Construction and calculation of the foundation slab.
When construction is at the stage of building a house, the heaviest load goes to the foundation, i.e. foundation. To ensure that the base can support the structure without cracking or sagging, pay special attention to it. Yes, you cannot save money during construction, especially when choosing a foundation slab.
This is the material from which a wonderful, simple and durable load-bearing structure emerges.
Construction of reinforced concrete foundation slabs: flat
LOCAL RESOURCE STATEMENT GESN 06-01-001-16
| Name | Unit |
| Construction of reinforced concrete foundation slabs: flat | 100 m3 of concrete, rubble concrete and reinforced concrete in action |
| Scope of work | |
| 01. Cutting and installing boards 02. Installing formwork panels 03. Fastening formwork elements with wire and construction nails 04. Installing reinforcement 05. Laying concrete mixture |
The price does not contain overhead costs and estimated profits; accordingly, the direct costs of work for the period 2000
(prices of the Moscow region), which are calculated based on
2009
. For further calculations, this cost must be multiplied by the conversion index to current prices.
You can go to the pricing page, which is calculated based on the standards of the 2014 edition with additions 1 The basis for using the composition and consumption of materials, machines and labor costs are GESN-2001
| № | Name | Unit Change | Labor costs |
| 1 | Labor costs of construction workers Level 3 | person-hour | 220,66 |
| 2 | Labor costs for drivers (for reference, included in the price of the EV) | person-hour | 27,31 |
| Total labor costs for workers | person-hour | 220,66 | |
| Workers' compensation = 220.66 x 8.53 | Rub. | 1 882,23 | |
| Payroll for drivers = 384.81 (for calculating invoices and profits) | Rub. | 384,81 |
OPERATION OF MACHINES AND MECHANISMS
| № | Cipher | Name | Unit Change | Consumption | Article number Rub. | Total RUB. |
| 1 | 020129 | Tower cranes when working on other types of construction 8 t | mach.-h | 26,06 | 86,4 | 2 251,58 |
| 2 | 021141 | Truck-mounted cranes when working on other types of construction 10 t | mach.-h | 0,98 | 111,99 | 109,75 |
| 3 | 030101 | Forklifts 5 t | mach.-h | 0,27 | 89,99 | 24,30 |
| 4 | 040502 | Installations for manual arc welding (DC) | mach.-h | 4,3 | 8,1 | 34,83 |
| 5 | 111100 | Deep vibrator | mach.-h | 10,71 | 1,9 | 20,35 |
| 6 | 331532 | Electric chain saw | mach.-h | 0,1 | 3,27 | 0,33 |
| 7 | 400001 | Flatbed vehicles, load capacity up to 5 tons | mach.-h | 1,47 | 87,17 | 128,14 |
| Total | Rub. | 2 569,28 |
| № | Cipher | Name | Unit Change | Consumption | Article number Rub. | Total RUB. |
| 1 | 101-0797 | Hot rolled wire in coils, diameter 6.3-6.5 mm | T | 0,0102 | 4455,2 | 45,44 |
| 2 | 101-1513 | Electrodes with a diameter of 4 mm E42 | T | 0,005 | 10315 | 51,58 |
| 3 | 101-1668 | Mat | m2 | 30 | 10,2 | 306,00 |
| 4 | 101-1805 | Construction nails | T | 0,002 | 11978 | 23,96 |
| 5 | 102-0061 | Edged softwood boards 4-6.5 m long, 75-150 mm wide, 44 mm thick or more, grade III | m3 | 0,04 | 1056 | 42,24 |
| 6 | 203-0512 | Boards made of boards 40 mm thick | m2 | 3,6 | 57,63 | 207,47 |
| 7 | 204-9001 | Armature | T | 8,1 | 0,00 | |
| 8 | 401-9021 | Concrete | m3 | 101,5 | 0,00 | |
| 9 | 405-0253 | Construction quicklime lump, grade I | T | 0,01 | 734,5 | 7,35 |
| 10 | 411-0001 | Water | m3 | 0,73 | 2,44 | 1,78 |
| Total | Rub. | 685,81 |
TOTAL BY RESOURCES: 3,255.09 RUB.
TOTAL PRICE: RUB 5,137.32.
Look at the cost of this standard at current prices open page
Compare the price value with the value of FER 06-01-001-16
To draw up an estimate, the price requires indexation of the transition to current prices. The price is based on the GESN-2001 standards, as amended in 2009.
in
2000
.
To determine intermediate and final price values, the DefSmeta
Features, advantages and disadvantages of a reinforced concrete slab for the foundation
A foundation made of slabs is the most advantageous option when constructing a building. A reinforced concrete slab under the foundation is used for laying in the foundation to a limited extent, as it is characterized by small depth and insufficient load-bearing capabilities. But in certain situations, this method is considered as an optimal design that combines reasonable cost and sufficient reliability. When choosing such a foundation, it is necessary to take into account the actual loads and the quality of the soil composition.
Feasibility of use
It is advisable to install a monolithic foundation made of reinforced concrete slabs in places with constant soil vibrations.
Carrying out a comparative analysis of pile, strip and slab type foundations based on the validity of their use, the option we are considering is more reasonable to use in the following situations:
- if the construction site has difficult soil;
- According to the project, the project under construction does not have basements or high ground floors;
- when the foundation base is also the base for the floor. In this case, it will be necessary to provide hydro- and thermal insulation protection;
- foundations made of reinforced concrete slabs are installed in areas with severe soil freezing.
