Foundation It is customary to call the load-bearing part of the building located between the soil and the main structure of all buildings.
The choice of foundation type and determination of its depth is determined by several important criteria:
- determination of soil type;
- at what depth does groundwater flow;
- soil freezing depth;
- capital construction.
How to check the soil under the foundation yourself
Checking soil by color
Drilling test wells. By drilling a small shaft 1-2 meters deep, you can visually determine some of the qualities of the soil. You can also dig a small pit, thereby determining the location of the load-bearing layer of soil, loam or clay. But this is all relative; if analysis is impossible, a reinforced foundation is laid on piles or concrete pillars.
Direct factors, such as the presence of water, sand particles and stones, will prompt the choice and direction. But they do not cancel the need to do an analysis.
Of course, in most cases of construction of country houses, few people conduct such an analysis. Then it is recommended to develop the trench to a dense load-bearing layer. Here we will analyze more precisely all the stages, both for a one-story house and for a two-story one.
Calculation of depth
The initial parameter for determining the laying depth is the level of soil freezing. Strip foundations must be laid at least half a meter below this level.
Since it is impossible to completely eliminate the impact of frost heaving, its impact at least on the sole of the supporting structure is avoided. It makes no sense to lay pile foundations less than two meters deep.
Of course, if a one-story house has little mass, you can use a structure made of screw piles, the depth of which can be from one meter.
If you do not take into account non-buried and shallow foundations, the depth of support structures is always determined taking into account the lower freezing mark of soils according to the following scheme.
Bookmark depth for a one-story building
Having set up several mines, we check after 24 hours whether there is any water in it. If it’s dry, you can look at the depth of the dense soil. When drilling with a change in soil layer (determined visually), measure the depth with a tape measure. It is better to make holes along the entire perimeter of the site, drawing up a map of the occurrence of load-bearing soil.
When checking, use a drill diameter of 200−250 mm. By drawing a preliminary sketch, you will have an idea of where and how much to dig. You will have to take into account several more important factors, the level of freezing and the depth of the bearing layer of the earth. This is also relevant for one-story and two-story houses made of any material, not just foam blocks.
Layouts of one-story houses with a basement
Even without taking into account the rather high price of construction, the costs can justify themselves. It is advisable to plan a cottage in the following situations:
- the house is designed for a large family on a small plot of land;
- poor quality soil base;
- it is necessary to free up additional area above the ground;
- the client is prepared for high construction costs.
The main reason for building a house with a basement is the customer’s desire, which we are always happy to fulfill at the highest level.
Freezing level
In the middle zone, ground freezing is not so deep, about 1.5 meters. In the northern regions, the level of freezing is always taken into account; development is carried out taking into account the average temperature over 3-4 years. Everything can be calculated using the formula. We will proceed from it.
Let's look at the notation. The M value shows the average monthly temperature taken in the desired climate zone. The D1 indicator is the depth figure, and D0 is the coefficient of the soil itself. Its limits can vary, from loam and clay 0.23 to rock and clastic rock 0.34. Having finished with the miscalculations, let's begin the process itself.
Types and varieties of soil
Homogeneous soil is considered a good option for building a house. Its settlement occurs equally over the entire area, as a result of which the building on it has greater stability.
It is customary to distinguish several types of soils:
- Rocky soil. The most preferred option for the construction of buildings. Laying the foundation is possible directly on its surface, since they do not freeze, are not washed away by groundwater and do not shrink.
- Gristly soil . This type of soil includes gravel and rocky debris. In this case, the foundation must be laid to a depth of at least half a meter, regardless of the level of soil freezing. This type of soil does not erode.
- Sandy soil. With this type of soil, the foundation is laid at a depth of 40–70 cm. Soil freezing is small, has high water permeability, and strong compaction occurs under pressure.
- Clay soil . Due to their ability to swell when frozen in a humid environment, the depth of the foundation must be chosen equal to the freezing level of the soil. Also, this type of soil is highly eroded and compressed.
- Loams and sandy loams. This type of soil is formed by mixing sandstone (3 - 10%) and clay particles (10 - 30%). The foundation of a building located in wet soil should be located at a greater depth than the ground can freeze. This type of soil is greatly transformed when moisture enters.
