Insulation of the foundation of a wooden house
Many owners of wooden houses are faced with the fact that in winter the floor freezes on the 1st floor. This phenomenon can only be eliminated in one way - to insulate the foundation of a wooden house from the outside. The foundation of a wooden house is built from different materials. The method of insulating the foundation of a wooden house depends on the type of supporting structure of the building. Modern thermal insulation materials are used to insulate the foundation of the house. This article presents options for insulating foundations of various designs.
When is it better to insulate the foundation of a wooden house?
It is more convenient and cheaper to insulate the foundation before installing the walls, while the earthen trenches are not yet backfilled, and there are no structures above the base that would interfere with the work. As for insulating an already finished house, the floors of which are too cold, and the walls of the unheated basement are covered with drizzle in winter, then it’s better late than never.

It is most convenient to insulate the foundation before erecting the box
The easiest way to insulate the outside
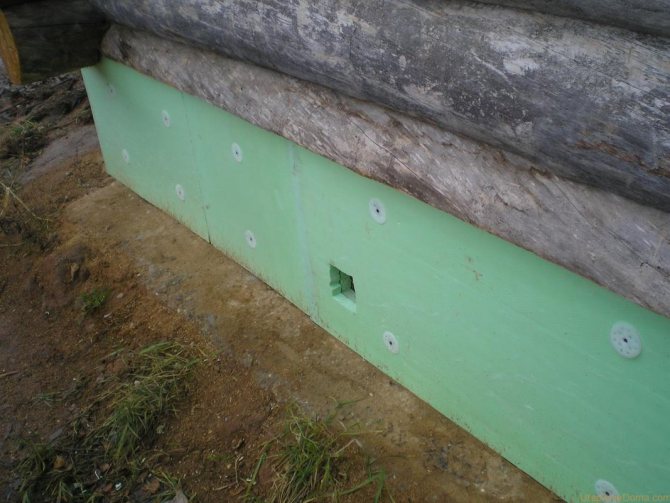

You can insulate the foundation of a wooden house from the outside with your own hands.
The simplest way to improve the thermal insulation of the foundation is to insulate the base with soil. It has been used for more than a century. As a last resort, it can still be used today if it is not possible to purchase special thermal insulation materials. In this case, sand or earth is poured around the house to a level corresponding to the floor level.
This type of foundation insulation has advantages and disadvantages. The advantages include accessibility due to the fact that there is no need to purchase insulation, and the ability to prevent freezing of the basement. Disadvantages can be considered:
- low thermal insulation characteristics of the soil;
- the need to level large sand and/or soil;
- there is a high probability that the cold will still be able to penetrate through the walls.
Advice! Soil insulation is an affordable but ineffective method. In order for the foundation to be insulated efficiently and for a long time, it is worth purchasing modern thermal insulation material. It will significantly increase the efficiency of work and reduce heat loss in the future.
General principles of foundation insulation and materials used
To understand how to properly insulate a foundation from the outside, you need to know that freezing occurs not only above ground level, but also below. Moreover, it is advisable to insulate not only the foundation itself, but also the soil on which the support cushion rests. In this way, it is possible to exclude the impact of frost heaving forces on concrete, which tend to deform the strip structure. Consequently, not only the vertical concrete surface, but also the blind area is subject to insulation. Level - slightly higher than the foundation depth or freezing depth.
To maintain heat in the house, the ground floor should also be insulated. If the floor is monolithic, it is better to fill the space under it not with soil, but with a relatively inexpensive insulation material - expanded clay. Under the frame structure of the floor, waterproofing should be done, insulation should be laid between the frame elements, not forgetting to leave the possibility of ventilation of wood and fibrous materials (mineral wool).
It is also necessary to waterproof the foundation or basement walls, and this should be done in the early stages of construction by laying horizontal roll bitumen waterproofing on the base of the strip foundation. In the second stage, bitumen or polymer-cement insulation is applied to the walls from the outside, and if the house does not have a basement, from the inside too.
The optimal material for external foundation insulation is polystyrene foam: relatively inexpensive PSB-50 foam or more durable and durable extruded polystyrene foam (EPS). Although expanded polystyrene does not absorb moisture and is difficult to biodegrade, its surface should be protected from ultraviolet radiation above the ground and exposure to plant roots underground. Below the ground level this can be done with flat asbestos-cement sheets, above with thin-layer plaster reinforced with a polymer mesh.
The thickness of the insulation boards is determined by thermal engineering calculations and the effect that needs to be achieved. The minimum recommended thickness is 5 cm. Any non-hydrophobic, rot-resistant and sufficiently durable materials are suitable for external insulation. It’s not cheap, but foam glass has proven itself, and special boards based on bentonite are also used, which simultaneously provide insulation from moisture.
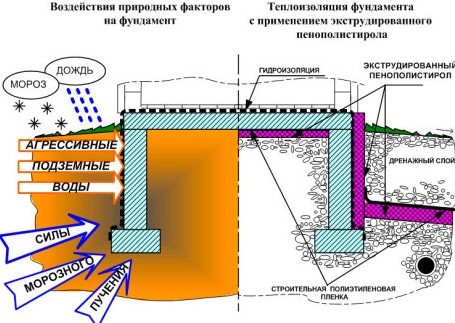
Foundation thermal insulation technology using extruded polystyrene foam
Let's consider in which case it is recommended to use one or the other insulation option.
Thermal insulation materials