Advantages and disadvantages
First, let's look at the advantages of a foundation made of reinforced concrete slabs. These include:
- the ability to install such foundations on any type of soil. The existing floating platform completely eliminates possible soil movements without damaging the entire structure;

- monolithic slabs make it possible to install a “warm floor” heating system, and this is a direct path to savings in winter;
- foundations made of reinforced concrete slabs are highly resistant to loads and can easily withstand different weights of vehicles;
- structures built on monolithic slabs are not subject to the negative effects of groundwater;
- installing a monolithic foundation does not cause any difficulties, all work is carried out on our own;
- no additional floor installation work is required, you can begin finishing immediately;
- the design has a long operational period and does not require repair work, which allows you to save certain amounts of money;
- there is no need to prepare a deep pit, because the slabs are able to evenly distribute all loads;
- Reinforced concrete slabs are considered a durable and reliable building material and provide excellent protection for premises from the penetration of rodents and insects.
Unfortunately, there are still certain disadvantages:
- foundations made of monolithic reinforced concrete slabs have certain restrictions on their use. When working, you have to focus on the temperature regime, which should not be lower than fifteen degrees. It turns out that in order to achieve good results in terms of strength and durability, the mortar will have to be laid in the warm season;
- Initially, you will have to spend a decent amount on purchasing building materials, but after a certain number of years it will be compensated.
Installation of slabs
Let's consider the algorithm for constructing a foundation made of flat foundation reinforced concrete slabs.

Preparation
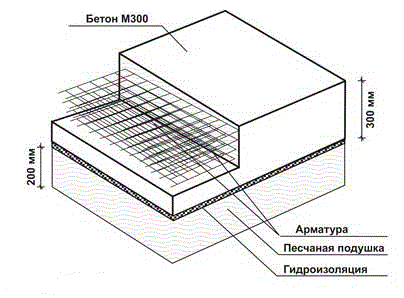
Certain preparatory work needs to be done. The slab should be laid evenly, carefully leveling the base and removing vegetation. A foundation pit is prepared for the entire area of the building being constructed, the depth of which reaches fifty centimeters (the cushion and the thickness of the slab are taken into account). Crushed stone and sand are poured onto the bottom in a layer of fifteen to thirty centimeters, taking into account the heaving of the soil. The layers are filled to a height of eight to twelve centimeters, and careful compaction is performed.
Waterproofing and insulation
We lay a layer of waterproofing material on the prepared pillow. Most often, roofing felt is used, from which two or three layers are made, leaving overlapping strips of fifteen to twenty centimeters.
A thermal insulation layer is laid over the rolled material. It is recommended to use foam boards or polypropylene foam as insulation. The main advantage of this material is its excellent thermal insulation properties, increased resistance to the negative effects of moisture and low temperature conditions. It is allowed to make the insulation layer from expanded clay, pouring a ten-centimeter layer.
Installation of slabs
To cover the entire foundation surface, you will need a certain number of ready-made reinforced concrete flat slabs. They are laid using lifting mechanisms as close to each other as possible. Product thickness parameters are determined taking into account the expected load forces created by the future object.
Under light outbuildings, it is enough to lay slabs of standard sizes, the thickness of which varies between twelve and fifteen centimeters. For the heaviest objects, slabs from twenty-five to thirty centimeters thick are used. The steel bars of the laid products are joined to create an overall reinforcing system. The surface of the laid slabs is carefully leveled relative to each element.
Concreting
There are gaps in the joining areas of the laid slabs, which should be sealed with a solution of sand and cement. To prepare the mixture, use cement material grade m 300 and higher and sand, taken in a proportional ratio of “one to three.” As soon as the solution has dried, a leveling screed is placed over the entire foundation surface.
To carry it out, use a similar mortar mixture, pouring a layer from three to five centimeters thick. The main goal is to form a perfectly smooth surface, for which during work you will have to use a building level for control and a rule that needs to be used to level the surface.
The next stage is to properly dry the poured screed, eliminating the appearance of cracks on the surface. To prevent the material from shrinking sharply, the surface layer is periodically moistened for eight to ten days. To retain moisture longer, it is recommended to cover the screed with polyethylene material.

Installation of foundation slabs
Start
Before you start installing the structure, prepare everything in advance. We have prepared for you a list of all the necessary materials and tools:
- Foundation slabs.
- Materials for foundation slabs.
- Mixture for joining slabs.
- Construction mixer or concrete mixer for preparing the mixture.
- Sand to create a cushion for the structure.
- Devices for transferring materials to the construction site.
- Construction tools such as a building level, tape measure, level, etc.
Installation of slabs should only be carried out in warm and dry weather. There is no need to lay the slabs on wet ground.
So, first of all, we draw levels and axes on the site. Next, you should prepare the area and proceed to preparing the sand cushion. To do this, you will need to sift the sand and pour it onto the bottom of the trench in a layer of 6-11 cm. The width of the pillow should be 20 cm wider than the future foundation. After falling asleep, compact the sand well, pour water on it and leave to dry. Under a columnar foundation, the cushion should be made of sand and gravel, and on top of it all should be watered with bitumen.
Important: do not make a pillow on wet ground. This layer needs to be removed. If the soil is sandy, you don’t have to make a cushion, but immediately lay the blocks on the ground.
Continuation
After the sand cushion is ready, you need to move on to transferring the axes and other design marks. The mooring cord is pulled so that it does not subsequently touch the side walls of the blocks. Let's start installing the foundation slabs that will be the beacons. They are placed in corners and at intersections of walls.
The results of the work depend on the correctness and accuracy of placement. After the beacons are placed, the mooring cord is moved so that it touches the edges of the side beacons. This will be a guideline for laying the remaining slabs. Deviation from the dimensions according to the plan can be up to 1 cm. To eliminate the deviation, use a crowbar, which you can use to move the blocks. After the first row is ready, you can proceed to the second, doing everything by analogy.
Before you begin installing the foundation slabs, consider the location of all communications, and in the places where they are installed, make breaks between the blocks.