Excavation and compaction
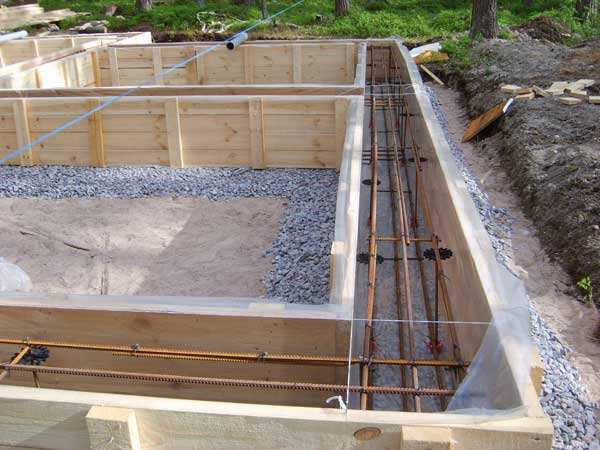

At a short distance from the city, soil development is carried out using a tractor. A house made of foam blocks weighs little, so a trench is dug to a depth of 1.3-1.4 meters, taking into account the crushed stone cushion. The width for a one-story house is 800 mm, leaving space for insulating the base. The standard foundation for a small building made of foam blocks is 600 mm in width. The cross-section of the monolith will be 1200x600 mm, reinforcement with fittings is mandatory, the optimal thickness of the rod is 12 mm, for both transverse and longitudinal strapping.
Compaction of the bottom of the trench is carried out with vibrating plates or gasoline rammers weighing from 100 kg. The coefficient must comply with the regulatory framework SNiP (building codes and regulations). Usually it is adjusted to 1.85−2.15 in relation to non-compacted soil. In muddy, silty or clayey soils, when tamping is carried out, a cushion of sand 200-250 mm thick is arranged, compacting it in stages.
Advice: If the bearing capacity of the soil is weak, piles are driven along the bottom of the trench at a distance of 3 meters from each other. The diameter of the pipes is chosen to be no less than 89 mm, with a length of 2.5–3.0 meters. These measures will prevent the foundation from sagging under the load of a one-story house.
Technical specifications
Before starting construction, you need to know what the height and depth of the foundation for a one-story house should be. These dimensions can be calculated with only initial data on the planned thickness of the walls and the material of the buildings in general. First, you need to calculate what bearing capacity the soil has in your region.
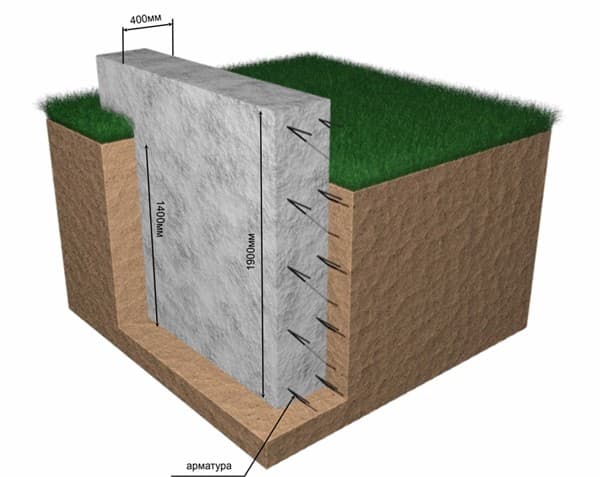
Photo - shallow foundation
You will find this indicator in the geological bureau of your region. Then you need to calculate how much pressure the building exerts on the foundation. To do this, all loads are summed up: floors, roofing materials, walls, doors, windows, insulation, etc. The resulting number is multiplied by a conditional coefficient of 1.3 - this is the approximate pressure that will be exerted by furniture and residents. A certain number of tons will come out - this is the mass of the building.
Next, you need to calculate the dimensions of the foundation. Here, each type has its own characteristics. For example, if with pile and columnar everything is very simple (the selected support and the weight of the house is divided by its load-bearing capacity), then with strip and monolithic it is more complicated. The minimum permissible depth for a foundation for a one-story house with an attic is 30 cm for rocky soil, 60 for sand and 85 for loam. For greater reliability, similar indicators can be taken for a monolithic slab, but in this case it will be very expensive. This is a normally buried foundation; for a wooden structure or frame house you can make a shallow foundation, but its parameters need to be calculated more accurately.
