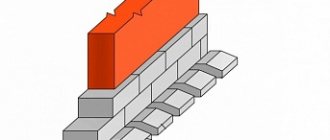
Strip foundation
It consists of a reinforced concrete strip poured along the entire perimeter of the walls being built. A trench is dug to the depth of soil freezing. The depth of freezing varies in different regions. This information can be found in various reference books.
- After digging the trench, a sand cushion 10-15 cm thick is poured . This is necessary so that when the soil swells, the soil does not act on it from below.
- The pillow is carefully compacted, with periodic wetting with water, for better compaction.
- After this, the concrete preparation is poured without reinforcement. It is necessary in order not to contaminate the reinforcement with various earth or clay.
- Once the concrete preparation is ready and hardened, you can proceed to knitting the reinforcement cage. The frame usually consists of a connected mesh in several rows.
- After this, the formwork is erected. It is made of plywood and boards. It is needed so that when concrete is poured, it does not spread, but takes the form of a tape.
- Until the foundation has hardened, it is necessary to carry out vibratory ramming immediately after pouring.
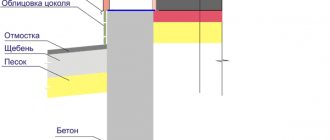
After 21 days it is completely ready. It is also necessary to carry out coating waterproofing with bitumen mastic or primer so that water coming from the soil is not absorbed into the base. Otherwise, this can lead to corrosion of concrete and its premature destruction.
This type is the most common and most reliable of all existing ones.
But it requires the involvement of a large workforce and equipment. It will last for centuries if it is made and maintained correctly. After the construction of the walls, it is imperative to arrange a blind area to drain all excess water. The cost of construction varies everywhere, depending on the region and volume. Approximate cost with materials and work from 10 thousand rubles.
Collecting loads
Let's consider what loads the foundations of buildings are subjected to. These are permanent and temporary loads.
The permanent ones include:
- The weight of all building materials used in the construction of external and internal walls.
- Floors.
- Roofs and roofs.
- Window and door structures.
- Weight of staircases and landings.
- Stationary equipment, if we are talking about an industrial enterprise.
Temporary or dynamic loads include:
- The weight of mobile equipment, furniture, people living or working in a given building.
- Engineering equipment that ensures safety and comfort - fire escapes, aerators, bridges and ladders on the roof, air conditioners, ventilation, etc.; snow and wind loads.
- Load on the ground from nearby roads, railways, airports, and underground structures.
- All values of the collected loads are taken into account when developing projects, where on this basis the type and type of foundation, its dimensions and depth are selected.
Soil condition
But the depth of occurrence is mainly influenced by the geological condition of the soil in the area where the industrial facility is being built. Soils, as is known, consist of different layers of rocks located at different levels.
To calculate, for example, the foundations of the frames of industrial buildings, it is necessary to carry out geological survey work. It is their results that will determine which type of foundation is suitable for a particular industrial building.
In addition to the condition of the soil, the choice of foundation is also influenced by the depth of groundwater and the level of soil freezing in a given building location.
Pile-screw foundation
The piles are a solid iron pipe with blades at the end .
- To begin with, the places where the pile will be needed are marked.
- After this, the depth to which they need to be screwed into the ground is determined.
- After which they are screwed into the ground, like a fishing drill. The ends remain sticking out of the ground, to which they are then welded for the subsequent construction of the wall frame.
Such foundations can be erected even in winter. Most often they are used when constructing a building in wetlands or on soft soils. The depth of drilling of a pile is determined by the depth of hard soil rocks capable of bearing a load-bearing load, but the depth cannot be less than the depth of soil freezing. Not very difficult to install. Quite reliable as a supporting structure . When constructing such a foundation in rocky areas, the steel may be scratched or the blade may even break, which will lead to corrosion of the metal and a short service life. The price for such a foundation is from 5,000 to 18,000 rubles , depending on the diameter and depth of the pile.
Chapter 2. TECHNICAL SOLUTIONS AND TECHNICAL AND ECONOMIC JUSTIFICATIONS FOR THE APPLICATION OF PILE FOUNDATIONS
Pile foundations for industrial buildingsTypical designs of industrial buildings and structures are very diverse, which is explained primarily by sharp fluctuations in loads on foundations: from 40 to 4000 tf or more.
But since mainly concentrated loads are transferred from the structures of industrial buildings and equipment to the foundations, pile foundations of such buildings and structures are usually taken in the form of clusters of piles united by a common reinforced concrete grillage of a square, rectangular or trapezoidal shape in plan. The number of piles in a bush is determined by the magnitude and type of load and the bearing capacity of the piles.
In addition to cluster pile foundations, they also use platform foundations with piles located under the entire building or structure, and figured foundations with piles located according to the supporting load-bearing elements (for various structures and equipment).
Foundations made of driven piles and shell piles with or without grillages
. Such foundations are used for workshops for various technological purposes.