Advantages and disadvantages of concrete foundation slabs
Such a foundation has many advantages when compared with monolithic blocks:
. If when laying a strip foundation you need to wait about a month to continue construction, then a block foundation will allow you to start work in just a couple of days.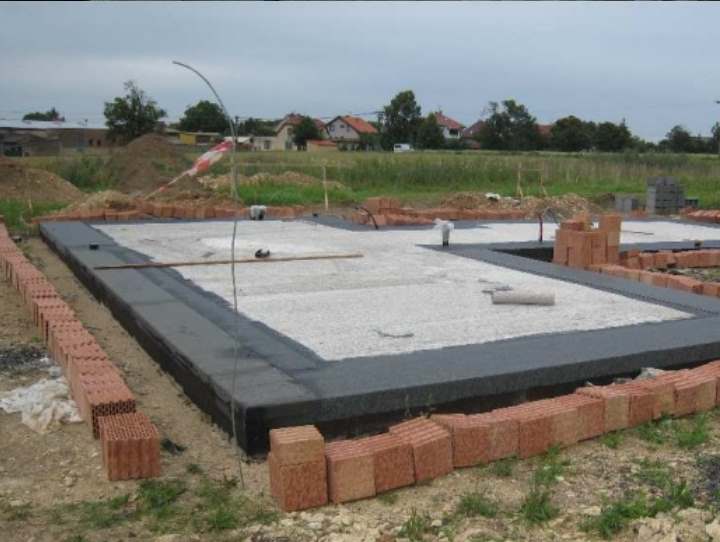
Construction speed- Reliability and durability . Foundation blocks are manufactured according to all parameters and standards using specialized equipment.
- Foundation slabs are suitable for installing the foundation of any building. Using this material you can mount a structure of any complexity and configuration. The sizes come in different sizes, which makes it possible to use this building material both for the construction of houses and high-rise buildings.
- Ease of use. With the help of loops on the upper borders, you can easily mix the blocks, and the grooves and uniform dimensions make it possible to quickly and easily connect the slabs together.
- Foundation slabs can be used in any climate conditions.
Despite this, there are a number of disadvantages:
- Large financial costs. Considering the weight of the slabs, you will need to rent lifting equipment.
- After the installation is finished, you will need to double waterproof.
- The service life will need to be extended, and this is only possible thanks to insulation of the seams. For this you will need polystyrene foam and a lot of money.
Required Tools
To arrange a slab foundation that meets the requirements of GOST, you will have to rent lifting equipment and prepare the following set of tools:
- for preparatory work - shovels, crowbars, picks, devices for compacting pillows;
- for installation work - a grinder, hammers and sledgehammers, scissors, pliers, a sharp knife;
- At the concreting stage, you will need a trowel and trowel, usually a spatula, a construction mixer, and a grater.
The quality of the work performed is checked by the construction level. In addition, a tape measure and a metal ruler will come in handy.
APPLICATION AREA
A standard technological map has been developed for the installation of flat monolithic reinforced concrete foundation slabs in general purpose buildings and structures with slab thicknesses up to 1200 mm.
The parameters of the monolithic reinforced concrete slab of the technological basement were taken on average based on those actually used in the projects of the Promstroyproekt Institute.
Reinforcement of foundation slab structures is assumed to be flat meshes and spatial frames; The joints of the mesh and frame reinforcement are overlapped, without welding, and spaced apart.
Calculation of labor costs, work schedule, need for material and technical resources, technical and economic indicators were carried out for a slab measuring 37.2 ´ 44.35 m (temperature block) with a thickness of 1.2 m (basic version).
This map also allows, using facets, to calculate the above indicators for a slab with a thickness of 0.8 and 0.4 m.
The technological map provides for the construction of a monolithic foundation slab using the unified dismountable formwork “Monolit-77”, enlarged into formwork panels.
Kinds
Monolithic reinforced concrete slabs are divided into the following types. Depending on the area of application, they are used for the construction of:
- roads;
- floor slabs;
- foundations.
The slabs are also flat and ribbed.
Return to contents
Flat
A flat slab is a popular type of foundation; it does not contain additional protrusions and has the appearance of a flat sole. Flat slabs are used for floors of residential and public buildings, which take on a distributed load over the entire base area. The slabs are made from concrete mortar and reinforcing mesh. A distinctive feature of flat slabs is their high quality, strength and durability.
Return to contents
Ribbed
Slabs with a ribbed structure are used for the construction of load-bearing structures or other industrial structures. Ribbed slabs are distinguished by their small thickness and the ability to transfer the load-bearing capacity of the slabs to the ribs of the product. The ribs of the slab strengthen the structure being built, but also complicate the construction process. Self-construction of a slab ribbed foundation involves additional digging of trenches. The resulting voids between the relief bends are filled with crushed stone and sand.
Return to contents
ORGANIZATION AND TECHNOLOGY OF WORK EXECUTION
Before installing the foundation slab, the following work must be completed:
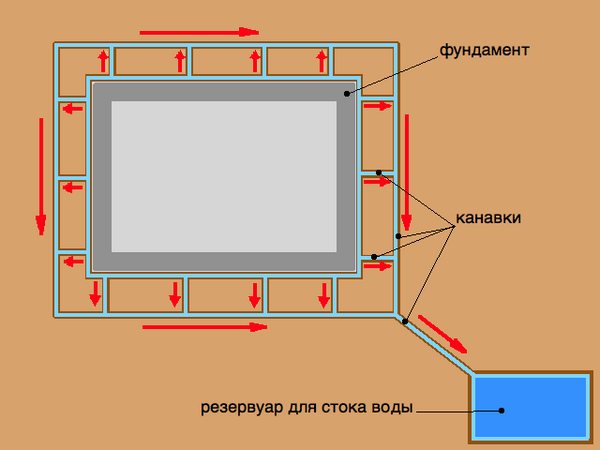
drainage of surface water from the pit is organized;
access roads and roads have been constructed;
the paths of movement of mechanisms, places for storing reinforcing mesh and enlargement of formwork are indicated, installation equipment and devices are prepared;
concrete preparation for the foundations has been completed;
reinforcing mesh, frames and formwork kits were delivered in quantities to ensure uninterrupted operation for at least two shifts;
foundation acceptance certificates were drawn up in accordance with the as-built diagram;
Temporary electric lighting for workplaces was installed and electric welding machines were connected;
a geodetic alignment of the axes and marking of the position of the foundation slab were carried out in accordance with the project; marks are applied to the surface of the concrete preparation with paint, fixing the position of the working plane of the formwork panels.