After calculating the depth, you need to decide on the width. The minimum permitted width of a strip foundation is 25 cm, and it is very important that the sole, i.e., the base of the support system, is slightly wider than the top. Of course, the thickness of the walls plays a big role here. Masters advise taking a size for the width of the foundation that is 5-10 cm greater than the thickness of the walls. You can choose the right proportions based on the finished building design.
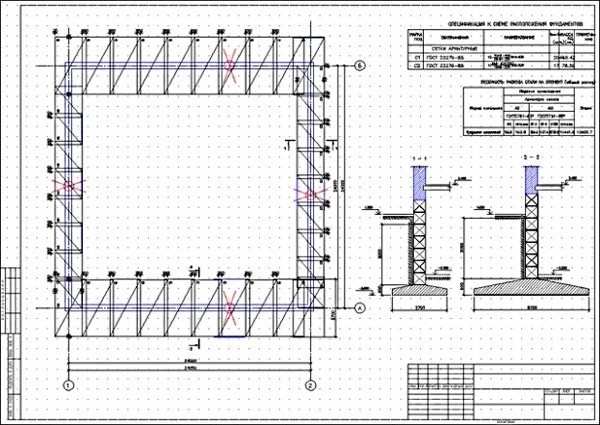
Photo - foundation project for a one-story house
Preparing a foundation pit and load-bearing cushion for a two-story house

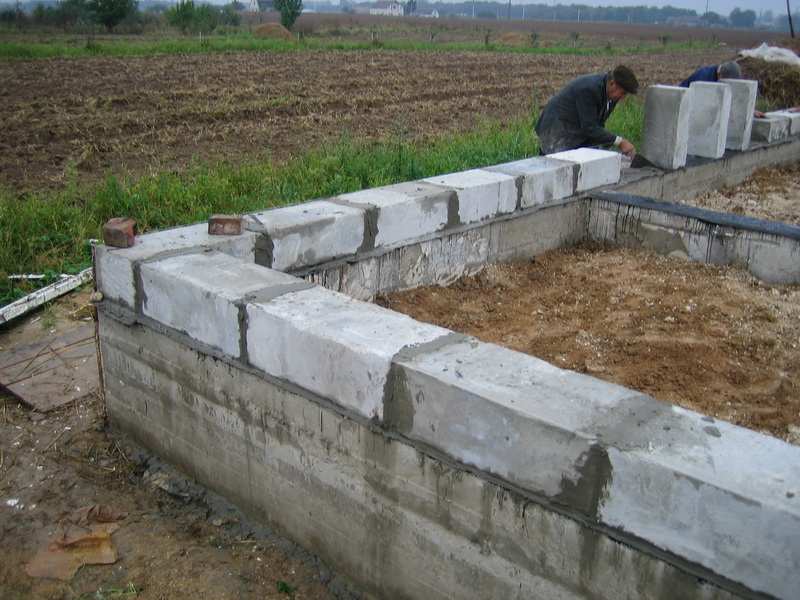
Having developed a pit for the foundation, the bottom is measured using a level and the edge and area are cleared of crumbling soil. Then markings are made for the load-bearing concrete pad. The width of such concrete preparation is 100−1200 mm, with a thickness of 150−250 mm. It can be used to mount both a monolithic foundation and a block one. The formwork is prepared according to the diagram, installed around the perimeter, using reinforcement as stops, simply driving them into the ground.
Reinforcement is done in one tier, with class A 1-3 reinforcement. The mesh cell has a size of 200x200 mm, the joints are knitted with wire. The laying depth of the load-bearing belt is at least 1.8−2.2 meters for medium heaving soils of type 2. What is important when laying is to make a cushion of crushed stone under the base. The thickness of the pillow for a two-story house must be at least 120 mm. Crushed stone is laid on compacted soil. Then water drainage measures are installed or waterproofing material is laid. If construction is frozen for the winter, a pit is dug at the lowest point of the pit to collect water. The size of the sump (storm pit) must be at least 6 cubic meters.
Choosing a foundation type
Since a building made of foam blocks is almost fifty percent lighter than a stone one-story house with walls of similar thickness, the bearing capacity of the foundations, and therefore the amount of work and the estimated cost of the supporting structure, will be significantly lower. The minimum thickness of a foam block wall without cladding is 300 mm, and if it is not intended to line the house with bricks, the width of the foundation can be taken in accordance with the transverse size of the foam blocks.
