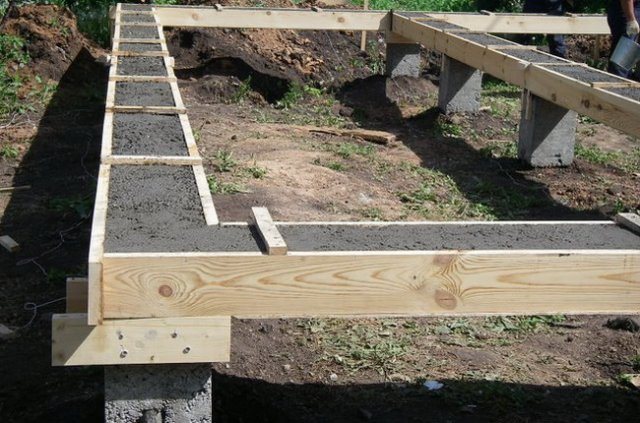

Advantages of a columnar foundation:
- relative simplicity and low cost of arrangement;
- Ideal for building small houses on stable soils.
Flaws:
- difficulties in arranging basements and underground garages;
- low strength and impossibility of use on highly moving soils - the supports can tilt and even tip over, which will lead to deformation of the building.

Pouring formwork with concrete
One of the final stages of constructing a strip foundation is pouring concrete. In most cases, the required volume is significant, which means the best option is to order delivery of a ready-made solution. This will significantly reduce your labor costs and help you comply with some important rules. Namely:
- The time allotted for pouring the foundation should not exceed one day;
- The break between batches of poured concrete should not exceed two hours;
- It is best to fill the formwork from several points.
Important
You should not get carried away with “stretching” the mortar along the formwork. This will reduce the quality of the finished product. It is not recommended to fill from a height of more than two meters. This will disrupt the structure of the concrete, which will lead to a deterioration in quality.
The optimal weather conditions for the foundation to lay down well, become and strengthen are:
- Air temperature from +18 to +22;
- Normal humidity is from 60 to 70%;
- Moderate solar activity.
In order to maximize the time for moisture evaporation, it is recommended to cover the foundation with plastic film upon completion of work. The complete formation of the foundation, after which it will be possible to begin laying the walls, occurs no earlier than 14-21 days from the moment of pouring. Its final readiness for operation is regulated by an even longer period and depends on the volume, depth and weather conditions.
No. 6. Pile foundation for a private house
A pile foundation consists of a system of piles, long pointed posts that are driven or screwed into the ground directly or at an angle. The large length of such elements allows them to be used in areas with weak and loose soil , because they are installed at such a depth as to rest on stronger and denser layers of soil that do not freeze in winter. This principle allows the use of pile foundations even in the most difficult conditions. The piles are connected on top with a concrete slab or beam - grillage . This type of foundation is used for the construction of wooden, frame, panel and other lightweight houses, as well as fences on swampy and peaty soils.
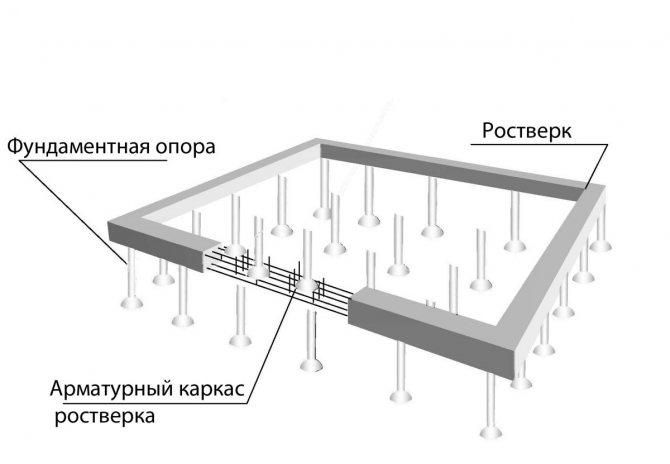
Piles can be made of the following materials:
- tree. They are used to support light wooden houses, made from pine processed using special technology;
- reinforced concrete is the most durable material that is suitable for the construction of more or less heavy structures;
- the metal also has high strength characteristics and is not inferior to reinforced concrete;
- combined piles, usually combine metal and concrete - such strong foundations are suitable for even the most difficult marshy soils.