The works covered by the map include:
auxiliary (unloading, storing, sorting reinforcing mesh, reinforced frames and formwork kits);
The entire range of work is carried out in accordance with SNiP 3.03.01-87.
Unloading and laying out of reinforcing mesh, reinforced frames, formwork elements, as well as installation of reinforced frames, mesh and formwork panels is carried out using a KS-2561D truck crane.
Reinforcing mesh and reinforcement frames arrive at the construction site in assembled form.
The assembly of formwork panels is carried out at the installation sites in a certain sequence:
the boards are laid with the working surface down, wooden slats are placed in the places where mounting and working fasteners are installed;
the overall dimensions of the panels are checked, wooden limiting bars are nailed along the contours of the panels;
the shields are connected to each other with spring clips or crimps;
at the locations of wooden slats, the boards are connected with bolts;
holes with a diameter of 18 - 20 mm are drilled in wooden slats in places where the ties pass;
fights are laid out on top of the shields;
fights with shields are connected with tension hooks with a wedge or screw lock;
on top of the contractions, rigidity ties are laid perpendicular to them, for which the same contractions are used;
contractions with ties are connected with bolts;
on the upper tier of contractions, mounting loops are strengthened;
Struts are attached to the lower tiers of the contractions or stiffeners, ensuring the stability of the panels in a vertical position.
The formwork is assembled from enlarged panels for a temperature block of 37.2 ´ 44.35 m.
Reinforcement work is carried out in the following order:
install the lower nets on the clamps, providing a protective layer of concrete according to the project;
install upper meshes on frames;
lay individual reinforcing bars.
When laying reinforcing mesh and frames, formwork panels should be secured to the latter through holes in wooden slats with wire.
Within the temperature block, concreting of the foundation slab is carried out with replaceable grips. The number of replaceable grips is determined based on the performance of the adopted mechanisms for concreting.
Within the shifting area, concreting should be carried out without interruption.
When constructing a working seam at the boundaries of interchangeable grips, it is recommended to use metal woven mesh with small cells as formwork.
The concrete mixture is supplied to the laying site using a concrete pump (basic option), tower cranes (option 2), and a concrete paver (option 3).
Concreting the slab using a concrete pump in combination with the required number of concrete mixer trucks is carried out on the first grip from the edge of the pit, and on subsequent grips - from the previously concreted grips of the foundation slab.
The concrete mixture should have a cone settlement within 4 - 12 cm.
The composition of the concrete mixture is selected in the construction laboratory.
When concreting a slab with a tower crane, the concrete mixture is supplied in rotary hoppers. The bunker is slung using a two-legged sling with a lifting capacity of 5 tons.
When concreting a slab with a concrete paver LBU-2, the concrete mixture should have a cone settlement within 1 - 4 cm.
The concrete mixture is laid in horizontal layers 0.3 - 0.5 m thick.
Each layer of concrete is carefully compacted using deep vibrators. Overlapping the previous layer of concrete with the next one must be done before the concrete in the previous layer begins to set.
Measures for the care of concrete during the period of strengthening, the order and timing of their implementation, control over the implementation of these measures must be carried out in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 3.03.01-87. The exposed concrete surfaces of the slab must be protected from moisture loss by watering them with water or covering them with damp materials. The holding period and frequency of watering are determined by the construction laboratory.
When carrying out work in winter conditions, measures are taken to ensure normal hardening of concrete with an expected average daily outside air temperature below 5 °C and a minimum daily temperature below 0 °C in accordance with SNiP 3.03.01-87.
Options for recommended machines and equipment when constructing a monolithic reinforced concrete foundation slab
Name of the set of machines and equipment
Construction of a monolithic foundation slab
A monolithic slab is the most reliable type of foundation. The design is selected if the future building will be located on an area with difficult soil. In practice, a monolithic slab is erected in the following cases:
- close location of groundwater;
- wetlands;
- peat bogs.
This type of foundation is also called floating in construction. The structure received this name because when the soil subsides or heaves, the foundation floats as if on waves. The base is a reinforced concrete slab. The monolithic slab reliably protects the walls of the building from deformation, since any changes in the soil spread across the surface of the foundation slab.
Advice! A foundation slab is an ideal solution for a house with two or more floors. Craftsmen also recommend choosing this type of construction for brick or block buildings.
A disadvantage of the design is the fact that with such a foundation it will be problematic to build a basement. This disadvantage can be circumvented if you choose a deep foundation. In this material we will analyze in detail the structure of the base, and also consider the process of preparing and installing a monolithic slab.
Slab foundation with downward stiffening ribs
It is mainly used instead of a conventional slab foundation to save material, that is, the slab is made thinner, and the strength is compensated by stiffening ribs that strengthen the slab along the perimeter (usually under load-bearing walls), where the maximum load is concentrated.