Insulating the foundation with foam plastic
When choosing materials for thermal insulation, you should select products that are characterized by low thermal conductivity, durability, water resistance and lack of hygroscopicity.
Insulation options for the foundation:
- Styrofoam. It is a slab of porous balls consisting of 98% air. The heat insulator is affordable, easy to process and install. Low thermal conductivity provides reliable protection against temperature extremes.
- Penoizol and penofol. It is manufactured in the form of rolls, where the base is foamed polyethylene, enclosed between layers of aluminum foil. The small thickness of the material allows it to be used for interior work and exterior decoration with minimal excavation.
- Polyurethane foam. The material has the lowest thermal conductivity, durability and environmental safety. Available in the form of slabs up to 10 cm thick or sprayed onto the surface with a spray bottle.
- Expanded clay. Vulcanized clay balls have excellent performance characteristics, but are hygroscopic and prone to shrinkage. Based on this, it is used in conjunction with cement mortar.

Expanded clay

Penofol

Polyurethane foam
The choice of insulation is determined by the foundation material and soil properties.
How to insulate the foundation from the outside using polystyrene foam boards
- Soil preparation
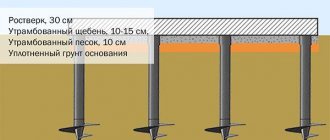
Along the entire perimeter of the foundation, a trench is selected with a depth to the support pad of the concrete strip. If the freezing level is low, then it is enough to dig just below the maximum limit. It is better to rest the slabs on a rigid base; to do this, you should sprinkle the trench with a layer of sand and gravel (10 cm) from below and compact the soil.

The deeper the trench is dug, the higher the thermal insulation of the foundation slabs will be.
- Foundation preparation
The foundation surface must be clean and as level as possible. If vertical waterproofing has not yet been applied, defects must be eliminated with cement mortar or repair compound.
- Foundation waterproofing
The next stage of work is waterproofing the foundation. The insulation itself does not need insulation, but concrete should be protected from moisture, then it will last longer. If there is a basement floor, good waterproofing is especially necessary. Even if we are talking about reconstruction of the foundation and there is no horizontal waterproofing between the sole and the tape, we still recommend doing a vertical one - even such a half-measure will significantly reduce the moisture saturation of the concrete. It doesn’t really matter what material is used: rolled bitumen, liquid rubber or cement-polymer mixtures. The main thing is to adhere to the recommended work technology. It is more difficult to work with rolled materials; you need to have a professional burner and know how to handle it. Mastic and cement compounds are easier to apply; you only need brushes and a spatula.
- Fixing insulation boards
To attach polystyrene foam to the foundation, polyurethane glue or mastic based on bitumen and polymers, cement-polymer compositions are used. Bituminous materials should not contain organic solvents, they destroy polystyrene. The adhesive can be applied to the wall in a continuous layer using a tiler's comb with a large tooth, or, if the walls are not level enough, apply it to the slabs themselves pointwise, at a distance of about 25 cm between points. Install starting from the bottom corner, resting the slabs on a concrete support or sand cushion . Having laid the first row, continue the second so that its seams fall in the middle of the underlying sheets, like brickwork. Connect the slabs with overlapping grooves, but if you have to trim the edge, then be sure to lubricate the joint with mastic or glue. When joining corners, it is recommended to seal the seam with foam to close any possible cold bridge. If necessary, the slabs are additionally secured with special dowels with a large head (fungi), first filling the holes drilled for the dowels with silicone sealant.
- Laying outer protection
The last stage in installation is to isolate the insulation from external factors. The underground part can be covered with flat slate (ADS), roofing felt. Sometimes it is recommended to simply sprinkle EPS with soil, because it is stronger than PSB. But we still believe that it also needs to be protected, because the roots and shoots of plants grow even through a thick layer of asphalt and split the masonry. You can also install a reliable wall made of solid, well-fired brick, if there is support for it. True, such protection will not be cheap.