In relation to the dimensions and loads of typical reinforced concrete single-leg and two-leg columns of the KE-01-49, KE-01-52, KE-01-56, II-22-1 and II-22-2 series, the Fundamentproekt Institute has compiled a table for selecting bushes piles taking into account the action of the moment in one direction.
Bored pile foundations
. Foundations made from bored piles are used for columns of industrial buildings in the form of a single pile or a bush consisting of 2, 3, 4 or 5 piles, united by a common monolithic grillage. Examples of technical solutions for foundations made from bored piles of one-story and multi-story industrial buildings for various soil conditions have been developed by the institute Foundation project jointly with Ukrspetsstroyproekt. For each of the variants of soil conditions, the corresponding designs of bored piles have been adopted.
Three types of pile foundations have been developed for prefabricated reinforced concrete columns of a one-story industrial building: foundation F-1 - with three drilled piles 18 m long with a widened heel, united by a monolithic reinforced concrete grillage with a glass for the column; foundation F-2 - of two bored piles 18 m long with a widened heel, also united by a monolithic reinforced concrete grillage with a glass and foundation F-3, similar to the foundation F-2, but with a pile without an anchor heel.
Two types of foundations have been developed for the columns of a 5-story industrial building with a width of 18 x 6 x 6 x columns: along the outer row - foundation F-1, similar to foundation f-2, and along the inner rows - foundation F-2, similar to foundation F -1.
An example of the effective use of pile foundations is the experience of constructing the Kama Automobile Plant. During the construction of the main buildings, columnar foundations were replaced by foundations with bored piles, which cut through the top layer of subsidence loams, layers of silty sands and rest on non-subsidence underlying soils. Bored svans with a diameter of 60 cm with a widened base of 160 cm, as well as diameters of 100, 120 and 170 cm without entrenchment, were arranged in bushes, usually in groups of 2, 4, 5 or 6 pieces. in a bush at a laying depth of 13-16 m. Reinforced concrete monolithic grillages made of grade 200 concrete were laid on a preparation made of grade 50 concrete with a thickness of 10 cm.
The magnitudes of the given loads on the foundations: vertical loads in the range of 400-1000 tf, bending moments up to B50 tf and transverse forces 30 - 200 tf. In most buildings, deep 6-Yum technological tunnels are designed, directly adjacent to the pile foundations of the building’s load-bearing structures and located both along and across the workshop spans. The use of bored piles in this case made it possible to construct technological tunnels after the construction of buildings.
Institute Hydroproject named after. S. Ya-Zhuk developed and used during the construction of the communication overpass of the Kama Automobile Plant, about 12 km long, foundations made of bored piles with the installation of grillages in the ground (without cutting the soil to the bottom of the grillage). Vertical loads on the foundations of the overpass reach 600 tf, horizontal loads - 80 tf and bending moments - 50 tf m. The foundations are made of one, two or three piles with a diameter of 100 and 120 cm, the laying depth is from 14 to 18 m.
The technical solution of pile foundations with the installation of grillages in pits drilled by the MBS-1.7 unit according to the design dimensions of the grillages made it possible to completely eliminate excavation work below the planning level, amounting to about 150 thousand MS of excavation and then backfilling of soil, to reduce labor costs for the installation of zero cycle for more than 2400 person-days.
Ready driven piles. Piles and pile foundations
Foundations and Foundations
| According to this pile foundations are divided into grillage and... 16.5, Frame of one-story |
Construction of pile foundations
. Pile driving works...
| Device pile foundations according to their responsible structural significance ..... Pile supports for |
Load-bearing capacity of piles and pile foundations
| For industrial pile foundations and civil |
Point reinforced concrete piles (drive-in piles)

The principle is the same as the pile-screw foundation. Only the piles are not twisted, but driven into the ground. The piles are a concrete pillar. This foundation, when properly manufactured, lasts more than 90 years. The only drawback is the involvement of large equipment to drive them. The price for one pile depends on its size, usually the price is around 5500–7500 thousand rubles per pile with installation and delivery.
Installation of metal columns
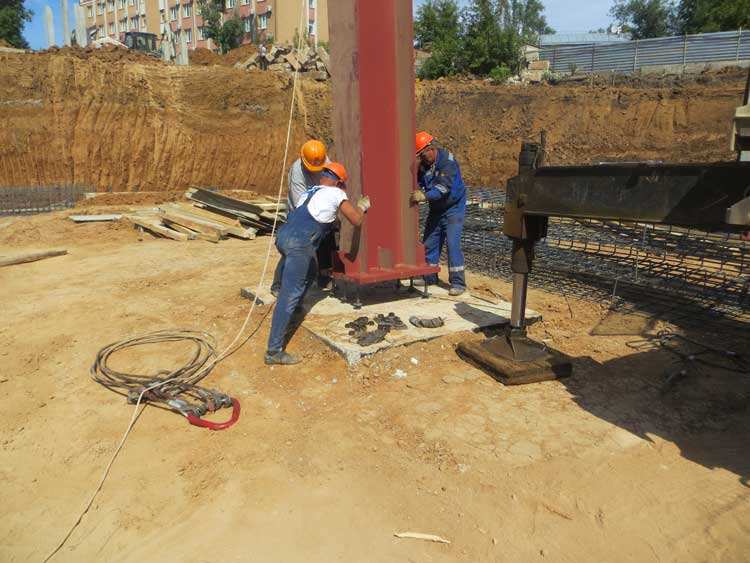

Metal columns are mounted on bases in which anchor bolts are built in advance for their fastening. After design, the standard position of the supports is ensured by the precise placement of anchor bolts at the fixation points. In this case, the accuracy of installation is ensured by serious preparation of the base plane.