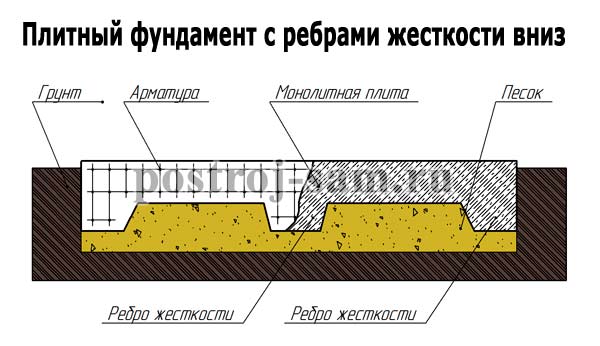
This type of slab foundation is somewhat reminiscent of a shallow strip foundation, monolithically poured over a slab. The stiffeners and the slab must be a single whole, that is, a monolith. The reinforcement of this type of foundation must be treated with extreme care.
The technology for laying such a foundation is simple. The soil is excavated according to the dimensions of the future foundation, then a trench is dug where there will be stiffening ribs near the slab. If necessary, formwork and a sand cushion are constructed, then the reinforcement is tied together with tying wire and the whole thing is filled with concrete of a grade not lower than M200. Well, don’t forget that concrete gains most of its strength 28 days after pouring.
The technology of tying reinforcement for the foundation is described in detail in one of my articles, so I will not focus on this.
Preparation for foundation construction
The construction of any type of foundation begins with preparatory operations; a monolithic slab is no exception. When a suitable scheme has been selected, preparatory work can begin:
- Selection of the “pie”. This definition refers to the composition and number of layers of which the slab will consist. In addition to concrete, the “pie” includes a sand cushion, as well as insulating layers.
- Selection of reinforcement method. To select a suitable structure, it is necessary to conduct an analysis of the soil, landscape, and also know the approximate load of the future building.
- Selection of suitable thermal insulation materials. The house will stand on a solid concrete slab, so it’s worth thinking about thermal insulation in advance.
- Waterproofing for walls. We are talking about structures that will rest on the edges of the base after construction is completed.
- Calculation of fortifications from armored belts, which are a mandatory requirement when constructing a building made of brickwork or blocks. Otherwise, cracks will form in the base and supporting structures.
Readers probably have a question: “Is it possible to build this type of foundation with your own hands?” In theory, this is possible, but many people must be involved when pouring concrete, since the foundation needs to be poured quickly and evenly. As for the preparatory stages, it is mandatory to participate in them.
Installation process
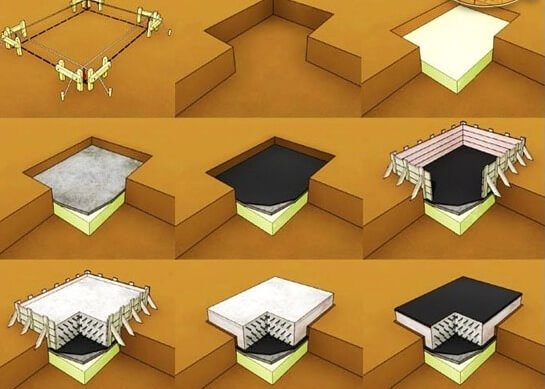
When installing a monolithic base, use the following tools and materials:
- vibrator for compacting concrete mortar;
- buckets;
- mixer for preparing mortar or concrete mixer;
- shovel;
- building level;
- rope;
- pegs;
- wooden boards for constructing formwork;
- reinforcing mesh;
- sand;
- cement;
- crushed stone;
- water.
The installation process includes the following steps:
- choosing a location for the foundation;
- calculation of site parameters and selection of reinforcement type;
- carry out a geological section of the soil;
- calculate the dimensions of the future structure;
- they are digging a pit;
- lay a sand and gravel cushion;
- if necessary, lay a layer of waterproofing;
- install formwork;
- strengthen the structure with reinforcing mesh;
- perform concreting;
- Leave the poured solution until it dries completely for 28 days.
Return to contents
Preparation
Installation of a reinforced concrete monolithic slab begins with preparing the base. To do this, you need to get rid of the plants, removing the top layer of soil with the roots of the vegetation. Next, garbage and other unnecessary elements that interfere with the work process are removed.
After cleaning the construction site, markings are made for the future structure and a trench is dug. The dug pit should be leveled using measuring instruments and leveling materials, which are sand and gravel. After leveling the recesses with a sand and gravel cushion, materials are prepared for installing formwork, laying reinforcing mesh and pouring mortar.
Return to contents
Clearing the area
Work on installing a slab foundation begins with clearing the area. To do this, the top layer of soil, which contains vegetation and roots, is removed. This layer can be removed with a bulldozer. Depending on the properties of the soil and the weight of the planned structure, the thickness of the monolithic base can be from 15 to 40 centimeters. The work area should be cleared of debris and excess tools and materials. The equipment should be stored in one place near the construction site in such a way that it does not interfere with further work and at the same time is at hand.
Return to contents
Marking
After preparing the site, they begin to mark it. Marking is carried out with hammered pegs, which are connected to each other with a rope. When marking the site, it is important to maintain the evenness of the sides and central intersection points, which are checked both manually and using a level.