Protective brickwork will protect the foam from moisture coming from the soil
Strip foundation
First, they dig a trench all the way to the bottom of the foundation. Its width is 80-100 cm, since the blind area is also insulated at the same time. If the foundation is of a recessed type, then the first 40 cm deep trench is dug to the width of the blind area, and then, to save effort, you can make it 50 cm wide.
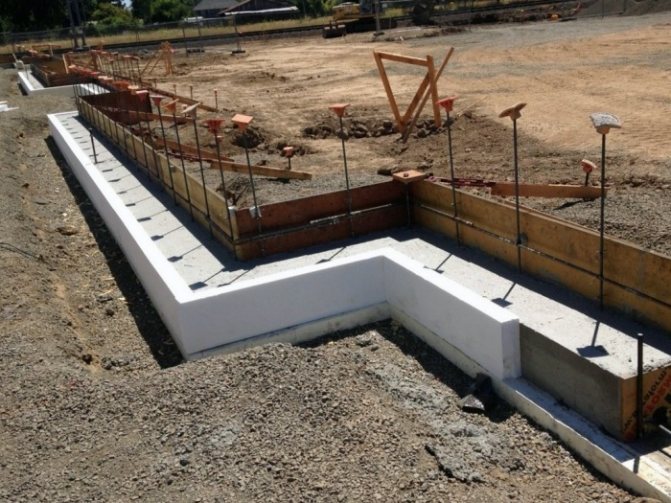

If the house was built some time ago, cracks may appear in the concrete. They are covered with a mixture of cement and construction adhesive if the cracks are small. Larger damage is repaired with cement mortar.
The next step is waterproofing. To do this, the surface of the foundation tape is covered with bitumen mastic, onto which roofing material is glued. The sheets are glued overlapping, the seams are additionally coated with mastic. More modern roll materials are also used, such as self-adhesive roll waterproofing.
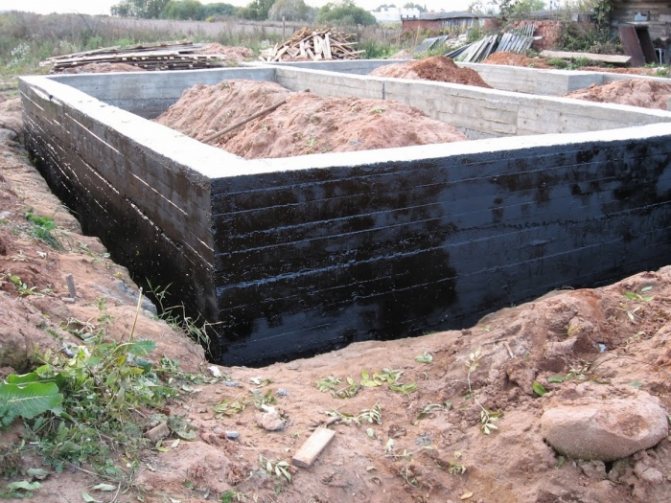

After this, the insulation is glued. Although penoplex is often attached to dowels, it is still better to give preference to glue or liquid nails - they do not violate the integrity of the sheets. How to insulate a strip foundation with polystyrene foam, watch the video:
The joints between the sheets are foamed with liquid foam.
After installing the insulation, geotextiles are glued onto it. It will reduce the effect of soil heaving on the heat-insulating layer.
Next, the trench is backfilled to the level of the blind area. Sand and small crushed stone are poured under the blind area in a layer of 0.15-0.2 m, and the cushion is thoroughly compacted. This layer will protect the blind area from loads arising from soil movement. A layer of dense insulation is placed on top. The same penoplex is suitable due to its resistance to compression loads. Concrete is poured on top; it can additionally be reinforced with mesh.
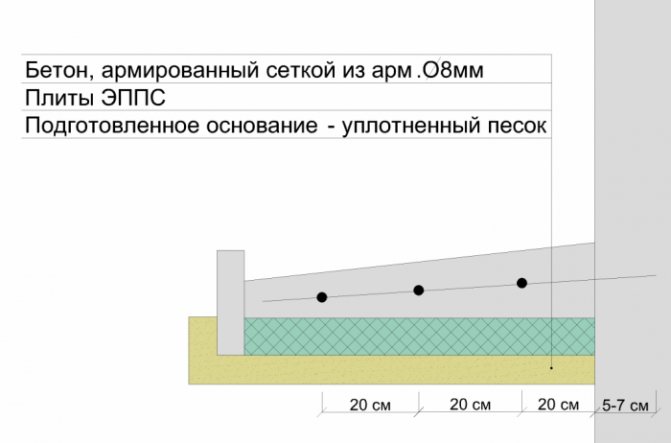
Attention! To reduce the effect of frost heaving, the insulation layer is placed at the level of the base of the foundation. The most effective combination of penoplex insulation up to the level of the walls in combination with insulation of the blind area at the level of the sole.
External foundation insulation with polyurethane foam
How to insulate the foundation of a wooden house as quickly as possible? For this purpose, sprayed polyurethane foam insulation can be used. Workers will mix the components right at the construction site and apply the liquid composition to the entire external surface within a day. After hardening, polyurethane forms a dense, continuous, seamless coating with characteristics similar to penoplex. True, the cost of insulation will be high.