According to the installation technology, piles are:
- driven piles are, as a rule, reinforced concrete piles with a pointed end, which are driven into the ground using special impact installations. Not suitable if there are buildings nearby, as the shock wave can damage them;
- drilled ones involve preparing a well, arranging a frame of reinforcement in it and filling it with concrete;
- screw piles are hollow metal rods with blades at one end; they can be installed manually or screwed in with specialized equipment. Suitable for soils of any density;
- indentation piles installed with special hydraulic pumps, they are rarely used in private construction, since the shock wave can deform neighboring buildings.
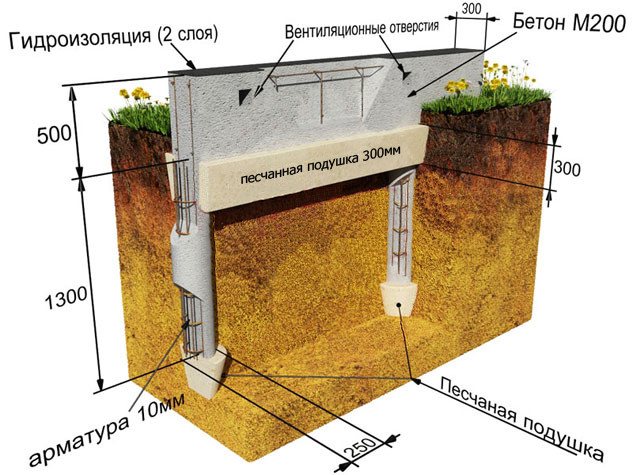
Among the main advantages of a pile foundation:
- possibility of installation on any type of soil, no dependence on groundwater level;
- reducing the amount of concrete consumed;
- reducing the amount of excavation work;
- relative speed of installation.
Flaws:
- the need to use specialized equipment for transporting and installing piles;
- relatively high cost.
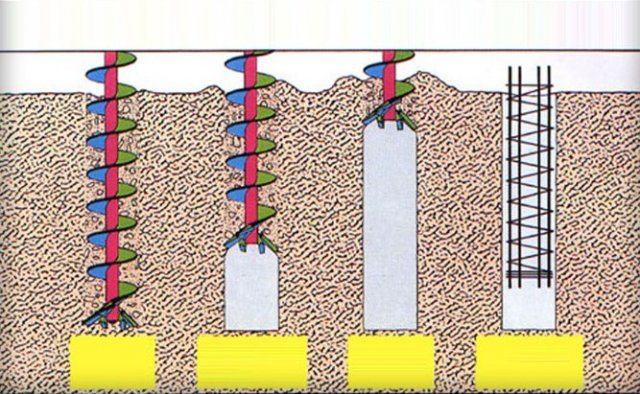
No. 7. What is important to consider when choosing the type of foundation?
It is better to entrust the calculations and design of the foundation to specialists, especially if we are talking about a large house with heavy load-bearing walls and ceilings. If a private house or small dacha is built on its own and is light in weight, then many prefer to do without detailed calculations, which is not entirely true. To avoid mistakes, it is necessary to take into account a lot of factors, and the basic principles for choosing the type of foundation for a house and its arrangement are:
- on highly heaving soils, the foundation must be built below the soil freezing level. In conditionally non-heaving, the depth of the foundation can be 0.5-1 m;
- The average and maximum depth of soil freezing are variable values, and they are not always easy to determine. The organization that owns the land must have the relevant data, along with other soil characteristics, otherwise you will have to conduct your own research. The most unreliable way is to ask the neighbors on the site, but the soil may be heterogeneous, so such data is not always accurate;
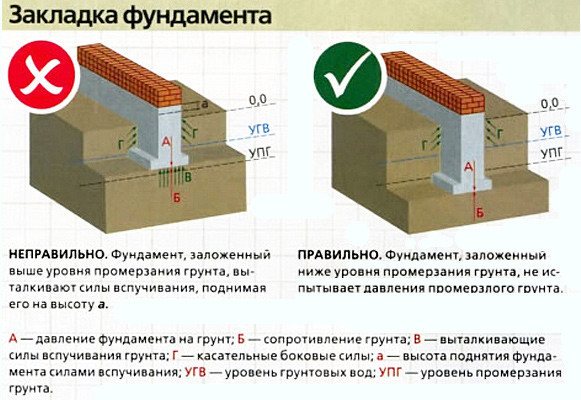
- The more dense and moist the soil, the more it freezes during the cold season. The most difficult in this regard is clay soil, which not only swells, but also unevenly. The most effective way to prevent possible deformations is to replace difficult soil with sand or create a sand cushion;
- sandy soil It is considered ideal for constructing any type of foundation and building houses made of brick, aerated concrete, foam block and other materials; it allows water to pass through well and almost does not swell. Rocky soils They practically do not swell, do not freeze and do not change their properties under the influence of external factors, but it is also difficult to organize a foundation in them due to their increased hardness. Clay soils require either the construction of a sand cushion or the use of piles;
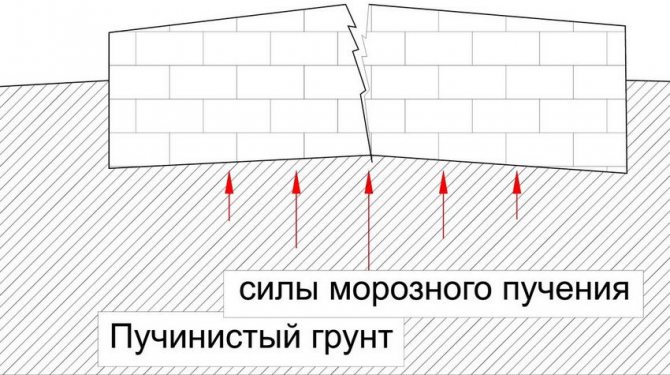
- if there are other massive structures located near the proposed construction site, then it is necessary to take into account the total load on the ground;
- on silty and heaving soils it is better not to use strip and columnar foundations;
- a pile foundation is justified only when other options are not suitable at all - it is expensive to construct.
The foundation will last for many years if you don’t forget to also take care of its waterproofing and insulation. Much also depends on the quality of the materials used and the responsibility of those who build the foundation.
Tags: construction
What were we aiming for?
The fact that its construction takes approximately 25-30% of the construction budget of the entire house shows how important the process of building a foundation is. The time that your home will serve you depends on its high-quality installation and the correctness of associated work. Therefore, if you have even a shadow of doubt about your strengths and abilities, entrust this work to professionals.
Strip foundation is the most popular type of arrangement of support for construction projects. Its main advantage is its versatility. It is suitable for any soil and in any latitude. It is optimal both for small-format construction sites and for the construction of large objects. It is reliable and uncomplicated in its range of materials, technology and means for their implementation.
Foundation marking and digging with installation of formwork and reinforcement - Domtvoy RF