Return to contents
Creating a site
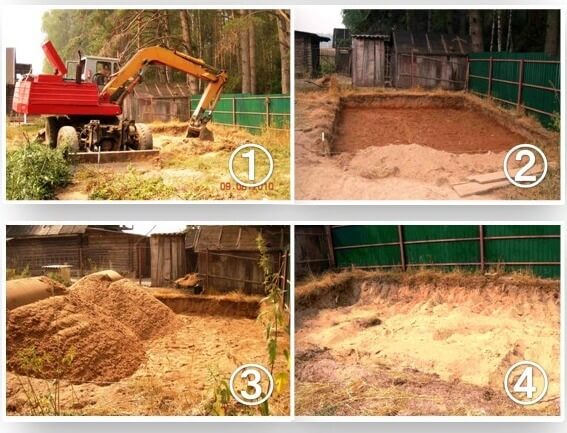

After the construction site has been cleared and marked, they begin to create the site by digging a pit. They dig a pit to a depth of fifteen centimeters and pour a layer of crushed stone and sand onto its bottom, forming a cushion. Crushed stone is selected from the middle fraction, the bottom is filled with it and compacted with a piece of log. A layer of crushed stone is covered with sand and watered. The sand should be compacted thoroughly. Next, level the surface with a building level until the slopes disappear.
Return to contents
Formwork installation
After laying the gravel and sand cushion, the installation of wooden formwork begins. Wooden boards are used, which are installed at an angle and secured with self-tapping screws. Periodically check the horizontality of the structure using a building level.
Return to contents
The working process
The process of constructing a reinforced concrete monolithic foundation includes work on laying a waterproofing layer, reinforcing mesh, which will increase the strength of the foundation, and pouring mortar. If necessary, lay a layer of thermal insulation using polystyrene foam.
Return to contents
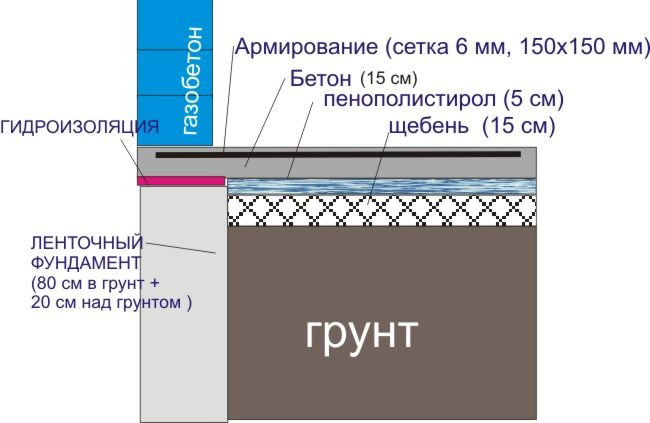
Waterproofing
Before erecting buildings and structures, it is recommended to isolate them from moisture penetration, which negatively affects the service life of the building and its quality characteristics. For waterproofing, roofing felt material is taken and pasted in strips onto the walls and surface of the structure. Waterproofing should be carried out in 2 layers, laying roofing felt strips overlapping.
Return to contents
Reinforcement
After installing the formwork and waterproofing layer, they begin laying the reinforcement. The monolithic slab is reinforced with a mesh in two tiers. Steel rods are connected to each other using a welding machine or knitting wire. Inside the formwork, the reinforcement structure is driven in to the required depth and the longitudinal lines of the reinforcing mesh are tied to them from above.
Return to contents
Fill
Concreting of the base must be carried out continuously. Concrete grades of at least 250 are used. The prepared concrete solution is fed along a tray to the initial far edge of the slab, gradually moving to the near one. During the concreting process, the solution is compacted, this will get rid of air bubbles and make a concrete solution with high strength characteristics. You can make the concrete mixture yourself, but this will require more time and effort. After the solution has been laid, it should be provided with optimal hardening conditions.
Return to contents
The process of constructing a monolithic foundation
It cannot be said that a monolithic slab is the most complex structure, but there will be more work here than with a strip, column or pile type of foundation. You should start construction and calculations only after consultation with professionals who will draw up a project for you. It is also recommended to take care of special equipment; it will significantly speed up the construction process.
Having studied the device, you can start working:
- The first step is to mark the site where construction will take place. The next step will be digging a pit - in construction this stage is called excavation.
- When the pit is dug, you can start laying insulating materials, the choice of which professional builders will advise you on. Quite often Dornit is used in the construction of slabs. This layer is placed to prevent sand from penetrating into the clay.
- Now you can move on to the sand cushion. The site is filled with crushed stone and sand, after which compaction is performed. The pillow is placed in several layers of about 10 centimeters each, the sand must be clean. This stage is performed using a vibrating plate. As an alternative, wooden tampers can be used.
- After the pillow, the laying of communications begins, which include water supply and sewerage.
- Next, concrete preparation is carried out. This is a 10-meter screed, which is located above the sand cushion. For this work, you can use M100 cement, since high quality is not required here. The solution is most often prepared from sand concrete grade M300.
- The concrete slab is already there, now you need to take care of waterproofing. For monolithic slabs, rolled materials are used, the installation of which is carried out using a special soldering iron or torch. This way they are securely attached to the base. The next waterproofing layer should be polystyrene foam; usually builders choose the extruded version. By performing additional waterproofing of the foundation, the owner will not have to insulate the floor of the basement or first floor.
- The result is a layer cake, onto which the device is mounted using reinforcement. The frame must be erected from two meshes; for this purpose it is necessary to purchase reinforcement bars of 12-16 millimeters. The connection of the rods should form cells of 20x20 and 30x30 centimeters. The first mesh should be placed at the bottom of the base of the monolithic slab, and the second - on top.
Scheme of reinforcement of a monolithic foundation slab
- Having completed all the above steps, you can proceed to installing the formwork. The supports must be secured as securely as possible, as the monolithic slab has very high pressure.
- Now the concrete mixture is poured again, the compaction of which must be done manually. Deep vibrators will help with this. Next, you need to smooth and level the concrete. Since the area is large, this process must be carried out by several people, the number of which depends on the size of the monolithic slab.
- The main work is completed - the slab should be covered with film and wait for complete hardening (usually this occurs 25-30 days after pouring). Concrete must be moistened once a week.