Home construction
Depending on the type of soil, an appropriate foundation should be selected. For slightly heaving and non-subsidence soils, it is rational to use strip foundations, since it is enough to lay the base of the foundation slab below the freezing mark. Waterlogged, weak soils require deeper laying of supports, and pile foundations successfully cope with the task within a reasonable budget.
When constructing pile foundations, it is necessary to take into account the installation features of the strapping structure. Pile foundations can be installed under walls made of foam blocks, with both low and high grillages. To install a grillage on the heads of metal piles, you should use reinforced concrete and rolled steel profiles, since it is not recommended to support walls made of foam blocks on wooden frames, as well as an unreinforced metal profile.
In addition, it is easier to lay a waterproofing layer on concrete.
Laying the foundation

The depth of laying the concrete foundation for a house made of foam blocks plays an important role. The entire system of load-bearing concrete structures has considerable weight. Monolithic casting (frame) of the future house is made of class B-26 concrete.
The main weight of a two-story house falls on the monolith. The entire load falls on the monolithic frame and grillage. The walls are self-supporting structures; foam concrete is simply placed in the openings. Therefore, the optimal laying depth for a house made of foam blocks in normal soils will be minus 2200 mm from the zero level of the project. But this is for the middle zone. In each case, the depth will be different; when building a two-story building, you need support with the installation of special load-bearing pillars or pillows (glasses).
Types of structures
Before starting construction work, it is necessary to develop design documentation. These are diagrams and drawings that will help you choose the optimal type of supporting base. For a one-story house you can make the following foundation with your own hands:
- Monolithic;
- Columnar;
- Pile;
- Tape;
- Columnar-flying.
Monolithic is a type of construction when a large trench is dug under the future house, repeating or slightly exceeding the area of the building itself. It is compacted with sand or crushed stone cushions, and then filled with cement mortar. Sometimes foam concrete or gas silicate is used, but most often such materials are used in the construction of a country house. Sometimes such a support is built by installing a ready-made monolithic slab of concrete and reinforcement, which significantly reduces construction time.
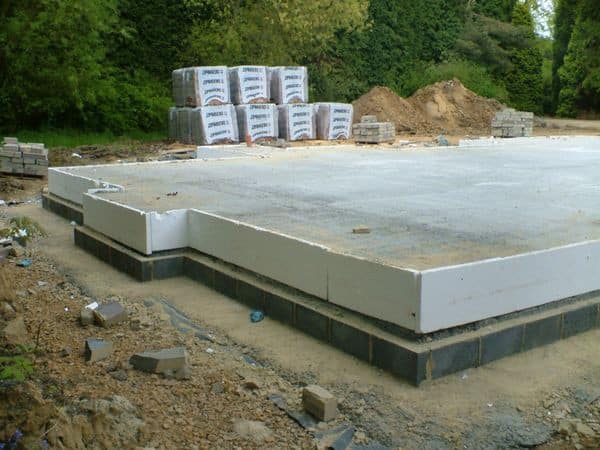

Photo - monolithic foundation with a sole
Columnar is a very popular type of base, which is considered one of the most economical options. It can be made using poured pillars, installing supports from foam blocks or bricks, and also driving concrete foundations into the ground. Mainly used for wooden houses, block or residential premises made of timber.
Pile is an analogue of columnar, but it is used on problem soils. At first glance, the unreliable support system copes well with high loads - on average, one pile can carry up to 18 tons. Pile construction is used on sand, rocky and clayey soils, and houses are also built on swampy soils using this system.
A strip foundation for a one-story residential building is, in most cases, the ideal solution. Due to the combination of high load-bearing performance and economical consumption of building materials, most home craftsmen choose just such a system for their home. The strip type of base can also be made from block bricks, aerated concrete, foam concrete, cement mortar and reinforcement bundles.