The columns are supported as follows:
- On the surface of the base, which is mounted to the required level of the supporting sole, without subsequent addition of the cement mixture. Used for supports with milled shoe soles.
- Metal slabs are installed in pre-calibrated locations and filled with concrete mixture. The base is concreted to a level 5-8 cm below the level of the base of the support, which is indicated during the design.
- After that, the installation of support columns is carried out, combining the axial marks of the alignment axes on the elements built into the foundation with their marks. The set screws adjust the position of the individual support in height, taking into account that the top surface of the slab will be located at a given level of the support plane of the shoe. The supporting planes of the pillars must be planed in advance.
- The base is concreted to a level 0.25−0.3 m below the surface of the shoe, marked during its design.
After completing this work, the embedded elements and components of the supports are installed. The upper part of the base is cemented to a level 4-5 cm below the upper plane of the supporting elements. The supporting surface of the shoe is made at right angles to the axis of the pillar itself.
Slab foundation
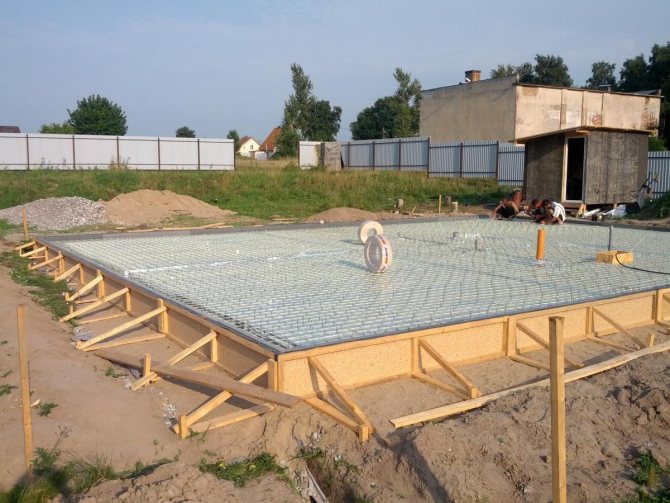

The slab foundation is a reinforced concrete slab poured under the entire workshop area.
- To begin, dig a pit 50-70 cm deep.
- After this, a sand cushion is erected and compacted.
- Next, a layer of waterproofing is laid, and insulation is laid on it.
- After this, the slab is reinforced and filled with concrete, completely all at once.
Such a foundation is not susceptible to frost heaving due to its large area of contact with the ground. The top of the slab can be used as the floor of the 1st floor, which reduces costs. However, such a foundation is more expensive than all of the above. The price for such a foundation is around 3500-6500 thousand per square meter .
Our services
The construction company is engaged in the arrangement of the most universal type of foundation - pile. We guarantee high-quality performance of the entire range of piling work: from foundation design to the supply of reinforced concrete piles from the best domestic manufacturers and their driving.
Our company has at its disposal experienced employees and modern equipment - pile drivers, capable of effectively performing leader drilling and driving reinforced concrete piles using the impact and vibration method.
The reliability and durability of any foundation directly depends on the correctness of its design and the quality of work performed. Without the proper experience and qualifications, it is extremely difficult to do everything according to technology. If you want the foundation of your house to be built to last, contact us and we will do everything conscientiously. We only engage in pile driving, leader drilling, and sheet piling.
REGULATIONS
- SP 26.13330.2012 “Foundations of machines with dynamic loads”
- GOST R 54257-2010 Reliability of building structures and foundations. Basic provisions and requirements
- GOST 12.1.012-2004 SSBT. Vibration safety. General requirements
- GOST 25100-95 Soils. Classification
- SP 16.13330.2011 “Steel structures”
- SP 20.13330.2011 “Loads and impacts”
- SP 22.13330.2011 “Foundations of buildings and structures”
- SP 24.13330.2011 “Pile foundations”
- SP 25.13330.2012 “Foundations and foundations on permafrost soils”
- SP 28.13330.2012 “Protection of building structures from corrosion”
- SP 43.13330.2012 “Structures of industrial enterprises”
- SP 63.13330.2012 “Concrete and reinforced concrete structures. Basic provisions"