- Once fully cured, additional waterproofing work can be carried out if necessary. In any case, this is discussed when drawing up the project.
Scheme of waterproofing the foundation slab - the material is selected depending on the type of soil, climate and landscape. The builders who will draw up the project for the future construction will tell you in detail about this.
Foundation slabs and their characteristics
Form
Reinforced concrete foundation slabs for strip foundations have a rectangular shape. For this product, heavy concrete (marked T), expanded clay concrete (marked P), and sometimes silicate concrete (marked C) are used. Typically used for laying basements, basements and foundations.
Standards
They are manufactured in strict compliance with GOST standards. Concrete blocks have differences in characteristics and areas of application:
- FBS – solid foundation blocks. They are often used to create load-bearing structures, basements and basements.
- FBP are hollow slabs that have a hole on one side.
- UDB are slabs that are called “perforated”. The holes in them are in the form of truncated pyramids or simply uniform.
- FL – foundation pillows. They are used as a base for concrete blocks.
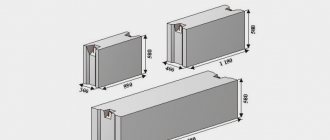
On the end-view planes there are special grooves that connect the plates to each other. To make it more convenient to work, two loops are placed on the plates. The slabs themselves differ from each other in the presence/absence of voids, as well as in size and weight. FBS slabs come in lengths of 90 cm, 120 cm, 240 cm, widths of 30 cm, 40 cm and 50 cm, and heights from 30 to 60 cm.
The purpose, material and dimensions of the foundation slab are encrypted in the markings. If you see the FBS 12.4.6 marking, this means that this block is intended for the construction of walls made of heavy concrete, with dimensions of 1.2 m in length, 0.4 m in width and 0.6 m in height.
Kinds
FBS - application and characteristics
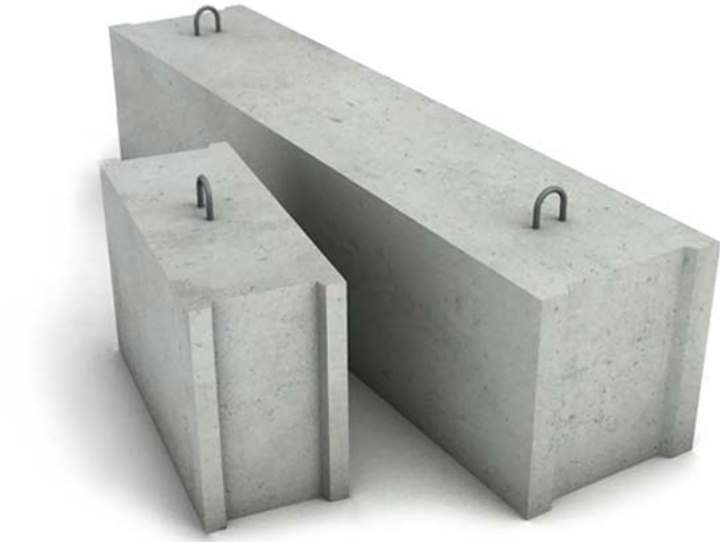

Wall foundation blocks (solid) are an iron structure, which is similar in shape to a parallelepiped. Such blocks are made of high quality solid concrete, reinforced with steel reinforcement, which makes it possible to withstand heavy loads. In terms of characteristics, FBS is not inferior to monolithic bases. The scope of application is wide, as it can be used in the construction of high-rise buildings, making floors and partitions.
Often used in the construction of industrial buildings and fencing panels on construction sites. Below are some characteristics:
- Compressive strength – B12.6 (M150).
- Material strength – 105-111 kg/cm.
- Density up to 2.4 t/m3.
- Frost resistance grade F200.
- Waterproof grade W2.
FBS also has different sizes; they are also classified by this indicator. The size determines the level of load that the slab can withstand. And for good reason - the main purpose of foundation slabs is to uniformly distribute the load on the surface of the base. For this reason, dimensions should be selected according to the expected load.
Typical parameters:
- Lengths – 90 cm, 120 cm, 240 cm.
- Width – 30 cm, 40 cm, 50 cm and 60 cm.
- Height – 60 cm (very rarely there is an indicator of 30 cm).
Please note that occasionally there may be an error in weight and size. As a rule, the size error is not higher than 2 cm.
An important characteristic is the mass of the slab. FBS is a solid structure without voids, which affects the weight. First of all, these are difficulties during transportation. Depending on the brand, the slabs can weigh from 250 kg to 2 tons.
In the manufacture of this building material, components such as water, cement and filler are used. The consistency is maintained, and to connect the elements they are mixed in a concrete mixer. After obtaining a homogeneous mass, it is poured into molds with vibrators, which shake the solution and compact it. The slabs are removed after a day and a protective coating is applied to them, after which they are washed well with water. The material can be used after 28 days.
Attention! If you are installing a foundation made of reinforced concrete slabs, take care of waterproofing that will protect them from moisture. This can be a composite mixture of water repellents and bitumen.
FBP and its application
Hollow-core foundation blocks are a very durable concrete material. It is widely used in the construction field. Typically, builders use it when laying the foundation of industrial premises, for the construction of basements and ground floors.