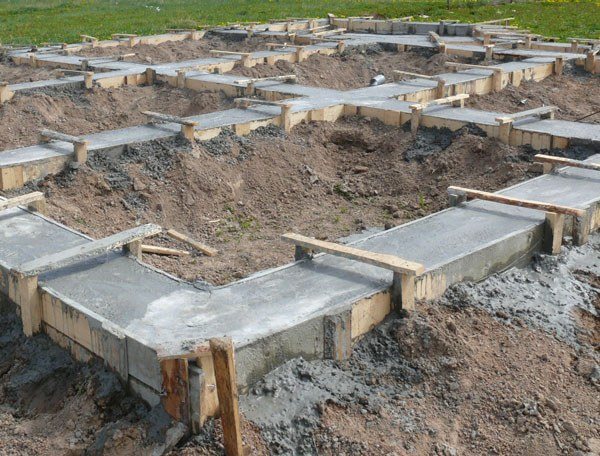

Photo - strip foundation
Columnar-tape or strip pile is a combined type of load-bearing structure for a private house. In most cases, it is a simple structure with point supports, which are additionally reinforced with a grillage. But some craftsmen use a more complex system for their buildings. The technology of internal pillars is the principle of building a foundation, when first a trench is dug, suitable in depth for the foundation. Afterwards, additional cylindrical holes are dug in it, and they, together with the upper trench, are filled with solution.
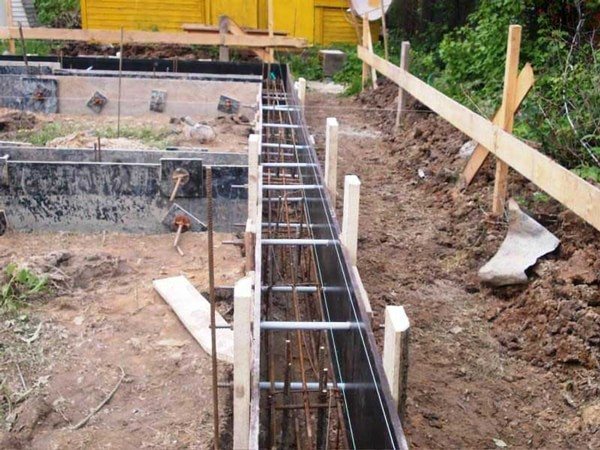

Photo - high strip foundation
All types have their advantages and disadvantages; to choose the right option, be sure to consult with specialists. Video: foundation on screw piles
What besides the monolith
So, let's figure out what kind of foundation for a house, in addition to a monolith, can be provided for block masonry.
Let’s say right away that if you still choose a slab, then there are no other alternatives. Depending on the design of the building and climatic conditions, one or another technology can be used (with burial, with insulation, with drainage), but the essence does not change - the foundation will be monolithic. It is only in industry that it can be assembled from prefabricated reinforced concrete slabs.
What to make a strip support for walls from - alternatives
As for the strip foundation, there are more options. Since it is shaped like a wall, for its construction you can use all those materials that building codes allow for the construction of basement walls.
In addition to monolithic reinforced concrete, these are:
- Rubble concrete;
- Rubble masonry;
- Ceramic brick;
- Precast concrete (FBS blocks);
- Prefabricated reinforced concrete (UDB blocks, strip slabs and FL, FP cushions).
Note: If the walls are not at the same time a foundation, but rest either on a slab or on a foundation pad, they can also be erected from small-format blocks of heavy concrete, manufactured in accordance with GOST 6133.
Rules for the design of reinforced masonry structures
Please note: On the Internet you can encounter the most contradictory information, including regarding materials for building foundations. In this regard, many are interested in whether it is possible to make a foundation for a house from foam blocks? According to the rules of SP 15.13330.2012, an excerpt from which is given above, this is unacceptable. This material does not have enough strength or moisture resistance for such “work”.
Rubble stone is an excellent building material for low-rise buildings
- Rubble stone, which in a large format and with bedded edges is used for masonry, and in a smaller fraction - as a filler for concrete, is good for those areas where it is a local material.
- True, there are not so many such places - therefore, in most cases in private construction, strip foundations are laid from red brick or FBS blocks.
- Both options are available and are an excellent alternative to monolithic reinforced concrete. Moreover, they are very often combined, using FBS in the buried part, and brick in the above-ground (basement) part.
- Firstly, brickwork creates a rigid reinforcing belt on top of large-format blocks, which, in fact, are not fastened together in any way. And secondly, having taken a face-quality brick, you no longer have to worry about finishing the base. Moreover, walls made of foam blocks are often lined with brick.
There is no way to object to a foundation made entirely in a monolithic manner, because this is the most durable option. It has only two disadvantages: the need to wait 28 days until the concrete gains full strength, and the significant labor intensity of the work associated with concreting.
Some people don’t have this time - they want to do it faster, cheaper and without spending too much effort. In this case, the foundations of houses made of foam blocks can be erected using alternative methods, which were mentioned above. Including the use of various options for permanent formwork.