Due to the absence of seams, sprayed polyurethane provides high thermal insulation
Frost protection, its types
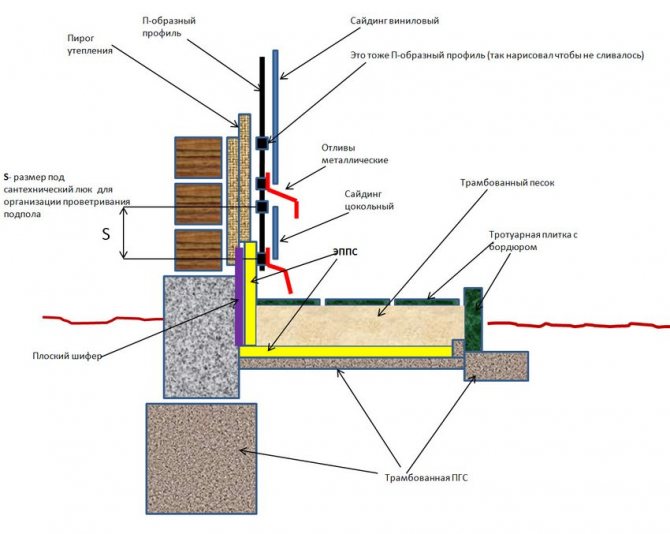
Scheme of insulation of the foundation of a rammed ASG.
This is not the name of the method, but just the main task of insulation. To install such protection you will need:
- shovel;
- boards or other material for formwork;
- roofing felt;
- insulation directly (it is better to take expanded clay, but other material may be suitable);
- cement and sand.
A layer of soil is removed along the perimeter of the wooden house in the immediate vicinity of the base. Your instinct should tell you the depth, but you shouldn’t overdo it in this direction: with a large trench depth, you can ensure that the foundation under the influence of the gravity of the entire house can give additional shrinkage.
The walls, of course, will not crack (this is also an advantage of wooden houses), but the foundation may lose its integrity. Then it will have to be insulated more radically. It is enough to limit yourself to a depth of about 45 cm. In order to adequately insulate the foundation, depth does not have to be considered the basis of all work. A wooden house needs a solid foundation, so it is better not to dig deeper.
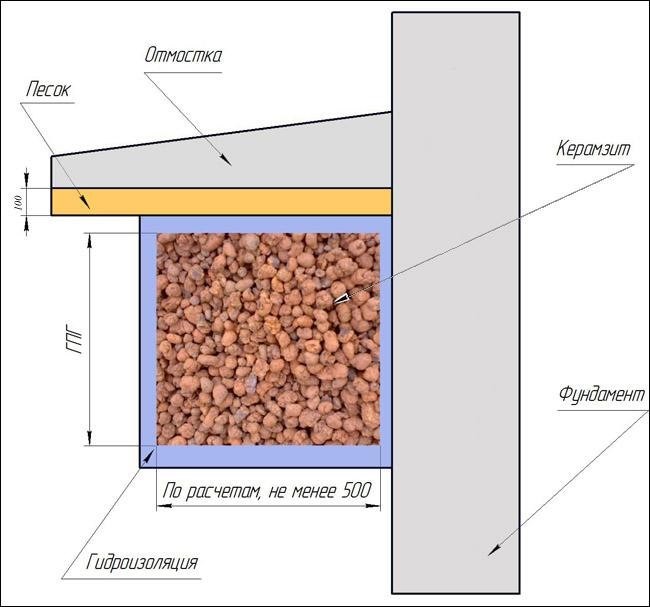
Scheme of foundation insulation with expanded clay.
So, the trench is already ready, and you have to make the formwork. The design can be anything, since it is not of fundamental importance. The bottom and walls of the resulting structure will have to be laid with roofing felt. This measure is necessary to ensure that the insulation does not fill with moisture, otherwise it will not “work.”
Next, insulation comes into play: we pour expanded clay into the resulting foundation pit, cover it all with another layer of roofing felt and fill it up. The work is not finished yet, as there is a blind area to be made. Do not forget that the width of the blind area should cover the laid thermal insulation.
It makes sense to take care of forming a certain slope around the foundation of a wooden house from the outside. This is necessary to ensure that rain or melt water does not stagnate and penetrate into the insulation. This will be a kind of guarantee that the insulation will not have to be replaced soon.