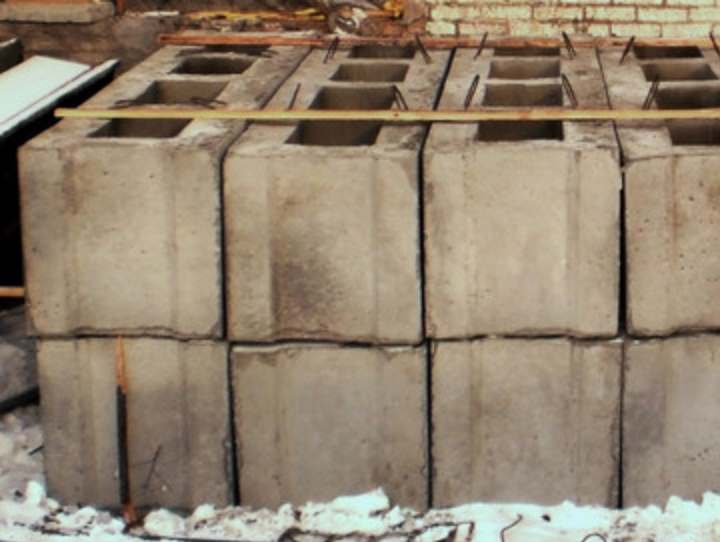

FBP has a rectangular shape with some voids that are located at the bottom of the slab. The presence of voids is necessary in order to subsequently fill them with insulation or fill them with concrete and make a monolithic structure. FBP is often used for foundations in industrial premises.
With their help, it is possible to mount a protective casing when laying pipes for water supply and heating systems. They are often used in road construction, namely to create fences. Recently, it has also been used in the construction of walls in unheated rooms.
UDB blocks
Universal perforated blocks are quite an interesting material for building underground premises. This is practical in cases where they plan to have high ceilings in the building. It makes sense to use them if you are laying a foundation in a place where there will be a heavy load.
The structure of the UDB is reinforced concrete foundation slabs that have a certain number of holes. During installation, they are laid so that the holes coincide with each other. This creates channels that can later be reinforced and filled with high-strength concrete. This is necessary to ensure that the structure is very durable and has a high level of wear resistance.
Please note that quite often, to save money, not all channels are filled with concrete, but this process is required for corner and some other channels that are evenly spaced around the perimeter.
Dimensions:
- Lengths from 120 to 600 cm. Each parameter increases by 60 cm.
- Width 60 cm.
- Height 58 cm.
- The holes can be from 2 to 8, it depends on the length of the block.
FL blocks and their features
Foundation pads are used when installing a strip foundation. This is a trapezoidal concrete foundation slab. Inside, the slab is reinforced with a frame made of steel reinforcement.
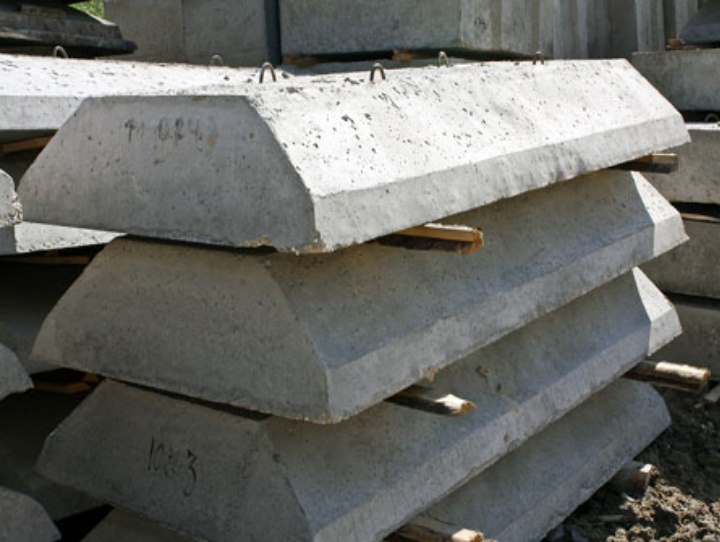

It is designed to distribute the load on the base, thereby increasing the supporting area. When producing FL, the rules must be followed to ensure that the strength of the material is guaranteed, and the board itself will be resistant to corrosion and cracks. Typically, heavy concrete is used in the manufacture of FL, as well as steel reinforcement and a reinforcing frame made of rods.
But now pillows, or rather foundation slabs reinforced with string-concrete rods, have begun to appear frequently. There are two types of foundation pillows - ribbed and lattice. New technologies make it possible to spend less metal and concrete in such production, which does not negatively affect the properties. Usually used in the construction of buildings that have a large load. Also relevant for the construction of ground and basement floors.
“These slabs can be used when laying on any type of soil. They are suitable for any climate conditions. Such pillows are resistant to seismic changes"
Positive and negative sides of a monolithic slab
If a foundation slab were the best solution, it would be used for absolutely all buildings. Like any type of foundation, a monolith has its pros and cons.
It's worth starting with the positives. These include maximum strength among other structures and durability (a building on a slab can last up to 150 years). The monolith can be used for different types of structures. If a deep foundation is chosen, then the slab becomes the floor for the first, basement or ground floor of the house.
The diagram demonstrates that a monolith can also be made in the strip foundation of a house.
The disadvantages include the high cost of work, because a foundation slab requires much more material than a standard strip or column base. Also avoid complicated calculations, which simply oblige you to contact a construction bureau. And the last thing is the labor intensity of the process, because workers have to perform a large amount of excavation work.
Some features of the construction of slabs with ribs down
It is imperative to remove a layer of humus over the area of the future building. Expand the perimeter of the trench taking into account the need to add material or cushion. The dimensions of the pit are calculated using the so-called diagonal method.
A sand cushion no thicker than 250 mm thick is placed on the bottom of the earthen layer. If the designed structure has a large area or mass, then the thickness automatically increases to 450 - 500 mm. In this case, it is necessary to compact each layer with a vibrating plate. Simultaneous construction of such thickness is not envisaged.
A separate formwork is constructed under each side of the rib to avoid damage to the structure. A layer of fabric - geotextile - is covered at the bottom before filling with a mixture of sand and crushed stone. In order to increase the service life, it is necessary to carry out waterproofing.